Musculoskeletal problems cause inconvenience to many people. They interfere with motor activity and worsen the quality of life. The list of such problems includes inflammation of the knee joint.
The cause of this pathology can be both diseases and injuries. Problems arising in the knee joint area should be treated by experienced physicians. A properly developed course of therapy allows you to determine the optimal treatment program.
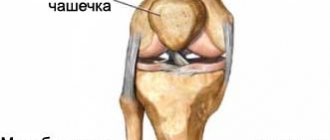
Anatomical structure of the knee joint
The anatomical structure of the knee joint is determined by its main task, which is to cushion the body when walking.
It consists of three bones:
- Tubular tibial.
- Tubular femoral.
- A rounded small knee pad.
The lower femur bone forms protrusions covered with cartilage (condyles). The condyles are in contact with a large plateau consisting of two halves. In addition, they form a jelly-like depression in which the knee pad moves.
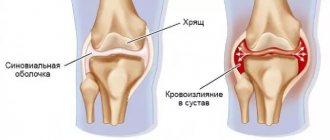
Cartilage plays a significant role in the functioning of the knee joint. They provide shock absorption. The cartilage tissue of the knee joint belongs to the hyaline type of such tissue.
Its composition is characterized by a large amount of water in the intercellular substance. This structure protects the knee joint from damage. It provides resistance to heavy loads.
Structure of the knee joint
Causes of inflammation of the knee joint
Inflammation of the knee joint is a common pathology. This problem is faced by elderly patients, athletes, and children. Pathology can begin after injury or significant physical activity. Most knee inflammation is related to knee joint disease.
Inflammation due to joint disease
The cause of inflammation can be the following joint diseases:
- arthrosis;
- arthritis;
- osteoarthritis:
- synovitis:
- Baker's cyst.
At the first pain symptoms, you need to immediately consult a doctor, who will accurately determine the diagnosis and develop the optimal treatment option.
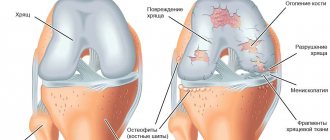
Osteoarthritis
Most often, this disease affects patients in the older age group. The pathology is associated with age-related changes. It is characterized by gradual pathological inflammation occurring in the knee cartilage. Treatment of diseases can only be lifelong.
Development of knee osteoarthritis
Rheumatoid arthritis
As a rule, it affects both knees at the same time. Exceptions are rare and almost unique. It occurs as a result of the destruction of the knee cartilage. Requires complex treatment. The diagnosis is most often hereditary.
Development of joint rheumatism after infection with streptococcus
Post-traumatic arthritis
As the name suggests, it is a pathology caused by injuries to the knee joint. Can only be purchased. Symptoms of the pathology that require treatment occur both immediately after the injury and several years later.
In each case, the symptoms are approximately similar:
- A swelling of the knee appears , the temperature rises, a distinct crunching sound is heard when bending, and the knee hurts greatly.
- Pain occurs on palpation and can be constant; it intensifies and often becomes unbearable when bending.
- With severe damage to the knee joint, it continues at rest . Deformation of the kneecap may occur.
- The area of inflammation turns red . Various reasons lead to defeat.
Knee diseases: symptoms
The manifestation of pathologies of the knee joints is different and depends on many factors: the cause of the pathological process, the immune status of the patient, his lifestyle, etc. There are general symptoms of knee joint disease, here they are: - pain of varying intensity and duration in the knees; - clicks and crunches when walking; - swelling of the knee(s); - sometimes deformation is visible; - sometimes swelling of the knee occurs; - increased temperature in the affected areas... By the combination of these and other symptoms, you can determine the type of disease of the knee joint: 1. Tendyitis and bursitis are characterized by pronounced, constant pain (even with a relaxed state of the legs). The pain may be accompanied by swelling of the knee and radiate to the muscles of the leg or thigh. 2. Tendopathy, chondropathy, meniscopathy - diseases of the knee that arise as a result of dystrophic lesions in it. As a rule, these pathologies begin unnoticed by a person and do not manifest themselves for some time (asymptomatic). Then minor pain begins when bending and straightening the leg, and a crunching sound is heard in the joint. Sometimes “weakness” occurs in it - spontaneous bending of the leg when resting on the sore joint. It is important to diagnose diseases of the knee joint, the symptoms of which we have now examined, as early as possible, because the success of treatment of this pathology depends on it.
Muscle and tendon diseases
The onset of inflammation of the knee joint is often caused by diseases of the muscles and tendons:
- Inflammation of the joint capsules located in the area of the knee joint (bursitis).
- Inflammatory processes in the tendon area (tendinitis).
Development of knee bursitis
Features of pain syndrome
Pain is the first and most intense symptom that prompts patients to make an appointment with a specialist. Increased discomfort that accompanies any physical activity persists until complete recovery. The disease never ceases to remind itself of itself with aching pains under the knee, and if the treatment is prescribed incorrectly, they are disturbing even at rest.
There are such features:
- pain precedes walking, especially going down stairs;
- there is a high probability of an attack worsening after prolonged standing;
- prolonged physical activity, running, intense squats and intense training also accompany an increase in discomfort inside the knee;
- a painful sensation spreads along the anterior and medial surface.
At stages 3-4 of the pathology, the unpleasant sensations become so strong that they awaken the patient from sleep. The causes of severe pain are caused by the spread of the inflammatory process to the bone, synovium, and soft tissue. To effectively relieve inflammation of the knee joint, it is important to establish accompanying processes: identify periostitis, subchondral fractures, muscle spasms.
Due to knee arthritis, it is sometimes necessary to relieve pain attacks with narcotic analgesics. Exacerbations occur due to irritation of nerve endings by osteophytes. The fibers are characterized by sensitivity, and with systematic exposure to them, you have to constantly take strong painkillers. But there are other reasons for continuous pain inside the knee that occurs against the background of an inflammatory process.
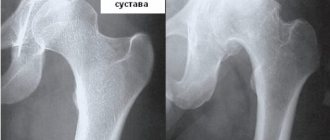
X-ray examination will reveal tissue damage by osteophytes and degenerative phenomena within the periarticular tissues. MRI of the knee is an indispensable diagnostic option that allows you to detect impaired blood circulation, since this phenomenon is an equally common cause of pain.
Other causes of inflammation
Vascular diseases can also cause an inflammatory process. The cause of inflammation in the knee joint area is most often associated with varicose veins of the popliteal vessels.
Inflammation may be associated with a disease of the nerve tissues passing through the knee joint. Pain due to osteoporosis may radiate to the knee. Another cause of inflammation in the knee joint is a complication after surgery on the knee joint, for example, when treating a meniscus or tendons.
Knee Reflex Diagram
What is infectious arthritis
Infectious arthritis is caused by a virus, fungus, or bacteria. Microorganisms enter the joint cavity through the blood or lymph flow from another source of infection in the body. This happens, for example, with an open joint injury, after a puncture or arthrotomy - medical intervention in the joint.
The causative agents of arthritis of an infectious nature are gonococcus, Staphylococcus aureus, streptococcus, Pseudomonas aeruginosa or Haemophilus influenzae, and also much less frequently - various fungi.
In the acute period, arthritis of an infectious nature has the following symptoms:
- increased body temperature to 39 °C;
- severe pain that increases with movement;
- swelling of the joint, increased local temperature, redness of the skin;
- general intoxication of the body - headache, nausea, lethargy.
Sometimes infectious arthritis becomes chronic, and the symptoms change:
- body temperature remains at 37-37.5 °C;
- the pain becomes less intense;
- swelling is almost invisible;
- joint movements are possible in a limited manner;
- signs of intoxication include weakness, sweating, loss of appetite.
Infectious arthritis affects one large joint
Diagnostic procedure
If there is pain in the knee joint, you should immediately consult a doctor. If the pain is severe, you can call an ambulance, whose specialists will prescribe the first stage of treatment and relieve discomfort.
Numerous causes of pathology require different treatment options. These may be injuries that a traumatologist deals with. An examination is prescribed, based on the results of which treatment is carried out by a surgeon, orthopedist, and rheumatologist.
When carrying out diagnostics, both instrumental and laboratory research options are used:
- A blood test, the results of which will show the need to treat inflammation of the knee joint by an increase in the number of platelets and leukocytes, the appearance of C-reactive protein in the blood, and an increase in the erythrocyte sedimentation rate.
- X-ray is a standard procedure.
- Arthroscopy is needed if it is impossible to make a diagnosis.
- MRI and computed tomography.
Treatment of knee diseases
Treatment of inflammation of the knee joint should be comprehensive. Physiotherapeutic procedures are required, medications are prescribed to help reduce the level of inflammation, medications are prescribed that can improve the quality of cartilage tissue, and much more.
Drugs
The main goal of using medications is to reduce the amount of fluid in the diseased joint and kneecap. They are designed to slow down the rate of spread of inflammation and cure it by improving nutrition and blood circulation of the knee joint.
Are used:
- Chondoprotectors. Including Dona, Artra, Teraflex, Aflutop injection solution.
- Ointments and solutions that help improve blood circulation, such as Vishnevsky ointment, Doxycycline, Espol, Menovazin.
- Intra-articular injections that help treat the immediate source of inflammation. These include hyaluronic acid, Diprospan, Flosteron, Hydrocotisone.
- Knee braces that promote healing by creating a rest zone. In such a situation, orthoses and taping are used.
Dona in tablet form
Teraflex Advance
Vishnevsky ointment
Menovazin
Diprospan
Hydrocortisone for external use
Knee braces
When choosing a professional means of knee immobilization, you need to pay attention to the choice of its type; the following are offered for sale:
- Fabric elastic knee pad. The product is made from animal wool or fabric. It is characterized by a low degree of fixation and favorable cost. Due to the use of natural materials, it provides an additional warming effect.
- Neoprene knee brace - knee joint support. Convenient due to ease of use and minimal maintenance requirements. It fixes the knee joint well, simplifying treatment by reducing motor activity.
- Modernized circular bandages (orthosis) . It fits tightly to the sore area of the affected area, fixes it, and helps in treatment.
- The splint is the most reliable fixation. In terms of the degree of immobility of the knee joint, it is comparable only with the use of a plaster cast.
Elastic knee pad
Knee brace
Articulated knee pad
The choice of a device for fixing the knee joint for the period of treatment is determined with the help of the attending physician. For preventive purposes, it is recommended to use models with a low degree of fixation.
Physiotherapy
Physiotherapy is used in treatment. Patients are shown such types of physiotherapy as ultraviolet irradiation, electrophoresis, UHF, inductothermy.
All physiotherapy options can only be prescribed by a doctor and only in a state of remission of the area of the leg affected by the pathological process:
- They are convenient because they activate restoration processes in the affected area of the knee joint; blood flows to the pathological area, providing an increased level of nutrition.
- Exercises help relieve pain even with strong development of pathological processes in the painful area.
- The use of different physiotherapy options helps to quickly remove the acute stage of the pathological process in this affected area. The procedures are best carried out approximately forty minutes after eating.
- It is advisable not to do them on an empty stomach or, conversely, in case of severe overeating. After completing classes, at least an hour and a half should pass before the next meal.
Physiotherapy after knee surgery
It is important to remain in the classroom for at least 30 minutes after completion. Knee joint therapy requires mandatory rest.
Physical therapy for knee inflammation
In the treatment of inflammation of the knee joint, the use of physical therapy is indicated. It is recommended to start performing the complex only after the acute stage of treatment.
Exercises are performed if dull pain persists. Exercises must be stopped in a situation where the pain becomes sharp and sharp.
Among the exercises that can be used in the treatment of all types of inflammation of the knee joint:
- Squeezing a ball between your legs with your knees. It can be performed standing, lying or sitting.
- An exercise is shown in which each leg is lifted up alternately . Actions can also be performed either standing or lying down.
- If the stage of inflammation is no longer very acute , you can do a “bicycle”.
- Patients who are treating inflammation of the knee joint are advised to dance, especially step.
- To develop the affected joint, it is recommended to do half squats.
Exercises for rehabilitation
All exercises are performed in a quantity convenient for the patient. Gradually the number of actions increases. The total duration of therapeutic exercises can ultimately exceed 30 minutes.
Surgery
If therapy is started in the early stages of lesion development, a non-surgical treatment option is recommended.
Surgical methods are indicated in the case of:
- the appearance of adhesions in the synovial bursa of the knee joint;
- osteomelitis;
- purulent toxicity;
- foreign body.
Technology is used that allows making minimal incisions and laser therapy methods. In the most difficult situations, knee replacement is used.
Diagnostics
Only a thorough, comprehensive examination allows us to understand what caused the inflammation of the knee joint. What to do and how to ensure the patient’s recovery can only be determined by a doctor. Therefore, if you experience prolonged discomfort in the leg flexor, you should consult a doctor and undergo an examination. It includes:
- Laboratory diagnostics . Hemoglobin level, leukocyte concentration in peripheral blood, ESR, CRP content, as well as other acute-phase indicators, may be normal. This is observed in 85% of all identified cases of inflammation of the knee joint. In 15% of cases, it was possible to establish a slight increase in the volume of highly sensitive CRP. More often, this was found in elderly patients and people of advanced age.
- Joint puncture followed by analysis of synovial fluid. Synovial fluid does not reflect the presence of an inflammatory process; it has a viscous consistency, sterile, transparent color with slight turbidity. Cytosis does not exceed 2000 mm3. If the development of synovitis is urgent, the ESR will moderately increase, and an increase in the volume of leukocytes of the polynuclear type is possible.
- X-ray examination . The technique involves obtaining an image of hyaline cartilage, and simultaneously provides information about all articular segments. With inflammation at an early stage, the image will visualize a slight thickening and swelling of the cartilage tissue. Changes within the menisci are also displayed. When the pathology reaches a moderate or severe stage of development, they are thinned, the articular cartilage is characterized by exposure of the subchondral bone. Intra-articular structures are damaged, synovitis is present.
- Ultrasound. Ultrasound examination allows us to identify pathological changes in soft tissues, determine the thickness and structure of cartilage. Thanks to the technique, it is possible to determine the condition of the synovial membrane and free fluid inside the knee. Exposure to ultrasonic waves determines bone growths.
- MRI . Tomography is an effective way to visualize the actual clinical picture. To understand how to treat inflammation of the knee joint, the doctor is guided by the data from the research obtained. The information value of MRI is undeniable. The procedure allows you to determine whether the ligaments are intact, whether there are any pathologies and severe inflammation inside the tendons, and how severe the swelling of the bone marrow is (this is the main sign of osteitis). MRI even has advantages over ultrasound, since the diagnostic method is more sensitive in terms of detecting osteochondral changes. Ultrasonography is somewhat weaker in establishing degeneration and damage.
Depending on the doctor’s assumptions, these diagnostic methods may be supplemented with other options, which is aimed at a comprehensive study of the patient’s condition.
Treatment of knees in children and adolescents
Patients of any age can suffer from inflammation of the knee joint. Including teenagers and even children.
Treatment methods for children:
- To minimize trauma, it is recommended to use treatment options that exclude surgery.
- The main goal of treatment is to relieve inflammation using injections, injections, ointments and tablets.
- and exercise therapy are actively used
The defenses of a young body almost always give a positive result if the correct version of complex therapy is developed.
Baker's cyst
It occurs when synovial fluid leaks into the popliteal fossa, resulting in the formation of a capsule filled with fluid. The size of the cyst can vary, sometimes reaching the size of a fist. The fluid-filled cyst is easily palpable.
Baker's cyst symptoms
The main symptoms are difficulty moving the knee and pain. The more active the patient, the more pronounced the symptoms of the disease. In some cases, with small cysts, there may be no symptoms. When a cyst ruptures, fluid is released into the surrounding tissue, increasing pain.
Treatment of Baker's cyst in Germany
If there are no complaints, there is no need for treatment. However, if pain occurs, both conservative and surgical therapy may be indicated. As a rule, taking anti-inflammatory medications is sufficient. If there is no success, removal of the cyst is recommended.
Types of folk remedies
A complement to drug treatment is the use of folk remedies, the most common ones include:
- Applying iodine to the affected area of the mesh. It is usually done before bed. Alcohol can be used instead of iodine. Alcohol compresses are applied to the knee for successful treatment for several hours and are fixed with a bandage, which includes polyethylene, fixed with a bandage or bandage.
- made from water and yellow clay will help relieve pain
- relieve inflammation and pain .
- When rubbing, a tincture of potato or calendula flowers in alcohol helps a lot . All compresses and rubbing are performed in courses of 14 days. Most often they are done at night.
- made from 100 grams of honey, 1 teaspoon of mustard, 1 teaspoon of salt and 1 teaspoon of soda is a good warming agent
- A lard compress has a warming effect. It's easy to do. Pork lard is wrapped in gauze or a clean rag and tied to the sore knee. Both fresh and defrosted lard is used.
Additionally, the healing properties of familiar products can be used. For example, dishes containing food gelatin. To help your joints, a diet that includes a large number of foods rich in potassium, calcium and vitamins is useful.
Prevention of inflammation of the knee joint
Inflammation of the knee joint can affect a patient at any age. This is a common disease and the use of preventive measures helps to avoid long-term treatment. The best prevention option is a healthy lifestyle.
To prevent inflammation of the knee joint, which may require long-term treatment in the future, follow the rules of a healthy lifestyle:
- Maintaining optimal body weight.
- Treatment of infections that can provoke the development of joint inflammation.
- Avoiding hypothermia and colds.
- Follow safety rules to help avoid knee injuries.
Certain methods of prevention are used in the presence of systemic diseases, which, without a proper course of treatment, can lead to complications in the form of inflammation of the knee joints. In this case, strict adherence to the recommendations of the attending physician and taking the medications prescribed by him are required.
Diseases of the knee joint: treatment
Treatment methods for these pathologies are always determined by the appropriate doctor. There are three main methods of therapy: - a conservative method of treating knee joint disease; - surgical method; - alternative method (traditional medicine). Almost all pathologies of the musculoskeletal system can be treated conservatively - using various drugs. For example, etiotropic drugs are used to eliminate the cause of the disease: - if the disease of the knee joint is infectious, antibiotics are used; - with an autoimmune nature - steroids. It should be borne in mind that both antibiotics and steroids cause quite severe side effects and weaken the immune system, which already functions poorly. A paradoxical situation arises: in order to get rid of any whiteness of the knee joint, we must strengthen the person’s immunity, but we, on the contrary, weaken it. Therefore, the use of hormonal drugs and antibiotics should only be in extremely severe cases; never use these drugs unless absolutely necessary. Also, symptomatic drugs (eliminating the symptoms of pathology) are used treat diseases of the knee These drugs include anti-inflammatory, antibacterial and antiparasitic drugs. The greatest benefit comes from complex therapy - the use of immune drugs, vitamins, mineral complexes, probiotics and prebiotics along with conventional medications. The immunomodulator Transfer Factor is of particular importance in the complex treatment of knee joint disease. Once in the body, it performs several functions at once: - restores the functionality of the immune system, as a result of which the body’s metabolic processes are normalized, which activates the restoration of joints and cartilage tissue; — enhances the health-improving effects of drugs in combination with which it was taken (in this case, simultaneous use of probiotics is recommended); — being a carrier of immune memory, this immune drug “remembers” all foreign microorganisms that caused diseases of the knee joint, and when they reappear, gives a signal to the immune system to neutralize them. Taking this immunomodulator is also necessary during the surgical treatment of knee joint disease - to quickly restore a person’s immune status after surgery and to prevent various infectious complications.