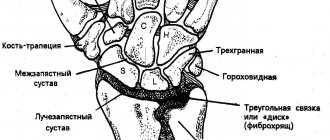
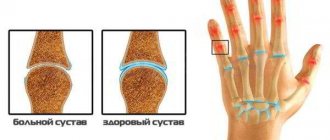
The wrist joint is one of the complex joints and has more than two articular surfaces. It differs from most other joints, because it involves 5 bones (and not 2-3, as, for example, in the knee or interphalangeal joints). In addition, the wrist joint has two axes of rotation rather than one. This allows you to move the brush in all directions and even rotate it in a circle.
Such a complex mechanism ideally adapts human hands to work and life associated with many small manipulations. Therefore, failure of this joint often leads to disability and loss of ability to work. What are the symptoms and treatment of arthrosis of the wrist joint?
Specifics of the degenerative process in the wrist joint
The fragile wrist joint is located between the hand and forearm and, due to its location, is susceptible to injury (for example, from a fall). In everyday life, it experiences less functional load than, say, the knee joint, but its joint capsule is thinner. Therefore, the joint is vulnerable to even minor damage.
Cases of arthrosis of the wrist joint due to natural abrasion of cartilage are extremely rare. Therefore, in the absence of injuries or work stress, the likelihood of contracting it is low.
At-risk groups
In principle, each of us may need treatment for the wrist joint, which will restore the hands to their former mobility, the ability to lift your own child, pet a dog, or easily perform professional duties. But for some people, the risk of becoming semi-disabled (and sometimes completely) for a long time is much higher. These include:
- those who are engaged in heavy physical labor , where the load falls mainly on the hands. For example, rowers, loaders, lumberjacks;
- office workers - from secretaries to programmers. Here the risks even increase, since many of these employees work in non-design conditions. For example, the ratio of the height of the table and the chair is not observed, and excess pressure is constantly placed on the wrists;
- athletes whose hands are actively and constantly working - badminton players, tennis players, boxers (the latter are at greatest risk in terms of injuries and bruises of the wrist joint);
- people whose profession requires constant use of fine motor skills . These include seamstresses and lacemakers; signers of dishes, eggs, cups; musicians, especially those who play stringed instruments and those who work with the piano.
Treatment of the wrist joint may also be required for ordinary people - those who cannot imagine life without playing online games. Spending a lot of time at the computer, such people have to make a huge number of monotonous movements with the hand, which seriously overload the radial joint. At a certain stage, this approach to one’s own hands turns into acute illnesses that turn into chronic forms.
Causes of arthrosis of the wrist
Arthrosis of the wrist joint can be either a primary (idiopathic) or a secondary disease. In the first case, we have a healthy joint that changes due to adverse external influences - injury or occupational stress. In the second, there is an underlying disease (gout, diabetes, rheumatoid arthritis and others), which leads to degenerative changes in the cartilage.
Among the factors that influence the development of arthrosis of the wrist joint, it is worth mentioning:
- excessive load and injuries - sports, household, professional (for example, when working with a vibrating tool);
- hypothermia;
- advanced inflammatory pathologies in the joint or periarticular tissues;
- endocrine and metabolic disorders and autoimmune diseases;
- past infections (reactive arthritis, tuberculosis, osteomyelitis and others);
- female;
- heredity (affects collagen synthesis, cartilage density, anatomical structural features).
Trauma is the most common cause of the disease. In this case, symptoms of cartilage destruction may not appear immediately, but after several years.
Osteoarthritis of the wrist often begins due to arthritis of the wrist joint and proceeds in parallel with it. Age factors have little effect on the development of wrist arthrosis. Although menopausal hormonal changes in women can affect the strength of cartilage tissue.
Most often, osteoarthritis of the wrist joint is observed in builders, craftsmen working in factories and in the finishing of premises, office employees, as well as professional athletes (especially in the presence of dislocations and subluxations, fractures, ruptures and sprains of ligaments or muscles).
Causes
The main cause of inflammation is prolonged tension in the wrist joint, which appears due to microtrauma and increased physical activity. Constant load on this place contributes to the deposition of salts in the tissues of the tendon and cartilage.
This occurs due to monotonous, frequently repeated movements. The disease can be called occupational; people of certain professions are susceptible to it:
- musicians;
- seamstresses;
- builders;
- athletes (rowing, tennis, golf);
- people employed in agriculture;
- mining workers;
- if the profession involves working on a computer.
Styloiditis can develop after bruises, fractures, dislocations and any other injuries. Sometimes the cause is a local metabolic disorder, heredity or a complication after infectious diseases or other inflammations.
Signs of arthrosis of the wrist joint
In the early stages, arthrosis rarely makes itself felt. Key signs of arthrosis of the wrist joint are observed already in osteoarthritis - when the destructive process proceeds to the heads of the bones. The disease begins with discomfort in the wrist area, a feeling of tightness, and mild pain. The sensations are somewhat reminiscent of sore throat.
It is characteristic that signs of arthrosis of the wrist joint are observed only in this joint, while other rheumatic diseases seem to “move” from one joint to another, affecting several at the same time.
If the following symptoms appear, you should contact a rheumatologist as soon as possible:
- pain in the joint, especially after physical activity on the wrist, stress, dehydration;
- difficulty in movement, which increases as the disease progresses (a feeling as if something is preventing you from moving your arm freely);
- encircling swelling of the wrists, swelling of the hand (optional, but a characteristic symptom);
- a rough crunch in the joint (instead of the normal light click, a dull sound appears, which is accompanied by tension).
The pain intensifies when carrying heavy objects, even holding them suspended for a short time, trying to lean on the palm, or stretching the hand. It is typical that it is felt in extreme positions for the joint (bending the hand) or during specific movements. If after an injury, inflammatory symptoms in the joint are observed for more than 2-3 weeks, this may also be a symptom of the onset of the disease.
At first, stiffness in movements may go away after warm baths and warm-up. Over time, mobility decreases by 30-50%. When cartilage wears away and exposes the surface of the subchondral bones, osteophytes appear. They significantly impede movement in the wrist - especially when trying to rotate the hand. Small fragments of osteophytes sometimes cause acute pain and severe inflammation in patients.
The presence of osteophytes can usually only be determined using an x-ray. But the patient can recognize it by the following manifestations:
- limited range of motion in the joint;
- frequent uncontrollable spasms, especially when moving the hand;
- On palpation, hard subcutaneous lumps are revealed.
Pain due to osteoarthritis of the wrist should be distinguished from arthritic pain. With arthritis, pain intensifies at rest, closer to night, in the morning. With osteoarthritis, on the contrary, in the daytime - during everyday activity.
Deformation of the wrist joint during the disease is usually absent, as is severe swelling. The characteristic “thinning” of the limb due to muscle atrophy is also characteristic of wrist arthritis rather than arthrosis.
Symptoms of the disease
What is the characteristic of styloiditis of the wrist joint?
- aching pain in the wrist area, which can extend to the elbow or hand;
- increased discomfort in the joint when moving the thumb or hand, at night or when weather conditions change;
- if the cause was injury, pain is felt even if you just touch your hand;
- the appearance of all signs of inflammation - redness, swelling, increased temperature;
- the joint crunches when moving;
- the tendon tightens and becomes hard;
- decreased sensitivity, including pain;
- problems with fine motor skills and finger movements, difficulty grasping and holding objects;
- fingers become numb, tingling or burning may be felt;
- muscle tone and strength deteriorate.
Degrees and stages of arthrosis of the wrist joint
The progression of carpal arthrosis is slow - before treating wrist arthrosis, the patient may not be aware of the disease for ten years. During the course of the disease, the cartilage becomes soft, its regeneration process is disrupted, and the synovial fluid loses its viscosity and is produced in ever smaller quantities. Depending on the severity of the lesions, the following stages of the disease are distinguished.
Arthrosis of the wrist joint 1st degree
The destructive process begins with mild pain in the wrist, which periodically bothers the patient - mainly after heavy exertion. They are not so intense that patients attach importance to them. The sensations with arthrosis of the wrist joint of the 1st degree resemble aching pain - like “the weather”. There is slight swelling and other symptoms of deterioration of tissue trophism, and occasionally a soft crunching sound is heard.
At this stage, the symptoms and treatment of wrist arthrosis are tolerated quite easily.
Arthrosis of the wrist joint 2nd degree
At this stage, the cartilage is almost completely destroyed on the supporting surfaces. The first bone growths appear, clearly visible on x-rays, and a clear narrowing of the joint space. Sometimes osteophytes can be felt independently. The pain becomes noticeable, almost daily. When moving, the patient hears a distinct crunching sound. Your hands get tired faster than before. Full recovery from grade 2 arthrosis of the wrist joint is no longer possible, but treatment greatly improves the patient’s quality of life and maintains mobility in the joint.
Arthrosis of the wrist joint grade 3
Stiffness in the wrist imposes significant restrictions on patients in daily life. Ultimately, ankylosis develops - complete immobility of the joint, in fact its fusion, since the edges of the osteophytes close. Pain with advanced osteoarthritis of the wrist joint bothers the patient even at rest, after rest. The curve of your arm may look unnatural. At the third stage, only surgical treatment is possible. It is not possible to completely restore mobility even after surgery.
Please note: the less developed the muscles around the affected joint, the faster the disease progresses. A healthy muscular system maintains the natural position of the joint, provides it with nutrition, and protects it from damage.
Frequently asked questions about the disease
I have arthritis in my hand since childhood. Will they take me into the army?
If the function of the joint is impaired, then no.
I had arthritis in my wrist after gonorrhea. Can it be completely cured?
Infectious arthritis can be completely cured if the correct treatment is prescribed in time.
What is the best way to smear your brushes so that they don’t hurt?
You need to consult your doctor. The best painkillers are Voltaren emulgel and Menovazin rubbing solution.
Arthritis of the hand joints is best treated in the early stages. But if you were unable to seek medical help in time, then do not be discouraged: everything can be treated.
At the Moscow Paramita clinic, arthritis of the hands is treated at any stage. Our patients forget about pain after the first acupuncture sessions. Further rehabilitation therapy takes place in comfortable conditions and is completely painless. We will restore your health!
Literature:
- Shelepina T.A. Rehabilitation therapy in the complex treatment of JRA. Pediatric rheumatology. !995, 13 – 16.
- Blokhin V.N. Trauma and reconstructive surgery of the hand. Orthopedist, traumatologist and Prosthetics, 1973, 6, 63-38.
- Woog PHNFular Publishers, Basle, 1978.
Themes
Arthritis, Joints, Pain, Treatment without surgery Date of publication: 11/17/2020 Date of update: 04/03/2021
Reader rating
Rating: 4.67 / 5 (3)
Diagnosis of arthrosis of the wrist joint
Symptoms of osteoarthritis of the wrist are similar to other rheumatic diseases. Therefore, to make an accurate diagnosis, the doctor requires the following studies:
- oral questioning of the patient, palpation and examination of the affected joint at the initial appointment;
- x-ray (2 or 3 projections);
- general blood test and, if necessary, urine;
- biochemical blood test according to indications;
- rheumatic factor analysis;
- Ultrasound, computed tomography or magnetic resonance imaging as indicated;
- Occasionally, a puncture may be necessary to assess synovial fluid.
Risk factors for thumb arthrosis
- Female
- Age over 40
- Obesity
- Congenital features such as joint hypermobility, joint deformities
- Previous thumb injuries such as sprains or fractures
- Systemic diseases affecting the structure and function of articular cartilage, such as rheumatoid arthritis. Despite the fact that arthrosis of the base of the first metacarpal is in most cases osteoarthritis (also known as arthrosis deformans), rheumatoid arthritis can also affect this joint, but less frequently than other small joints of the hand.
- Working or other repetitive activity that puts a lot of stress on the thumb.
Treatment of osteoarthritis of the wrist joint
The treatment strategy is selected by the doctor individually for each case, taking into account the causes of the disease, its stage, the general health of the patient, and other things.
The standard approach to the treatment of arthrosis of the wrist joint stage 1-2 includes:
- pharmacotherapy;
- physiotherapy;
- therapeutic exercises;
- a healthy diet and daily routine;
- compliance with the orthopedic regimen.
At stage 3, the decision to operate is usually made.
Treatment of arthrosis of the wrist joint occurs in stages. At the first stage, the acute symptoms of the disease - pain and inflammation - are “extinguished”. The second requires complex treatment. And the third involves rehabilitation of the patient to consolidate the effect after the main course.
Due to the difficulties in daily activities caused by joint dysfunction, physical discomfort is accompanied by psychological discomfort. It can be one of the factors in the development of depression, so patients are recommended to visit a psychologist and rehabilitation specialist.
Please note that osteoarthritis of the wrist joint is a chronic disease that requires lifelong adherence to the doctor’s recommendations.
Pharmacotherapy
In the treatment of arthrosis of the wrist joint, the following pharmacological groups are used:
- non-hormonal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs, NSAIDs) - courses up to 21 days;
- glucocorticosteroids;
- chondroprotectors;
- vasodilators;
- muscle relaxants;
- vitamin and mineral complexes;
- if the disease is infectious - antibiotics
They are used in the form of tablets and capsules, ointments, gels, compresses and intra-articular injections.
Self-medication of wrist arthrosis can lead to worsening of the condition and problems with the gastrointestinal tract. Before using all drugs (except ointments and gels for topical use), you must consult a doctor.
Tablets for osteoarthritis of the wrist joint
To relieve inflammation, pain and heat in case of arthrosis of the wrists, the following tableted NSAIDs are recommended: diclofenac, celecoxib, ibuprofen, piroxicam, ketoprofen, indomethacin, meloxicam, nimesulide, butadione and others.
To prevent further cartilage degeneration, the doctor may prescribe chondroprotectors: artracam, teraflex, structum and others.
During the rehabilitation period, drugs are used to improve tissue trophism (pentoxifylline, trental) and muscle relaxation (mydocalm, tizalud).
If pain cannot be eliminated with tablets, injections are added to the prescription: methylprednisolone, diprospan, hydrocortisone.
Ointments for osteoarthritis of the wrist
Non-steroidal ointments and creams for external use are widely used as aids in the treatment of osteoarthritis of the wrist joint. For example, fastum gel, dollit, voltaren, diclak gel, ketoprofen. Chondroprotectors are also produced in these dosage forms - artracam, structum, rumalon.
Surgical treatment of arthrosis of the wrist joint
Surgical treatment of arthrosis of the wrist is indicated for stage 3 of the disease and in cases where other methods are ineffective.
Preference is given to plasma lifting and endoprosthetics of synovial fluid - minimally invasive manipulations. They involve the injection of the patient's blood plasma or hypoallergenic polymers that act as a lubricant directly into the joint capsule. This helps relieve pain and inflammation and prevent erosion for up to 24 months.
If this approach does not work, it is possible to implant a pyrocarbon prosthesis that simulates cartilage. It is not attached to the proximal bones, and therefore does not become loose and can be used even with severe damage to the articular surfaces.
If it is not possible to preserve or replace the joint, doctors resort to the last resort of orthopedic surgery - partial arthrodesis with the implantation of a titanium plate. During this operation, the destroyed joint is completely immobilized. So at least the patient will not be bothered by constant pain and inflammation.
Physiotherapy for osteoarthritis of the wrist
To relieve pain, improve microcirculation and mobility with wrist arthrosis, the following techniques are used:
- acupuncture;
- manual therapy;
- medicinal, incl. acupressure;
- post-isometric relaxation;
- hirudotherapy;
- infrared laser therapy;
- magnetic therapy;
- cryotherapy;
- electrophoresis;
- ultrasound therapy;
- electromyostimulation;
- paraffin therapy;
- balneotherapy (therapeutic mud);
- other.
Physiotherapeutic treatment of arthrosis of the wrist joint is carried out in courses.
Treatment of hand arthritis
How and with what to treat arthritis of the hands, the doctor decides after examination and establishing a final diagnosis. Any treatment carried out without examination will not be effective, since different types of arthritis are treated differently. In any case, the patient is prescribed an individually selected comprehensive treatment. It includes:
- drug therapy;
- physiotherapeutic procedures;
- Exercise therapy, massage;
- reflexology (RT);
- traditional methods of treatment.
If conservative therapy is ineffective, surgical treatment methods are prescribed.
Read our article “Treatment of rheumatoid arthritis in women.”
Drug therapy
For hand arthritis, the following medications are prescribed:
- NSAID groups – relieve pain, inflammation and fever. The most effective NSAID drug is Diclofenac, but it causes irritation of the gastric mucosa, so today more modern drugs of this group are prescribed - Meloxicam, Celebrex, Nimesulide in the form of injections (injections), tablets or capsules for oral administration and external agents (ointments, creams, gels). ).
- For severe swelling and pain that cannot be relieved with NSAIDs, glucocorticoid hormones are prescribed in the form of short courses of oral tablets, intravenous infusions or intra-articular injections. They perfectly eliminate all unpleasant symptoms.
- In subacute and chronic cases, drugs that suppress immune processes (basic therapy) are prescribed: Methotrexate, Sulfasalazine, Azathioprine, etc.
- Medicines from the group of biological agents that include antibodies and cytokines (MabThera) also suppress immune reactions.
- If the cause of the disease is an infection, drugs are prescribed that suppress it.
- Antihistamines to reduce allergies - Claritin, Erius, Cetrin, etc.
- Chondroprotectors - agents that restore cartilage tissue of joints - Teraflex, Dona, etc.
- Vitamins and minerals that restore metabolism.
Drug treatment for arthritis of the hands is carried out using drugs from the NSAID group, drugs that suppress immune processes, and other drugs.
Physiotherapeutic procedures
Depending on the stage of the disease, physiotherapeutic procedures are added to the drug treatment of arthritis of the hands, which significantly enhance the therapeutic effect and accelerate the process of tissue restoration:
- at the stage of inflammation
- electrophoresis and phonophoresis with painkillers, anti-inflammatory drugs; - at the recovery stage
- magnetic therapy, laser therapy, thermal procedures (paraffin, ozokerite).
In a state of stable remission of arthritis of the hands, sanatorium-resort treatment is recommended - mud, baths in combination with hardware physiotherapeutic techniques. Kavminvod sanatoriums are perfect.
Crunching in joints - when to worry
Intra-articular injections of hyaluronic acid
Massage
These procedures are done in a state of remission. Both therapeutic massage performed by a massage therapist and self-massage are very effective. You can independently perform the following most effective, but at the same time gentle massage movements every day after applying massage oil to your hands:
- rubbing the back surface: with sliding movements of one hand, rub the back surface of the other in the direction from the wrist to the fingertips; then change hands;
- rubbing the side surfaces of the fingers: interlock your fingers and move your hands so that the side surfaces of the fingers are rubbed;
- rubbing the palms: with the fingers of one hand, forcefully rub the palms of the other in the direction from the wrist to the fingers;
- soft massage movement “hand washes hand”;
- stroking hands with light sliding movements.
Daily massage improves blood circulation, helps revitalize metabolic processes and restore tissue.
Physiotherapy
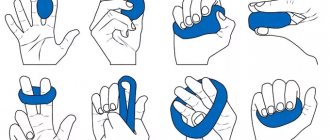
Physical therapy (physical therapy) complexes are prescribed by a doctor. It is better to undergo the first training sessions under the supervision of a physical therapy instructor, and then continue at home. The following exercises will help improve your well-being:
- rolling an apple or a tennis ball
- roll a medium-sized apple (to fit in the palm) or a tennis ball between the palms, actively pressing on the soft tissues; also actively roll the apple on the table; - rolling chestnuts between palms and fingers
- take 2-3 chestnuts at once and roll between palms and fingers, as well as on a smooth table surface; - clenching and unclenching a fist
- clench your palms into a fist and hold it tense, then sharply unclench it with all fingers straightened like a fan; repeat 10 times; - beating out the rhythm with your palm
- with open palms, beat out any clear rhythm on the table (march, rap, whatever you like); - flexion-extension
- place your elbows on the table, raise your forearms parallel to each other; make a simultaneous tilt of the hands forward, then back, right and left; repeat everything 5 times.
Therapeutic gymnastics helps improve blood circulation, restores the strength of muscles and ligaments, improves joint mobility, and prevents the destruction of cartilage. It is carried out in a state of remission.
Reflexology
Therapeutic exercises with a ball and reflexology will help cure arthritis of the hands
An ancient Chinese method, successfully integrated into modern medicine. It is based on a reflex effect on the entire body, as well as on individual organs and tissues through certain points on the human body. Most often, the effect is carried out using acupuncture (acupuncture), but you can also cauterize (warm up) the points with wormwood cigarettes, do acupressure and use other techniques. This method has proven itself in the treatment of hand arthritis.
Traditional methods
Folk remedies (herbal decoctions and tinctures) are also actively included in complex treatment as additional methods. But the doctor prescribes them ,
self-medication should be excluded. Traditional recipes:
- compresses from dry elm bark; grind the raw materials, grind them into powder, dilute with water to a pasty state, transfer to a napkin and apply to the affected joints; Apply polyethylene and insulation on top and leave overnight; perfectly relieves pain and swelling;
- ointment from dried poplar buds; crush the raw materials in a mortar, add the same amount of melted butter and rub into your hands several times a day; analgesic effect.
Surgery
In the acute period, surgical treatment is carried out for a purulent inflammatory process: the pus is removed, the joint cavity is washed with an antiseptic solution.
Surgery is sometimes required for long-term, wave-like arthritis with severe pain and swelling: part of the synovial membrane is removed (synovectomy). This gives a positive result and brings relief to the patient.
When a complete loss of joint function occurs, endoprosthetics is performed - replacing the destroyed joint with an artificial one.
Read about new treatments for rheumatoid arthritis in this article.
Therapeutic exercises (physical therapy) for osteoarthritis of the wrist
Therapeutic exercise for osteoarthritis of the wrist is designed to consolidate the results of therapy, prevent further erosion and help the patient lead a full life.
The volume and types of exercises are determined by the exercise therapy instructor on an individual basis. Exercises (for example, pinch-spread of the indicated fingers, rotation of the forearm while fixing the wrist with the healthy hand) are performed 2-3 times a day as a warm-up and do not require special equipment. Exercises with a ball are advisable.
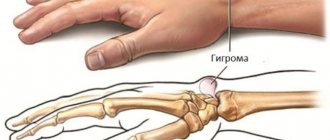
In a hopeless situation
In case of purulent inflammation of the wrist joint, drainage is placed, and in most cases this is enough for recovery. However, in some cases this technique does not produce results. And under other circumstances, with different diagnoses, conservative treatment may be ineffective. If remission is incomplete, and relapses are too frequent, if joint degradation progresses, surgical intervention is required. During the operation, the sheaths of the inflamed tendons are excised; in the case of hygroma, the capsule of the neoplasm is excised or it is burned out with a laser. Treatment is carried out under local anesthesia. After the operation, a tight bandage is required, and in some cases, immobilization of the hand. Sutures are removed between the fifth and seventh day after the intervention. Typically, the postoperative period requires injection of antibiotics.
For the final rehabilitation of the wrist joint, physiotherapeutic procedures will be required: mud applications, paraffin therapy, electrophoresis, ozokerite and laser exposure. Exercises will be prescribed aimed at restoring full mobility of the hand and developing the joint itself. Limiting the load on the affected arm can last for quite a long time.
Take care of your hands, and you will never need treatment for your wrist joint. But if you already feel discomfort from your hands, please go for an examination so as not to lose the ability to self-care and not be left without work.
Nutrition for osteoarthritis of the wrist
Maintaining a healthy diet while treating wrist osteoarthritis is easy. It is necessary to exclude salty foods from the diet, which lead to dehydration, and also include in the diet dishes rich in vitamin A (antioxidant, chondrocyte growth), C (cell protection, collagen synthesis), E (protects cartilage from free radicals and aging), B5 and B6 (regeneration, relieve inflammation), copper (improves cellular “respiration” of cartilage), selenium (for the production of synovial enzymes), as well as collagen, chondroitin and glucosamine (building material for cartilage tissue). To do this, eat fish, meat and bone broths, jellied meat, fruit jellies, animal cartilage, wheat germ and other healthy foods.
General clinical recommendations
To prevent exacerbation of the pathological process and its progression, the following recommendations must be followed:
- follow all doctor's orders;
- conduct courses of anti-relapse treatment;
- promptly treat all acute and chronic diseases;
- avoid colds and hypothermia, especially of the hands;
- do not lift heavy objects, do not engage in long-term painstaking activities involving the hands;
- avoid prolonged stress;
- get rid of bad habits.
Prevention
Prevention of arthritis of the hand is especially important for people with a family history (close relatives suffering from this pathology). To prevent the development of the disease, you need:
- lead a healthy active lifestyle, eat right;
- do not overload your hands with heavy physical work and long, tedious painstaking work;
- do not smoke, do not abuse alcohol;
- avoid hypothermia of hands;
- promptly treat all diseases and hormonal disorders.
How to eat healthy
Only gout requires a special diet; it is imperative to adhere to its requirements. For other types of arthritis, a healthy diet is sufficient. Fatty meat and dairy products, fried, spicy, smoked, and canned foods should be excluded from the diet. It is necessary to limit sweets, baked goods, and sweet carbonated drinks. The diet should contain a lot of fresh vegetables, fruits, cereals, and low-fat animal products.