What is ulnar neuritis? How does the ulnar nerve work, what functions is it responsible for? Why does the disease occur? Modern effective treatment methods.
Our expert in this field:
Lashch Natalia Yurievna
Neurologist of the highest category, candidate of medical sciences, associate professor. Laureate of the Moscow City Prize in the field of medicine.
Call the doctor Reviews about the doctor
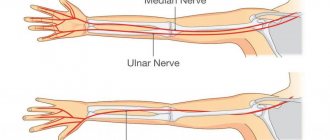
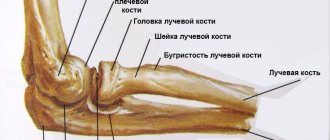
Ulnar nerve neuritis is an inflammatory disease. It ranks second in prevalence among arm nerve lesions after radial neuritis. The ulnar nerve runs along the inner surface of the shoulder, then descends to the forearm and hand. In the area of the internal epicondyle - the bony protrusion at the bottom of the shoulder on the inside - it is close to the skin, so it is often bruised in this place.
The ulnar nerve innervates the elbow joint, provides movement in the muscles of the forearm and hand, and sensitivity of the skin in the area of the little finger and ring finger. With neuritis, these functions are disrupted.
The main causes of the development of ulnar nerve neuritis:
- Compression of the nerve where it passes near the elbow. Most often this occurs in people who constantly rest their elbows on a table (office workers), a workbench, or a machine in a factory.
- Injuries. Damage to the nerve trunk can occur with fractures of the internal epicondyle at the bottom of the humerus.
- Some infections. For example, typhoid, typhus.
- Poisoning. The disease often occurs in people who chronically abuse alcohol.
- Endocrine diseases. Neuritis can develop against the background of diabetes mellitus and thyroid dysfunction.
- Hypothermia.
If you experience numbness or impaired movement in the muscles of your arm, do not engage in self-diagnosis or self-medication. The correct treatment is the one prescribed by a competent medical specialist after examination and examination.
Take care of yourself, book a consultation now
Message sent!
expect a call, we will contact you shortly
Causes
SLN in the cubital and Guyon's canals occurs due to repetitive compression due to support on the elbows or wrists (cyclist's palsy) or prolonged flexion of the elbow. It can also occur due to trauma, swelling, fracture, vascular and bone pathologies/disorders.
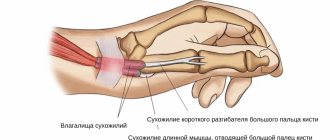
Ulnar carpal syndrome occurs when the ulnar nerve becomes compressed between the hook of the hamate bone and the transverse carpal ligament. Guyon's canal syndrome is considered an overuse injury that is typically caused by direct pressure on the handlebars (eg, bicycle handlebars, weight lifting, heavy equipment) and is thus sometimes referred to as "steering wheel palsy." This syndrome may also result from intense gripping, rotation, or repetitive movements of the wrist and hand. Impingement can develop if the hand is flexed and the elbow is abducted for an extended period of time.
The incidence of injuries leading to ulnar nerve compression is unknown; however, ulnar neuropathy has been documented after distal humerus fractures, of which up to 10% are associated with elbow dislocation, and can also develop following any complex trauma to the elbow or wrist.
Treatment of ulnar nerve neuritis
Treatment of ulnar neuritis is carried out in several directions:
- If the disease is caused by a bacterial infection, antibiotics are prescribed; if it is caused by viruses, antiviral drugs are prescribed.
- If the underlying cause is vascular disorders (the nerve does not receive enough oxygen and nutrients due to impaired blood flow), vasodilators are used.
- If the neuritis is associated with injury, you need to unload the affected arm. For this purpose special tires are used.
- To combat pain and inflammation, the neurologist prescribes drugs from the group of non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (diclofenac, ibuprofen).
- To reduce nerve swelling, diuretics are prescribed: diacarb, furosemide.
- Physiotherapeutic procedures are usually prescribed towards the end of the second week of the disease. Pulse currents, UHF, ultraphonophoresis with hydrocortisone, electrophoresis with novocaine are used.
The best results are obtained if treatment is started in the early stages, as soon as the first symptoms appear. If, despite the therapy, there is no improvement after 1-2 months, the neurologist may raise the question of surgery.
When the first symptoms occur, do not delay visiting a doctor. The earlier treatment is started, the better the result can be achieved. Book a consultation with a neurologist now. At the medical center International Clinic Medica24, this can be done at any time of the day by phone.
Take care of yourself, book a consultation now
Message sent!
expect a call, we will contact you shortly
The ulnar nerve has a mixed structure: it consists of motor, sensory, autonomic (responsible for the regulation of blood circulation, the work of the sweat and sebaceous glands, and other functions) fibers. It performs the following functions:
- Bending the hand.
- Flexion of the little finger and ring finger, partly the middle finger.
- Spreading and closing the fingers.
- Adduction of the thumb.
- Sensitivity of the inner (ulnar) part of the hand, little finger, partly ring finger, sometimes middle finger.
Accordingly, with ulnar nerve neuritis, symptoms are associated with a violation of these functions. They can be identified and correctly assessed by a doctor during a neurological examination.
Symptoms of Elbow Arthritis
The symptoms and course of elbow arthritis depend on its clinical form. But the first manifestations and obvious symptoms also have common characteristics.
First signs
When arthritis of the elbow joint begins, the symptoms may be severe or mild. The skin over the site of inflammation swells, turns red, and it is difficult to move the hand due to severe pain. Fever and chills may appear.
In subacute and chronic cases, the disease can begin unnoticed. The pain syndrome is erased, the swelling in the elbow area is insignificant. Limitation of mobility also increases unnoticed and manifests itself in the form of morning stiffness, which quickly passes after the person begins to move.
When the first symptoms of elbow arthritis appear, you should immediately seek medical help!
Obvious symptoms
In an acute course, characteristic signs appear immediately and cannot be ignored. In the absence of adequate treatment, the inflammatory process becomes less acute over time and the course becomes chronic and protracted and much more difficult to treat.
Obvious signs of chronic arthritis of the elbow joint: increasing pain and periodic swelling in the elbow area, limitation of movements in the arm. If at first movement in the elbow was limited due to pain, then after some time the limitation of movement will become permanent and will not depend on exacerbations of arthritis.
It is better to consult a doctor as soon as possible, but if you do not immediately notice signs of arthritis, do not despair, you can help in any case.
When you need to see a doctor urgently
Sometimes arthritis of the elbow joint occurs with complications, as evidenced by the presence of the following symptoms:
- high fever more than 5 days after the onset of the disease;
- a sharp rise in temperature with existing arthritis;
- significant increase in pain and swelling.
If these symptoms appear, you should call a doctor at home!
To better understand how elbow arthritis develops, you need to know how the elbow joint works.
What symptoms most often occur with ulnar nerve neuritis?
Sensitivity disorders due to neuritis are manifested by numbness in the area of the little and ring fingers, and the inner surface of the hand. At the same time, unpleasant sensations appear in these places: tingling, a feeling as if “goosebumps are crawling” on the skin. Pain in the hand may be bothersome.
Among the movement disorders, weakness is noted in the muscles that spread in different directions and bring the fingers together. The main phalanges (those that connect directly to the hand) of the fingers are extended (since another nerve, the radial one, is responsible for their extension), and the distal ones are bent. As a result, the hand acquires a characteristic appearance - doctors call it a “clawed paw” in their jargon. Gradually, the small muscles of the hand decrease in size and atrophy.
Autonomic disorders with ulnar nerve neuritis manifest themselves in the form of symptoms such as dryness or increased moisture of the skin, cyanosis, and coldness.
Causes and symptoms (radial tunnel syndrome)
Radial tunnel syndrome is caused by increased pressure on the radial nerve, which runs in the bones and muscles of the forearm and elbow. Causes of radial tunnel syndrome include:
- Injury
- Benign tumors (lipomas)
- Bone tumors
- Inflammation of surrounding tissues
Symptoms of radial tunnel syndrome include:
- Sharp, burning or stabbing pain in the upper forearm or back of the hand, especially when trying to straighten the wrist and fingers.
- Unlike cubital tunnel syndrome and carpal tunnel syndrome, radial tunnel syndrome rarely causes numbness or tingling because the radial nerve primarily affects the muscles.
Just like with cubital tunnel syndrome, if any of these symptoms are present, your doctor may diagnose radial tunnel syndrome based on a physical examination alone. If necessary, electromyography may be prescribed to confirm the diagnosis, determine the level of damage and the degree of damage to the nerve fiber.
How does a neurologist identify symptoms of ulnar nerve neuritis?
First of all, the doctor conducts a conversation with the patient - from it it becomes clear that the main problem with which the person came is neurological disorders of the arm and hand. A general neurological examination is required - the doctor needs to assess the state of the nervous system as a whole, because the symptoms of neuritis can be caused by another, more serious disease.
The neurologist can then perform some simple tests that will help identify the characteristic signs of ulnar neuritis:
- If you clench your hand into a fist, the little finger, ring finger and partly the middle finger will not bend completely.
- If you put your hand on the table, palm down, and try to “scratch” the surface of the table with your little finger, you won’t be able to do it.
- Also, in this position, it will not be possible to bring your fingers together and spread them apart; this will be especially noticeable on the middle, ring, and little fingers.
Physiotherapeutic examination
Elbow carpal syndrome: It is important to rule out other diagnoses that may be related to the elbow joint. Physical examination includes:
- Assessment of range of motion of the wrist and fingers.
- Manual muscle testing of the ulnar nerve muscles innervated distal to Guyon's canal.
- Sensory examination of the cutaneous branches of the ulnar nerve distal to Guyon's canal
- Assessment of atrophy of the deep muscles of the hand.
Friends, on April 11-12 in Moscow there will be a seminar by Anna Ovsyannikova “Fundamentals of anatomy and biomechanics of the hand. Diseases and injuries of the hand and fingers." Find out more...
Special tests
- "Card" test.
- Froment's sign
- Tinnel's sign in Guyon's canal.
- The Ulnar Nerve Neurodynamic Test (ULTT3) may increase the patient's symptoms.
Diagnostic tests to determine ulnar nerve compression
- Visualization of osteoarthritis, osteophytes or bone cysts.
- Nerve conduction studies (EMG).
- If there is a suspicion of a fracture/dislocation, a plain X-ray.
Treatment of symptoms of ulnar neuritis
For symptoms of ulnar nerve neuritis, a neurologist prescribes treatment, which may include medications, physiotherapy, massage, and physical therapy.
Sometimes they resort to acupuncture
In severe cases, surgery may be required. The surgeon frees the ulnar nerve from pathologically altered tissues that compress it, or sews the ends together if its integrity is compromised.
The sooner you contact a competent doctor, the sooner the correct treatment will be prescribed, and the restoration of impaired functions will occur more quickly and fully. Make an appointment with a specialist right now: +7 (495) 230-00-01.
The material was prepared by Natalya Yurievna, a neurologist at the international clinic Medica24, Candidate of Medical Sciences Lasch.
Diagnostics
The diagnosis of elbow arthritis is made based on a survey and examination of the patient and is confirmed by laboratory and instrumental examination data. Without an accurate diagnosis, it is impossible to prescribe adequate treatment, so if you suspect elbow arthritis, you should immediately contact the clinic. It is impossible to conduct a full examination at home.
Examination plan:
- Laboratory tests
of blood and urine, as well as examination of synovial fluid taken during arthroscopy; signs of inflammation, autoimmune process, infections are revealed. - Instrumental studies
:- radiography of the joint
- reveals bone changes; - Ultrasound
– reveals the presence of an increased volume of synovial fluid; - computed or magnetic resonance imaging (CT or MRI)
- give a clear picture of the pathological process in the elbow; - arthroscopy
- examination of the inner surface of the synovial membrane using endoscopic equipment and taking synovial fluid for laboratory testing.