Pathogenesis of neck pain on the left side
Pain can be caused by a variety of reasons. A symptom often indicates the presence of pathology and its progression or exacerbation. As a rule, pain in the left neck appears due to:
- osteochondrosis in this part of the spinal column;
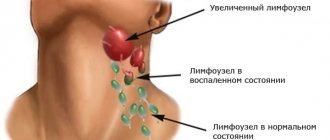
- infectious processes (colds, etc.) that provoke inflammation of the lymph nodes in the neck;
- injuries to the muscles or ligaments of the neck;
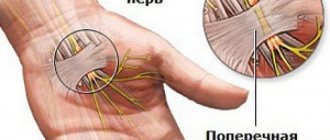
- pinched nerves with subsequent inflammation;
- muscle spasms, which are provoked by high levels of stress, hypothermia, drafts, etc.
How often a person will experience neck pain depends on age and the specifics of their lifestyle and work. If you have a sedentary job, don't like walking, and don't exercise even minimally, you'll most likely experience discomfort in your neck more often.
Causes of inflammation of the trigeminal nerve
Doctors believe that the main cause of inflammation of the trigeminal nerve is compression of it either inside the skull or outside it. Inside the skull, the trigeminal nerve can be compressed as a result of the formation of tumors, in most cases resulting from some kind of head injury.
Also a fairly common cause of inflammation of the trigeminal nerve is internal venous or arterial displacement.
Other causes of trigeminal neuralgia include:
- the presence of a chronic inflammatory process, viral or bacterial infection in the body;
- herpes infection (herpes);
- a brain tumor;
- scarring in the brain stem;
- failure of anesthesia during treatment or tooth extraction.
Most often, inflammation of the trigeminal nerve affects women at pre-retirement and retirement age (usually from fifty to seventy years). If trigeminal neuralgia is diagnosed in a young man or girl, then most likely its cause is a change in the arteries of a sclerotic nature or a strong dilatation of blood vessels.
Types of neck pain
To identify the causes of pain in the left neck and prescribe treatment, you need to pay attention to the nature of the pain, the frequency of its manifestation, as well as the conditions under which the pain intensifies. All this will help to more accurately determine the cause and undergo exactly those diagnostic measures that are needed in your case to confirm the disease.
Pain in left front
In this case, problems may be associated with inflammation of the pharynx, tonsils, and vocal cords, which leads to pain in the left side of the neck in front. If the process is bilateral, the same sensations will appear on the other side. In this situation, a person has symptoms associated with inflammation - sore throat, cough, fever, etc.
Pain in the left back of the neck
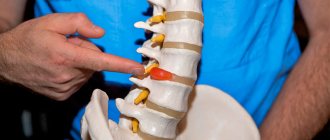
If pain appears in the left neck, the cause may lie in osteochondrosis of the cervical spine. The nature of the pain can be cutting, shooting, aching, but in any case, such a symptom will provide constant discomfort. The same sensations are provoked by a hernia in the cervical spine. Often the problem lies in spinal stenosis, which leads to a narrowing of the spinal canal. Most often, this disease affects the upper parts of the spine and can lead to compression of the spinal cord, nerve endings and subsequent disruption of the functioning of the upper extremities, numbness and severe pain.
Pain on the left side
The neck hurts on the left side for the same reasons as in the front and back. That is, pain syndrome can develop from hypothermia and muscle strain, as well as due to the development of osteochondrosis and other diseases of the spinal column in the neck. Often a person receives neck injuries in this area; the pain can even be caused by turning the head too sharply.
Left and goes to the head
In this case, the problem may be the development of osteochondrosis, injury to neck structures, as well as circulatory disorders. If you feel pain that radiates to the back of your head, it is worth measuring your blood pressure, since a common cause of pain is its increase. With atherosclerosis of the vertebral artery, the symptoms are more or less identical. If the pain in the left neck is acute, the cause may lie in occipital neuralgia. In this case, very strong, even unbearable pain will “rise” from the neck to the head, temples, and eyes.
On the left side under the jaw
In this case, muscles may ache, but most often the problem is that the tonsils are inflamed, the person has developed pharyngitis or laryngitis, and there are also problems with the thyroid gland, inflammation of which is called thyroiditis
.
Types of trigeminal neuralgia
Trigeminal neuralgia is divided into two types. The first, the so-called true trigeminal neuralgia, is a holistic disease caused in most cases by compression of the nerve or disruption of the blood supply. The second type - secondary trigeminal neuralgia - is a symptom of a general disease of the body. It could be a tumor or a serious infection.
In most cases, doctors diagnose inflammation of one of the processes of the trigeminal nerve, but in some situations inflammation of two or three processes occurs at once. Inflammation can affect either one side of the face or both, and in different combinations.
Causes of neck pain on the left side
It becomes clear that the area around the neck on the left can hurt for many reasons. It is worth learning more about each disease and determining the symptoms in order to roughly understand what triggered the development of pain and discomfort in the neck.
Osteoarthrosis and osteochondrosis
Osteochondrosis manifests itself in the fact that the cartilage tissue of the spinal column gradually begins to deteriorate. The intervertebral discs become thinner, the distance between them decreases, and nerve roots are pinched. Osteoarthritis also affects the joints of the spinal column.
Neck muscle damage
One of the most common cases of neck pain is damage to muscle tissue. If you hit yourself or simply overstrain your muscles by being in a not very comfortable position for a long time, or get too cold, inflammation may begin, accompanied by pain and sometimes fever.
Features of the development of cervical cysts and treatment in childhood
Lateral neck cysts in newborns and young children occur in a latent form and are not expressed by clinical symptoms until a provoking factor appears - trauma to the child, the appearance of a respiratory infection or other inflammatory processes. Sometimes hormonal changes in the body can become such a factor.
Clinical practice shows that in children the formation of a lateral cyst is always preceded by acute respiratory infections, influenza and other diseases of the upper respiratory tract. There is a connection between the tumor and the lymphatic tract, during which microbes of a pathogenic nature penetrate into the internal cavity of the cystic formation, causing suppuration.
In childhood, surgical treatment of a lateral cyst is carried out from three years of age outside the acute stage. But in case of serious complications leading to a threat to life, surgical intervention is indicated at an early age of the child.
Diagnosis of the disease
To understand what to do and how to treat if the neck on the left is very painful, first of all, the doctor needs to understand what caused the pain syndrome. It is not enough to relieve the condition by taking painkillers; you need to identify what the pain indicates and eliminate its cause. To determine the exact reasons you may need:
- x-ray
; - Ultrasound;
- MRI
; - general blood test, etc.
Based on the results of the diagnosis, the doctor will tell you why the neck hurts in the lower left and how to cope with this phenomenon in order not only to feel better, but also to eliminate the root cause.
Treatment of lateral neck cyst
Treatment of a lateral (branchiogenic) cyst is carried out only surgically. To avoid complications, the development of inflammatory processes and suppuration, surgery to remove the cyst should be performed as early as possible. Nowadays, operations for radical dissection of the cyst are not complex surgical interventions, but require high professionalism, attention and experience, since the remaining particles of the neoplasm epithelium can subsequently cause a relapse with subsequent surgical treatment.
These operations are performed under endotracheal anesthesia (tracheal intubation), the duration of the operation is from 30 minutes to one hour, depending on the location of the tumor, the age of the patient and the complexity of the case. At the end of the operation, the patient is given antibacterial and anti-inflammatory treatment. Physiotherapeutic procedures and UHF. Five to seven days after surgery, the sutures are removed. To exclude relapse, the patient is under clinical observation for one year.
How to treat pain on the left side of the neck
Most often, treatment is needed in the presence of pathologies of the musculoskeletal system in the cervical region. Treatment of pain may include the use of lidocaine and novocaine, injections of which are otherwise called “blockade”. This is necessary when the pain intensifies to unbearable. In other cases, various medications, physiotherapy and medical procedures are prescribed that relieve pain and inflammation and are selected individually.
Medicines
A nagging pain on the left side of the neck requires timely treatment, since otherwise the state of health will only worsen. Most likely, for pathologies of the structures of the musculoskeletal system, you will be prescribed:
- non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, which should reduce pain and stop inflammation;
- muscle relaxants to relieve muscle spasms;
- chondroprotectors that will stop degenerative processes in the joints;
- drugs to normalize blood circulation;
- Antidepressants, which will reduce anxiety and nervousness, will create a favorable basis for treatment.
Sometimes, when shooting pain appears on the left side of the neck, you need to use hormonal medications, as well as warming ointments that are applied to the collar area. If you have pain in the neck, do not delay visiting a specialist, make an appointment with a doctor.
How does inflammation of the trigeminal nerve manifest?
The main symptom of inflammation of the trigeminal nerve is severe pain that occurs in the facial part. The pain really has a powerful force and shooting character, so it is very difficult for the patient to calmly endure painful attacks. The pain intensifies when performing the slightest actions with the facial muscles and jaws - yawning, chewing, laughing, and performing daily oral hygiene. At the same time, the sensitivity of the skin on the inflamed side of the face decreases.
The next painful attack is accompanied by a rapid dilation of the patient’s pupils and the same rapid contraction of facial muscles. Increased tear production may begin.
Pain with trigeminal neuralgia is severe, but not constant. The pain occurs for a few seconds and is interrupted for a while. But if the intervals between painful attacks are short, then it seems that the pain is constant. Trigeminal neuralgia is dangerous because the interval between attacks can be several weeks, and sometimes even several months. But after this period, the pain will certainly return. A long break does not mean that the disease has passed, so if you have already noticed symptoms of neuralgia once, you should immediately consult a doctor.
Clinical case in the larynx department of the Federal State Budgetary Institution National Medical Research Center of the Federal Medical and Biological Agency of Russia
Patient M. , 26 years old, on June 20, 2016, sought medical help from specialists from the Department of Laryngeal Diseases of the Federal State Budgetary Institution National Medical Research Center for Medical and Biology of the Federal Medical and Biological Agency of Russia with a complaint about the presence of a mass on the right side of the neck. According to the patient, the formation appeared in September 2015, and gradual growth was noted. After an MRI examination and ultrasound of the neck, a diagnosis of “lateral neck cyst” . On the right side of the neck, the contours of the cyst are visualized from the mastoid process of the temporal bone to the clavicle; upon palpation it is dense, the surface is smooth.
View of the patient's neck before surgery | MRI images of patient M. | |
On June 21, 2016, the patient underwent removal of a benign neck tumor.
Surgery to remove a lateral cyst in patient M. | ||
Size of removed tumor: 20 cm by 6 cm
In the postoperative period, patient M. received antibacterial therapy, the suture was removed on the 7th day.
She was discharged on June 29, 2016 with improvement.
Photo of the patient immediately after surgery | Photo of the patient upon discharge |