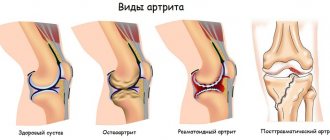
Arthritis and polyarthritis are an inflammatory process in one or multiple joints. There are several types of disease, which are caused by injury, infection, excessive physical activity, and bad habits. Both ailments are accompanied by severe pain in the moving joints, swelling and limited movement. At the first symptoms, you should immediately consult a doctor and strictly follow his recommendations.
The main difference between arthritis and polyarthritis is the extent of damage to the joints of the body.
What is polyarthritis and arthritis?
Both diseases affect joints in any part of the musculoskeletal system. With arthritis, one movable joint becomes inflamed, and with polyarthritis, several joints become inflamed. This is the whole significant difference. Otherwise, the diseases are similar - the causes, symptoms, types and treatment are the same. The most severe and incurable form is rheumatoid polyarthritis, when the pathology spreads from small joints to large and nearby tissues. There are several causes of inflammatory processes:
- infections;
- autoimmune disorders;
- obesity;
- hormonal imbalances;
- regular lifting of weights;
- bad habits;
- wrong diet.
If inflammation in the joints or the underlying ailment that causes arthritis is not treated, it can progress to the stage of polyarthritis.
Return to contents
How are the illnesses similar?
Symptoms of disorders
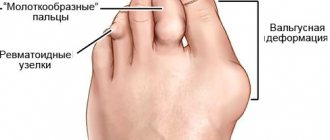
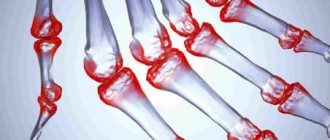
Arthritis and polyarthritis are accompanied by pain, swelling, and deformation of the inflamed joint.
Depending on the type of joint inflammation, the clinical picture can be expressed in increased temperature, skin rashes, and the appearance of tophi. Rheumatoid arthritis and polyarthritis are severe and have common symptoms, which include the following:
- severe joint pain;
- swelling;
- skin hyperemia;
- limited movement;
- stiffness in the limbs after waking up in the morning;
- joint deformity;
- atrophy of muscles and tissues, leading to disability.
Return to contents
Treatment of both pathologies
Therapy is prescribed after determining the cause of the disease. Arthritis of infectious etiology is treated with antibiotics. For gouty type, doctors recommend a diet that regulates the level of uric acid in the body. Rheumatic arthritis is incurable, but the patient’s condition can be alleviated by using gold-based drugs, as well as anti-inflammatory ointments and tablets - Diclofenac, Ibuprofen, Ketonal, Piroxicam. Hormonal medications are effective - Prednisolone, Dexamethasone, Triamcinolone.
The complex includes physiotherapy - electrophoresis, massage, magnetic therapy, as well as mud therapy, diet, exercise, meditation and yoga. Traditional treatment consists of external and internal use of herbal preparations from knotweed, nettle, sage, chamomile, wheatgrass, licorice, and pine needles.
Return to contents
Diagnosis of diseases
Joint pain, redness and swelling of the skin are the first symptoms indicating that you need to consult a doctor. Ignoring health problems or self-medicating can lead to irreversible complications and disability. The external signs of both pathologies are quite similar, so only a specialist can make an accurate diagnosis based on the research performed.
Diagnostic methods:
- examination of the patient to assess the extent and nature of damage to connective tissues, as well as skin and mucous membranes;
- laboratory tests to identify pathogens and the presence of rheumatoid factor in the blood;
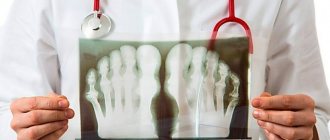
- instrumental studies (radiography, MRI, etc.) to clarify the degree of tissue damage and the degree of development of the disease.
You may also be prescribed an ECG, ultrasound, scintigraphy and some other types of examinations to monitor the functioning of internal organs.
How are diseases different?
Arthritis differs from polyarthritis in one feature: it can occur in a migratory form. That is, having arisen in one joint, the disease eventually moves to another. If the disease is not treated, the rheumatic type develops from the migratory type. Multiple arthritis is characterized by the fact that it can affect several joints at once or sequentially.
Often polyarthritis and arthritis are considered as different pathologies, although both ailments belong to the same group of diseases. They affect both older and younger people and often lead to partial loss of ability to work. The main difference between diseases lies in the scale of the lesions. With polyarthritis, several joints are affected at once, while arthritis develops only in one articular joint.
- Polyarthritis of the joints: symptoms, treatment of polyarthritis of the hands and feet
Comparative characteristics
Arthritis is a group of pathologies that are of infectious origin and are characterized by dystrophic and degenerative disorders in the structure of osteochondral tissue. Basically, the disease occurs as a consequence of an infectious lesion of the body, in rare cases it is a separate ailment. The causative agent of the inflammatory process in the joint cavity is infections of the streptococcal and staphylococcal groups.
The disease can simultaneously affect more than five joints.
Polyarthritis belongs to the group of arthritis and is considered a fairly common pathology that affects not only adults, but also young children. There is damage to several joints at the same time. A symmetrical distribution of pathology is often observed. It tends to involve joints and periarticular soft tissues close to the affected joint into the pathological process. Often polyarthritis is infectious-allergic in nature.
Rheumatoid polyarthritis is considered one of the most common forms of the disease.
Return to contents
Reasons for the development of pathology
The main root causes of the development of arthritis include: an allergic reaction, injuries to joints and infectious damage to internal organs. Pathogenic microorganisms spread throughout the body through the bloodstream and accumulate in the structure of the joints. Under the influence of an irritant, the protective properties of the immune system decrease, which causes the development of a chronic form of the disease and severe degenerative-dystrophic destruction in osteochondral tissue. Against the background of such a failure, autoimmune changes occur, in which the body produces antibodies that attack the cells of its own organs and systems.
Excess weight puts additional stress on your joints.
There are a number of negative factors that provoke the development of arthritis:
- obesity;
- hormonal disruptions and metabolic disorders;
- decreased immunity;
- congenital anomalies of the musculoskeletal system;
- hypothermia;
- concomitant infectious diseases;
- injuries with damage to the skin;
- severe stress;
- avitaminosis;
- poor nutrition;
- bad habits;
- excessive consumption of alcohol and caffeine;
- heredity.
The development of polyarthritis is caused by:
- regular allergies;
- connective tissue diseases;
- adenovirus infection.
Return to contents
Main symptoms
The surrounding tissues become inflamed and swollen.
The symptoms of arthritic joint damage depend on the type of pathology and the factor that provoked it. The following types of arthritis or polyarthritis are distinguished:
- Rheumatoid. It becomes chronic and develops against the background of genetic, hormonal and environmental disorders. As a rule, joints are affected symmetrically. The patient complains of fatigue, loss of appetite, decreased performance, pain in the affected area and swelling of the periarticular tissues. An increase in body temperature is often noted.
- Infectious. Unlike rheumatoid arthritis, it develops rapidly. The cause of inflammation is a purulent infection. The following symptoms are noted: swelling and hyperemia of the skin, sharp pain when moving, contracture, fever and fatigue. Visually noticeable deformation of the joints.
- Allergic. It occurs against the background of allergies and manifests itself acutely. Pain appears in one or more joints, swelling and rashes on the skin.
- Dystrophic. Develops after injuries. Destruction of the joint brings severe pain, impaired mobility and tissue swelling.
- Rheumatic. Affects large articular joints. It is characterized by severe pain, swelling of the affected joints, a rapid increase in body temperature and impaired mobility in the inflamed area.
There are arthritis that develop against the background of concomitant pathologies under the influence of specific groups of microorganisms. These include psoriatic and gonorrheal forms, arthritis, which occurs after influenza and sore throat. The symptoms of the pathologies are identical to the main signs of the arthritic group of ailments.
- What is the difference between arthritis and polyarthritis?
Return to contents
Diagnosis of polyarthritis
Before prescribing treatment for any disease, it is mandatory to first undergo a full medical examination to accurately determine the diagnosis. Polyarthritis is no exception. First of all, the doctor examines the patient, takes an anamnesis in order to be aware of all previous diseases, since they can cause the development of pathology. Next, blood tests are prescribed from a finger and from a vein, a urine test, laboratory tests, hardware diagnostics, x-rays, and ultrasound are performed.
How is the treatment carried out?
Antibacterial agents will eliminate the cause of inflammation.
At the initial stage, therapeutic measures are aimed at eliminating the main cause that provokes the inflammatory reaction. For this purpose, antibiotics, immunosuppressants and hormonal agents are used. To relieve pain and reduce inflammation, non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs and analgesics are used. To minimize the harmful effects on the digestive system, warming ointments and local gels are used for pain relief.
During the treatment of arthritis, special attention is paid to vitamin and mineral complexes. It is recommended to take medications with a high calcium content.
Exercise therapy, massage and physiotherapy are used to treat pathology. Exercise improves blood circulation and eliminates congestion. Massage helps normalize local trophism and microcirculation. Physiotherapeutic procedures have an anti-inflammatory and analgesic effect.
Return to contents
What is known about the disease
Have you been trying to heal your JOINTS for many years?
Head of the Institute for the Treatment of Joints: “You will be amazed at how easy it is to cure your joints by taking the product every day for 147 rubles ...
Read more "
It is not possible to name the exact cause of the development of rheumatoid arthritis, although the disease has been known for a long time; traces of it are found even on the bones of dinosaurs. Doctors put forward two options for prerequisites:
- Difference between arthritis and rheumatoid arthritis
OUR READERS RECOMMEND!
Our readers successfully use Sustalaif to treat joints. Seeing how popular this product is, we decided to bring it to your attention. Read more here...
- from the point of view of genetic predisposition, the reason is the inadequate functioning of the immune system, attacking the lining of the joint (synovial);
- Another point of view on the cause of the disease is associated with the pathogenic activity of microbes that contribute to the destruction of joint tissue (streptococci).
The onset of the inflammatory process leads to thickening of the synovial membrane with subsequent destruction of cartilage and bone tissue. As tendons and ligaments weaken, they stretch, leading to displacement of the joint, signaling deformity.
Doctors believe that the cause of the destruction of one’s own synovial tissue is a problem with the body’s immune system. The main risk factors can be allergic reactions or stress, as well as trauma.
Causes of the disease
The disease can develop as a result of repeated infections (flu, sore throat, etc.). The trigger for the development of the disease is several factors at the same time.
IMPORTANT TO KNOW! The only remedy for the treatment of joints recommended by doctors! Read more…
Probable causes of rheumatoid polyarthritis:
- hereditary predisposition - the risk of developing the disease increases fourfold if you have close relatives diagnosed with rheumatoid polyarthritis;
- infections;
- hormonal imbalances;
- frequent hypothermia;
- lack of vitamin D;
- negative environmental factors.
The disease can develop for many reasons.
There is no obvious cause for arthritis, this situation is similar to that with other autoimmune diseases.
Rheumatoid arthritis and rheumatoid arthritis: differences
Rheumatoid arthritis
Type of disease. Infectious, secondary.
Speed of development . Rapid onset of all symptoms.
Causes . Past infection (flu, sore throat, sinusitis, otitis media, etc.).
Main symptoms . Fever, severe pain.
Complications. Damage to the respiratory and cardiovascular systems.
Laboratory results. Increasing the number of antibodies to pathogens.
Forecast. With timely consultation with a doctor, a complete cure is possible.
Rheumatoid arthritis
Type of disease. Autoimmune, primary.
Speed of development . Slow, progressive increase in impairment.
Causes. Autoimmune disorders.
Main symptoms . Moderate pain with gradual development of inflammation.
Complications. Restrictions in movement, joint deformation.
Laboratory results. Detection of rheumatoid factor in the blood.
Forecast. Final recovery is impossible, but with quality treatment the condition improves markedly.
The differences between rheumatoid arthritis and rheumatoid arthritis also concern the factors contributing to the development of these pathologies. The risk of rheumatism increases:
- upper respiratory tract infections;
- reduced immunity;
- severe allergic reactions;
- hypothermia.
The development of rheumatoid tissue damage is caused by factors that can disrupt the functioning of the immune system. This:
- emotional overstrain and constant stress;
- hormonal disorders;
- lack of nutrients and minerals;
- taking medications that impair the functioning of the immune system;
- injuries.
A genetic predisposition to chronic autoimmune processes is also possible.
How does rheumatic arthritis differ from rheumatoid arthritis?
As the name suggests, the cause of rheumatoid arthritis is rheumatism, which occurs after a severe flu or sore throat. The disease develops acutely, the temperature rises, and the joints suffer symmetrically, they become painful to the touch. Painful sensations are usually “volatile” in nature. The disease usually affects the small joints of the arms and legs, but the main danger of this disease is that in the absence of the necessary treatment, damage to the heart valve can occur, which leads to the development of its defects. But the treatment of this form of the disease is well known - antibiotics and some non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs are used, which gives a noticeable effect within a few days of treatment.
With rheumatoid polyarthritis, everything is more complicated, since the cause of its development is still unknown. This disease also develops differently - in this case, the progression of the disease is quite slow and gradual. The pain is quite moderate, and it is localized in slightly different joints - wrist, metatarsophalangeal, metacarpophalangeal and interphalangeal. Stiffness and swelling of these joints is also noted. Gradually, the process spreads to larger joints - hip, shoulder, knee and elbow, and after a while a characteristic feature of this disease begins to appear - deformation of the joints, which is not observed in the rheumatic form of the disease. In addition, damage to the joints also leads to atrophy of some muscles. As you can see, the outcome of rheumatic arthritis can be much more complicated than with the rheumatoid form, since there are a number of problems with diagnosis and selection of appropriate treatment.
The essence of the disease
Arthritis means inflammation of the connective tissues of a joint. Rheumatoid arthritis is a systemic inflammation of connective tissues throughout the body. Joint inflammation is just one of the forms of its manifestation. Along with this, it affects the connective and muscle tissues of internal organs, primarily the heart and kidneys.
In ordinary arthritis, cardiac manifestations are usually absent. In the rheumatoid form, heart damage almost always occurs. Early symptoms also indicate the systemic nature of this disease. They may not be related to the joints - increased fatigue, weakness, muscle pain, strange increases in temperature, sweating.
Comparative characteristics
Arthritis is a group of pathologies that are of infectious origin and are characterized by dystrophic and degenerative disorders in the structure of osteochondral tissue. Basically, the disease occurs as a consequence of an infectious lesion of the body, in rare cases it is a separate ailment. The causative agent of the inflammatory process in the joint cavity is infections of the streptococcal and staphylococcal groups.
The disease can simultaneously affect more than five joints.
Polyarthritis belongs to the group of arthritis and is considered a fairly common pathology that affects not only adults, but also young children. There is damage to several joints at the same time. A symmetrical distribution of pathology is often observed. It tends to involve joints and periarticular soft tissues close to the affected joint into the pathological process. Often polyarthritis is infectious-allergic in nature.
Rheumatoid polyarthritis is considered one of the most common forms of the disease.
Return to contents
Reasons for the development of pathology
The main root causes of the development of arthritis include: an allergic reaction, injuries to joints and infectious damage to internal organs. Pathogenic microorganisms spread throughout the body through the bloodstream and accumulate in the structure of the joints. Under the influence of an irritant, the protective properties of the immune system decrease, which causes the development of a chronic form of the disease and severe degenerative-dystrophic destruction in osteochondral tissue. Against the background of such a failure, autoimmune changes occur, in which the body produces antibodies that attack the cells of its own organs and systems.
Excess weight puts additional stress on your joints.
There are a number of negative factors that provoke the development of arthritis:
- obesity;
- hormonal disruptions and metabolic disorders;
- decreased immunity;
- congenital anomalies of the musculoskeletal system;
- hypothermia;
- concomitant infectious diseases;
- injuries with damage to the skin;
- severe stress;
- avitaminosis;
- poor nutrition;
- bad habits;
- excessive consumption of alcohol and caffeine;
- heredity.
The development of polyarthritis is caused by:
- regular allergies;
- connective tissue diseases;
- adenovirus infection.
Return to contents
Main symptoms
The surrounding tissues become inflamed and swollen.
The symptoms of arthritic joint damage depend on the type of pathology and the factor that provoked it. The following types of arthritis or polyarthritis are distinguished:
- Rheumatoid. It becomes chronic and develops against the background of genetic, hormonal and environmental disorders. As a rule, joints are affected symmetrically. The patient complains of fatigue, loss of appetite, decreased performance, pain in the affected area and swelling of the periarticular tissues. An increase in body temperature is often noted.
- Infectious. Unlike rheumatoid arthritis, it develops rapidly. The cause of inflammation is a purulent infection. The following symptoms are noted: swelling and hyperemia of the skin, sharp pain when moving, contracture, fever and fatigue. Visually noticeable deformation of the joints.
- Allergic. It occurs against the background of allergies and manifests itself acutely. Pain appears in one or more joints, swelling and rashes on the skin.
- Dystrophic. Develops after injuries. Destruction of the joint brings severe pain, impaired mobility and tissue swelling.
- Rheumatic. Affects large articular joints. It is characterized by severe pain, swelling of the affected joints, a rapid increase in body temperature and impaired mobility in the inflamed area.
There are arthritis that develop against the background of concomitant pathologies under the influence of specific groups of microorganisms. These include psoriatic and gonorrheal forms, arthritis, which occurs after influenza and sore throat. The symptoms of the pathologies are identical to the main signs of the arthritic group of ailments.
Return to contents
Danger
Ordinary arthritis can be localized in one or several joints for a long time without spreading beyond them. This leads to the fact that the patient gets used to using anti-inflammatory, pain-relieving ointments (NSAIDs) for years to relieve symptoms and may not think about normal treatment.
Rheumatoid arthritis, on the other hand, spreads slowly but surely, affecting the joints one by one. At the same time, the deformation of the fingers becomes increasingly greater. Therefore, it is this form of inflammation that most often leads to disability. This prospect often causes panic.
If you start treatment on time, disability can be avoided and not only slow down the development of the process, but even stop it. But this requires a serious, comprehensive approach. No folk remedies or other self-medication methods can do this.