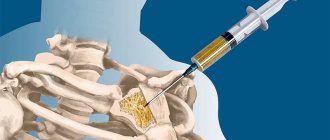
In addition to its widespread use for diagnostic purposes, ultrasound is used in medicine as a therapeutic agent. Ultrasound has an analgesic and relaxing effect. In addition, it accelerates wound healing, therefore it is effective in combating inflammation of the joints of the spine, ligaments of the knee and hip joint, any muscle pain and bruises.
Sometimes, to enhance the therapeutic effect, medications are used, which during the procedure are quickly transported directly to the pain site.
The method of simultaneous exposure to ultrasound and medications is called ultraphonophoresis .
Ultrasonic waves:
- increase the permeability of the skin;
- increase the sensitivity of nerve endings;
- stimulate metabolism;
- accelerate the passage of drugs to their destination and enhance their effect;
- activate the activity of leukocytes;
- massage the skin;
- relieve pain and inflammation;
- dilate blood vessels and relieve muscle spasms;
- improve blood circulation and change its acidity;
- stimulate restoration processes in tissues;
- promote the resorption of exudates;
- have a tonic effect.
Phonophoresis uses 2 operating modes: continuous and pulsed. In pulse mode, oscillatory movements are performed in short pulses (60 pulses per second). In this case, the thermal effect is weakly expressed. If a stronger effect of heat is required, a continuous mode of ultrasonic vibrations is used.
During the procedure, various medications are administered: hydrocortisone, prednisolone, aminophylline, heparin, pilocarpine, naphthalan, methionine, antibiotics, vitamin E, ascorbic acid, vasodilators and painkillers, medications that include bee and snake venom. For diseases of the musculoskeletal system, analgin and hydrocortisone are most often used. Medicines relieve pain and stop inflammatory processes. With osteochondrosis, the vessels supplying the spinal cord are pinched. The procedure improves blood circulation and restores muscle function.
Some drugs containing enzymes and novocaine cannot be combined with ultrasound exposure: ultrasound destroys their structure.
Advantages of phonophoresis
Based on most clinical pictures, it is noted that physiotherapy has a positive effect on the dynamics of treatment, thus, the patient’s rehabilitation and recovery are many times faster. This happens for a number of reasons:
- ultrasound promotes accelerated and deep penetration of medicinal substances into the skin and tissues, targeting the affected area;
- there is no need to endure painful procedures and expose the body to stress;
- affordable session cost and ease of use.
You need to know that phonophoresis will not give instant results. It will take several sessions to notice the effect of use. The medicine must accumulate in the skin within 5–7 days and reach the required therapeutic value. However, being developed quite a long time ago and being an old-generation drug, hydrocortisone has a number of serious contraindications.
Indications for use
Phonophoresis with hydrocortisone is recommended for:
- lumbar osteochondrosis;
- lumbar radiculitis;
- arthrosis and arthritis;
- second degree scoliosis;
- joint diseases;
- diseases of the ENT organs;
- neurodermatitis and eczema;
- disorders of the nervous system;
- gastritis with low acidity;
- Sjögren's disease;
- enuresis;
- trigeminal neuralgia;
- eye diseases: presence of cataracts, hemorrhage, cataracts;
- sluggish follicular prostatitis;
- hypogalactia and adnexitis;
- serous mastitis;
- ovarian hypofunction and infertility;
- diseases of the uterus and appendages;
- muscle atrophy;
- clubfoot;
- fresh injuries accompanied by severe pain;
- heel spurs;
- scar contractures;
- ulcers of varicose and trophic origin;
- fractures of tubular bones;
- post-burn scars;
- postoperative wounds.
Purpose of treatment
When prescribing ultrasound therapy with hydrocortisone, the doctor must take into account the indications and contraindications for the use of this method. Ultrasound with corticosteroids is used for the following conditions:
- inflammatory lesions of the joint and periarticular tissues of any cause, including rheumatic and autoimmune arthritis;
- damage to the menisci and other cartilaginous intra-articular formations;
- violation of the integrity of ligaments and tendons;
- presence of bone spurs or gouty nodes;
- rehabilitation period after injuries or surgical interventions.
In addition to the indications, to prevent the negative consequences of physical treatment, contraindications are also taken into account when prescribing the procedure:
- allergic reactions or individual intolerance to Hydrocortisone, including excipients in its composition;
- intolerance to allergic current;
- malignant and benign tumors;
- acute period of infectious pathologies;
- pregnancy period;
- the presence of implanted electronic devices, such as a pacemaker;
- serious condition of the patient associated with decompensation of diseases of internal organs.
If any contraindication is identified, ultrasound with Hydrocortisone should be postponed until it is eliminated. Otherwise, the patient may develop side effects, including life-threatening conditions.
When performing ultrasound with Hydrocortisone at home, you should carefully study the operating instructions for the phonophoresis device, and also consult with a physiotherapist.
Contraindications
Phonophoresis cannot be performed with hydrocortisone if:
- individual intolerance to the drugs used;
- diseases of the circulatory system, especially hemophilia;
- bleeding tendency;
- atherosclerosis;
- hypertension of the second to fourth degrees;
- chronic nephritis;
- diabetes mellitus in later stages;
- thyrotoxicosis;
- pulmonary tuberculosis;
- neuralgia;
- facial nerve paralysis;
- infectious diseases caused by viruses and bacteria;
- pustular inflammation of the skin;
- pregnancy;
- cancer diseases.
About the medicine
Physiotherapy procedures are used with various medications, one of which is Hydrocortisone. This medicine belongs to the group of steroid glucocorticoids and in a healthy person is formed in the adrenal glands.
Hydrocortisone is used in the treatment of various human diseases: rheumatic diseases, damage to the skin and organs of vision, in emergency care, in gynecology, and in pathologies of the osteoarticular system. The drug quickly penetrates deep into the tissues and has a direct effect on damaged structures. In clinical practice, Hydrocortisone can be used in tablet form, gels and ointments, as well as in injection solutions.
The biological effect of glucocorticosteroids is as follows:
- suppression of the inflammatory reaction of any causality, including autoimmune processes;
- reduction in the intensity of pain and swelling;
- antiallergic effect.
Despite this effectiveness, Hydrocortisone, like other corticosteroids, has a wide range of side effects on the body. In this regard, the use of the drug with physiotherapy methods can increase its safety for patients.
Phonophoresis with drugs plays a supporting role in the treatment of diseases of the osteoarticular system. In this regard, it should be used only as part of complex therapy.
How effective is ultrasound?
Ultrasound is used for arthrosis mainly for pain relief and inflammation. The optimal effect can be achieved by combining this procedure with the introduction of chondroprotectors. Under this condition, the regeneration of cartilage tissue occurs faster, and the body’s own forces are activated. Therapy takes at least 15 days.
Ultrasonic waves differ in characteristics, which makes it possible to obtain completely different results with their help:
- improve metabolism and normalize blood circulation;
- warm up the affected tissues;
- accelerate the production of enzymes that affect tissue repair.
Ultrasound therapy is prescribed mainly during the rehabilitation period after surgery. In advanced stages, for example, with grade 2 arthrosis of the joints, especially on its own, the procedure is ineffective.
Ultrasound improves metabolism in joints
What types of physiotherapy are there?
Physiotherapy methods in combination with the administration of medications are widely used in various fields of medicine. Electrophoresis with solutions of iodine, bromine, potassium, calcium is used to treat cardiovascular diseases.
In chronic inflammatory processes, UST and electrophoresis can be used to administer antibiotics and anti-inflammatory drugs. In case of postoperative scars, finger contractures, or burns, products containing hyaluronic acid (lidase, ronidase), which has a reparative (healing) effect, are used.
In neurology and rheumatology, physiotherapy is widely used in combination with novocaine, which has an effective analgesic effect.
Ultrasound
What is the effect of ultrasound therapy (UWT)? For treatment, devices are used that create a vibration effect in a limited area of the body, for example, the knee joint. This leads to the following effects:
- Vibration of tissues under the device is similar in effect to massage: in response to stimulation, blood vessels are activated, swelling is relieved, and muscle fibers are relaxed.
- Intense blood circulation in the area of the affected knee joint leads to maximum delivery of oxygen and nutrients to the tissue. Increased metabolism causes healing of the joint elements.
- Increasing venous tone promotes the outflow of stagnant blood, lymph, and tissue fluid. As a result, edema syndrome is relieved in the area where ultrasound is used. Massage of muscle tissue with short-wave exposure leads to relaxation of the fibers and the disappearance of reflex spasm.
Electrophoresis
Another way to effectively influence the affected knee joint is the use of hydrocortisone with electrophoresis. The source of electrical influence - the apparatus for carrying out the procedure creates a flow of particles that pass through the skin and muscle structures into the joint area:
- If a medicinal substance (hydrocortisone) is applied to the area where electrophoresis is used, the ions created by the device will capture the drug molecules and transfer them into the affected tissues.
- Thanks to the influence of charged particles, a relaxing, anti-inflammatory effect is achieved. Under the procedure site, blood vessels dilate and metabolism is normalized.
- But the most powerful effect is delivered to the knee joint by hydrocortisone. The drug relieves swelling, reduces pain, and promotes healing of inflamed tissue. The drug is delivered to the site of action in active form due to the preliminary effect of ions on hydrocortisone molecules.
Scars and scars: their types
Scars on the skin differ according to classification types:
1. Scars are classified according to the type of tissue formation:
- Atrophic type scars are small in thickness and are located lower than the tissue surrounding the scar.
- Scars of the normotrophic type do not affect the relief of the skin surface and the area around it; more often, these formations do not have a distinct color and have good elasticity.
- Scar formations of the hypertrophic type are pink in color and protrude above the skin surface without extending beyond the wound area. This type of scarring can occur as a result of a tissue reaction to injury and if the healing of the injured area occurs with complications and the scars are not treated correctly. After 2 years, such scars can resolve, and in their place scars of normotrophic and atrophic types form.
- Keloid type scars can continually grow, enlarging the injured area. Endocrine disorders and disruptions in the immune system can cause the formation of keloid scars. They occur in places of strong skin tension - in the back, shoulders, chest. Sometimes an ear piercing can cause such a scar to form.
2. Division of scars according to the type of their active formation:
- Active growth scars are visible
- Scars of stable formation.
3. Duration of scar formation:
- Education of young origin
- Scars of old formation.
4. According to the existing qualification division, scars of physiological and pathological origin are distinguished. Physiological scars are painless and do not affect motor functions. Pathological scars are removed surgically or using a conservative treatment method.
How many sessions are scheduled?
Typically, for the treatment of joints, 10 to 15 sessions are prescribed, which last about 10 minutes. Sometimes a reduced number of treatments may be required. If necessary, up to 4 sessions per year are performed. Simultaneously with these procedures, dietary nutrition, therapeutic exercises, and drug therapy are prescribed.
On a note!
Phonophoresis with hyaluronic acid is not used for the treatment of joint diseases. This technique has found wide use in cosmetology.
Two innovative physiotherapy methods
1. Cryotherapy
Treatment of arthrosis and osteoarthritis with cold began to be practiced relatively recently. Cooled gas has a beneficial effect on inflamed tissues, relieves swelling, and blocks pain receptors. Due to cooling, muscle tone decreases, which allows you to get rid of muscle spasms and joint pain.
2. Homeosynia.
This innovative method involves the introduction of homeopathic remedies into biologically active points of the body through superficial injections. The specialist individually selects acupuncture points and homeopathic medicines for each patient, depending on the severity and location of arthrosis. The technique is actively used in the West, but has not yet become widespread in Russia.
Another popular physiotherapeutic method is shock wave therapy:
Operating principle
If we talk about ultrasound treatment, then in this case we are talking about special equipment that is capable of creating certain vibrations in different parts of the human body. Thanks to this it is possible to achieve:
- Stimulation of blood vessels, which reduces swelling and relaxes muscles.
- Improved blood circulation process. Thanks to this, more nutrients are delivered to the sore joints. The joints heal much faster.
- Increased venous tone, which is necessary in order to prevent stagnant processes. Thanks to this, spasms are reduced and swelling is relieved.
Thanks to such therapeutic procedures, it is possible to reduce inflammation and relieve pain. Typically, this type of treatment does not cause pain or other discomfort to patients. Phonophoresis is used for arthrosis, arthritis and other pathologies. Simultaneously with ultrasound, you can attend massage sessions, exercise therapy, and engage in heat therapy.
Consequences of the procedure
Some patients complain about some side effects in their reviews. For example, hydrocortisone can cause itching and swelling in the area that was directly affected. Some people begin to experience symptoms of hyperemia. There have also been cases of increased blood pressure.
If such a reaction is observed, then do not worry and completely refuse treatment. In most cases, it is possible to avoid unpleasant consequences if you adjust the dose of the drug (reduce it) or reduce the number of procedures. The doctor will help you create the correct treatment schedule based on the patient’s complaints.
conclusions
1. The goal of physical therapy in the first 10 days after rhinoplasty is to accelerate the outflow of metabolic products, in the second phase (up to 3 months) to prevent excessive scarring.
2. Compliance with the proposed algorithm for managing the postoperative period, which includes visits to the doctor to correct the position of the Denver splint and a number of physiotherapeutic interventions, can significantly reduce the severity of the body’s inflammatory reaction to surgical trauma and shorten the period of postoperative rehabilitation.
The author declares no conflict of interest.
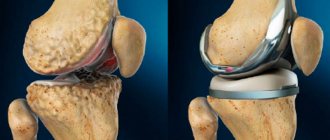
Physiotherapy of the knee joint
Physiotherapy for the knee joint can provide positive results. Physiotherapy for arthritis of the knee joint is aimed at relieving pain, achieving long-term remission, etc.
Physiotherapy methods used for arthrosis of the knee joint:
- Irradiation with medium wave ultraviolet irradiation. Erythema appears at the site of exposure. The method allows you to reduce the sensitivity threshold in the irradiation zone, which affects the pain center in the brain. Sessions of mid-wave ultraviolet irradiation are carried out daily or every other day.
- Laser infrared therapy. This method allows you to reduce sensitivity, improve nutrition and blood flow, and reduce stress. Sessions are held daily.
- Low-intensity ultrahigh-frequency therapy, which makes it possible to reduce pain and prevent the process from spreading to nearby tissues. This method improves joint nutrition, regenerates tissue, and reduces swelling.
- High intensity centimeter wave therapy. The method allows you to establish blood supply and improve the nutrition of cartilage tissue.
- Ultrasound therapy. Reduces the inflammatory process, improves trophism, and shows an excellent regenerating effect.
- Magnetotherapy. Reduces swelling, activates the regenerative abilities of cartilage, and normalizes trophism.
A course of physical therapy for the convenience of the patient is most often carried out during a hospital stay.
Patients and methods
The work was carried out at the children's clinic Edkar LLC (Kaliningrad). We examined and treated 109 patients with acute bacterial rhinosinusitis aged 5 to 17 years. Using simple randomization, all patients were divided into 2 groups: the main group and the comparison group. Patients in the main group received treatment using low-frequency ultrasound, patients in the comparison group received complex treatment with lavage of the nasal cavity according to generally accepted methods. The main group consisted of 54 patients: 29 (53.7%) boys and 25 (46.3%) girls (average age 11.04±0.3 years), the comparison group - 55 patients: 28 (50.9%) boys and 27 (49.1%) girls (mean age 10.64±0.4 years). To verify the diagnosis of acute bacterial rhinosinusitis, a comprehensive examination was carried out, including anamnesis, analysis of patient complaints, objective examination, instrumental (endoscopy of the nasal cavity, computed tomography of the paranasal sinuses) and laboratory (general blood test, determination of immunoglobulins of classes A, M and E, cytological study of discharge from the nasal mucosa, microbiological study of discharge from the middle nasal passage) research methods, as well as assessment of mucociliary transport time (saccharin test). All patients were additionally examined by a pediatrician.
Criteria for inclusion of patients in the study: age from 5 to 17 years; established diagnosis of acute bacterial rhinosinusitis; the duration of the disease is at least 10-14 days; informed consent and patient compliance. Exclusion criteria: age under 5 years; the presence of acute and/or chronic diseases affecting the results of the study; violation of the architectonics of the structures of the nasal cavity; severe and/or complicated course of acute bacterial rhinosinusitis; non-compliance of patients.
An assessment of the patient's subjective feelings was carried out using a special questionnaire SNOT-20 through a cross-sectional survey (researcher—parent of the subject—subject). Patients filled out this questionnaire before treatment, on the 3rd, 6th, 14th day and 1 month after therapy. After surveying and obtaining data, items for which patients scored less than 1 point in total before treatment were excluded from the study. Thus, out of 20 points, 10 remained: desire to blow your nose, sneezing, runny nose, cough, discharge down the back wall, nasal discharge, headache/pressure, difficulty falling asleep, waking up at night, decreased concentration. The leading complaints were identified in all patients: difficulty in nasal breathing, nasal discharge, cough, drainage of discharge from the nose into the throat. Patients (or their parents) rated the intensity of subjective symptoms on a 5-point scale. In this case, a score of 0 corresponded to the absence of symptoms; 1 point - mild, periodically occurring manifestations; 2 points - mild, constantly observed manifestations; 3 points - moderately severe symptoms that do not affect daily activity; 4 points - severe symptoms affecting daily activity; 5 points - significantly severe symptoms. The severity of the disease was determined using a 10-cm visual analogue scale. Values from 0 to 3 cm (points) corresponded to a mild degree of the disease, from 4 to 7 points to a moderate form of the disease, and from 8 to 10 points to a severe form of the disease.
All patients underwent complex treatment of acute bacterial rhinosinusitis: protected aminopenicillins or cephalosporins of the second and third generation, macrolides (for allergic reactions to protected aminopenicillins), antihistamines (for histamine-induced processes), and nasal decongestants were used.
Local therapy in the comparison group consisted of rinsing the nasal cavity, paranasal sinuses and nasopharynx using a nasal douche with 50 ml of saline. In the main group, irrigation of the nasal cavity and paranasal sinuses and nasopharynx with 0.9% saline solution was used using low-frequency ultrasound.
The effectiveness of the therapy was assessed by the dynamics of the intensity of nasal symptoms. The treatment period was 6 days, the observation period was 1 month.
Statistical processing of the results was carried out using the SPSS 16.0 computer program. For data on an interval scale, the mean value, its standard deviation, median, minimum and maximum were found; for data on a nominal scale, frequency and percentage of the total volume of the group were indicated. To compare mean values, parametric (Student's t-test for comparison of mean values) and nonparametric (Mann-Whitney test for unpaired observations, Wilcoxon test for paired observations) tests were used.