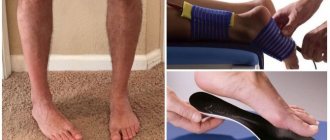
Such a fairly common injury as damage to the tendons of the hand usually occurs as a result of a direct open injury (cut wound, hand getting caught in moving mechanisms, etc.) or, which happens much less frequently, as a consequence of a closed type injury.
Any traumatic impact on the hands causes severe scarring and interferes with the normal functioning of ligaments, tendons and muscles. A person experiences significant difficulty moving his hand and fingers. The victim needs to know that suturing the site of a tendon rupture is possible only within 15-20 hours after the incident, otherwise additional surgical intervention will be required later.
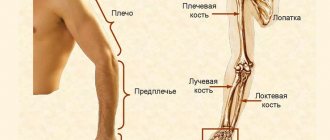
Anatomy of the wrist joint
The anatomy of the wrist joint and carpal bones is extremely complex, probably the most complex of all joints in the human body. The joints and bones of the wrist allow us to perform a variety of movements in all planes. At the same time, the wrist ligaments must provide strength to the joints.
The wrist is made up of eight individual small bones called carpal bones. The bones of the wrist are connected on one side to the radius, on the other they are connected to the metacarpal bones.
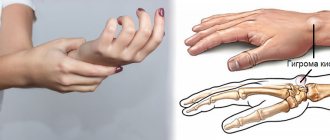
Ligaments hold all the bones of the wrist together and allow the hand to move in all directions. These ligaments fuse together to form the wrist joint capsule. The joint contains a fluid called synovial fluid, which lubricates the joint surfaces as they move against each other. Almost all movements of the hand are transmitted by the tendons of the flexor and extensor muscles. Hygroma, increasing in size, usually pushes apart the surrounding tissues, tendons, and ligaments. Like a ball containing intra-articular fluid (hyaluronic acid).
70 percent of carpal hygromas form on the back of the wrist.
Hygroma of the palmar surface of the wrist or wrist joint is much less common and is usually localized in the projection of the radial artery - where the pulse is checked.
Material and methods
To identify and describe various morphotypes of aging, we developed a questionnaire consisting of four blocks of questions that revealed information about heredity, morphometric data, clinical signs of aging, self-assessment of the condition of the skin and soft tissues of the hands. A 10-point rating system was used, in which the significance of a feature was determined from 0 to 10 (with explanations). The questionnaire was filled out by the patient and an independent medical expert. Filling out the questionnaire took about 5 minutes.
We also collected information about hand dominance at work, profession, preference for using the right or left hand, calculated BMI, and determined the morphotype of aging in interviewed individuals over the age of 40.
At the Vallex Med clinic, from November 2014 to November 2021, a study was conducted in which 310 healthy women of the Slavic type who were cosmetology patients took part. Questionnaires and questionnaires for the subjects were approved by the ethics committee of the Vallex Med clinic.
Inclusion criteria: healthy women aged 25-65 years of Slavic type, I-III phototype, with a BMI of 18-30 kg/m2.
Exclusion criteria: skin, rheumatic diseases, gout, deforming arthritis, various types of injuries to the hands (burns, fractures, scars in the hand area, neurovascular disorders), previously performed cosmetic procedures in the area of the back of the hands.
Standard photography of both hands was performed in oblique radial and dorsal projections in full size, as well as from above during flexion, in the same room with constant temperature and lighting, with the same camera. The photographs were assessed by the same expert (cosmetologist) using the merz scale.
The photographs were assessed and the dominant signs of aging for each participant were identified.
Subjects were weighed and height measured to determine BMI. Next, we measured the length and width of the brush; wrist circumference. Information was collected about the dominant hand, the time of appearance of signs of aging in the area of the back of the hands, and the hereditary nature of skin aging in this area.
At the next stage, the severity of contouring of veins and tendons, loss of volume of the pancreas, and pigmentation were assessed.
The most standard options for aging brushes were selected, and trends in brush aging were determined from photographs.
Test to determine wrinkles and sagging.
The patient's skin was gathered into a fold in the center of the back of the hand (above the area of the third finger) in the longitudinal and transverse direction (pinch test). They raised it above the level of the back of the hands and measured the time during which the skin returned to its original position, and also measured its thickness using a caliper with an accuracy of 0.2 mm.
Causes of hygroma of the wrist joint
The main causes of hygroma:
- Wrist injury
- Large loads on the hand and wrist joint;
- Consequences of hand surgery.
- Repetitive injuries such as playing tennis or golf.
Hygromas on the hand form when the joint capsule becomes thinner due to injury or degenerative changes. The damaged tissue forms a weak spot in the joint capsule, like a weak spot on a car tire, allowing the inner layer to herniate. The joint fluid begins to squeeze out the weakened layer of the capsule, pushing apart the surrounding tissue. Over time it gets bigger. But if you limit the load on the wrist joint, this will lead to a decrease in the production of intra-articular fluid and stop the growth of hygroma. Cases of spontaneous healing of hygroma after reducing the load have been described.
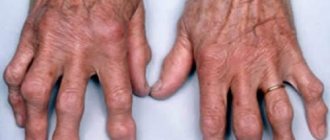
The main causes of hand tendon injuries
Of course, the main cause of dysfunction of the tendons of the hand is traumatic injury (cut with a knife, scissors, glass fragments, etc.). In this case, the flexor tendons lose their function of transmitting muscle force to the phalanges of the fingers. The causes of damage can be not only traumatic in nature:
- tendon rupture under heavy loads;
- rheumatoid arthritis;
- carpal tunnel syndrome;
- violation of muscle fiber tone;
- rheumatic arthritis.
Treatment of hand hygroma
Treatment of wrist hygroma can be surgical or conservative. The relative risks and benefits of any treatment should be carefully analyzed.
Conservative treatment
Previously, hygromas were treated simply by crushing them. That is, under pressure, the “ball burst” and the contents poured into the surrounding tissue. This is an absolutely harmless procedure. The intra-articular fluid is sterile and cannot in any way inflame the surrounding tissues. But 90% of all those crushed by hygroma recur, because... the edges of this burst capsule grow together very quickly and the liquid begins to accumulate again. This type of treatment is now used only by patients themselves out of ignorance.
50% of hygromas can disappear on their own if you reduce the load on the hand and wrist joint.
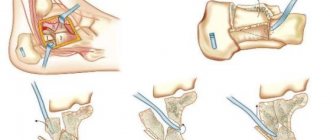
Hygroma puncture
A fairly effective method, but it is possible only in the early stages of the disease, when the size of the hygroma does not exceed 1 cm.
Methodology:
Local anesthesia is performed over the area of the hygroma. Next, the hygroma is punctured and its contents are removed with a syringe. Without removing the needle, the syringe is changed and a sclerosing agent is injected. A pressure bandage and orthosis is applied to the wrist joint for 5 weeks to allow the edges of the emptied hygroma to stick together and grow together.
If the patient does not wear an orthosis after the procedure, then movements in the wrist joint will provoke the release of intra-articular fluid and the fragile internal scar will not be able to withstand the pressure. What can cause recurrence of hygroma formation.
Therefore, one of the mandatory conditions and the strictest recommendation is to wear an orthosis.
If the hygroma is more than 1 cm or has a cellular structure (formed by several sacs), then there are indications for surgery, if the hygroma, of course, bothers the patient at all.
Rehabilitation period
After the operation, a splint is applied to the site of injury and until the tendons heal, the patient undergoes a period of immobilization and a course of full rehabilitation. Specialists at the multidisciplinary clinic “Osnova” have developed effective methods for treating various types of injuries to ligament and tendon tissue using modern types of rehabilitation measures:
- osteopathy completely restores blood circulation and improves repair processes;
- therapeutic massage sessions restore muscle tone, stabilize the process of cellular nutrition of tissues;
- the reflexology procedure has a targeted effect on the process of muscle tissue regeneration;
- physiotherapy has a beneficial effect on the metabolic processes of cells, which allows you to achieve the desired effect from the rehabilitation.
Video about the procedure:
The back of the hands is practically devoid of subcutaneous fat, in addition, there are practically no sebaceous and sweat glands. With age, metabolic processes slow down, and with them, cell regeneration. The genesis of the proteins that form the natural framework of the dermis - collagen and elastin - no longer occurs so quickly. That is why the already thin and dry skin of the hands becomes covered with a network of small wrinkles, and the hands look sinewy and angular. Other factors aggravate this process:
- lack of hand skin care or use of incorrectly selected cosmetics
- aggressive effects of temperature changes, sun, salt water and other external factors
- contact with household chemicals containing aggressive substances
- poor nutrition
- presence of bad habits
How is the diagnostic procedure performed?
The method is convenient because it can be carried out at any time and does not depend on external circumstances. You do not need any special preparation to undergo an ultrasound.
Unlike most types of ultrasound examination, in this case the patient is in a sitting position. His hands should be folded on his knees or on a special pillow. During the procedure, the diagnostician may ask you to change the position of your hand in order to better visualize a particular part. All manipulations last from 20 to 30 minutes. The patient receives the results of the study immediately after its completion.
During scanning with a sensor, the doctor can examine in detail the soft and bone tissues of the wrist. The device allows you to carefully examine articular cartilage, tendons, and muscles.
Stages of development of Dupuytren's contracture
Taking into account existing statistical data, it can be stated that Dupuytren's contracture of the hand is observed in 3% of people in the world. Moreover, the most susceptible to the disease are males in the age category - from 40 to 60 years. In women, this pathological process is quite rare, in only 4-5% of cases.
Taking into account how pronounced palmar Dupuytren's contracture is, the following stages of development of the disease are distinguished.
First stage
It is characterized by the presence of a small subcutaneous nodule located under the ring finger. In this case, the patient does not feel any discomfort and continues to perform the usual hand movements. The fingers also do not lose their activity at this stage. As a rule, such nodules resemble ordinary calluses of a working person.
Second stage
Progressive stage. During this process, a scar cord appears on the palm. In this case, redness and roughening of the skin in this area are observed. Mobility in the damaged finger deteriorates and, most often, its ability to fully extend is impaired. However, pain syndrome is not detected in this case.
Third stage
The area of spread of the fibrous cord covers the entire finger. In this case, the skin located near the seal takes on a folded and wrinkled appearance. The affected finger is located at an angle of 90° relative to the palm. In addition, in this situation, a sudden deterioration in functional characteristics is monitored.
Patients note the absence of any pain in this part of the body. However, it is quite difficult to move this limb. At this stage, fusion of the joint surfaces may be observed.
Fourth stage
The affected area covers the entire palm or several fingers at once. As a rule, they coalesce into one large scar. The first injured finger assumes a bent position without the possibility of changing it, and significant deformation of the hand occurs. In some situations, patients note the appearance of severe aching pain, which is constant. The ability of the hand to perform any movements in this case is reduced to zero.
Make an appointment Online booking
- Clinic on Krasnopresnenskaya +7 (499) 252-41-35 Volkov lane, 21
- Clinic on Varshavskaya +7 (499) 610-02-09 Varshavskoe highway, 75, building 1
- Clinic in Annino +7 (495) 388-08-08 Varshavskoe highway, 154, building 1
Discussion
When a patient presents with an asthenic type of aging of the hands, it is recommended to carry out correction of the “skeletal hand”, taking into account the identified features. Autologous fat, fillers of various natures, and revitalizants are used to fill tissues [1, 9, 12, 13].
There is a wide variety of fillers based on HA of varying viscosity, which allows you to choose the most suitable drug adapted to age-related problems [9, 12-17]. In 2012-2014 In our own works (in double-blind and placebo-controlled studies to study the effectiveness of intradermal injections of revitalizants), we have shown the high clinical effectiveness of 3-fold administration of stabilized HA gel (20 mg/ml HA), increasing the elasticity and hydration of the skin on the back of the hands. The procedure for rejuvenating the skin of the hands is generally well tolerated, accompanied by mild pain, swelling and ecchymosis. The skin becomes significantly less rough, less wrinkled, and more hydrated. The clinical effect lasts up to 6 months with a gradual decrease by the 12th month (Fig. 5)
Rice. 5. Atrophic morphotype of aging. Photo of the hands of a 50-year-old patient: before the procedure, on the left is a drug based on stabilized HA with a concentration of 18 mg/ml. a - saline solution on the right; b - after 3 months. [13, 18].
For patients with a normotrophic type of hand aging, procedures are recommended aimed at improving the visco-elastic properties of the skin: fractional photothermolysis, microneedle radio wave lifting, biorevitalization with preparations of unstabilized HA and amino acid complexes, calcium hydroxyapatite. The accumulated almost 13-year experience of using revitalizants based on stabilized HA confirms the high safety profile and commitment of aesthetic medicine doctors to the method [7-11, 16, 17]. It has been proven that this group of drugs not only provides long-term tissue hydration, but also promotes the restructuring of the intercellular matrix of the dermis, which has a positive effect on the appearance and biomechanical properties of the skin [18-21].
When a patient presents with a hypertrophic type of hand aging, cosmetic correction is aimed at eliminating the identified signs of chrono- and photoaging, which are usually mild or moderate. Improving skin tone and elasticity through mesotherapy may be recommended. The emphasis of rejuvenation is on improving skin microrelief and correcting pigmentation. When correcting dry, wrinkled skin, preparations based on unstabilized HA (HA concentration 20 mg/ml) are recommended (Fig. 6)
Rice. 6. Normotrophic morphotype of aging. Correction of age-related changes with calcium hydroxyapatite. [1, 22-25].
Where to get an ultrasound of the joints of the hands in Krasnoyarsk?
We, in medicine, know how important it is to promptly identify and treat diseases of the musculoskeletal system so that they do not interfere with leading an active lifestyle and do not cause discomfort. With us you can perform an ultrasound without waiting or queuing at any time convenient for you.
Why do patients choose Medunion Clinic?
- With us you can consult a doctor, undergo diagnostics and receive a conclusion. And everything is in one place! No waiting or queuing.
- After the examination, the doctor will tell you about the results of the conclusion and recommend who to contact next.
- We employ experienced diagnosticians of the highest category with 20 years of experience. They will carry out the procedure quickly and painlessly so that you do not feel any discomfort.
- We work even on weekends.
To sign up for an ultrasound procedure at a medical clinic, leave a request on our website or by phone number: +7.
Characteristics/Clinical picture
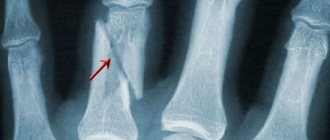
The following are characteristics of tendon injuries depending on the damaged area:
- Zone I: hammertoe;
- Zone II: partial tendon damage without complete rupture;
- Zone III: destruction of the insertion of the extensor tendons at the base of the middle phalanx of the finger, also known as Weinstein contracture (characterized by flexion of the proximal interphalangeal joint, extension or hyperextension of the distal interphalangeal joint);
- Zone IV: injuries are often partial with or without loss of proximal interphalangeal joint extension;
- Zone V: open wounds or blunt trauma (a possible effect of such injuries may be rupture of the sagittal band, accompanied by tendon displacement, causing difficulty when trying to straighten a flexed metacarpophalangeal joint);
- Zone VI: The metacarpophalangeal joint can still be extended by the intertendinous joints;
- Zone VII: physical damage to the extensor retinaculum.
Clinically Relevant Anatomy
Anatomy of the finger extensor tendons
The extensor tendons are located in the dorsal part of the hand and fingers. The function of these tendons is to extend the wrist and fingers. According to Kleinert and Verdan (1983), there are eight anatomical zones into which the extensor mechanism is divided:
- Zone I: distal interphalangeal joint;
- Zone II: middle phalanx;
- Zone III: proximal interphalangeal joint;
- Zone IV: proximal phalanx;
- Zone V: metacarpophalangeal joint;
- Zone VI: metacarpal bones;
- Zone VII: wrist (retainer of extensor tendons);
- Zone VIII: distal third of the forearm.
Anatomical zones of the hand
Survey
The study of extensor tendon injuries is of interest from various points of view. First, characteristics of the injury, such as size and location, should be assessed to give the physical therapist an idea of what structures may have been injured. Next, the function of the fingers and wrist is tested in three ways: passively, actively and then with resistance. It is important that each finger is tested separately because the intertendinous junctions between the extensor digitorum tendons may mask dysfunction. In addition, neurovascular examinations must be fully completed. The Elson test may be performed specifically for zone III.