What features of the cervical spine cause symptoms of osteochondrosis?
- There are openings in the lateral processes of the vertebrae; the carotid arteries, which supply blood to the brain, pass through them to the right and left.
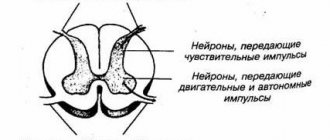
- The initial part of the spinal cord passes through the cervical region - it contains fibers that carry nerve impulses to all parts of the body, provide movement and sensitivity. If the spinal cord is compressed in the neck, neurological disorders occur throughout the body.
- This section of the spinal column has great mobility, and this predisposes to the occurrence of osteochondrosis (although, in most cases, the disease still develops in the lumbar region - it not only has high mobility, but also experiences the greatest stress).
- In the neck area, nerve roots emerge from the intervertebral foramina, forming the cervical and brachial nerve plexuses. They are responsible for movements in the muscles of the neck, arms, shoulder girdle, skin sensitivity, and regulation of autonomic functions.
- The first vertebra does not have a massive front part - a body - it is a bone ring that fits onto the tooth - a bone outgrowth on the second vertebra. Thanks to this, it is possible to turn the head to the sides.
Neck pain, headaches, feeling of weakness, numbness in the hands are symptoms that should make you consult a neurologist. An examination by a specialist and examination using modern equipment will help you understand the causes of the pathology and take the most effective measures.
Take care of yourself, book a consultation now
Message sent!
expect a call, we will contact you shortly
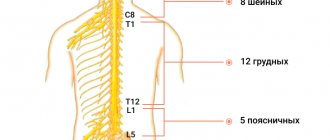
A little anatomy
Founder of the “Club of Former Hypertensive Patients”, Ph.D. honey. Sciences, senior researcher Alexander Yuryevich Shishonin notes that in the structure of all vertebrae of the lumbar, thoracic and cervical regions there are transverse processes.
In the thoracic region, the ribs are attached to the transverse processes. The vertebral bodies of the lumbar segment are the largest, since this section accounts for significant mass. The deep muscles of the lower back are attached to the transverse processes of the lumbar vertebrae. Between the vertebrae there are elastic cartilages (discs).
Structural features
The cervical spine is characterized by certain anatomical features. Alexander Yuryevich draws the audience's attention to the fact that only in the transverse processes of the 1-6 cervical vertebrae there are openings through which vessels pass that supply the basal part of the brain (brain stem).
The basal region of the brain can be considered as a “computer center” in which data from the entire body is collected and analyzed. The organ represented controls all automatic processes in the body (movement, breathing, temperature, coordination, heartbeat, sweating, etc.).
Advice from Dr. Shishonin.
If you have been diagnosed with cervical osteochondrosis and your attending physician tells you that this is nonsense and this pathology can be cured with ointments and some lotions, then it is better to run away from such a doctor as far as possible.
Pathogenesis of osteochondrosis
With cervical osteochondrosis, there is a displacement of the vertebrae relative to each other, which leads to compression of the arteries. Compression of these vessels can provoke ischemic stroke of the brain. Such phenomena are recorded all the time.
If a person has a small cervical osteochondrosis, but no one treated it or treated it incorrectly, with minimal mechanical impact on the neck, displacement of the vertebrae is observed, blood circulation is impaired, patients often complain of dizziness and nausea. After some time, the patient loses consciousness. This often occurs in people injured in road accidents.
Join the Club of Former Hypertensive Patients
, download gymnastics, which has already helped hundreds of thousands of people overcome pressure surges and hypertension. Get the most current and correct information about problems related to blood pressure, osteochondrosis, atherosclerosis, ask your questions to Dr. Shishonin and just communicate.
What happens to the vertebrae with cervical osteochondrosis?
The obscure medical term “degenerative process” refers to the following pathological changes occurring in the cervical spine:
- First of all, damage to osteochondrosis affects the intervertebral discs. They become thinner, thus reducing the distance between adjacent vertebrae. Small tears and microcracks form in their outer parts. Over time, this can lead to a herniated disc.
- As a result of disc damage, the stability of the vertebral connection is disrupted.
- Intervertebral joints also suffer from osteochondrosis of the cervical region - spondyloarthrosis develops. It also contributes to compression of the nerve roots.
- The pathological process extends to the vertebrae themselves. Due to the fact that the functions of the intervertebral discs are disrupted, the load on them increases. The spine tries to compensate for this violation, and bone growths appear on it - osteophytes.
Physiotherapy
Physiotherapeutic procedures pursue a number of goals:
- Localization of the inflammatory process;
- Relieving muscle spasm;
- Pain relief;
- Launch of regenerative processes;
- Increasing general and local immunity;
- Restoring the normal position of nerve fibers, eliminating compression and pinching.
Most often, the following procedures are prescribed for cervical osteochondrosis:
- Shock wave therapy. Using a special device, the acoustic wave is directed directly to the cartilage tissue of the spine that has been damaged. As a result, metabolic processes are launched, salt and calcium deposits are destroyed, which interfere with the normal movement of joints and vertebrae. The procedure is characterized by a cumulative effect, often the first results become noticeable only 2-3 months after the start of treatment.
- Acupuncture. Acupuncture is often used to treat and prevent cervical osteochondrosis. It is important that the procedure is performed only by a qualified doctor, otherwise you may not only experience a lack of effect, but also a worsening of the current condition. The essence of the procedure is that special needles are installed on biologically active points, forcing the body to start metabolic processes and stimulate the production of natural painkillers.
- Massage. The main goal is to reduce pain and improve blood circulation in the damaged area of the cervical spine. With proper massage, the muscles acquire the lost tone, and as a result, it is possible to eliminate the risk of relapse of osteochondrosis in the future. When attending the first massage sessions, the patient encounters severe pain; it is important not to stop treatment due to pain, but to go through all the procedures prescribed by the doctor.
Surgery
It is mainly prescribed in advanced stages of the disease, when the use of medications and visits to physiotherapeutic procedures does not bring any results. The indication for surgical intervention is catastrophic narrowing of the spinal canal.
Modern surgical techniques allow the patient to be discharged from the hospital within 3-5 days and begin outpatient treatment of the symptoms of cervicothoracic osteochondrosis. Over the next three months, the patient undergoes rehabilitation.
Physiotherapy
A correctly chosen set of exercises for osteochondrosis can not only improve the patient’s general condition, but also speed up the process of treating the disease. There are several effective exercises:
- Turns and tilts the head in different directions. The exercise is performed in a sitting position, it is important not to jerk, all movements should be smooth with a gradual increase in the number of repetitions and the amplitude of the inclination.
- Tilt the head to the sides with resistance. Body position - sitting at the table, one elbow stands on the table, while the palm presses on the temple. Tilt your head towards your hand, creating slight resistance.
- Shoulder lift. Raise your shoulders as high as possible and hold in this position for a while.
- Self-kneading of the back of the head and neck with your fingertips. It is important that the movements are soft and do not cause pain. You can perform self-massage in any comfortable position.
It is important not to treat cervical osteochondrosis at home without consulting a neurologist; a set of exercises must be agreed upon with the attending physician.
Treatment of osteochondrosis of the cervical spine
During an exacerbation of osteochondrosis of the cervical vertebra, traction is used (the patient is placed on a bed with a raised headboard and the head is fixed using a special loop) to relieve the intervertebral discs. For the same purpose, you need to wear a Shants collar. Painkillers and anti-inflammatory drugs are prescribed to relieve pain. For severe pain that does not go away, the doctor can perform a blockade: inject an anesthetic solution into the area of the affected nerve roots. Physiotherapy is used: ultrasound treatment, electrophoresis with novocaine.
When the exacerbation subsides, treatment of osteochondrosis of the cervical spine involves massage, physical therapy, and physiotherapy.
Doctors at the Medical Center International Clinic Medica24 know how to effectively treat osteochondrosis of the cervical spine and will give recommendations that will help prevent another exacerbation. Our administrators will answer you at any time of the day, contact us by phone +7 (495) 230-00-01.
Take care of yourself, book a consultation now
Message sent!
expect a call, we will contact you shortly
One of the main signs of cervical osteochondrosis is neck pain. Many people who encounter this symptom do not go to the doctor, but prefer to treat “chondrosis” with home methods. There are at least two good reasons to refuse self-medication and consult a specialist doctor.
Firstly, painkillers and traditional methods, although they help temporarily relieve pain, do not solve the main problem. Pathological changes in the spinal column continue to increase. Over time, this can lead to more serious consequences. To the point where surgery may be required.
Secondly, neck pain occurs not only with osteochondrosis. There are plenty of other reasons. Only a doctor can understand and prescribe the correct treatment.
Drugs for effective treatment of osteochondrosis: release form
To treat osteochondrosis, agents for external and internal use are used. The choice of drug release form depends on the patient’s habits and lifestyle, concomitant diagnoses and stage of the disease.
Tablets and capsules
Tablets and capsules for osteochondrosis are the most popular form of release. They have high bioavailability and systemic effects on the body.
The tablets should be taken directly with meals, usually 2 times a day.
The main disadvantage of tablets (especially non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs) is that they act directly on the mucous membrane of the digestive system. Such drugs are not recommended for chronic use due to the risk of inflammation and stomach ulcers. They must be taken under the supervision of a doctor.
Treatment with drugs for osteochondrosis can only be started after consultation with a doctor.
Powders
Some medications for osteochondrosis are available in sachet form (a portion of powder in a paper bag for a single dose). Crystalline preparations are very well absorbed and easy to use - you need to take them only once a day, diluting them in about ½ glass of warm water. The effect of taking them comes a little faster. Powder preparations are easier to dose and contain fewer additional components. But not all patients like the need to prepare the mixture and its taste.
Ointments, gels, creams and solutions for compresses
Products for external use are excellent for local anesthesia, relieving inflammation and swelling. They are considered much safer for the body than tablets, since they do not come into contact with mucous membranes and are absorbed into the blood in small quantities. Local preparations do not have a cumulative effect, are easy to use and, as a rule, do not require a prescription. They can be used continuously, not in courses. Among the external forms of release, it is worth highlighting the patches - they are simply attached to the affected area of the spine, they can be worn under clothes all day.
Ointments, gels and creams are the best drugs for osteochondrosis for patients who have contraindications to taking tablets (with steroidal and non-steroidal anti-inflammatory components) from the heart and endocrine system.
The main disadvantages of this form of release are:
- low bioavailability (about 5% of the active substance overcomes the natural barriers of the skin);
- the possibility of local allergic reactions due to too frequent use;
- help to completely get rid of symptoms only in the early stages of the disease.
Please note that ointments with NSAIDs should be used with caution, especially if the patient has ulcerative-erosive lesions of the stomach and intestines. Their active ingredients, even in small quantities, block the enzyme that protects the mucous membranes of the gastrointestinal tract. They also reduce the natural production of enzymes responsible for relieving inflammation.
External products should be rubbed in with vigorous circular movements up to 6 times a day. And compresses (for example, with dimexide) - keep 1-2 times a day for about 10 minutes.
Solutions for injections
Medicines for intravenous and intramuscular administration have maximum bioavailability and reduced impact on the mucous membranes of the gastrointestinal tract, since the active substances enter directly into the blood.
Injectable medications for osteochondrosis can quickly stop the exacerbation of the disease, relieve pain, swelling, and restore the sensitivity of nerve endings. Injections are an excellent alternative to oral medications for those with lactose intolerance. After all, most NSAIDs in tablets (for example, meloxicam) are lactose-containing drugs.
For particularly severe back pain, the drug is injected as a blockade - directly into the nerve. The effect of such an injection lasts up to 3-4 weeks, but the procedure must be carried out by a qualified medical professional due to the proximity of the blockade site to the spine.
The main disadvantage of injection solutions is the need to administer them with an injection or dropper (usually in a hospital). Like other groups of medications, solutions with NSAIDs can only be used as prescribed by a doctor to avoid side effects.
Drugs for the effective treatment of osteochondrosis must be used strictly according to the regimen prescribed by the doctor.
What symptoms of osteochondrosis of the cervical spine should make you see a doctor?
The main symptom of cervical osteochondrosis is pain. It can occur in different places, depending on the level at which the pathological process is localized: in the neck, in the shoulder girdle, in the arm, in the heart area. The pain is dull in nature and can be burning or aching.
Other manifestations of the disease:
- Headaches, dizziness, spots before the eyes, noise, ringing in the ears.
- Weakness in the muscles of the neck, shoulder girdle, and arms.
- Impaired skin sensitivity.
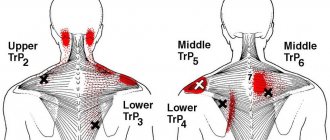
- Humeroscapular periarthritis: aching pain in the neck that spreads to the arm, difficulty abducting the arm above 90°, weakness and atrophy of the shoulder girdle muscles.
- Shoulder-hand syndrome: pain in the shoulder and hand, swelling and stiffness of the fingers, weakness and atrophy of the muscles of the hand.
- Vertebral artery syndrome. Bone growths appear on the vertebrae, which compress the nerves, resulting in a reflex spasm of the vertebral artery, which takes part in the blood supply to the brain. Symptoms of cervical osteochondrosis include constant headaches that start from the back of the head, spread to the temple, to the crown of the head, nausea, noise in the head, ringing in the ears, flickering bright spots before the eyes.
- Anterior scalene syndrome. On the neck there are the anterior and middle scalene muscles - they are nearby, and between them there is a small space in which nerves and blood vessels pass. With osteochondrosis of the cervical spine, the anterior scalene muscle becomes tense and compresses them, resulting in symptoms such as pain on the inner surface of the forearm, shoulder, and fingers. Sometimes the pain radiates to the back of the head. The skin of the hand may become cold, pale, and numbness occurs.
- Epicondylitis syndrome. In the lower part of the shoulder, on the sides of the elbow joint, there are bony protrusions - epicondyles. With epicondylitis syndrome caused by cervical osteochondrosis, pain occurs in them, which intensifies when pressed. Other symptoms also occur: pain in the neck, pain when pressing certain points in the area of the cervical vertebrae.
If two parts of the spine are affected at once, with cervicothoracic osteochondrosis, symptoms may include pain between the shoulder blades, in the area of the heart.
With osteochondrosis, the risk of intervertebral hernia and stroke increases. If you experience the symptoms listed above, consult your doctor.
Our expert in this field:
Vasinkina Inna Yurievna
Neurologist
Call the doctor Reviews about the doctor
Types of pain under the shoulder blade on the left
Before proceeding with diagnosis and treatment, it is important to understand the nature, localization, intensity of pain, their connection with movement, breathing, and eating. If it hurts below the left shoulder blade after eating, then heart pathologies and diseases of the musculoskeletal system can be ruled out. The cause of pain is diseases of the gallbladder, pancreas, and stomach.
The nature of the pain syndrome can be girdling, acute, burning, increasing, aching, dull, sharp.
Aching pain in the left shoulder blade
It can be constant or periodic, indicating both pathologies of internal organs and diseases of the spine. Without treatment, it can turn into a stabbing, burning sensation. Attacks more often occur when raising an arm, physical activity, or staying in one position for a long time.
Appears with scoliosis, chronic cholecystitis, scapular-costal syndrome, intervertebral disc herniation, initial stages of cervical osteochondrosis, bruises and other mild injuries, intercostal neuralgia.
Acute pain under the left shoulder blade
This is a severe pain syndrome in the back below the shoulder blade, which limits movement and makes breathing difficult. Characteristic for myocardial infarction, bursitis of the shoulder joint, exacerbation of osteochondrosis, spondylosis, hernia, subphrenic abscess, pleurisy, acute cholecystitis, intercostal neuralgia.
In case of myocardial infarction, pain under the scapula from behind is not relieved by analgesics, it decreases after taking nitroglycerin
Sharp pain in the area of the left shoulder blade
It may occur suddenly or be the result of prolonged aching pain. Shooting, sharp pain is a sign of osteochondrosis, hernia, trauma, intercostal neuralgia, tuberculosis of the scapula, aortic aneurysm, perforated gastric ulcer, radiculitis.
Stitching pain behind the left shoulder blade
It manifests itself as lumbago, which is typical for pinched nerve endings in diseases of the musculoskeletal system. If it is accompanied by compression of the chest and lack of air, then myocardial infarction or lung abscess cannot be ruled out.
With a perforated stomach ulcer, pain occurs, as if stabbed with a knife.
Nagging pain in the left side of the back under the shoulder blade
Inherent in most pathologies of the musculoskeletal system, as well as bronchopulmonary diseases.
Constant pain on the left side under the shoulder blade
Such pain does not leave the patient even in a lying position. It interferes with sleeping, breathing, and walking. More often, pain intensifies with physical activity, coughing, and sneezing.
Constant nagging or aching pain occurs with injuries to the spine or scapula, scapular-costal syndrome, bronchopulmonary diseases, pyelonephritis, and oncology. Girdle pain with disorders of the digestive system is characteristic of patients with acute pancreatitis.
Burning pain on the left side of the shoulder blade
It is simply unbearable and occurs with intercostal neuralgia, myocardial infarction, angina pectoris, muscle strain.
Important! If a burning sensation that spreads to the sternum is accompanied by shortness of breath, you should immediately call an ambulance. This is a sign of a heart attack.
Treatment of symptoms of cervical osteochondrosis
It is better not to self-medicate. Even if you have proven methods that usually help cope with pain, this does not mean that you are doing everything right.
Pain can be caused not only by osteochondrosis, but also by intervertebral hernia, muscle disorders (myofascial pain syndrome), and be a symptom of other diseases. In order to properly treat the disease, you need to understand its causes and carry out differential diagnosis. This is only possible in a clinical setting.
In order to identify the cause of the disease and properly treat the symptoms of cervical osteochondrosis, you need to visit a neurologist and undergo an examination.
Visit a specialist doctor at the Medical Center International Clinic Medica24. Make an appointment by phone at any time of the day: +7 (495) 230-00-01.
We will call you back
Message sent!
expect a call, we will contact you shortly
Cervical osteochondrosis is based on damage to the intervertebral discs. Their chemical composition is disrupted, first they swell, then decrease in size, cracks and tears appear in their outer part, and they become denser. Then the degenerative process spreads to the vertebrae and intervertebral joints. By reducing the height of the intervertebral disc, the load on the vertebrae increases, and bone growths – osteophytes – appear on them.
Treatment of pain on the left side of the shoulder blade
All therapeutic measures are aimed at eliminating the root cause and relieving pain. The doctor selects medications based on why the pain in the shoulder blade area occurs.
If the cause is a disease of the musculoskeletal system or its complications, then drug therapy looks like this:
- anti-inflammatory non-steroidal drugs;
- muscle relaxants;
- analgesics;
- local anesthetic agents.
Drug therapy must be supplemented with physiotherapeutic treatment, massage, and therapeutic exercises. A neurologist from the SmartMed clinic draws up a comprehensive therapy program, taking into account the individual characteristics of the patient.
If conservative therapy does not provide the desired therapeutic effect, the patient is indicated for surgery
What causes lead to the occurrence of osteochondrosis of the cervical spine?
There is no consensus on the causes of cervical osteochondrosis. It is believed that the disease is caused by different conditions, there are different points of view:
- Age-related changes in the spine. However, almost all people over 40 have skeletal changes, but not everyone develops osteochondrosis.
- Neck injuries. Often the causes of the disease include previous trauma: neck bruise, compression fracture, vertebral subluxation. Chronic injuries may be important, for example, during intense training in athletes, constant work in an awkward position, bent over, and repetitive whiplash injuries in motorists.
- Congenital anomalies of the vertebrae: cervical ribs, fusion of adjacent vertebrae, fusion of the first vertebra with the occipital bone, etc.
- Profession. More often, the disease affects people who work in a monotonous position and constantly make the same type of movements.
- Poor blood supply to the spine, venous insufficiency, swelling in the area of the nerve roots.
- Autoimmune disorders . Conditions in which the immune system does not function properly and attacks the body’s own connective tissue and ligaments.
Visit a neurologist. An experienced specialist will understand the source of your health problems and prescribe the correct treatment.
Prevention
The main rule of preventive measures is that they must be comprehensive and observed on an ongoing basis. This is the only way they will bring the expected results. Prevention is indicated for people who are at risk.
- Watch your posture. The ideal body position is that the head and back are on the same line. Always make sure that your shoulders are straightened, your stomach is pulled in, and your chest is raised. The gait also plays a role - it should be springy and smooth. Never give yourself any slack; at the initial stage, it is important to discipline yourself; in the future, correct posture will become a habit.
- A properly organized workplace. When working, the shoulders should be relaxed; constant tension in the lumbar girdle has a direct impact on the cervical spine. The basic requirements are a chair with a comfortable back and armrests, a monitor at eye level, a keyboard below the elbows (the angle between the shoulder and forearm is about 120 degrees). While working, make it a habit to take a break every 40-50 minutes and perform basic stretching exercises.
- Correctly adjust the car seat. Many motorists are faced with osteochondrosis of the cervical spine due to the fact that they adjust the driver’s seat not according to the rules, but in a way that is comfortable for them. Correct body position in a chair - the entire spine touches the back, not just the shoulders. It is advisable to purchase special lumbar pillows that will help support the body in the desired position. When driving for a long time, it is important to go out into the streets after 1.5-2 hours and warm up.
- Watch your diet. Problems with the cervical spine are often associated with the fact that the patient eats incorrectly. Dangerous foods that increase the risk of osteochondrosis include: white bread, baked goods, sweets, dishes high in salt and sugar, fried and fatty foods. The main danger is refined sugar - the substance helps wash calcium out of the body. Include legumes and nuts, foods high in protein, seasonal vegetables and fruits in your daily diet. Low-fat fermented milk products - kefir, fermented baked milk, cottage cheese, natural yoghurts - will also have a positive effect. If you have a problem with excess weight, visit a nutritionist.
- Daily physical activity. Treatment of cervical osteochondrosis at home with the help of physical exercise is an excellent preventative against spinal diseases. It is important to do the exercises at an easy pace, without exceeding the permissible load. If you don’t have time for a full set of exercises, make it a rule to take daily walks.
- Massage. Correct techniques restore muscle tone, relieve tension, and trigger metabolic and regenerative processes in the body. It is not necessary to visit specialists; proper massage of the cervical spine can be performed independently.
- Proper sleep. During the day, the intervertebral discs experience increased stress; complete relaxation and rest can only be achieved during night sleep. To prevent osteochondrosis, it is important to organize the right place to sleep and monitor the time (at least 8 hours).
Causes of exacerbation of cervical osteochondrosis
Osteochondrosis occurs in the form of alternating exacerbations and periods of improvement, when the symptoms cease to bother you for a while. Another exacerbation can be triggered by the following reasons:
- Awkward, sudden movement of the neck.
- Staying in a monotonous uncomfortable position for a long time. For example, your neck may begin to hurt after working on a computer for a long time, or after sleeping on an uncomfortable pillow.
- Stress, nervous tension. With chronic stress, spasms occur in the neck muscles, which can cause another exacerbation.
- Various diseases, exacerbations of chronic diseases.
- Hypothermia. For this reason, many people experience exacerbations in the fall.
- Incorrect, illiterate self-medication. For example, massage and therapeutic exercises are useful during remission, but are contraindicated during an exacerbation.
Fatigue and its hidden dangers
Every person knows what fatigue is and experiences it periodically. But if it has become a permanent part of life, it requires increased attention. After all, fatigue is not just an unpleasant symptom that can be ignored. It does not allow a person to fully fulfill his work and personal responsibilities. This inevitably affects the quality of life, affecting physical and intellectual abilities. This is often accompanied by:
- sleep disturbances of various kinds, and often with daytime sleepiness a person suffers from insomnia at night;
- irritability, anxiety;
- decreased memory and ability to concentrate;
- difficulties with mastering new information;
- loss of interest in work;
- apathy, etc.
At the same time, fatigue not only leads to a decrease in performance, which can affect a person’s financial and social situation, but also negatively affects the functioning of the body. After all, when tired, one’s functional capabilities are temporarily reduced, which is accompanied by a violation of the coordination in the work of individual organs and systems. Therefore, chronic fatigue is especially dangerous when such functional disorders accumulate. The result of this is:
- decreased immunity and increased susceptibility to various pathogens;
- exhaustion of the nervous system, which leads to depression;
- disturbances in the course of biochemical processes, which negatively affects the functioning of the whole organism and individual organs in particular;
- asthenia (a psychopathological condition accompanied by increased fatigue, irritable weakness, emotional lability, headaches, sleep disturbances and vegetative-somatic manifestations);
- hormonal imbalances caused by constant stress due to violation of one’s obligations, constant fatigue, etc.
According to various studies, about 10-20% of people suffer from increased fatigue and a resulting decrease in performance.
Therefore, it is important not to ignore increased fatigue and decreased performance, but to look for the cause of its occurrence and act directly on it. This will not only improve your overall well-being, but also avoid the development of undesirable consequences of chronic fatigue and complications of the underlying disease that causes it.
What diseases can have similar manifestations?
Very often, manifestations of “osteochondrosis” are actually associated with a completely different disease. For example, the cause may be hidden in the muscles - there is a condition called myofascial pain syndrome . Pain occurs due to constant tension in the same muscles.
Sometimes dizziness associated with otolithiasis, a condition in which crystals of calcium salts accumulate in the inner ear, is taken to be a manifestation of “cervical osteochondrosis.”
Each situation needs to be analyzed individually. A neurologist at the International Clinic Medica24 center will correctly assess your symptoms, prescribe the necessary examination, establish a reliable diagnosis and recommend effective treatment. Appointments can be made 24 hours a day by calling +7 (495) 230-00-01.
Get a consultation with a doctor
Message sent!
expect a call, we will contact you shortly
Pain and crunch in the neck, headaches - when these symptoms occur, many people “diagnose” themselves with osteochondrosis. Everything is clear - when it hurts, you need to take painkillers or get an injection, apply heat, and everything will go away. Why go to the doctor if you can handle it yourself?
However, self-medication often does not lead to anything good. Painful attacks may become more frequent, severe, and prolonged over time. If you uncontrollably take painkillers almost every day, you can get stomach or kidney problems. After all, any medicine has side effects.
And the cause of pain is not always due to osteochondrosis. In order to find out the real reason and understand how to effectively deal with it, you need to visit a doctor and undergo an examination.
How to treat exacerbation of pain due to lumbar osteochondrosis?
Thermal exposure, lifting heavy objects, or sudden movements can provoke a deterioration in the patient's condition. It should be noted that the disease has a dual nature: acute pain syndrome can occur unexpectedly or increase as the destructive process develops. As a rule, acute pain of increased intensity is characteristic of the exacerbation stage. In this case, muscle spasm occurs in the chest and lower back, which limits the mobility of the back.
Also, pain manifestations can radiate to the gluteal region and lower extremities, which are connected to the damaged area of the spinal column by long processes of neurons. As a result, a person tries to take a gentle position that minimizes discomfort. In such a situation, even the slightest movements can provoke a new pain attack.
Lumbar osteochondrosis of the spine, treatment of which was started in a timely manner, can be stopped within 1-2 weeks.
The medical team will help you relieve acute pain syndrome at any time of the day. In order to make an accurate diagnosis, we perform radiography and ultrasound diagnostics. After relieving the discomfort, our experienced specialists will help you choose the most effective treatment measures.
How does a neurologist diagnose cervical osteochondrosis? What happens in the doctor's office during an examination?
During your first appointment, the neurologist will ask you some questions:
- How long have you been bothered by headaches or neck pain?
- Where does the pain occur? What is their nature: stabbing, aching, shooting, pulling?
- When does pain usually occur? What triggers it? After what do you feel better?
- Have you already visited a doctor? Have you been examined and treated? Which? How long ago?
- What other symptoms bother you?
- What other chronic diseases do you have?
- Have you recently had a neck injury?
The doctor will then perform a neurological examination, checking your reflexes, skin sensitivity, and muscle strength and tone. You will be asked to turn, tilt your head to the sides, forward, backward. The doctor will press lightly on your head and on certain points in the neck to determine the occurrence of pain.
After the examination, you will be diagnosed and prescribed the necessary diagnostic methods.
The medical center International Clinic Medica24 employs experienced neurologists and uses the most modern diagnostic methods. You will be quickly and reliably diagnosed and prescribed effective treatment methods.
Take care of yourself, book a consultation now
Message sent!
expect a call, we will contact you shortly
Diagnostics
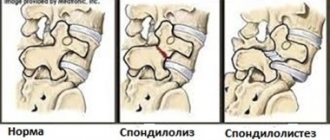
Cervical osteochondrosis is a chronic disease that can lead to the formation of hernias and compression of the spinal cord. Therefore, it is important to establish an accurate diagnosis in a timely manner and begin therapy. To identify cervical osteochondrosis, the following types of instrumental diagnostics are used:
- Spondylography or radiography of the spine. This research method is painless, highly informative and does not require special training. An X-ray of the spine allows you to evaluate its anatomical and functional features. In the picture, attention is paid to the structure of the vertebrae, their relationship to each other, the distance between them, the lumen of the spinal canal;
- Computed tomography - provides information mainly about the condition of bone tissue, allows you to identify narrowing of the spinal canal and disc herniation;
- Magnetic resonance imaging - allows you to determine changes in soft tissues. The MRI image clearly shows changes in the intervertebral discs and spinal cord.
At the Yusupov Hospital, the patient undergoes a comprehensive examination. Doctors take into account the individual characteristics of his body and concomitant diseases. An important advantage of the neurology clinic is the availability of modern, high-quality equipment and specialized specialists: neurologists, neurosurgeons, oncologists.
What diagnostic methods are used for osteochondrosis of the cervical spine?
Examination for cervical osteochondrosis usually includes the following diagnostic methods:
- X-ray of the cervical spine.
- According to indications, X-ray contrast studies are prescribed: myelography (injection of contrast into the space surrounding the spinal cord), discography (injection of contrast into the intervertebral disc), angiography (injection of contrast into the vessels).
- CT scan.
- Magnetic resonance imaging.
- If you have severe neurological disorders, you may be prescribed electroneuromyography, a study that determines the passage of electrical impulses in the nerves and muscles.
Often, manifestations of cervical osteochondrosis resemble angina pectoris. If after the examination the doctor still has doubts about the diagnosis, you will be prescribed an ECG and other diagnostic methods.
The material was prepared by Lev Gennadievich Kamyshev, a neurologist at the international clinic Medica24.
There is a common professional proverb among doctors that a correctly established diagnosis is half the successful treatment of a disease. Get diagnosed for osteochondrosis of the cervical spine at the neurology center of the International Clinic Medica24 in Moscow. Contact the clinic administrator by phone, we work around the clock.
Osteochondrosis under the left and right scapula
The innervation of the intercostal muscles is carried out by separate branches of the radicular nerves extending from the foraminal openings of the Th2, Th3 and Th4 vertebrae. These radicular nerves are also responsible for the innervation and functionality of the coronary circulatory system, lungs, bronchial tree, diaphragm, etc.
Therefore, osteochondrosis under the left scapula is always alarming, since compression of the root can actually lead to a sudden spasm of the coronary arteries and provoke the clinical picture of acute myocardial infarction. Osteochondrosis of the left scapula is always a reason to do an ECG and make sure that there is no threat to the patient’s life.
Osteochondrosis under the right shoulder blade may indicate damage to the lower intervertebral discs of the thoracic spine. The radicular nerves involved in the innervation and functioning of the stomach, duodenum, gallbladder, and kidneys depart here. Therefore, osteochondrosis of the right scapula may indicate irradiation of pain reflected from an inflamed gallbladder, a necrotized pancreas, or an enlarged kidney. In this regard, if there are complaints of pain under the right shoulder blade, it is necessary to exclude the following diseases when carrying out differential diagnosis:
- acute pancreatitis and necrosis of the pancreas;
- peptic ulcer of the stomach and duodenum;
- cholelithiasis (calculous cholecystitis), bile stagnation and obstruction of the common bile duct;
- acute and chronic pyelonephritis, glomerulonephritis, nephroptosis and polycystic kidney disease.
Various tumors and abscesses cannot be excluded. To identify somatic pathology, it is necessary to do a general clinical and biochemical blood test, fluorography, ECG, and ultrasound of internal organs.
Treatment of fatigue and its causes
To eliminate weakness, drowsiness, and constant fatigue, it is necessary to treat the disease that provokes them. If this is osteochondrosis of the cervical spine, the resulting vertebral artery syndrome or other disorders, treatment is selected by a neurologist. But in any case, it is always developed strictly on an individual basis, taking into account the nature of the existing pathological changes, the degree of their severity and the individual characteristics of the patient.
In the absence of critical changes, patients are prescribed conservative therapy. It is always comprehensive and aimed at:
- increasing the intensity of recovery processes in the intervertebral discs;
- improving the quality of blood circulation;
- relief of inflammatory processes;
- normalization of nerve conduction;
- restoration of normal anatomy of the spinal column;
- improvement of general condition by eliminating the symptoms of the disease (symptomatic therapy).
Thus, treatment is simultaneously carried out aimed at eliminating the underlying disease and improving the patient’s quality of life. Therefore, it is always comprehensive and includes:
- drug therapy;
- physiotherapy;
- exercise therapy;
- manual therapy.
In addition, when spinal pathologies are detected, it is important to adjust your lifestyle and bring it as close to healthy as possible. First of all, the level of physical activity requires a review: it is important to avoid prolonged stay in a static position, especially with a bowed head, as this contributes to the progression of degenerative changes in the intervertebral discs. Therefore, all patients with cervical osteochondrosis, and especially office workers, need to make it a rule to take breaks from work at least every hour and spend them actively.
But during exacerbation of the disease, bed rest and limitation of physical activity are indicated.
It is also recommended to review your diet. Eliminating processed foods, fast food and other harmful products from it will have a positive effect on the condition of blood vessels and will allow you to lose weight. This will reduce the risk of developing vertebral artery syndrome and rapid progression of the underlying disease.
Also, if you experience increased fatigue, it is important to:
- normalize work and rest schedules;
- review your work schedule and workload distribution in order to allocate the most productive hours for solving important tasks;
- use complex vitamin preparations, and also increase the amount of fresh fruits, vegetables and berries in the daily diet.
Often a change of environment and a short vacation have a positive effect on the psycho-emotional state.
Drug therapy
For diseases of the spine, the use of a complex of drugs is indicated, which can be prescribed in different dosage forms depending on the severity of its course. These may include:
- NSAIDs – used to relieve pain and inflammation;
- muscle relaxants - indicated to eliminate muscle spasms, which helps reduce pain and limitations in mobility;
- corticosteroids – used to relieve severe inflammatory processes and are prescribed exclusively in short courses;
- chondroprotectors - used to activate the processes of regeneration of intervertebral discs, but are most effective only in the initial stages of development of degenerative-dystrophic changes;
- B vitamins – indicated to improve nerve conduction;
- vascular drugs - prescribed to improve blood circulation;
- Vitamin D – is used to improve the condition of bone tissue and the processes of higher nervous activity.
In case of severe pain that makes a person unable to work, novocaine or lidocaine blockades can be performed. They allow you to almost immediately eliminate painful neck pain, but do not affect the causes of their occurrence. But such procedures are carried out exclusively in medical institutions.
To solve the problem of increased fatigue and decreased performance, especially mental, patients may additionally be prescribed a set of medications to normalize sleep, restore normal levels of mental and physical activity, and generally improve overall well-being. This:
- nootropics;
- neurometabolic drugs;
- herbal preparations;
- anxiolytics.
Taking such medications is absolutely safe and is not accompanied by the risk of side effects, provided they are selected correctly. They are prescribed in courses of varying durations and quickly allow you to:
- increase memory, attention;
- increase your waking time;
- increase resistance to stress and the negative influence of external factors;
- reduce symptoms of weakness and lethargy;
- eliminate anxiety, irritability, apathy.
Therefore, drugs from these groups are included in the treatment regimen for almost any disease and pathology of the spine, in particular in cases where patients complain of increased fatigue and decreased performance.
Physiotherapy
Physiotherapeutic procedures are prescribed outside the period of exacerbation and exclusively in combination with other treatment methods. Most often, for increased fatigue caused by diseases of the spine, the following courses are indicated:
- electrophoresis with the introduction of drugs;
- ultrasound therapy;
- traction therapy;
- detensor therapy;
- magnetic therapy;
- UHF.
Exercise therapy
Therapeutic exercise is one of the most important elements of treatment, acting directly on pathologically altered tissues. Thanks to it, it is possible to normalize muscle tone, in particular, to strengthen muscles that have weakened as a result of leading a sedentary lifestyle. This is important because a strong muscle corset is the basis for a healthy spine. Therefore, exercise therapy helps stop the progression of pathological changes in the intervertebral discs, and, in addition, activates blood flow and increases the intensity of metabolic processes. This has a positive effect on the condition of all anatomical structures and helps eliminate weakness.
But for each patient, the load and nature of the exercises are selected individually, taking into account the characteristics of the existing disease, the patient’s age, his level of physical fitness and other factors. But exercise therapy should always be performed in a calm environment without haste or sudden movements. At the same time, their regularity is extremely important. Therefore, in order to achieve maximum results, it is necessary to engage in physical therapy daily.
Manual therapy
Manual therapy sessions are one of the mandatory components of the treatment of diseases of the cervical spine. They can be carried out outside the period of their exacerbation and allow one to obtain a pronounced therapeutic effect, as well as improve the general condition and get rid of increased fatigue. But it is important to trust only qualified specialists to carry out manual therapy, since the cervical spine is easily injured. Therefore, errors in the technique of performing various techniques can lead to a deterioration in well-being.
Properly conducted manual therapy sessions allow you to:
- restore the normal position of the vertebrae as completely as possible and thereby reduce the load on the intervertebral discs, release the pinched spinal roots, normalize the position of the vertebral arteries and the length of the spinal canal;
- activate blood circulation, which has a positive effect on the course of regeneration processes;
- eliminate weakness and increased fatigue by normalizing blood supply to the brain and cerebrospinal fluid circulation;
- improve the functioning of internal organs that have undergone changes as a result of disturbances in their innervation due to compression of the nerve roots;
- increase the body's overall resistance to negative external influences.
Thus, fatigue and decreased performance may indicate not only professional burnout, but also be a sign of the development of disorders in the functioning of the body. Most often, spinal diseases and in particular osteochondrosis manifest themselves in this way. However, if you immediately pay attention to such changes in well-being and contact a neurologist, treatment will be as easy and quick as possible, and the condition will progressively improve. But even in more advanced cases, you can achieve a significant improvement in well-being and restoration of normal performance. The main thing is not to ignore the problem, but to seek qualified medical help.
0 0 votes
Article rating
Causes
A fairly large number of diseases of varying nature can be accompanied by the development of weakness, increased fatigue, decreased attention and performance. But most often the reason for this lies in the occurrence of pathological changes in the cervical spine, namely osteochondrosis and its complications.
According to statistics, cervical osteochondrosis is present in almost 30% of people, which is caused by a sedentary lifestyle and increased stress on the cervical spine when working on computers or gadgets.
Osteochondrosis is a chronic disease in which degenerative changes occur in the intervertebral discs. As a result, their height decreases and the elasticity of the outer shell, called the annulus fibrosus, decreases. This creates the preconditions for its gradual destruction, which ultimately, if left untreated, will lead to the formation of protrusion of the intervertebral disc (its deformation with the formation of a protrusion on one side), and subsequently a disc herniation.
Intervertebral discs are cartilaginous formations located between almost all vertebrae of the human spinal column.
The reason for the development of weakness and fatigue in cervical osteochondrosis is a decrease in the height of the intervertebral discs. Since against this background the length of the ligaments passing through the spine remains the same, they “sag” and lose the ability to fix the vertebrae in a normal position. Therefore, as the disease progresses and the height of the intervertebral discs decreases, the vertebrae lose the stability of their position and begin to shift. This negatively affects the condition of all anatomical structures passing through the cervical region:
- vertebral arteries;
- spinal canal;
- spinal roots;
- muscles of the neck and collar area.
We also must not forget about the development of the aseptic inflammatory process that accompanies pathological changes in the intervertebral discs. Since the body directs maximum forces to eliminate them, its resources are quickly depleted, which also contributes to weakness and decreased performance.
In addition, osteochondrosis of the cervical spine itself and, to an even greater extent, its complications cause pain of varying degrees of intensity. When the disease worsens, they can become very strong and affect the quality of sleep, causing insomnia. As a result, a person loses the ability to fully rest and recover at night, and therefore experiences drowsiness and fatigue during the day. This further aggravates his condition.
Vertebral artery syndrome
Two vertebral arteries pass along the lateral surfaces of the cervical vertebrae directly through the natural openings in them. They, like ligaments, retain their original length and, as the height of the discs decreases, they also change their course, bending. This causes a decrease in their lumen, and hence the amount of blood entering the brain. Therefore, in such situations, the brain experiences a deficiency of oxygen, and therefore disturbances in the functioning of its structures occur. This leads to a decrease in the ability to concentrate, performance, both mental and physical, fatigue and drowsiness.
Conditions in which the lumen of one or both vertebral arteries decreases are called vertebral artery syndrome.
Increased fatigue can be more pronounced with the formation of protrusions and intervertebral hernias. In addition, this is almost always accompanied by the appearance of other symptoms of the disease, especially acute pain, often radiating to the head or arms. This is due to the fact that displaced vertebrae or directly deformed intervertebral discs can compress the spinal roots passing near them, provoking the appearance of acute pain and disturbances in the innervation of the corresponding parts of the body or organs.
Also, compression of the vertebral arteries can be caused by disruption of the muscles of the neck and collar area. With osteochondrosis, protrusions and herniated intervertebral discs, they can reflexively spasm in response to pain.
In any case, the signs of vertebral artery syndrome cannot be ignored. After all, prolonged oxygen deficiency has an extremely negative effect on the functioning of the brain and leads to:
- decreased mental abilities;
- memory impairment;
- decreased attention.
In severe cases, oxygen deprivation can cause areas of ischemia and even ischemic stroke.
Increased cerebrospinal fluid pressure
Also, changes in the structure of the cervical spine can lead to a decrease in the length of the spinal canal, and in severe cases with large intervertebral hernias of the cervical spine and its compression, which is called stenosis. The arches and body of each vertebra form an oval foramen, which are aligned with each other along the entire length of the spinal column and thereby form the spinal canal. It contains the spinal cord, as well as cerebrospinal fluid (CSF), which constantly circulates, including through the skull.
If the vertebral bodies converge and the height of the discs decreases, the spinal canal also contracts. But at the same time, the amount of liquid present in it remains constant. Even with a minimal decrease in the length of the spinal canal, an increase in intracranial pressure is observed, which is manifested by drowsiness and increased fatigue. After all, this negatively affects the condition of the blood vessels of the head.