13 May 2020
100807
3
3.6 out of 5
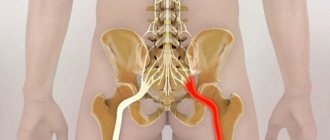
The sciatic nerve is one of the largest nerves in the human body. It is formed by two branches, each of which originates from the sacral nerve plexus, passes through the buttock, descends along the back of the thigh and calf muscle all the way to the Achilles tendon. Thus, the left and right branches of the nerve are responsible for the innervation of the corresponding legs. But under the influence of various reasons, it can become inflamed and pinched, which provokes severe pain along its course, which can deprive a person of the ability to move normally for a long time.
What is the sciatic nerve and why does it hurt?
The sciatic nerve is the largest structure of the peripheral nervous system. In addition to the fact that it is very long and runs through the entire leg, it also has a fairly large diameter - about 1 cm. It is formed by nerve fibers of the sacral nerve plexus and has motor, sensory and autonomic fibers. Therefore, this nerve is responsible for the innervation of muscles, blood vessels, and skin of the legs.
Damage to the sciatic nerve is one of the common types of neuropathy. Most often, people aged 25–60 years suffer from this, and not only isolated damage to the sciatic nerve may occur, but also complications from pathologies of the sacral plexus, diseases of the spine, etc. It can become inflamed under the influence of various factors, including local processes and diseases spine, pelvic organs, etc. The inflammatory process itself can cause pinching of the sciatic nerve and the development of corresponding neurological symptoms.
Nerves are sensitive to any changes in which there is a disturbance in the blood supply and compression of soft tissues; they are easily damaged by injury and tend to be destroyed by toxins, infectious agents, etc. Therefore, pain and inflammation can be a consequence of both local and systemic diseases.
When the sciatic nerve becomes inflamed or pinched, its membranes are gradually destroyed, which is called demyelination. This leads to severe pain and deterioration of nerve conduction, which provokes the occurrence of impaired mobility and sensitivity. Additionally, adverse vascular changes may occur. Most often, unilateral neuritis is diagnosed, leading to a serious decrease in the patient’s quality of life due to severe pain that limits his ability to work and can lead to disability.
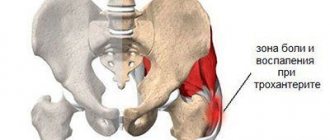
Damage to the sciatic nerve is characterized by acute, unbearable or nagging, aching pain in the buttocks or trochanter of the hip joint, the back of the thigh, the popliteal fossa, the inner or outer side of the calf muscle. It is often one-sided, but in some cases pain can be felt in both legs at once.
Causes of pain
Damage to the sciatic nerve is a consequence of prolonged exposure to negative factors. These may include direct damage to the nerve due to injury or as a result of compression by certain anatomical structures. Thus, any injuries in which the integrity of the bones is disrupted and the soft tissues of the back of the thigh are damaged are a significant risk factor for the development of inflammation and pinching of the sciatic nerve. In addition, a serious threat to its damage is posed by neoplasms of various natures, including vascular ones, as well as diseases of the spine of various natures.
Thus, the causes of pain along the sciatic nerve can be:
- fractures of the pelvic bones, hips (in this case, the nerve can be damaged not only directly at the time of injury, but also during immobilization);
- local infectious processes of any origin, as a result of which pathogenic bacteria can penetrate deep into the soft tissues and cause inflammation of the sciatic nerve;
- systemic infections that damage peripheral nerve fibers and weaken the immune system (HIV, tuberculosis, measles, herpetic infection, diabetes mellitus);
- intoxication caused by the use of drugs, alcohol, toxins;
- metabolic disorders, against the background of which harmful compounds accumulate in tissues and provoke damage to the vessels that supply the sciatic nerve;
- inflammatory diseases of the pelvic organs, including the uterus, appendages, intestines and others, which, in the absence of timely treatment, can provoke the spread of the inflammatory process involving the sciatic nerve;
- medical manipulations on the lower extremities and sacral region - non-compliance with the rules for performing injections, especially blockades often used for diseases of the spine, as well as surgical interventions can provoke inflammation and pain along the sciatic nerve.
In some cases, it is not possible to determine the cause of pain along the sciatic nerve and its inflammation. In such cases, idiopathic neuralgia is diagnosed.
Another common cause of pain along the sciatic nerve is sciatica. Most often, it is provoked by the presence of congenital and acquired pathologies of the spine, which may be accompanied by circulatory disorders in the affected area. As a result of nutritional deficiency and compression, soft tissues suffer, which can lead to the development of an inflammatory process, which may also involve the sciatic nerve.
Sciatica as a cause of pain along the sciatic nerve
Sciatica means pinching of a nerve by one or another anatomical structure, which provokes the appearance of characteristic pain. It is typical for pain to occur under certain conditions.
The appearance of pain can be provoked by getting out of bed, walking or standing for a long time, running, bending, etc. However, initially they can be barely noticeable and go away on their own over time. This condition can persist for several years and is often ignored by people. But over time, continued compression of the nerve leads to the development of neurological symptoms, and sooner or later careless movement or physical overexertion will lead to an acute attack of pain.
It is at this stage that people most often consult a doctor. During the examination, a neurologist using special neurological tests can almost accurately diagnose sciatica. After this, the patient is necessarily sent for a comprehensive examination, the purpose of which is to identify the causes that led to the pinching of the sciatic nerve.
These can include diseases of the spine, excessive physical activity, pregnancy, etc. The most common causes of sciatica are:
- Osteochondrosis and intervertebral hernias are the main cause of radicular syndrome, i.e. pinched nerves. As a result of a sedentary lifestyle, prolonged sitting or excessive physical activity, the intervertebral discs wear out and become thinner. They cease to cope with natural functions, and their shells become thinner. This causes back pain, and subsequently protrusion of part of the nucleus pulposus of the disc beyond the anatomical boundaries, i.e. the formation of a hernia. Pain along the sciatic nerve can be caused by intervertebral hernias that form in the discs of the lumbosacral spine.
- Spinal stenosis is a disease in which herniated discs or other formations compress the spinal canal. This is accompanied by severe pain, which intensifies while walking and doing physical work. Since the spinal cord suffers greatly due to such processes, this affects the quality of functioning of all other nerves and the functioning of internal organs.
- Spondylolisthesis is a disease of the spine, accompanied by a displacement of the vertebra relative to the underlying one by a greater or lesser amount, which can provoke compression of the nerves passing in the immediate vicinity.
- Facet syndrome is a disease in which nerve fibers are pinched in narrow openings between the vertebrae, causing their deformation by osteophytes and other disorders.
- Scoliosis – curvature of the spine in the lateral plane leads to pinched nerves, severe pain and can be accompanied by a number of other complications, the severity of which is determined by the degree of deformation of the ridge.
Also, the development of sciatica and pain along the sciatic nerve can be caused by piriformis syndrome. It is located under the gluteal muscle and in some people the sciatic nerve runs through it. Therefore, with strong physical exertion on the buttocks, a spasm of the piriformis muscle may occur, which will lead to compression of the sciatic nerve and the appearance of corresponding symptoms.
With sciatica, it is extremely important to determine the causes of sciatic nerve compression. Otherwise, prescribing only symptomatic therapy will give only short-term results, while the underlying pathology will progress and not only cause even greater damage to the sciatic nerve, but also cause other complications.
Therefore, for sciatica, treatment is always comprehensive. It includes means to eliminate pain and neurological symptoms, as well as etiotropic therapy. The second is given special attention, since the prognosis of the entire treatment depends on the correctness of its development. In some cases, patients are prescribed conservative therapy, including medication, physiotherapy, exercise therapy and massage, while in others, surgical intervention is required to effectively eliminate the cause of sciatica.
Prerequisites for pain
A number of factors reflecting the lifestyle and individual characteristics of a particular person can lead to the development of the above diseases and inflammation of the sciatic nerve. These include:
- age – middle-aged and elderly people are more at risk of developing neurological diseases due to natural age-related changes;
- excessive physical activity - loaders, athletes and people in other professions whose work is directly related to the need to perform heavy physical work are most at risk of pain along the sciatic nerve;
- pregnancy - increased load on the spine, compression of the internal organs by the pregnant uterus and hormonal changes do not have the most favorable effect on the body and can lead to pinching and inflammation of the sciatic nerve, but often the problem resolves on its own after childbirth.
How to treat a person suffering from pain in the buttock and leg
As a rule, severe and sudden pain in the buttock and leg shocks a person so much that he calls an ambulance. This is the first right thing. The problem is that before treating lumbago with sciatica, it is necessary to diagnose renal colic, ectopic pregnancy and other diseases that require emergency care.
After confirming the diagnosis of a disease associated with pathological processes in the spine, painkillers, sedatives, and anti-inflammatory drugs are prescribed. In this case, chondroprotectors are required.
Since to restore the healthy state of the spine and sciatic nerve it is necessary to normalize blood circulation, the following is carried out:
- physiotherapeutic procedures;
- rubbing with warming and irritating ointments;
- massage;
- compresses;
- therapeutic exercises under the guidance of a specialist.
After the acute period, it is necessary to undergo a set of restorative procedures. It includes first weak and then moderate physical training complexes in the form of swimming, contrast showers, running, cycling, etc.
It is necessary to exclude from the diet foods that cause swelling and fluid stagnation in the body. This category includes salty, fatty and spicy foods. It is necessary to focus on natural foods that contain many vitamins and minerals.
Features of pain due to damage to the sciatic nerve and accompanying symptoms
When the sciatic nerve is damaged, all symptoms that arise can be divided into 3 groups: pain, neurological disorders and movement disorders. The pain can have a different character from powerful, burning, cutting to aching, pulling. It manifests itself in the back, back of the thigh, lower leg and can radiate to the foot. In this case, pain can be either episodic or constant. In different cases, they occur with different frequency, up to several times a day.
Depending on the existing disease, pain intensifies during physical work, when sitting, standing, running, lifting heavy objects, or when exposed to low temperatures.
If inflammation is accompanied by pinching of the sciatic nerve, the pain is complemented by radicular syndrome. In this case, individual signs of neurological disorders or a whole complex of symptoms may be observed:
- the appearance of acute pain when trying to lift a straight leg up from a supine position and its weakening when bending the raised leg at the knee;
- a decrease in the severity of the Achilles reflex up to its complete absence, which is manifested by a decrease in the amplitude of movement of the foot when struck with the edge of the palm or hammer in the area above the heel;
- pain in the healthy leg when lifting the affected leg upward from a lying position;
- weakening of the knee reflex, accompanied by a lack of reaction to a blow with a hammer on the popliteal region, which normally should lead to rapid extension of the leg at the knee;
- violation of control over the processes of bowel and bladder emptying, up to involuntary defecation and urination;
- decreased erectile function (possible development of impotence);
- increased sweating;
- changes in the skin (it may become pale or, conversely, red, dry, thin and peel).
Damage to the sciatic nerve often leads to a deterioration in the conduction of nerve impulses along it, which is accompanied by impaired mobility of the legs and a decrease in their sensitivity. Therefore, patients often complain of:
- difficulty bending the leg at the knee and ankle joint;
- changes in gait, which is caused by walking on an almost straight leg;
- decreased skin sensitivity, numbness, tingling sensation in the back of the thigh, calf muscle area and foot;
- decreased muscle tone of the lower extremities;
- the patient is in a forced position of the body, bent forward and leaning slightly to the side;
- paralysis of the affected leg, especially the foot, which sometimes simply hangs helplessly and cannot perform a supporting function.
Thus, the nature of the clinical picture largely depends on what disease led to inflammation of the sciatic nerve and pain.
What to do for lower back pain radiating to the leg and buttock
First of all, if pain occurs in the lower back, buttock, or thigh, you should ensure complete rest. Gradually, the pain should subside due to muscle relaxation. You should also definitely make an appointment with a chiropractor - a neurologist, but before examining a specialist, it is important not to take any medications, since painkillers will blur the clinical picture and make it difficult to diagnose the disease.
It is important not to self-medicate when pain occurs and not to rely on ointments, creams or gels containing diclofenac sodium and other NSAIDs, since they have practically no therapeutic effect, but only dull the symptoms of the disease.
Diagnostics
For an experienced specialist, determining the presence of damage to the sciatic nerve is not difficult by the presence of characteristic pain, the addition of neurological disorders or movement disorders. But finding the reasons that triggered this may take some time.
To do this, the doctor must conduct a general examination and interview the patient. This allows you to assess the condition of the spine, the functionality of the nervous system, muscle tone, conduct specific tests and detect local changes in the skin. Having formed a general impression of the nature of the existing pathological changes, and sometimes having a preliminary diagnosis, the doctor refers the patient for a comprehensive examination. It allows you to obtain objective data about the condition of the patient’s body, diagnose the slightest pathological changes in the spine and other organs, and formulate a prognosis.
Therefore, patients are usually prescribed:
- radiography of the spine, pelvis and legs in two projections - allows you to assess the condition of bone structures, detect signs of osteochondrosis and its complications, displacement of the vertebrae relative to each other, which will be the reason for further examination with other instrumental methods;
- CT is a more advanced method for studying the condition of bones, allowing one to visualize the slightest changes in them, the presence of tumors of various natures;
- MRI is the most informative method for diagnosing diseases of soft tissues and cartilage, which, in fact, are intervertebral discs; with its help, even the smallest protrusions and hernias, vascular tumors, aneurysms, spinal stenosis and a number of other common spinal diseases are detected;
- electromyography – used to assess the quality of nerve impulses to muscles and the intensity of their contraction;
- Ultrasound is used to diagnose gynecological, urological and a number of other diseases of internal organs, which can cause the development of an inflammatory process.
Often, instrumental diagnostic methods are complemented by laboratory tests. Depending on what diseases the doctor suspects, the patient may be prescribed a general blood and urine test, biochemical blood test, etc.
Diagnosis of the causes of lumboischialgia
When pain in the lower back radiates to the leg and buttock, you need to consult a chiropractor or neurologist. Our center’s specialists use an integrated approach to diagnosis and treatment, so they can quickly make the correct diagnosis. Diagnosis begins with a survey of the patient, during which the nature of the complaints, as well as the characteristics of work and rest, are clarified. The doctor must carefully examine the patient, palpating the spine, as well as conducting special functional and neurological tests. This allows you to get a complete picture of the patient’s condition, detect signs of neurological deficit and assess the extent of damage.
In order to establish the exact cause of lower back pain radiating to the leg and buttocks, instrumental diagnostic methods are prescribed. They almost always start with assessing the condition of the bones, intervertebral discs, ligaments and muscles of the spine. For this purpose the following are assigned:
- X-ray;
- CT;
- MRI.
The most complete and accurate picture of the state of the soft tissue structures of the spine is provided by magnetic resonance imaging. The method involves conducting a study of the body using powerful magnetic fields that do not have a negative effect on the human body. Therefore, it has practically no contraindications, with the exception of the presence of metal foreign bodies or implants in the body. If there are any, the patient is referred to a CT scan or x-ray. But only MRI allows one to determine the size of protrusions and intervertebral hernias with millimeter accuracy and detect the slightest degenerative-dystrophic changes in the discs, as well as signs of compression of nerve structures.
In our clinic you can also learn in more detail about the composition of your body and the state of the vascular system, which is involved in the blood supply to internal organs, musculoskeletal muscles, and the brain. Our experienced doctors will explain the data obtained to you in detail. Bioimpendansometry calculates the ratio of fat, muscle, bone and skeletal mass, total fluid in the body, and basal metabolic rate. The intensity of recommended physical activity depends on the state of muscle mass. Metabolic processes, in turn, affect the body's ability to recover. Based on the indicators of active cell mass, one can judge the level of physical activity and nutritional balance. This simple and quick test helps us identify disturbances in the endocrine system and take the necessary measures. In addition, it is also very important for us to know the condition of blood vessels for the prevention of diseases such as heart attacks, hypertension, heart failure, diabetes and much more. Angioscan allows you to determine such important indicators as the biological age of blood vessels, their stiffness, stress index (which indicates heart rate), and blood oxygen saturation. Such screening will be useful for men and women over 30, athletes, those undergoing long-term and severe treatment, as well as everyone who monitors their health.
In this case, body composition analysis gives us information that adipose tissue predominates in the body, and the bone-muscle component is in relative deficiency. These data will help the rehabilitation doctor competently draw up a physical activity plan, taking into account the individual characteristics of the patient.
If during the examinations no abnormalities in the condition of the spine are found, the patient is referred for consultation to a proctologist, gynecologist or urologist, since pain in the lower back radiating to the leg and buttock can be accompanied by proctitis, paraproctitis, prostatitis, adnexitis, uterine prolapse, prostate adenoma and other similar diseases.
Conservative treatment
Treatment of pain and inflammation of the sciatic nerve always includes 2 directions: symptomatic and etiotropic therapy. Of course, the greatest importance is given to etiotropic therapy, since the outcome of the disease and the patient’s well-being depend on it. It is aimed at eliminating the causes of pain and inflammation of the sciatic nerve, while symptomatic therapy can only temporarily eliminate pain.
If the cause of inflammation and pain is not eliminated, they will recur regularly and become chronic over time. In this case, it will be extremely difficult, if not impossible, to cope with the disease in a conservative way.
At the same time, ignoring excruciating pain and impaired mobility will be inhumane towards the patient. Therefore, along with etiotropic therapy, medications are always prescribed to relieve pain and improve nerve conduction.
Thus, for each patient, treatment is selected individually based on the diagnosis and the detected cause of pain along the sciatic nerve. Therefore, it can be radically different even among people with the same complaints.
Most often patients are prescribed:
- drug therapy;
- physiotherapy;
- manual therapy;
- Exercise therapy.
However, conservative therapy is not always effective and does not lead to the expected results. And in some situations, its use is not at all justified, since existing pathologies can only be eliminated surgically. In such situations, the patient is prescribed symptomatic treatment to reduce pain and referred for consultation with a neurosurgeon to develop tactics for surgical treatment.
Drug therapy
The type of medications prescribed directly depends on the diagnosis. In most cases, patients are prescribed:
- NSAIDs - drugs in this group have anti-inflammatory and analgesic properties. They are prescribed in fairly long courses and can initially be administered intramuscularly or intravenously, and subsequently the injections are replaced by taking the same medications, but in the form of tablets or capsules with the simultaneous use of ointments, creams or gels with a similar effect.
- Corticosteroids - indicated for severe inflammatory processes that cannot be eliminated by NSAIDs. They allow you to quickly stop inflammation and eliminate swelling of soft tissues. Corticosteroids are mainly used in the form of injections, since when taken orally they provoke the development of a large number of side effects.
- Muscle relaxants - drugs in this group are used to break the vicious circle “pain - spasm - pain”, since the appearance of pain causes a reflex muscle spasm, which leads to pinched nerves and even greater pain.
- Antibiotics - used when the inflammatory process is bacterial in nature. Depending on its severity, drugs can be administered intramuscularly, intravenously, or used in forms intended for oral use.
- B vitamins are indicated to improve nerve conduction, as they are directly involved in the transmission of nerve impulses.
- Preparations for improving microcirculation and metabolism - help improve blood circulation in the affected area, which leads to the normalization of nutrition of all tissues, including the sciatic nerve, as well as the rapid elimination of toxins, inflammatory mediators and metabolic products.
For particularly severe pain, patients may be prescribed opioid analgesics. But their use is possible only in a hospital setting under strict medical supervision and short courses, since drugs of this kind quickly provoke addiction and dependence.
This list may be supplemented by other drugs that directly affect existing diseases. If the medications used do not relieve an acute attack of pain, and the patient complains of unbearable pain that interferes with normal mobility, he may be offered a novocaine or lidocaine blockade.
The procedure involves injecting an anesthetic directly into the area where the nerve passes, which leads to rapid pain relief. But since its implementation requires compliance with antiseptic conditions and the presence of certain skills, it can only be carried out in specialized medical institutions.
The blockade gives a quick, pronounced effect, but it is effective only for pain caused by a pinched nerve. It does not have any medicinal properties and can be used no more than 4 times a year.
Physiotherapy
In the presence of pathologies of the spine, as well as inflammatory processes, the use of physiotherapy methods is very effective to increase the effectiveness of drug treatment of pain along the sciatic nerve. The types of physical impact, duration of procedures and their number are selected individually. As a rule, patients are prescribed:
- UHF;
- electrophoresis;
- magnetic therapy;
- laser therapy;
- ultrasound therapy;
- reflexology;
- diadynamic currents, etc.
Physiotherapy helps reduce the severity of pain, accelerate the resolution of the inflammatory process, reduce swelling of soft tissues, and improve blood circulation. But the use of physiotherapeutic methods is allowed only after the completion of the acute inflammatory process.
Manual therapy
Manual therapy sessions are also indicated outside the acute period. When the techniques are performed correctly, the influence of the doctor’s hands allows you to achieve good results: reducing pain, normalizing the position of the vertebrae, increasing the distance between them, as well as eliminating muscle spasms, which helps reduce the load on the intervertebral discs and allows you to release the pinched nerve.
Also, manual therapy can improve local blood circulation, which will inevitably have a positive effect on the condition of the sciatic nerve and its conductivity. Improving microcirculation in the area of influence helps to normalize the nutrition of all tissues and the rapid elimination of metabolic products, inflammatory factors and harmful substances. Thanks to this, inflammatory processes are eliminated faster, the condition of the spine improves, and the pinched sciatic nerve is released.
But conducting manual therapy sessions can only be trusted by a highly qualified specialist who not only has a higher medical education, but has completed a full course of training in manual therapy and has the appropriate license.
Exercise therapy
Therapeutic exercise is one of the most important components of the conservative treatment of inflammation of the sciatic nerve. Dosed, correctly selected load is an effective means of preventing the onset of pain. In addition, it has a positive effect on the condition of muscles, improves blood circulation and normalizes metabolic processes.
For each patient, the exercise therapy program is selected individually in accordance with the detected disease. The specialist determines the level of physical development of the patient, takes into account his age, existing concomitant diseases and, based on this, creates a set of exercises that will solve the assigned tasks and will not cause harm.
It can be unsafe to engage in physical therapy on your own, using recommendations from friends or through programs offered online. Incorrectly selected exercises can only lead to increased inflammation, progression of existing pathologies, or even greater compression of the sciatic nerve, which will result in increased pain.
Therefore, to develop a physical therapy program, you should contact only a qualified specialist. The first classes are also conducted under his supervision. This is necessary so that the patient can fully master the technique of performing each exercise and perform it correctly.
In the future, you can engage in physical therapy independently in a comfortable environment. Classes are held daily, and it is important to avoid sudden movements and serious overload. After a certain time, the patient needs to see the doctor again so that he can adjust the exercise therapy program and increase the load.
Surgery
It will not be possible to do without surgery if conservative treatment does not bring positive results within 3 months or there are pathologies that cannot be eliminated non-surgically. Therefore, the help of a spinal surgeon is required when:
- spinal fractures;
- intervertebral hernias that compress the sciatic nerve or spinal cord and provoke the development of radicular syndrome;
- spondylolisthesis;
- scoliosis;
- tumors of different nature.
In each case, different types of operations are used, differing not only in the method of execution, but also in the level of trauma, the duration and complexity of the rehabilitation period, as well as the number of risks and possible complications.
The easiest, least traumatic and safest methods of percutaneous surgery are recognized, which can be used to remove intervertebral hernias and treat compression fractures. But such methods can only be used if there is a small hernia, otherwise they are ineffective.
Percutaneous surgery methods include hydroplasty and nucleoplasty. In both cases, operations involve destruction of the nucleus pulposus of the intervertebral disc using instruments whose diameter does not exceed several millimeters. But when using hydroplasty, the nucleus pulposus is destroyed by liquid pressure, and when using nucleoplasty, it is destroyed by cold plasma, laser or radio waves. In both cases, the postoperative wound is so small that it does not require stitches. It is only covered with a sterile bandage, and the rehabilitation period proceeds almost unnoticed by the patient.
A somewhat more traumatic way to remove intervertebral hernias is endoscopic surgery, which involves resection using a lateral approach. The operation is performed using special endoscopic equipment equipped with a video camera. It is immersed into the patient’s body through pinpoint punctures, the diameter of which does not exceed 1 cm. In this way, hernias of different sizes can be removed, but when they are located in hard-to-reach places, the technique is ineffective.
For large, complex or even sequestered hernias that have led to spinal canal stenosis, the operation is performed through a soft tissue incision in the projection of the affected disc and is called microdiscectomy. It can be used in all cases with virtually no restrictions, with the exception of obvious contraindications to surgical intervention (respiratory or heart failure, pregnancy, etc.). Microdiscectomy uses special small surgical instruments. But since the operation is associated with injury to soft tissues, recovery after it is more difficult and longer than when using other methods of surgical treatment of intervertebral hernias.
If pain and inflammation of the sciatic nerve are caused by a compression fracture of the spine, the patient urgently requires vertebroplasty or kyphoplasty. Both operations have an almost identical technique, which consists in filling the flattened vertebra with a special, quickly hardening bone cement, which ensures the formation of a strong bone conglomerate. But kyphoplasty has broader indications for use and can be used for severe compression fractures with a significant reduction in the height of the vertebra, since it involves the initial restoration of its natural shape and size using a balloon inserted inside. It is gradually taken off, thereby restoring the parameters of the spine, and then deflated and removed.
If sciatic nerve pain is caused by scoliosis or spondylolisthesis, special metal structures consisting of plates and screws screwed into the vertebrae are used to fix the vertebrae in the correct position and restore the normal axis of the spine. They are introduced into the body through small incisions and remain in the human body for life.
Thus, pain and inflammation of the sciatic nerve can significantly poison life and deprive a person of his ability to work. But with timely treatment, they can be completely overcome and disability can be avoided. Therefore, if you experience regular pain, and even more so if you detect other of the above signs, we recommend that you immediately contact a neurologist or a spinal surgeon.
Only a qualified doctor can correctly diagnose and prescribe optimal treatment.