Pain in the hip joint during pregnancy appears as a result of significant changes in the female body. Starting from the second trimester of fetal development, a powerful processing of a woman’s metabolic functions occurs. The future person needs to be fed, protected from damage, warmed and provided with high-quality physiological development. All these components increase the load on the female body and musculoskeletal system.
Possible causes of pain in the hip joint during and after pregnancy will be discussed in this material.
Causes of pain during and after pregnancy
Painful discomfort in women during pregnancy can be caused by various conditions. Causes of unpleasant symptoms of hip pain during pregnancy:
- hormonal imbalance;
- increased load on the pelvis due to an enlarged uterus;
- insufficient calcification of articular segments;
- reflective pain as a result of old injuries or chronic pathologies;
- dysfunction of the pubic symphysis.
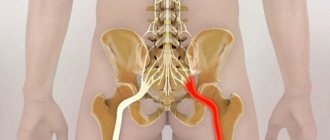
How the spine and hip angle are deformed during pregnancy.
Let us consider in detail each of the possible complications.
How does pain in the hip joints and pelvis manifest during pregnancy?
It will be useful to imagine the anatomical structure: the pelvis is a large bone formation at the base of the spine, which is located in the lower part of the torso. On both sides of the pelvis are the hip joints, which connect the thigh bones to the pelvis.
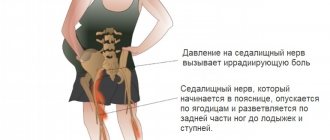
When there is pain in the pelvis or hip joints, it can be difficult to determine the exact location of the sensation. Sometimes such pain can even be mistaken for back pain, especially if it radiates to other places, and back pain occurs in many women during pregnancy. At the same time, pain is felt in different ways: for some it is a sharp and sudden painful sensation, for others it is a constant dull ache. Both may occur at different stages of pregnancy. Your attending physician will make an accurate diagnosis.
Pelvic pain is quite common during pregnancy. It can be dull and sharp, constant and intermittent, minor and strong. It can even radiate to the lower back, buttocks and thighs. Pelvic pain may occur with certain movements, such as walking, or in certain positions, such as when you lie down to sleep.
Be sure to tell your doctor if the pain interferes with your normal lifestyle, gets worse over time, or becomes severe immediately. It is also worth consulting with him if the pain is accompanied by dizziness, vaginal bleeding or high fever.
Hormonal changes
During pregnancy, endogenous steroids - progesterone and estrogen - are actively reproduced in the female body, which affect the reproductive system of the woman and the embryo. Both sex hormones have a number of physiological effects that activate metabolic processes in the body of the mother and unborn child. Progesterone activity increases only in the presence of estrogen. The hormone is responsible for transferring the endometrium to the secretory stage, reduces immune defense and the contractility of the uterine muscles so that the woman’s body safely accepts the embryo.
Estrogen stimulates the development and preparation of the uterus, fallopian tubes and vagina for pregnancy, and helps improve the ducts of the mammary glands.
In addition to the positive effects of hormonal steroids, there are negative aspects. Since all the efforts of female sex hormones are aimed at the reproductive system and embryonic support, bone and joint saturation with nutrients is significantly depleted. The cartilage tissue softens, the muscles relax, and the elasticity of the ligamentous-tendon apparatus increases. Under the influence of these factors, the woman’s body is rebuilt, that is, preparations are underway for future childbirth. This condition explains one of the reasons why hip pain occurs during pregnancy.
Possible treatments
Yoga for pregnant women strengthens muscles, improves blood flow.
After an examination and receipt of test results, appropriate therapy is prescribed. There is no specific method for treating pain in the hip joint during pregnancy, because discomfort can be caused by various factors.
If pain occurs due to weight gain, it is necessary to reduce the load on the joints. In this case, swimming, yoga for pregnant women, Pilates, and water aerobics are effective. Water procedures will be especially useful: they help strengthen muscles without loading the joint, and improve blood circulation.
A fairly effective method of treating pain in the hip joint during pregnancy is the use of traditional medicine. It is necessary to first consult a gynecologist, because some drugs can cause irreparable harm to the pregnant woman and the fetus.
Pathologies of the hip joint that arose before pregnancy and during pregnancy cannot be treated. Any operations, endoprosthetics and other radical methods of therapy can be used only after the birth of the baby, if the disease does not pose a threat to the life of the mother or child.
Medicines
The lack of calcium and iron is quite easy to compensate for by taking tablets or special vitamin complexes. Only a doctor can prescribe such medications after identifying a deficiency of microelements in the mother’s body. Uncontrolled use of calcium supplements can lead to the appearance of kidney stones, seizures, increased excitability and the development of other pathologies.
Most medications are contraindicated during pregnancy, so the issue of prescribing painkillers is considered separately in each case of the disease. The components of such drugs easily cross the placental barrier and can have a negative effect on the development and formation of the fetus.
Gymnastics and massage
Massage helps temporarily relieve severe pain. However, the points and methods of permitted manipulation are quite limited, so it is recommended that the procedures be performed only by a qualified specialist. Movements should be careful and light. Improper massage during pregnancy can trigger premature birth.
A safe and effective method for relaxing the muscles of the lower extremities, back and perineum is regular exercise. A set of exercises is selected depending on the stage of pregnancy. When performing gymnastics, a woman should not feel pain or discomfort.
Increased stress and mineral deficiency
Intrauterine development of the fetus contributes to a woman’s natural weight gain. During the entire period of bearing a child, the expectant mother can gain from 10 to 15 kg of excess weight.
Weight gain begins to actively manifest itself in the third trimester of pregnancy. The uterus is enlarged to the maximum, a layer of subcutaneous fat is formed. All these factors negatively affect the biomechanics of the spinal column and pelvis. The main load is borne by the pelvic bones and hips.
Such transformations in the osteoarticular apparatus of the supporting system cannot take place without leaving a trace. A woman complains of pain in the osteoarticular region of the pelvis, hip joint, ankle and distal limbs. As a rule, these are aching and/or nagging pain.
The skeleton of a future person begins to form at 7-8 weeks , and therefore it requires active saturation with mineral components, which can only be obtained from its mother. During this period, the female body requires an increased rate of calcination. In fact, the mother's required calcium intake increases threefold. To activate the mineralization of the musculoskeletal and ligamentous systems, the expectant mother also needs to consume as much vitamin D as possible.
Due to insufficient mineralization and natural stress during pregnancy, the hip joint hurts.
Diagnosis of pain in the hip joint
During pregnancy, most instrumental diagnostic methods are not available due to the likelihood of negative effects on the fetus. A survey and visual examination by a gynecologist is carried out, and a biochemical and general blood and urine test is prescribed. This is enough to exclude the development of pathology that threatens the course of pregnancy.
In the first trimester of pregnancy, the only available instrumental diagnostic method is ultrasound. Examination of the hip joint makes it possible to determine the distance between the parts and surfaces of the joint, the integrity and structure of the cartilage, and exclude the development of pathologies, injuries and other damage. For the same purpose, an ultrasound scan of the symphysis, symphysis and lower back is performed.
From the second trimester of pregnancy, a woman is allowed an MRI. It is carried out only in extreme cases, as it has some contraindications.
Referring pains
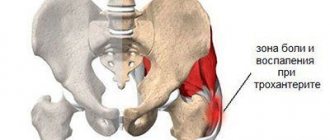
The cause of pain symptoms in the hip joint may be chronic inflammation of the osteoarticular segment of a rheumatic (arthritis) or arthrological (osteoarthrosis, coxitis) nature. With chronic arthritis, the inflammatory process can worsen in the hip joint due to the heavy load on the joints.
There are other etiological and pathogenetic mechanisms that involve the destruction of articular cartilage and subchondral bone:
- aseptic inflammation of the joints as a result of an extra-articular infection;
- hereditary predisposition to rheumatic diseases;
- infectious damage to articular cartilage by a bacterial, viral or infectious-allergic agent;
- stiffness and painful discomfort can be caused by a cutaneous form of psoriasis - psoriatic arthropathy.
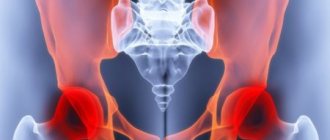
What healthy and diseased joints look like.
A more complex transformation of a degenerative-dystrophic disorder, when the hip joint hurts during pregnancy, is deforming osteoarthritis. In addition to pain symptoms in the hip joint, the woman feels a limitation in her range of motion. Abduction and adduction of the leg becomes problematic; pain is felt not only when walking, but also at rest.
With such a clinical pathology, the entire period of pregnancy will be accompanied by constant pain attacks. After childbirth, urgent treatment is necessary.
Preventive measures
The bandage significantly reduces the load on the spine and joints.
A healthy lifestyle, absence of stress, overwork and bad habits will allow you to avoid discomfort in the joints during pregnancy. A woman's nutrition should be complete. The diet should include dairy products, fish, vegetables, fruits and nuts.
Walking in the fresh air and water procedures are very useful for the expectant mother: they help strengthen the muscles and maintain the elasticity of the ligaments.
Heavy stress on the joints during pregnancy contributes to the exacerbation of chronic diseases of the femoral joint area and provokes neurological pain that radiates to the buttocks. It is recommended to wear special bandages and knee pads to reduce and redistribute the load on the joints. At the same time, they will help prevent degenerative changes in cartilage and bone tissue against the background of hormonal imbalance and lack of microelements.
Dysfunction of the pubic symphysis
Arthritis of the hip joint, or dysfunction of the symphysis pubis, is a fairly convincing argument for pain in the hip area. Having “learned” about pregnancy, the female body begins to actively prepare for childbirth. All articulating segments of the small and large pelvis begin to moderately soften, including the vertical connection of the upper branches of the pubic bones located in the middle of the pelvis - the pubic symphysis. By stretching, it will further facilitate the unhindered passage of the fetus through the mother’s bony pelvis.
In exceptional cases, physiological processes occur that exceed natural boundaries. Then pain occurs in the pelvic joint of varying degrees of intensity. Excessive relaxation of the osteoarticular joints of the pelvis can lead to rupture during childbirth.
A calming factor is dysfunction of the pubic symphysis, in which the hip joint hurts, disappears after childbirth. The causes of dysfunction of the symphysis pubis during pregnancy are metabolic, biochemical, hormonal or anatomical components.
Clinical signs of dysfunction:
- painful shooting localization in the symphysis;
- irradiation of the pain reflex to the groin area, lower abdomen, thigh or ankle joint;
- increased pain discomfort most often manifests itself during active actions: walking, bending and turning the body, when abducting the hip to the side;
- difficulties with bowel movements and urination.
Also, pain in the symphysis can be aching or pulling, causing a woman to experience unmotivated constant fatigue.
Possible complications after childbirth
Often, women even after childbirth have pain in the hip joint, and this is not always associated with pelvic deformation. In most cases, the female body, which has suffered physiological stress during childbirth, responds with periodically occurring pain in one or another anatomical area.
Dr. Sperling's recovery recommendations:
Thus, pain in the hip joint sometimes becomes a projecting reflection of pain symptoms in the lumbosacral spine. During pregnancy, all muscles, tendons and ligaments of the anatomical parts of vital activity were stretched, lengthened or, conversely, became shorter.
It takes time for the entire musculoskeletal system and ligamentous joints to return to normal. The exception is chronic diseases of neurological pathologies, which the attending physician should have known about before birth.
Recovery after childbirth
For a woman, the postpartum recovery period is very important, since the musculoskeletal system undergoes many changes at the very beginning of pregnancy. As the load on the hip joints and lumbosacral spine increases, the muscle ligamentous-tendon functionality completely changes.
During pregnancy, there is a slight shift in the center of gravity of the musculoskeletal system. Therefore, women often have problems with mobility in the knee, hip and lumbar joints. This situation leads to complicating pain symptoms. A woman who has given birth experiences pain in the joints, aches in the bones, and sometimes muscle spasms in the form of cramps.
Excess weight enhances the pain response, which can eventually transform into obesity, which leads to further provocation in the form of cardiovascular pathologies or the formation of metabolic syndromes.
Video about the nuances of excess weight during pregnancy:
Pregnancy means the appearance of stretch marks on the skin in the most undesirable places for a woman. All this negatively affects the well-being of sensitive and psychologically unstable individuals, causing them postpartum depression and a decrease in psychomotor reaction.
It is important that during the postpartum period a woman has a qualified mentor who would develop a special program for comprehensive and individual recovery. In some regional and district centers, specialized centers for postpartum rehabilitation have long existed.
When turning to specialists, the female body receives:
- slim and fit figure;
- strengthening the osteoarticular and muscle corset of the hip and lumbar girdle;
- reduction of subcutaneous fat;
- improvement of psychological and general physical condition;
- normalization of your own weight.
Consultation on individual postpartum recovery programs and treatment of certain diseases can be obtained by calling:
- In Rostov-on-Don: Family clinic “9 months”, tel. 8 (863) 288-00-00.
- In Vladivostok: Sports and recreation center, tel..
- In Sochi: Shaping Federation of Sochi, tel. 7 (918) 918-45-99.
- In Moscow: V.I. Dikul Center, tel.,.
How to prepare for pregnancy
For a woman, not only therapeutic and preventive postpartum rehabilitation is very important, but also preparation for pregnancy itself. It is necessary to cure the pathologies of the body, strengthen the main segments of the spine, thoracic and lumbosacral regions, and the bone joints of the hip skeleton.
Proper nutrition will help with this, when harmful components are excluded from the diet, for example, salty and fatty foods. After consulting with your doctor, in the absence of concomitant chronic diseases, you need to supplement your diet with mineral supplements and vitamins.
Exercises useful before pregnancy:
Water and air procedures, general physical training, that is, a set of therapeutic and preventive exercises for stretching the ligamentous-muscular apparatus of the supporting system and the pelvic floor muscles, and increasing the mobility of osteoarticular joints will help strengthen the immune system.
Recommended set of exercises
| Treatment and prophylactic purposes | Gymnastic exercises |
| Strengthening the pelvic floor muscles |
|
| Strengthening the hip joint |
|
| Lumbosacral support |
|
These gymnastic exercises can be done not only in preparation for pregnancy, but also during it and after childbirth. The only condition is the approval of the consulting gynecologist or other specialized specialist.
A set of physical exercises cannot be performed in the presence of pain syndromes in the corresponding areas of the support system.
Objectives of LH in the first trimester of pregnancy:
Activation of the cardiovascular and bronchopulmonary systems to improve overall metabolism and increase adaptive capabilities; improvement of the psycho-emotional state of the pregnant woman; improving blood circulation in the pelvis and lower extremities to prevent venous stagnation; strengthening the muscles of the back, abdominals and lower extremities to prevent pain syndromes of the musculoskeletal system; training in volitional tension and relaxation of muscles and proper breathing; preservation and development of mobility of the spine and other joints.
The characteristics of a pregnant woman’s body in the first trimester require individual sets of exercises. The complex includes dynamic exercises for training the muscles of the arms, legs, muscle “corset”, and relaxation exercises. Exercises should be simple and cover large muscle groups. The movements are performed in full. Therapeutic gymnastics classes also include training in abdominal and thoracic breathing.
When performing exercises, use all the basic starting positions. Therapeutic gymnastics procedures are carried out at a moderate, calm pace, avoiding excessive stimulation of the nervous system. Breathing should be calm and rhythmic. The coordination ease of the exercises performed, their low intensity, which gradually adapts the cardiovascular and bronchopulmonary systems to physical activity, make it possible to recommend them to all pregnant women, regardless of their general condition. However, women who were involved in sports before pregnancy can continue training, but at a lower intensity and excluding competitive loads.