Elbow pain is one of the most common problems. Elderly joints in the elbow hurt quite often, but young people can also experience a similar pathology. This discomfort not only interferes with life, but can also greatly limit the ability to work and lead to unpleasant consequences. First, you need to diagnose the cause of pain by contacting a specialist, and after making a diagnosis, you can treat the corresponding disease using a variety of methods, allopathic and traditional methods. The main thing is to find out the exact cause of the pain.
Elbow pain
Elbow structure
When most people hear the word “elbow,” they think of the bend of the joint (hitting with the elbow). In the old days, this was the name for the place from the wrist to the bend of the elbow; there was even such a measure of length: elbow - 35.6 cm. It is anatomically correct to distinguish:
- Shoulder - from the shoulder to the elbow joint.
- The joint itself.
- Forearm - from elbow to hand.
The elbow joint is a trochlear-shaped complex joint of three simple joints united into a common ligament. The three bones of the human body (radius, ulna and humerus) together with the corresponding muscles (biceps, triceps and brachialis) make it possible to bend and straighten the arm, raise and lower it, and also perform other actions.
Joint structure diagram
Potential danger
The elbow joints provide sufficient mobility of the limbs and forearms. In the absence of qualified treatment for these symptoms, a person risks encountering the following consequences of elbow pain:
- impaired blood and lymph circulation;
- a sharp decrease in physical activity;
- necrotic changes in soft tissues and nerve endings;
- severe swelling that interferes with arm movement.
If your elbow joints constantly hurt during exercise, you should immediately see a doctor, and you should also give yourself first aid in the form of analgesics and ointments to relieve swelling.
Common causes of pain
Pathologies of articular bones, ligaments, and muscles provoke pain in the elbow joints. The reasons for this can be varied.
Most often the problem is caused by:
- External or internal epicondylitis (in 80% of cases).
- Vertebral pathologies – intervertebral hernia of the thoracic region, when “referred” elbow pain appears (about 20%).
- Arthrosis (up to 10%).
- Arthritis (about 7%).
- Injuries.
Epicondylitis
One of the main causes of pain is epicondylitis, which a person can get at any age. Pain increases with loads, lifting and carrying loads; the cause is injury and overexertion. When palpated, unpleasant sensations occur on the sides of the joint, at the lateral bones.
Hernia
With problems with the thoracic curve of the spine, the nature of the pain is somewhat different. It usually radiates to the arm, so it seems that the whole limb hurts. Typically, pain is caused by pinched nerves due to a herniated disc in the thoracic spine. At first they are insignificant and appear only under load, but then they intensify, becoming sharp and acute. Such attacks are called lumbago.
Important! A sudden attack of pain in the right arm is an indicator of myocardial infarction.
Arthrosis
With arthrosis, aching pain is a consequence of the destruction of articular cartilage. When the arms are fully flexed/extended, discomfort and crunching occurs.
- Bruise of the elbow joint - symptoms, causes, treatment and consequences
Arthritis
With arthritis, pain occurs even at rest, and when touched it intensifies. The affected area is swollen, reddish in appearance, and there is an increase in temperature. Arthritis is often accompanied by bursitis - inflammation of the periarticular bursa as a result of injury or constant irritation of this area (a person leans on his elbows). In this case, a formation appears on the outside of the hand, elastic when pressed, which is filled with liquid.
Bursitis
Injuries
The most common injuries are fractures, dislocations, as well as sprains and ruptures of tendons. Pathologies are caused by mechanical damage, impacts, accidents. In such cases, severe pain occurs, which increases with movement or touch. There is swelling, hematomas, and the joint itself is deformed. Falls and impacts often result in tissue bruises, and dislocations occur if a person falls on an outstretched arm. With subluxations, the symptoms are similar, although somewhat weaker. Such injuries can be accompanied by ruptures of the ligaments and periarticular capsule, and the pain is very severe and it becomes impossible to move the injured limb.
Characteristics of pain in the shoulder joint in various diseases
As we have already found out earlier, pain in the shoulder joint can occur during a variety of diseases. Next, we propose to dwell in detail on each of them.
Osteochondrosis
Osteochondrosis affects the cervical spine, as a result of which a person may experience pain in the shoulder joint. To find out exactly where the source of discomfort is located, you need to make a circular movement with your shoulder. If there is referred pain, it will be felt immediately. Otherwise, unpleasant sensations occur when turning or tilting the neck.
Injuries
When considering injuries to the shoulder joint, the most common are: dislocation, rotator cuff injury, sprain, muscle tear. With these problems, a person also complains that his shoulder hurts when he moves his arm. Unpleasant sensations may vary depending on how a particular injury was received.
Arthritis
This disease develops when bone growths affect, and in some cases injure, nerve endings. If arthritis occurs, the pain in the shoulder joint does not subside either during movement or at rest.
Arthrosis
A disease such as arthrosis is characterized by degeneration and subsequent ossification of cartilage tissue. Over time, the bones begin to intensively rub against each other. With the disease, sharp pain in the shoulder when moving is additionally accompanied by a crunching sound. This occurs because cartilage tissue turns into bone, forming a mass of processes, as a result of which motor function decreases.
The danger of the disease is that it may not manifest itself for quite a long time. Gradually, joint mobility decreases and a person feels tired in the shoulder even after minimal load. The pain in this case is present throughout the day.
Brachial neuritis
Neuralgia of the shoulder joint occurs due to an inflammatory process. This problem is also called plexitis or neuritis. One of the most distinctive characteristics of a person having this disease is the loss of sensation in the hand, as well as stiffness and limited movement.
The fact is that the brachial plexus includes short and long branches that run throughout the human body. They begin in the area of the shoulder girdle, and end with the muscles that are located in the chest and on the back. If the nerve fibers located in the shoulder are damaged, this state of affairs will negatively affect the overall well-being of a person.
Tendinitis
Tendonitis is generally understood as inflammation of the tendons in the shoulder joint, which also causes pain. In most cases, the disease is provoked by an infection, therefore, at the time of collecting anamnesis, specialists are required to ask the patient whether he has recently had a cold or any health problems.
If a person does not treat tendinitis for a long time, the disease will very quickly lead to the appearance of nodules in the tendon area.
Capsulitis
Capsulitis is considered a rare pathology. The disease is accompanied by an inflammatory process in the joint capsule. In this case, the muscles become stiff, making it difficult for a person to make rotational movements. Discomfort extends to the entire shoulder joint. The pain when moving the arm is severe, making everyday activities unbearable.
Calcification of ligaments
Ligament calcification occurs when calcium accumulates in the tendon fibers. The surrounding tissues become inflamed, causing the person to experience severe pain. Such a pathological process is not uncommon and most often occurs in people over 40 years of age.
Other causes of pathology
In addition to the listed diseases, there are many other causes of pain, for example, problems of innervation, pathology of muscles and other tissues:
- Chondrocalcinosis is a joint disorder caused by salt deposits. The patient suffers from severe pain, there are mobility impairments, fever, redness, and the joint swells.
- Osteophytes - the formation of outgrowths on bone tissue. With activity, tissue injuries occur and the problem intensifies.
- Synovial chondromatosis. It is also associated with metabolic failures; pathological cartilaginous structures appear in the joint. Characterized by pain, swelling, difficulty bending and straightening the arm. Pain appears during activity, and then may be present at rest.
- Gout is an inflammation caused by deposits of urate salts. This, in turn, provokes a burning sensation and aching sensation.
- Tumors that can manifest themselves as mild nagging pain. As they grow, the malaise intensifies to the point of requiring the use of drugs to suppress them.
- Tendinitis is an inflammation of the tendon, a disease of athletes. It happens due to constant overload, injuries and infections. The elbow area is swollen, hyperemic, and the joint is very painful.
- Synovitis is an inflammation of the joint capsule in which fluid accumulates, which leads to compressive pain.
- Diffuse fasciitis is a disease of the fascia (ligaments) and the tissues closest to them. The pain is mild at first, but intensifies as the pathology develops. The skin on the hand looks like an orange peel, and a lump can be felt underneath it.
- Cubital tunnel syndrome associated with ulnar nerve entrapment. This pathology is caused by constant injuries resulting from prolonged monotonous movements, autoimmune diseases and inflammation. At the same time, stiffness is felt, it is difficult for the patient to hold objects, the hands and fingers, especially the little fingers, become numb.
- Neuritis is an inflammatory process of the ulnar nerve, in which severe pain appears, the hand begins to go numb, sensitivity disappears, and paralysis may even develop.
- Blood diseases (hemophilia), when internal hemorrhage causes pressure on the nerves, causing pain.
- Neurotrophic Charcot arthropathy is a sign of disorders of the spinal cord and peripheral nerves. The hand swells, its sensitivity decreases.
Joint pain
Why does my elbow hurt?
The elbow joint is a complex joint; it consists of the following parts: the radius, humerus and ulna. Essentially, these are three joints enclosed in a single joint capsule. The ulnar nerve passes through the joint and is located quite close to the skin, passing between the tendons of the muscles of the forearm. Therefore, it is easy to “knock out” the elbow by accidentally hitting the radial nerve. A person’s sensations when they bruise their elbow are similar to an electric shock, after which the arm remains immobilized for a short time. This is the simplest reason why pain in the elbow appears against the background of absolute health. Pain in the joint has many causes, leading to inflammatory processes in various tissues that make up the anatomical formation - the humeral-ulnar joint. The concept of "elbow" has two meanings. Both apply to the upper limb. Firstly,
This is the length of the arm from the wrist to the elbow.
Secondly,
the elbow joint itself.
Since the ancient measure of length is now obsolete, these parts of the arms are called forearms. And pain in the elbow in medicine is determined by the localization of sensations in the elbow joint. The following reasons lead to this condition:
- Traumatic lesions;
- Arthrosis;
- Arthritis;
- Gout;
- Lesions of bones and articular surfaces (osteophytes, chondrocalcinosis);
- Tumor processes.
In addition to damage to the articular surfaces, pain in the elbow causes inflammation of the muscles and ligaments:
Bursitis; Fasciitis;
- Epiconite;
- Tendinitis;
- Cubital tunnel syndrome.
Diseases of the cardiovascular and nervous systems lead to pain in the elbow:
- Cardiac ischemia;
- Hemophilia;
- Osteochondrosis and intervertebral hernia;
- Ulnar nerve neuritis.
The relationship between the vascular, neuromuscular and skeletal systems is so tight that it becomes clear why elbows hurt in the absence of damage to joint tissue. Pain in the elbow joint
Undoubtedly, dislocations, subluxations and fractures are accompanied by pain.
Diagnosis of traumatic injuries is simple and is confirmed by x-ray examination. It is much more difficult to determine arthrosis, which is a lesion of the cartilaginous plates of the articular surfaces. As a rule, pain in the elbow joint due to degenerative processes of cartilage tissue occurs only during movements that are accompanied by an unpleasant crunching sound. The articular surface becomes swollen, but no obvious signs of inflammation are detected. In patients suffering from arthrosis, the elbow hurts when flexing and maximally extending the upper limb. Arthritis
is translated into Russian as “inflammation of the joint.”
Accordingly, it is accompanied by all the signs of an acute process. These are pain in the elbow, dysfunction of the joint, redness, swelling and increased temperature in the area of the joint capsule. Gout and chondrocalcinosis
, in fact, represent one phenomenon: deformation of cartilaginous surfaces.
Roughness on the smooth parts of the contacting joints increases friction and irritates the receptor apparatus. This is why elbows hurt in diseases associated with metabolic disorders. The resulting tumors of muscle, nervous or bone tissue also compress the receptor field and blood vessels supplying the elbow joint. Inflammatory processes of connective and muscle tissues manifest themselves in the same way as lesions of the articular surfaces. Acute pathological changes, one way or another, manifest themselves as intense pain. However, the elbow does not hurt at all when bending due to microtraumas of the ligamentous apparatus. The disease is classified into a separate form - epicondylitis.
This is the so-called “tennis elbow”.
It occurs in people who are not related to this sport. With bursitis,
a protrusion appears in the area of the elbow joint, filled with inflammatory exudate.
Outwardly it resembles a hernia, is characterized by sharp pain and red-purple color. Cubital tunnel syndrome
, or tunnel syndrome, occurs when the ulnar nerve is compressed in the cubital tunnel area.
When the nerve is damaged, pain in the elbow joint occurs regardless of physical activity. The main manifestation of the pathology is a feeling of numbness, spreading to the shoulder and little finger. With coronary heart disease,
pain in the elbow spreads to the area of the forearm of the left hand.
They have an irradiative nature. In hemophilia
, due to a blood clotting disorder, hemorrhages occur in the joint capsule.
Blood elements irritate the articular surfaces and provoke the growth of granulations, which aggravate the pressure on the joint. Hemarthrosis develops, prone to suppuration and the formation of a cicatricial adhesive process. In hemophilia, pain in the elbow joint is acute and difficult to treat with non-narcotic painkillers. Intervertebral hernia
, as a consequence of osteochondrosis, compresses the nerve bundles emanating from the spinal cord trunk.
When a disc herniation appears in the thoracic region, pain is felt in the elbow on the affected side of the spine. A distinctive feature of damage to the nerve bundle is the prevalence of pain: from the shoulder girdle to the elbow joint. A patient suffering from a herniated disc may wake up at night with pain in the elbow, and this happens without any movement of the arm. Pain begins in the neck area and instantly moves to the elbow joint. Ulnar neuritis
often accompanies carpal tunnel syndrome, but can develop independently.
Symptoms of inflammation of the nervous tissue are not limited to pain, but lead to loss of sensitivity and atrophy of muscle tissue. With a prolonged course of the disease, the muscles weaken so much that a depression forms in the form of a groove on the forearm between the ulna and radius bones. Elbow pain, treatment
If you experience pain in the elbow joint, you should consult a doctor. A traumatologist deals with joint pathology, and a neurologist deals with problems with motor activity. In cases of injury, it is necessary to know about the first aid that needs to be provided to the victim. For pain in the elbows, treatment in terms of first aid is limited to applying cold to the bruised area. A heating pad with cold water or ice from the refrigerator will do just fine for this. If you do not have a first aid kit at hand, you should apply an improvised bandage in the form of a scarf to provide rest to the injured hand. Even a specialist cannot correct a dislocated complex joint without an x-ray examination, since there is a possibility of ligament rupture. When the cause of pain in the elbows is known, treatment is prescribed by a doctor of the appropriate profile. If suppuration or hemorrhage occurs in the joint, a puncture is performed followed by pumping out the contents of the joint capsule. Therapeutic treatment consists of prescribing painkillers and anti-inflammatory drugs. For acute pain in the elbow, any physical exercise is contraindicated, but physical therapy is effective.
Source: https://www.neboleem.net/stati-o-zdorove/7495-pochemu-bolit-lokot.php
Classification of pain sensations and features of their manifestation
If pain occurs when pressing near the elbow bones, moving and loading the arm, then the cause is most likely due to too intense training or physical work.
The pain may also be:
- Aching and pulling (the joint pulls) - symptoms of neuritis, oncology, arthritis, cubital tunnel syndrome, bone tuberculosis.
- Sharp, high intensity, indicating injury. Any inflammation also gives a similar reaction.
- Acute, which occurs with arthritis, epicondylitis and any injuries.
- Burning, which can signal angina or heart attack.
- Permanent – a symptom of joint deformation, untreated injuries or oncology.
- Shooting is an indicator of nerve compression.
- Chronic (aches in the joints) with periodic deterioration and improvement. Characteristic of gout, arthrosis and arthritis.
Diagnostic features
The elbow joint is easily accessible for examination and research, so diagnosis usually does not cause any particular difficulties for doctors. First, the doctor examines and collects anamnesis. Sometimes this is even sufficient, but additional examination is required to clarify. Typically, the doctor will order a blood test and refer you to:
- ultrasound;
- X-ray of the spine and joints, radioisotope scanning;
- MRI;
- CT;
- electromyography;
- biochemistry, general blood test, rheumatic tests;
- joint puncture.
Pain: first aid
If your elbow suddenly hurts, but there is no way to see a doctor, then first aid may consist of relieving these sensations by taking painkillers. You can take any analgesic or non-steroidal anti-inflammatory medication (ibuprofen, nimesulide). Injections are usually much more effective than ointments and tablets. It is necessary to try to provide rest to the elbow, immobilize it, giving the arm a comfortable position.
If the pain is acute and lasts a long time, you should definitely visit a doctor. You should also immediately contact a medical facility if you are injured. If pain appears after overloading the arm (due to sports activities, lifting and carrying heavy objects, heavy work, etc.), then you should wait a couple of days. In case of increased pain, swelling, redness and further deterioration of health, you should immediately consult a doctor.
Treatment
If the sick person does not seek help on time, therapy will take longer, and the disease will become chronic, worsening the quality of life and reducing performance. In case of injury, you need to fix the limb with a splint and contact a traumatology department. If the patient:
- Ligaments in the elbow joint hurt: what to do?
- a displaced fracture, the doctor will compare the fragments and apply a plaster cast;
- dislocation, it will be reduced;
- Tendons are torn; they are usually stitched surgically.
If the problem is not the result of an injury, then you need to contact an orthopedist.
If there is loss of sensitivity, numbness, or weakness, a neurologist will help. Limited mobility, pain, and swelling require examination by a rheumatologist.
To properly treat pain, it is necessary to make a correct diagnosis:
- The main way to get rid of unpleasant sensations is to treat the underlying illness that caused them, eliminate stress and ensure rest for the affected limb.
- For inflammation, anti-inflammatory drugs are prescribed, sometimes additionally antibiotics.
- If the pain is unbearable, sometimes a blockade is performed. Physiotherapy, gels, ointments are used, and medicinal cream is applied to the damaged area.
Ointments and gels
Drug treatment
If pain occurs during flexion and extension, the doctor decides how to treat the problem. The following drugs are usually prescribed:
- non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs – diclofenac;
- hormonal – diprospan;
- chondroprotectors – alflutop;
- analgesics – ketaro;
- medications containing hyaluron - synvisc;
- antidepressants – for diseases of neurological etiology;
- B vitamins.
Relief of pain using fixatives
Orthosis
If pain is caused by injuries, severe physical exertion, intense sports exercises, then such problems are often treated with orthopedic methods. Doctors recommend wearing splints, plaster, orthoses, and other types of braces to limit the mobility of the affected limb or so that the athlete can continue to train.
Physiotherapy methods
Of the physiotherapeutic methods of treatment, the most effective are:
- cryotherapy;
- electro- and phonophoresis;
- laser and magnetic therapy;
- UVT, UHF;
- paraffin applications;
- exercise therapy;
- massage.
Shock wave therapy (SWT)
Surgical solution to the problem
If the process has already gone far, it will be possible to get rid of the problem only through surgery. Surgeons make incisions to remove pus or fluid, replace a joint, or remove bone spurs or diseased areas of bone.
UHF
Treatment with folk remedies
If the patient:
- Arthritis, it is recommended to crush eggshells and add a little milk. Use the resulting pulp for compresses.
- Arthrosis, you need to mix vinegar (apple) and honey, taken in equal parts, rub into the elbow, wrap warm.
- Epicondylitis, freeze the infusion of green tea, apply the cubes to the sore elbow.
- Bursitis, brew the same amount of chamomile flowers, burdock raw material, St. John's wort herb. The infusion is drunk for a month three times a day before meals.
Causes of pain in the elbow joint
Elbow pain can occur as a result of injury from a fall or indicates the development of a dangerous disease of the joint tissues:
- arthritis and arthrosis;
- gout;
- osteochondrosis;
- ligament rupture and joint dislocation.
If the elbow joint often hurts during exercise, doctors regard the symptoms as a clear sign of osteochondrosis. With such symptoms, the patient is in dire need of professional medical care, so it is impossible to delay contacting a traumatologist, otherwise the overall clinical picture may worsen in the shortest possible time.
Elbow pain when bending and straightening the arm
If the elbow joint hurts when bending, the discomfort may be caused by bursitis, an inflammation of the interarticular fluid. The main function of the fluid is to prevent joint friction during physical activity. For a number of reasons, the volume of the joint fluid can increase sharply, and its composition undergoes dramatic changes, which is manifested by severe pain. Often such discomfort appears along with other symptoms:
redness and swelling;
itching;
increased body temperature (fever);
bumps and compactions in the area of inflammation.
Doctors distinguish two types of bursitis - chronic and acute form. In the first stages, a person complains of the periodic appearance of acute pain in the elbow area; over time, the symptoms become more pronounced, and the disease is accompanied by extensive swelling.
In the chronic stage of bursitis, the patient no longer experiences such serious pain in the elbow area. The hand remains capable of performing its main functions, but the inflammatory focus is clearly visible even with the naked eye; its diameter can reach 10 cm.
Elbow pain when lifting weights
Acute pain in the elbow joint when lifting weights directly indicates the course of arthrosis. If there is a history of such a disease, lifting heavy objects and any other movements of the elbow are often accompanied by a characteristic crunch. If the disease is chronic, the nature of the pain may not be acute, but aching, constantly causing significant discomfort to the person.
The absence of therapeutic measures aimed at treating arthrosis will lead to a worsening of the disease, which is fraught with complete loss of motor function of the hand, as well as damage to other joints.
Pain when clenching your hand into a fist
If a person feels pain in the elbow joint when clenching a fist, doctors tend to consider this symptom as one of the first signs of the development of osteochondrosis. Other causes of pain may include:
- ligament ruptures and sprains;
- infectious diseases;
- problems with the immune system;
- elbow and hand injuries.
In the absence of timely assistance, there may be an increase in swelling of the arm in the elbow area, which will significantly affect motor function. In addition to hand discomfort, the patient risks experiencing frequent migraines, increased fatigue, decreased appetite and increased body temperature.
Pain syndrome when pulling up
Aching pain in the elbow when doing pull-ups on the bar is regarded as a consequence of excessive physical exertion or may indicate injury in the form of sprained or ruptured joints. If an athlete has not been injured, but pain in the elbow joint during exercise still makes itself felt, doctors regard the clinical picture as a symptom of the development of osteochondrosis, which is a fairly common sign of displaced intervertebral discs.
When you feel pain during pull-ups on the horizontal bar, the elbow often remains unchanged in appearance. If the diagnosis does not confirm osteochondrosis, the traumatologist will offer the patient symptomatic treatment.
Pain after intense exercise
Severe pain after physical activity indicates a possible course of epicondylitis - inflammation of the bony processes of the shoulder. Discomfort often manifests itself only when trying to bend or straighten the arm, or clench the hand into a fist. During palpation, the pain shoots only to the inner part of the palm, so treatment involves fixing the hand in a bent position.
Preventive measures
Prevention consists of avoiding overstrain of the joint in work and sports. Recently, orthoses or taping are often used for this purpose. If possible, you should avoid sudden and inadequate stress on your hands, colds and hypothermia, which can cause inflammation. You should also promptly treat other diseases that can cause joint diseases, and regularly visit doctors to promptly identify developing pathologies.
Elbow pain can be caused by a variety of different pathologies. Correct medical diagnosis is necessary to prescribe effective treatment. Timely treatment can help avoid serious consequences.
- Pinched nerve in the elbow joint - symptoms and treatment of the disease
The elbow joint has a complex structure: it is an articulation of 3 different bones and 3 small interacting joints. There are also muscles, nerve endings and blood vessels. Therefore, it is impossible to immediately determine where the pain in the elbow joint on the outside of the arm came from. Even a doctor will need a thorough examination and test results.
How to determine the cause of pain
To identify the cause of elbow pain, a person needs to undergo an examination. First of all, doctors take x-rays of the elbow joint in 2 projections for all patients. It allows you to identify gross changes in the bones that appear with arthrosis and severe chronic arthritis.
Hidden trauma.
On radiographs, one can often detect signs of epicondylitis: elbow spurs, areas of enostosis, decreased bone density and periosteal growths in the area of the epicondyles.
To identify cubital tunnel syndrome, the patient is checked for Tinnel's sign. When it is necessary to assess the condition of the periarticular tissues, synovial bursa and articular cartilage, an ultrasound is performed. If pain of a referred nature is suspected, the person is referred for consultation to other specialists.
If you experience pain in your elbow, do not try to treat yourself, it is better to immediately contact a specialist. This way you will maintain your health. Orthopedists and traumatologists treat pain in the elbow joint during exercise. Thus, it is not the elbow joint itself that needs to be treated, but a specific diagnosis that will be established during the diagnosis.
Causes of pain
Pain in the area of the elbow joint of the right arm can occur due to frequent repetition of actions or after prolonged muscle strain (from welding, sawing wood and other similar work).
Acute pain in the right elbow joint occurs in professional athletes. Either both arms hurt, or one, the “working” one, if it is strained more often due to regular training (for hockey players, tennis players, etc.).
The cause of joint pain may indicate the development of some disease, injury, bruise or pinched nerves. Painful sensations can cause a fracture or dislocation.
Pain when lifting weights
Any injury to the shoulder joint is accompanied by pain. Athletes often face this problem: when lifting or benching heavy weights, the likelihood of spraining the ligaments is too high.
A sign of such an injury is pain in the shoulder, which intensifies when moving the arm. In addition, you can visually notice swelling and redness in the shoulder area.
Movement of the arm is limited to such an extent that the person experiences noticeable pain when he tries to lift it high or simply put it behind his back.
Possible diseases
Let's look at what diseases can provoke pain in the elbow joint on the outside.
Lateral epicondylitis
It is called “tennis elbow,” although in practice many patients are people who have never held a racket.
Patients complain of the development of edema in the affected area. It is difficult to bend the elbow, and it is difficult to grasp and hold objects in the hand. Any tension in the elbow muscles causes a painful spasm.
Causes of development of lateral epicondylitis:
- increased load (strain) of the forearm;
- damage to the shoulder muscles;
- active movements accompanied by physical activity (professional or sports activities).
Arthritis
A common disease that is not limited to older people. Sometimes arthritis is caused by injuries to the tendons, muscles, or bones of the elbow.
Main symptoms:
- pain is preceded by inflammation of the joint;
- complications may develop;
- acute pain intensifies when trying to flex/extend the affected elbow;
- the elbow swells, redness is observed, the skin temperature in the damaged area rises;
- a “twitching” is felt inside the resulting lesion;
- a complication of the disease is characterized by increased body temperature, the elbow cannot be bent/extended.
Arthrosis
It is characterized by degenerative-dystrophic pathological changes in the elbow joint. A serious disease that can drag on for years; most patients are 45–50 years old, but there are cases of arthrosis developing in young people.
It is difficult for a person to move his arm in any way; attempts to bend/extend the injured elbow are accompanied by mild pain and a characteristic crunch.
Bursitis
An inflammatory process localized in the area of the posterior surface of the elbow joint. The cause is an infection entering the synovial fluid, causing the accumulation of serous exudate. Complications: suppuration of the affected area, increased temperature.
It is not difficult to identify bursitis. The disease can occur:
- after injury (fractures, bone dislocations);
- infectious disease (brucellosis, syphilis);
- prolonged heavy load;
- gout or the development of rheumatism.
Fracture, fissure or dislocation
Even mild injury to the joint is accompanied by acute pain: many active nerve endings are concentrated in the elbow area. Severe injuries can cause painful shock.
How to identify the problem:
- the damaged area quickly swells, hurts and turns red;
- local subcutaneous hemorrhage (in fractures), lacerations are observed;
- the elbow hurts (the pain is sharp and acute, difficult to endure);
- the injured limb loses mobility.
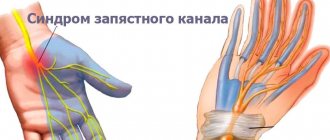
Carpal tunnel syndrome
A nerve located in the inner side of the right arm was pinched. May cause the development of a disease with severe symptoms. You can hear “shooting” when moving, the elbow and the entire right arm are numb, it is difficult to bend/extend the limb and lift objects.
Causes of carpal tunnel syndrome:
- Staying the injured elbow in one bent position for a long time. Excessive tension on the ulnar nerve occurs, which can trigger the development of unpleasant symptoms.
- A common habit is to sit at a desk or dining table, rest your elbows on the surface and rest your chin on your palms. The longer a person is in this position, the higher the risk of getting a pinched nerve.
Gout
Severe pathology that can worsen the condition and performance of joints. Gouty nodules often develop lower, affecting the big toes, but there are cases when the disease affects the joints.
The cause of gout is the appearance of disturbances in metabolic processes involving uric acid. Instead of being broken down and removed from the body, urate salts are deposited inside the joints and accumulate, gradually disrupting natural mobility. Osteophytes (bone growths) may develop.
Gout is characterized by the following symptoms:
- the elbow of the right hand hurts (both elbows often hurt at the same time);
- the affected joint turns red, hardens, and the temperature rises;
- excruciating pain, impossible to move, limbs practically “do not obey”.
Osteochondrosis
The doctor suspects a pathology if the joint hurts only when the hand is clenched tightly into a fist. The causes of the disease are the presence of endocrine pathologies and some metabolic disorders.
Symptoms of osteochondrosis, in addition to pain in the joint: numbness of the fingers, gradual change in the shape of the affected elbow, limitation of natural mobility.
Diseases that cause pain
The main cause of elbow pain is epicondylitis. It affects about 8% of the population of developed countries. The disease most often develops in athletes, people over 40 years of age and people whose work requires long-term performance of stereotypical movements (painters, builders, seamstresses, massage therapists). The cause of the pathology can be injury or regular physical activity.
Epicondylitis is characterized by degenerative-dystrophic changes in the muscle tendons that attach to the epicondyles of the humerus. Over time, this process is joined by reactive inflammation, which also involves nearby tissues. Because of this, a person experiences pain in the elbow joint during exercise.
Types of epicondylitis:
- outer. It is characterized by damage to the tendons that attach to the lateral epicondyle. It develops in many tennis players, which is why the pathology is also called “tennis elbow”;
- interior. In a person, the tendons attached to the medial epicondyle become inflamed. The pathology affects people who are forced to perform flexion-extension movements at the elbow frequently and for a long time. Internal epicondylitis occurs 10 times less frequently than external epicondylitis.
In 10% of cases, the elbow hurts during exercise due to arthritis. In orthopedic practice, monoarthritis is quite rare. Much more often, the elbow joint is affected together with joints of other locations. In this case, it is more correct to talk about polyarthritis. The disease may be rheumatoid, infectious, reactive or traumatic in nature.
Elbow pain can also occur due to traumatic damage to ligaments or tendons, synovitis, bursitis, deforming osteoarthritis, cubital tunnel syndrome and some other diseases. Unpleasant sensations in the left arm during physical activity may be the first sign of cardiovascular pathology.
Some people with cervical osteochondrosis may feel that their elbow joint hurts when they exercise. Such pain is of a reflected nature, that is, it is localized far from the source of the pathology. It can be caused by degenerative joints in the spine, overstrained shoulder muscles, or pinched nerves.
Table 1. Features of pain syndrome in various diseases
| Disease | Its distinctive features |
| Epicondylitis | The pain is localized on the inside or outside of the joint. It intensifies with extension and grasping movements, outward rotation of the hand, muscle tension and pressure on the tendon attachment sites. There is also limited movement in the elbow and decreased muscle strength in the upper limb. |
| Cubital tunnel syndrome | A person is bothered by pain in the elbow and sensory disturbances in the forearm. Unpleasant sensations always intensify when bending the arm. It is curious that with cubital syndrome, seamstresses and musicians usually have pain in the elbow of their right arm during exertion. But for drivers who like to place their bent elbow on the car door, the pain is localized on the left |
| Arthritis | The pathology is characterized by deterioration of elbow mobility, mild swelling, local increase in temperature and redness of the skin. The nature of pain varies with different arthritis. For example, with gout it is acute, with rheumatoid arthritis it is crippling. |
| Deforming osteoarthritis | The disease develops in old age and rarely affects the elbow joints. If this happens, at first aching pain occurs during physical activity and disappears after rest. Over time, it is constantly present. People with arthrosis also have decreased range of motion in the elbow. |
| Synovitis | It can develop as a result of injuries, against the background of arthritis or arthrosis. With synovitis, effusion accumulates in the joint cavity, which is why the elbow looks swollen and its contours blurred. Pain due to inflammation of the synovial membrane is localized directly in the joint area |
| Cervical osteochondrosis | Patients are bothered by aching pain in the neck and shoulder muscles. In some cases, they radiate to the back of the head and upper limb. Sharp pain in the elbow can occur when a nerve root or nerve innervating this area is pinched. |
Recommended Treatments
The treatment regimen will depend on the pathology identified by the specialist.
If it is a dislocation/bruise or sprain, the doctor will prescribe a therapeutic course, accompanied by the use of ointments, painkillers, traditional recipes, physical therapy and physiotherapy.
Necessary procedures to help establish the diagnosis:
- radiography;
- Ultrasound;
- laboratory tests (urine and blood tests).
In case of inflammatory processes (development of arthritis, bursitis or epicondylitis), the specialist’s task is to quickly eliminate the focus that is causing dangerous changes, that is, stop the inflammation, and at the same time reduce pain. Used: NSAIDs, various glucocorticosteroids, essential vitamins with antibiotics.
Stages of recovery: chondroprotectors, courses of physiotherapy, regular physical therapy, massage, manual therapy. Traditional methods: natural herbal decoctions, compresses (burdock or cabbage leaves are used), clay wraps, treatment with homemade ointments, honey.
With degenerative-dystrophic changes (development of gout, osteoarthritis or arthrosis), the inflammation is weak, there are no acute signs. The main problem is the destruction of cartilage, so the goal of therapy is to stop the process of abrasion and destruction of cartilage tissue and restore cartilage. Treatment: use of chondroprotectors, NSAIDs, development of a diet.
For gout, uricosuric and uricodepressive drugs are needed to eliminate acid accumulation. Various dietary supplements and multivitamins, special mineral complexes that can improve the condition of cartilage will be useful. Physiotherapy with exercise therapy will be mandatory, preferably sanatorium-resort treatment. Folk remedies will be a good help.
In case of neurological pathologies, consultation with a neurologist and rapid elimination of the factors that caused the pinched nerves are necessary. Recommendations include immobilization of the most damaged joint, the use of special exercises and drugs that can normalize neurohumoral regulation, and the prescription of painkillers (Analgin, Ibuprofen and other drugs). B vitamins (via injections) will be helpful. Severe injuries may require surgery.
If an injury occurs (fracture, crack), then examination by a traumatologist or orthopedic surgeon is mandatory. Fixation of the affected joint is required: the use of a plaster, an elastic bandage or an orthosis. The patient is prescribed anesthetics, a course of NSAIDs, the necessary antibiotics and muscle relaxants, vitamins, and chondroprotectors.
Severe injuries may require surgery.
Rehabilitation period: special exercises, vitamins, anti-inflammatory drugs, useful physiotherapeutic procedures.
Treatment is prescribed after diagnosis by a specialist.
Treatment for elbow pain
Before you begin treating elbow pain, you need to find out the cause of its occurrence. When you contact Mogilev Hospital No. 1 if you have pain in your elbow, you can get advice from our experienced specialists, traumatologists, who will always provide qualified medical care.
Diagnostic measures to help determine the cause of the disease and begin effective treatment of elbow pain:
- X-ray examination;
- Joint arthroscopy;
- Joint puncture (usually performed in conjunction with arthroscopy);
- Ultrasound of joints;
- Computed and magnetic resonance imaging;
- Laboratory tests for suspected gout, rheumatoid arthritis, etc.
An important diagnostic measure in the treatment of elbow pain is joint arthroscopy.
Arthroscopy is a way of examining a joint using an arthroscope (video camera). Arthroscopy makes it possible to conduct the most accurate examination of the joint.
Benefits of arthroscopy in the treatment of elbow pain:
- Minimally invasive surgical method of treatment;
- In this study, postoperative wounds are minimal in size, leading to rapid healing;
- Early recovery after joint arthroscopy can reduce the patient's stay in the clinic.
After conducting a series of diagnostic studies, traumatologists at our medical center will offer you the best treatment methods. Treatment for elbow pain depends on the disease, its stage, and the presence of complications. More often the treatment is complex. Drug therapy, physiotherapy (electrophoresis, magnetotherapy, paraffin baths), as well as surgical treatment methods are used.
Surgical treatment of elbow pain in our hospital is based on the latest achievements of domestic and foreign science in the field of traumatology and orthopedics. In addition, our hospital is one of the few that perform joint replacement surgery. The use of the methods of our center, as well as the modern equipment that our center has, allows us to guarantee only positive results of surgical treatment.
Methods of pain relief
First aid can be provided to yourself immediately, especially if acute pain occurs:
- eliminating any physical activity;
- fixing the injured elbow in one, half-bent position (a scarf will help);
- ensuring rest of the injured limb;
- for swelling, a cold compress will help (put ice in a bag, wet a towel or take a bottle of chilled liquid), apply periodically for 10-15 minutes, then wait half an hour;
- Painkillers will help eliminate pain: ointments (Traumel S, heparin ointment or Lyoton-gel);
- if the pain is unbearable, then painkillers Ibuprofen, Analgin or Nise will help.