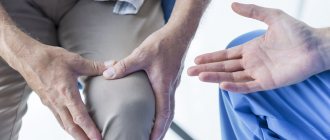
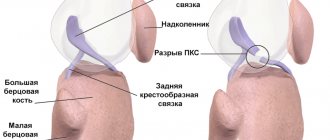
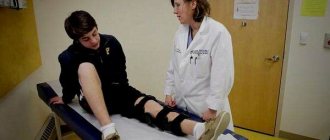
A tendon is a special structure made of collagen fibers that attaches muscles to bones. Tendons transmit muscle force to the skeleton and play an important role in providing movement. Thanks to their collagen composition, these structures are very strong and have little stretch. Sometimes there is a danger - damage to the tendons of the limbs. If trauma is ignored, it causes a number of dangerous consequences. Can a tendon heal and how to treat its ruptures? Specialists at Ladisten Clinic answer these questions.
Rupture of tendons in fingers
Due to the fact that the fingers do not have muscles, the hands move thanks to connective tissue - tendons, which ensure coordinated mobility.
© shutterstock
Tendon injuries rank first among all injuries. According to statistics, 30% of them are due to partial or complete rupture of the tendons of the hands. This is due to the special location of the connective tissue, which is easy to damage.
The most common injuries are tendon ruptures in the thumb, which limit the functionality of the hand by half. In 20% of cases, the tendons of the index and middle fingers are affected.
Rupture of tendons in the hands is divided into traumatic and degenerative types of origin.
A painful incident occurs due to such predisposing factors:
- Thinning of the tendons of the hands;
- Sudden lifting of weight;
- A certain gap between physical activities;
- Starting a workout without warming up;
- Reassessment of capabilities;
- Failure to comply with safety regulations.
The risk group also includes overweight people and elderly citizens.
Signs of illness
Symptoms of a hand tendon rupture will depend on the location. Common features include:
- Sharp pain;
- Impaired flexion or extension function;
- Numbness;
- Paresthesia.
If such signs appear, you should go to a hospital, since it is easier to get rid of arm tendon pain immediately after injury.
To reduce severe pain and not harm the affected tendons of the hand, before meeting with the doctor, you must:
- Raise your hand above your head;
- Apply a bandage;
- Apply a cold compress.
Treatment options
The tendons of the arms are restored through surgery, after which the patient is placed in a cast. The doctor also prescribes medications to relieve pain and inflammation.
During the rehabilitation period, a person must visit a massage room, exercise therapy and do therapeutic exercises.
Diagnostics
Injuries to the tendons of the extremities are first diagnosed by taking a medical history. Main symptoms:
- a characteristic click and sharp pain at the site of rupture at the time of injury;
- swelling in the damaged area;
- motor dysfunction. A person cannot bend or straighten a finger if the tendon of the finger is torn, cannot stand “on tiptoe” if the Achilles tendon is damaged, etc.;
- deformation or numbness of the limbs and fingers.
To confirm the diagnosis, doctors prescribe:
- x-ray (not always informative);
- Ultrasound;
- MRI.
Tendinitis
The tendons in your hands can become sore due to a condition called tendinitis. The disease is an inflammation that affects the elbow, shoulder joints and wrist.
© shutterstock
Inadequate load and degenerative changes are considered the main causes of tendinitis, which causes pain in the tendons of the hands.
As people age, the chance of getting tendonitis increases as the number of elastin fibers decreases. But they are the ones responsible for the elasticity of the tendons of the hands.
Among other causes, experts identify:
- All kinds of injuries;
- Various infectious lesions;
- Venereal diseases;
- Autoimmune system diseases;
- Arthritis;
- Gout and other metabolic disorders.
Signs of illness
Pain in the joints of the hands is the main symptom of the disease. At the initial stage of development of tendonitis, pain occurs only after physical exertion. But over time, in the absence of appropriate treatment, pain in the tendons of the hands becomes permanent and becomes unbearable.
When inflammation has reached an intense peak, the disease manifests itself:
- Impaired joint mobility;
- Local redness;
- High temperature;
- Crunch;
- Formation of nodules on the tendons of the hands.
If timely treatment is not started, the disease threatens to completely rupture the ligaments, which leads to surgical intervention.
Treatment options
You can get rid of arm tendon pain caused by tendonitis only after consulting a qualified doctor who will select the necessary treatment.
Often, treatment of the disease is carried out using:
- Anti-inflammatory drugs;
- Pain relievers;
- Locally irritating ointments containing capsaicin;
- Glucocorticoids;
- Physiotherapeutic procedures;
- Therapeutic physical education.
During the rehabilitation period, the patient is advised to avoid putting stress on the tendons of the arms so that the pain does not return and complications do not arise.
Problems with the tendons of the foot and ankle
The exact incidence of ankle tendinitis is unknown, but available evidence suggests that tibialis posterior and peroneal tendonitis are fairly common conditions. The tibialis anterior tendon is less commonly affected, except in younger athletes who are increasing their training programs or starting to run on inclines.
Risk factors for developing peroneal tendon problems include high arches, which can occur at any age. Lesions of the tibialis posterior tendon are associated with flat feet and are more common between the ages of 40 and 50 years.
Pathology of the tibialis anterior tendon.
Tibialis anterior tendinitis is characterized by pain and swelling on the front of the ankle. The disease usually occurs in middle and old age. The cause is often physical activity or injury to the ankle joint, and may be due to changes in the nature of physical activity or the type of shoes used. Symptoms are worse with prolonged standing and walking and relieved with rest. Upon examination, local pain and sometimes swelling in the area of the anterior surface of the ankle joint is revealed. Resisted dorsiflexion of the ankle often increases symptoms.
In Fig. Localization of pain and swelling with tendinitis of the tibialis anterior tendon.
Risk factors for tibialis anterior tendonitis include excessive tightness of the calf muscle, obesity, flat feet and exercise.
Pathology of the posterior tibialis tendon.
Tibialis posterior tendinitis is characterized by pain in the area of the inner surface of the ankle joint and arch of the foot, which intensifies with prolonged standing and is often accompanied by collapse (dropping) of the arch of the foot and visible protrusion of the navicular bone. The main objective signs of the disease are local pain along the tendon and in the area of its attachment to the scaphoid bone. If there is only local tenderness at the tendon insertion, it may not be tendonitis, but accessory navicular bone. This latter diagnosis can be confirmed radiographically.
Rheumatoid diseases lead to a decrease in the strength of the joint capsule and a gradual thinning of the tendons, and can cause, in particular, dysfunction of the tibialis posterior tendon.
The integrity of the tibialis posterior tendon can be confirmed by asking the patient to rise onto his toes on one leg. Some patients with severe tendinopathy simply will not be able to raise themselves onto the toes of one leg. This may be due to muscle pain or weakness, or both.
Pathology of the peroneal muscle tendons.
Patients with peroneal tendonitis complain of pain and sometimes swelling along the posterolateral aspect of the ankle joint. Concomitant involvement of the sural nerve (due to inflammation or damage to nearby tendons) may lead to decreased sensation or a burning sensation along the outer surface of the foot. The pain may be localized to the insertion of the peroneus brevis tendon on the metatarsal bone and, if preceded by recent trauma, radiography is necessary to rule out a fracture.
Rice. Localization of pain and swelling with tendinitis of the peroneal tendons.
If the retinaculum of the peroneal tendons is damaged, they can slip out of the groove of the lateral malleolus at the level of the ankle joint. This condition is called chronic peroneal tendon subluxation. Patients with this condition may describe a clicking sensation in the affected area during physical activity, and sometimes subluxation can be provoked by physical examination.
Tendinosis
Pain in the tendons of the arms is caused by tendinosis, an inflammatory process that leads to degeneration of the structure.
© shutterstock
People often confuse tendonitis and tendinosis, considering these ailments to be identical. But the diseases differ in etiology, nature and duration of course. Without proper treatment, tendinosis quickly leads to disability.
Experts have also established some differences in the causes. Tendinosis is caused by:
- Infectious factor;
- Genetic inheritance;
- Autoimmune causes;
- Various injuries.
A tennis player, a builder, a loader, a copywriter, an office worker, and a musician are always at risk. People whose activities are related to these professions should be careful and attentive to their health.
Signs of illness
This insidious disease manifests itself as intense pain in the affected area after physical exertion. In this connection, many are in no hurry to visit a doctor, as they associate these pains with ordinary overload. But with tendinosis, pain intensifies during palpation and persists with weak movements.
In addition to pain, a person observes:
- Formation of compactions;
- Deformation;
- Gradual loss of function.
Treatment options
To relieve the patient from pain in the tendons of the arms, doctors prescribe:
- Non-steroidal drugs that kill inflammation;
- Antibacterial agents;
- Electrophoresis;
- Magnetotherapy;
- Ultrasound therapy.
Achilles tendon treatment
Conservative treatment of the Achilles tendon
is based on pain relief, relieving swelling and providing rest to the affected tissues.
The etiology of the problem makes its own adjustments to the treatment strategy. For example, if an x-ray reveals calcification of the Achilles tendon
, characteristic of tendonitis, it is recommended to use shock wave therapy, and, if necessary, surgical treatment.
If the Achilles tendon
pain due to injury, local anesthesia (for example, novocaine) and a plaster cast are used. For complete ruptures and avulsions, suturing surgery is always performed.
Medicines
For the treatment of Achilles tendon
There are 2 main groups of drugs used: NSAIDs (non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs) and chondroprotectors.
NSAIDs (same as NSAIDs) help relieve symptoms of inflammation and reduce pain and swelling. They are usually prescribed in the form of gels, ointments and compresses, but in case of severe inflammation of the Achilles tendon
, tablets can also be used.
The course of treatment with oral NSAIDs usually lasts 10-12 days. You can use external remedies for inflammation for several weeks or even months (for tendon injuries). If the Achilles tendon hurts
even after taking NSAIDs, with severe tendonitis or inflammation, glucocorticosteroids are prescribed.
The value of chondroprotectors for the treatment of Achilles tendon
lies in their effect on collagen synthesis and the health of joint structures. This group of drugs also has a preventive effect, and therefore is recommended for regular use by people who are at risk for Achilles disease (professional athletes, patients with musculoskeletal diseases). Because the Achilles tendon lacks blood vessels, tissue repair is usually very slow. Taking chondroprotectors helps speed up this process and prevents the appearance of abnormal, unstable collagen fibers.
Chondroprotectors should be taken for at least 2-6 months a year, since they have a cumulative and prolonged effect. A classic example of a chondroprotective drug is Artracam - these sachets with glucosamine should be taken daily for 2-4 months. Artracam not only relieves pain and promotes normal collagen synthesis in the tendon, but also protects other joints and tendons involved in maintaining upright posture.
Fixation
Since the Achilles tendon is extremely sensitive to loads associated with body movement, patients are recommended to wear fixing bands and orthoses. It is also important to provide rest to the sore limb: you should avoid running, jumping, and suddenly stepping on the foot and heel; During everyday activities, such as climbing stairs, the body weight should be compensated by the calf muscles.
Ankle bandages help prevent further injury to the Achilles tendon, relieve swelling and promote normal tissue repair without unwanted scarring. At the first signs of an inflammatory process, it is recommended:
- applying a pressure bandage;
- rest with the ankle joint raised higher than the hip joint (for example, you can place a pillow or sofa cushion under your leg);
- applying ice or an ice compress (for no longer than 20 minutes).
To fix the affected tendon, you can tightly bandage the foot and lower leg with a regular or elastic bandage. It is advisable to consult a doctor before doing this. Practicing traumatologists say that it is extremely rare for patients to be able to apply the bandage correctly the first time and actually fix the muscles, ligaments and tendons in a stable position.
Exercises
For diseases and injuries of the Achilles tendon, therapeutic exercises are allowed only after the inflammatory process has resolved. At the initial stages, gentle stretching of the ankle muscles is performed. Strengthening them allows you to reduce the load on the tendon, and stretching them helps to properly structure the “young” collagen fibers, which were initially twisted like spaghetti.
With painless movements in the ankle joint, incl. when rotating the foot or lifting on the toes, you can move on to the main exercise therapy complex. Physical activity is increased gradually. adding from 5 to 10% per week. If your Achilles tendon hurts
after exercise, the load is reduced. Each therapeutic exercise session should begin with a warm-up (warming up the muscles) and a cool-down (stretching). This helps to avoid re-injury of the tendon and adjacent structures of the musculoskeletal system. The following groups of exercises are used:
- Balancing exercises. They train not only large, but also small muscles that are responsible for maintaining balance and serve to prevent tendon injuries.
- Stretching exercises for the short and long calf muscles.
- Exercises to stretch the muscles of the foot.
- Exercises to strengthen the calf and other muscles.
Therapeutic and preventive gymnastics for injuries and diseases of the Achilles tendon involves all the muscles of the legs, lower back, abdominals - i.e., those parts of the skeletal muscles that are directly responsible for stabilizing the human body and keeping it in an anatomically correct position. Such complex training, carried out every day to maintain tone, can significantly redistribute the load from the Achilles tendon.
During exercise, it is recommended to wear sports shoes that stabilize the ankles and provide good shock absorption of the foot (especially the heel). As an example, the following are effective exercises for restoring and strengthening the tendon.
- Stand upright until you feel a stretch in your ankles, then gently shift your weight to your affected leg. Trying to take the weight off your ankles through your calf muscles, shift your weight to your heel, lifting the front of your foot. Use your healthy leg to return to the starting position. When performing the exercise, noticeable discomfort is possible, which, however, should not turn into acute pain. The exercise is performed in 3 sets of 15 times twice a day. If necessary, you can increase the load with a small backpack.
- Place your heels on a step or other small raised surface so that your toes hang freely from it. Extend your right hand in front of you and place your left hand on your belt. Without losing your balance, slowly squat down and then straighten up. It is recommended to perform 3 sets of 10 exercises daily.
- Stand facing a wall at arm's length (not including your palm). Place one foot on the wall, pressing your heel into the surface with both hands. After a minute, change legs.
- Sit on the floor with your legs straight. Place a rolled towel over the instep of your foot, holding it by the ends. Gently extend your foot away from you, creating moderate resistance using the towel. It is recommended to perform 2 sets of 10 times throughout the day.
- Place a massage roll under your shin. Perform back and forth movements on it, trying to knead the calf muscles, but without touching the sore tendon. The shin can be rotated in different directions to increase the area of the muscles being stretched.
- Sitting on a chair, alternately “write” in the air with the toe of first one foot and then the other (letters, numbers, shapes). 10-15 approaches are recommended at intervals of 20 seconds.
To strengthen the calf muscles, patients may be recommended swimming, water aerobics, and cycling.
Physiotherapy
Physiotherapeutic procedures contribute not only to the elimination of local symptoms and speedy recovery from injuries. They also trigger the formation of healthy collagen fibers in the Achilles tendon (i.e., straightening and strengthening them). If your Achilles tendon hurts
, the following physiotherapeutic techniques are used:
- magnetic therapy;
- shock wave therapy;
- ultrasound therapy with medications (most often these are anti-inflammatory drugs that prevent the formation of unstable and rupture-prone scar tissue in the tendon and its sheaths);
- ozokerite;
- cryotherapy;
- paraffin applications;
- balneotherapy (especially mud therapy);
- therapeutic massage and exercise therapy.
As a rule, the duration of a course of physiotherapy is 10 sessions, but it can be extended as prescribed by the attending physician.
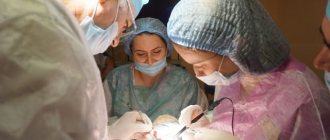
Surgery
Surgical treatment of Achilles tendon is used in cases where the Achilles tendon hurts
, despite complex therapy - i.e., when conservative treatment methods have already been exhausted or a priori cannot resolve the pain syndrome.
Typically, it is indicated for the formation of a bone spur on the back of the heel bone (called Haglund's deformity), severe ruptures, or even complete separation of the Achilles tendon. There are 3 main types of operations used:
- removal of bone growths;
- excision of damaged tissue that cannot be restored;
- stitching the tears with a lavsan or nylon seam.
Also, in case of ruptures, tendon repair may be recommended. Recovery after surgery on the Achilles tendon involves immobilizing the limb (including the knee joint) and wearing a special “boot” made of plaster or other material for 45-60 days. In the absence of contraindications, for a speedy recovery, massage, physiotherapy and exercise therapy are carried out under the supervision of a qualified rehabilitation physician.
Tenosynovitis
Pain in the tendons occurs due to tenosynovitis, which is also an inflammatory disease, but of the synovium. The disease is divided into acute and chronic forms, with periodic exacerbations of pain.
© shutterstock
Among the causes are:
- All kinds of injuries;
- Diabetes;
- Tuberculosis;
- Problems with the endocrine system;
- Weakened immune system.
Signs of illness
The earliest symptom of the onset of tenosynovitis is discomfort, which is not always paid attention to. Such thoughtless actions become a consequence of the transition of the disease to the chronic stage.
Then pain of varying intensity awakens and the following occurs:
- Edema;
- Redness;
- Heat;
- Stiffness of movements.
Doctors recommend that at the first incomprehensible symptoms you go to a hospital in order to begin treating the disease at an early stage.
Treatment options
Before prescribing treatment, specialists make a diagnosis to rule out other ailments.
Therapy is carried out using conservative methods, including medications and physiotherapeutic procedures.
Diseases that cause pain
Diseases that accompany constant pain in the tendons are well known to doctors. There are several such diseases - enthesitis, tendonitis, tendovaginitis, tenosynovitis.
Let's consider these problems in more detail.
- Tendinitis is a disease associated with changes in the structure of tendon tissues, their degeneration, and inflammation. The development of tendinitis is facilitated by adynamia, as well as frequent long-term stay in an uncomfortable body position (for example, in the workplace), and performing sports exercises without warming up. For example, truck drivers and auto mechanics experience tendonitis in the hand. Among the signs of this disease: severe pain in the tendon areas, as well as the tissues adjacent to them, frozen joint syndrome - a violation of its normal mobility. The symptoms of all other tendon diseases are similar.
- Tendinosis is a disease similar in symptoms to tendonitis, caused by tendon rupture.
- Tenosynovitis, tenosynovitis - inflammation of the connective membranes of the tendons. With this disease, one of the functions of the tendon is blocked, for example, the ability to flex at the joint. The disease occurs due to constantly repeated pressure on the joint or directly at the location of the tendon. Active friction also provokes tenosynovitis. You can recognize this disease by the nature of the pain: discomfort occurs only when moving, while at rest there is practically no discomfort.
- Enesitis or enthesopathy is a disease caused by inflammation of the areas where tendons attach to joints and muscles. This condition leads to the inability to make even minimal movements due to exceptionally sharp pain. The disease is provoked by physical overstrain and excessive load. Tennis players, golfers, and weightlifters often experience enthesitis.
Read also: Deforming arthrosis of the ankle joint
Stretching
Often, the reason why a tendon hurts in the arm is a sprain. Probably every inhabitant of the planet has encountered such a problem. Although this is a common pathology, it cannot be left to chance, as complications may arise.
© shutterstock
Sprains can be caused by:
- Unsuccessful landing on the hand;
- Sports activities;
- With a strong blow.
Signs of illness
Sprain pain occurs immediately after injury to a limb. In a short period of time, the bruised area becomes red and swollen. The victim can move his arm, but this causes pain and discomfort.
With such symptoms, it is better to seek medical help to avoid possible complications.
Treatment options
Common hand tendon sprains do not require complex treatment.
Before going to the doctor, a person must limit the mobility of the limb and lift it up so that a hematoma does not form. If you have pain intolerance, you can take a pain reliever.
The emergency room will apply a cast or a special pad to help keep the limb immobile.
Paratenonitis
Another inflammatory disease of the hand tendon can be paratenonitis. In medicine, the disease is also called crepitant tenosynovitis.
© shutterstock
The disease occurs due to the following factors:
- Various injuries;
- Overvoltage;
- Long repetition of monotonous movements.
Signs of illness
Manifestations of paratenonitis are:
- Pain in the injured limb;
- A tumor developing into a hematoma;
- Tendon crunching;
- Rapid hand fatigue.
Treatment options
To cure the disease, a comprehensive approach is required, including:
- Novocaine blockade;
- Plaster cast;
- UHF therapy;
- Therapeutic exercise.
This disease has a tendency to recur, so you should follow all the recommendations of your doctor.