- home
- Articles
- How to choose a knee orthosis?
A knee brace or brace is a way to prevent various diseases, as well as a method of recovery for fractures, sprains or other injuries. At the same time, questions arise about how to choose a knee orthosis, how to choose it best and how to use it most effectively. There are several types of orthoses, which differ in rigidity, elasticity, and types of fastening. Only a consultation with a doctor will help you choose an orthosis, since the doctor will take into account factors affecting the condition of the joint.
Purpose of orthoses
Not everyone knows what an orthosis is, because we practically do not notice this means of therapy until one of our loved ones is faced with joint disease or another similar ailment. However, the majority have seen orthoses - these include corsets, bandages, special shoes and even orthopedic insoles . They are required to be worn in the following cases:
- for problems with joint ligaments (congenital instability, weakness, damage);
- after injuries during sports activities;
- due to arthrosis or arthritis of the joints;
- during recovery after surgery.
The main reason why orthotics are used is the need to provide rest to the damaged organ. The device allows you to reduce the load on a limb or joint, fix it, correct movements and even increase activity. However, an important criterion is the correct selection of the orthosis.
Rehabilitation after arthroscopy
After arthroscopy, the rehabilitation period proceeds quite easily and quickly, in contrast to open access surgery, and no large scars are left on the patient’s body. A rehabilitation plan is developed individually by a rehabilitologist, taking into account the characteristics of the pathology, the treatment performed, age characteristics, concomitant pathologies, and his lifestyle. Following all recommendations is the key to a successful and quick recovery.
The main methods include:
- Kinesiotherapy. Otherwise, this method of rehabilitation can be called physical therapy. This is a set of exercises aimed at strengthening the muscles in the desired area and developing the motor activity of the joint.
- Manual therapy. Relieves spasms, stimulates atrophied muscles to activity, and promotes better innervation.
- Mechanotherapy. Exercises on machines that strengthen the muscle frame in the required area.
In addition, kinesiotaping (application of special patches that regulate the load on certain muscles), physiotherapy, including: ultrasound, myostimulation, shock wave therapy, magnetic therapy and others, are used. As a rule, recovery takes about one and a half months, after which patients return to their normal lives, and athletes can begin training.
Classification by purpose
The characteristics of the disease dictate the rules for selecting an orthosis. The specialist determines the most rational option, based on the condition of the patient’s body. Thus, the following types of devices can be offered:
- preventive, relevant for people at risk or patients with minor joint changes;
- treatment and rehabilitation, suitable for restoring organs after injury;
- functionally permanent, used to restore the ability to move limbs whose joints have undergone irreversible changes.
As a rule, in the latter case, it is very important to choose the right orthosis or have it made to order - this will ensure its maximum functionality.
Diagnostics
By the time of consultation with a specialist, as a rule, extensive swelling has already formed in the injured area, and the pain syndrome is reduced due to the use of painkillers. Anamnesis data, as well as special functional tests, allow the doctor to conduct a differential diagnosis. They are simple, relatively painful, but help clarify the picture of the disease. Tests help determine the presence and location of pathology. The doctor decides which ones to use.
The most common of them include:
- Baykov's method. The knee is bent at a right angle, after which the joint space is palpated, while simultaneously extending the leg. The occurrence of sharp pain symptoms confirms the presence of damage.
- Shteiman's sign. The knee joint is bent 90 degrees, then the shin is rotated. If the pain increases with inward rotation, it means the medial meniscus is damaged, and with outward rotation, the lateral meniscus is damaged.
- Chaklin test. There are two types of such testing. Firstly, the presence of a rupture is indicated by a crunching sound when flexing and extending, and as if “rolling” the lower leg over an obstacle. In the second test, the patient raises his straight leg, and the doctor in this position palpates it for muscle atrophy in the thigh area.
- Polyakov's symptom. He lifts the healthy leg up, while trying to raise the pelvis and lean his elbow on the heel of the injured one. There is pain at the rupture site.
- Landau test. It consists of sitting in a “Turkish” position. Such an attempt in the presence of deformity will result in pain in the area of the rupture.
- Mac Murray's method. The patient, lying on his back, bends his leg and then rotates his knee. Painful sensations will appear, and a click will also be heard.
- Perelman's symptom. It has two varieties - climbing stairs or putting on shoes without hands. In both cases, pain appears, localized in the area of injury.
In addition, X-ray diagnostics (x-ray or computed tomography) and MRI (magnetic resonance imaging) are performed. They give a clear picture of the location and degree of deformation. Arthroscopy is also used for diagnosis. It also allows you to immediately perform the necessary surgical treatment.
Classification by manufacturing technology
Manufacturing technology can include both the method of creating a product and the materials from which they are made. Parts of the devices may consist of tire-leather inserts, plastic and textile elements, or be bandages or lamination materials. Depending on the method of creation, there are three types of orthoses:
- serial, assembled from standard modules;
- prefabricated modular, which are formed and installed directly in the area of the damaged joint;
- individual, made according to the measurements and casts of a specific patient.
Many patients believe that a finger, leg or shoulder orthosis should always be ordered specifically for the patient, but this is not necessary. The issue of individual production should be decided by the doctor. It is often much more efficient to use a standard solution right away than to waste time waiting for a special device.
Types of knee replacements
Knee endoprostheses are divided into types according to three main characteristics - materials of manufacture, the type of endoprosthesis surgery for which they are suitable, and the method of installation.
- The following materials are used for various elements of the knee prosthesis:
- metal alloys (the part installed on the femur is usually made from them);
- high-strength plastic (used in the construction of the inner part of the patella for total knee replacements );
- combined materials (metal and special plastic), from which parts are often made intended to replace part of the joint on the tibia.
- According to the method of endoprosthetics (volume of intervention) there are: types of knee replacements, intended:
- for unicondylar arthroplasty (partial replacement of damaged joint components);
- total endoprosthetics (an operation to completely replace the knee joint with an endoprosthesis with the installation of artificial components on the femur, tibia, and, if necessary, on the inner surface of the patella).
- Based on the method of fixation, prostheses are divided into:
- for cemented knee replacements ;
- cementless;
- products installed in a combined way (with elements of cement and cementless installation).
Cement endoprostheses
Prostheses for cement fixation differ from analogues in that they have a special surface on which bone cement is applied to securely fasten the fixed part of the endoprosthetic component. This installation is highly reliable and has been successfully used in all types of operations.
An important point: success is determined not only by a high-quality replacement, but also by the composition itself for securing the prosthesis. In modern arthroplasty practice, cases where the cement composition weakens are quite rare (the material has been significantly improved in recent years), but still.
Cementless fixation
Prostheses for cementless fixation also have their own characteristics. Their surfaces must be porous and textured to ensure the speed and quality of natural integration - the growth of bone tissue into the components of the artificial joint.
The rehabilitation process when using such implants takes longer. In addition, there are restrictions for their use (the bone must be in good condition, any disease of it, starting with osteoporosis, is a limitation for cementless arthroplasty).
Classification by design characteristics
Depending on the function performed by the shoulder, knee or any other orthosis, it is manufactured in a certain shape. The most common types:
- bandage. Soft and elastic orthosis;
- orthopedic splint. Rigid fastening for a damaged joint;
- splint. A soft orthosis that completely envelops the limb. Provides immobility of joints.
In addition, there are orthopedic devices that are used to facilitate limb movement. They are usually prescribed for the duration of rehabilitation.
Design features also include the degree of rigidity of the product. Thus, among orthoses there are hard, medium-hard and soft devices. The choice of one type or another is usually influenced by the degree and nature of the damage to the diseased joint. For example, when healing an injury, hard orthoses are used, and during rehabilitation, soft ones are often used.
It is not difficult to understand what orthoses are; it is much more difficult to purchase a suitable product. That is why it does not matter at all whether you need a cervical orthosis or need to correct the functioning of the hip joint - the choice must be made by a specialist . The doctor will ask you to take all the necessary tests, prescribe the necessary studies and, based on them, make a decision about whether or not you personally need to use the orthosis.
How to choose?
How to choose a knee orthosis depends not only on the required functions, but also on the size, characteristics of the blood vessels in the legs, the presence of injuries to the ankle, spine and other nuances. Therefore, it is extremely important when choosing orthopedic devices
consult your doctor. Otherwise, you can cure one disease and aggravate another disease.
Consult a doctor when selecting knee braces and arm orthoses
important for several reasons:
- the doctor will select a design;
- concomitant diseases, susceptibility to allergies or skin diseases will be taken into account;
- the doctor will recommend the necessary physical exercises to gradually restore the joint;
- The specialist will give recommendations on the care of knees and orthopedic products.
With this professional approach, your knees will be strong and healthy.
Return to list
Causes
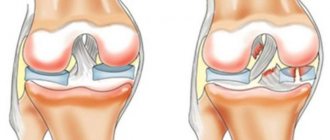
The main causes of damage to the meniscal cartilage of the knee joint are usually:
- sharp bending of the knee joint with simultaneous rotation. This mechanism of injury is the most common;
- landing on your feet when falling from a great height.
All injuries occur during rotation in a bent knee during physical activity. This often happens in professional sports: hockey, kickboxing, football, figure skating. There is a direct connection between rotation and injury. If the shin rotates outward, then the inner meniscus is damaged, and if inward, then the outer one. You can also get injured if there is a strong blow to the knee area or when landing on straight legs (often found in extreme sports).
Rupture of the cartilage pad occurs rarely and is mainly due to regular injuries in the knee area, rheumatism, gout, and leaching of minerals. Often the pathology occurs against the background of damage to the capsule, ligaments and cartilage tissue.
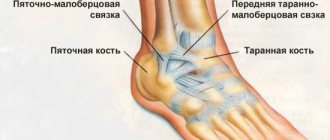
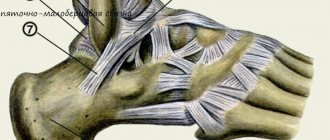
Anatomy
The meniscus is the outer and inner cartilage pad in the knee joint, which is located between the femur and tibia. The menisci absorb shock during walking and running and also stabilize the knee joint capsule. During physical activity, they change their shape due to their high elasticity.
Usually the internal meniscus is injured, since its mobility is much lower than that of the external one. In the absence of pathologies, sufficient blood supply is ensured by the vessels located in the joint capsule. But there is no blood supply to the internal cartilage pads, since nutrition comes from synovial fluid. Because of this, regeneration does not occur in case of injury to the medial part. But since sufficient blood supply to the external cartilage is ensured, rapid fusion occurs in case of marginal injuries.
Orthopedics and traumatology services at CELT
The administration of CELT JSC regularly updates the price list posted on the clinic’s website. However, in order to avoid possible misunderstandings, we ask you to clarify the cost of services by phone: +7
| Service name | Price in rubles |
| Appointment with a surgical doctor (primary, for complex programs) | 3 000 |
| X-ray of bones and joints of the limbs | 2 200 |
| MRI of the knee joint (1 joint) | 7 000 |
All services
Make an appointment through the application or by calling +7 +7 We work every day:
- Monday—Friday: 8.00—20.00
- Saturday: 8.00–18.00
- Sunday is a day off
The nearest metro and MCC stations to the clinic:
- Highway of Enthusiasts or Perovo
- Partisan
- Enthusiast Highway
Driving directions
Symptoms
At the time of injury, severe pain occurs. Usually the joint is immediately fixed in a bent position. Attempts to straighten it lead to increased pain. Such blockades of the knee joint are repeated many times over time.
Then the signs characteristic of any injury increase: swelling, hemorrhage, limitation of movements. Due to swelling of the soft tissues, the outline of the patella is smoothed out, it is contoured less than on a healthy leg.
Damage to blood vessels during injury leads to the accumulation of blood in the joint cavity (sometimes in large quantities - up to 100 - 150 ml).