Author of the article: Victoria Stoyanova, category 2 doctor, head of the laboratory at the diagnostic and treatment center (2015–2016).
Article publication date: 12/03/2014
Article updated date: 12/02/2018
Arthrosis of the knee joint (or gonarthrosis) is a degenerative-dystrophic disease in which the cartilage and bone tissue of the articular structures are affected (destroyed). There are 3 degrees of severity of the pathology, but most often patients seek medical help specifically for grade 2 gonarthrosis. Sometimes only from the second stage of the disease do patients take their condition seriously and begin treatment, and the earliest symptoms of the disease are often ignored.
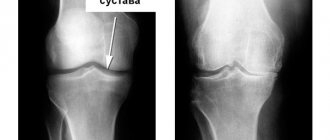
At the first stage of gonarthrosis, changes in the cartilage are slightly expressed and are often reversible. At stage 2 of the disease, significant destruction of cartilage tissue occurs, a decrease in the amount of intra-articular fluid, and the formation of a large number of osteophytes (bone growths). X-ray photographs reveal a pronounced narrowing of the intra-articular space, disruption of the structure of the joint, and compaction of bone tissue.
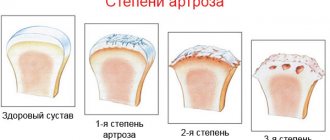
Three degrees of arthrosis of the knee joint. Click on photo to enlarge
Features of the development of osteoarthritis of the knee joint
Osteoarthritis of the knee joint
is a common pathology that belongs to the category of the most common diseases that have an extremely negative impact on a person’s quality of life.
Degenerative-dystrophic processes most clearly manifest themselves in the form of physical dysfunction of the legs, accompanied by severe pain. Depending on how much the pathological process progresses, further forecasts for the course of the disease are made.
One of the disappointing forecasts is paralysis of the lower limbs. The seriousness of the consequences of pathological processes necessitates seeking qualified medical help.
What is arthrosis
Arthrosis is a disease of the joints of a degenerative-dystrophic nature with the gradual destruction of cartilage and proliferation of bone tissue. The process is accompanied by deformation, impaired joint function and pain. Recently, the term osteoarthritis (OA osteoarthritis) is more often used - a group of diseases that are based not on purely dystrophic, but on dystrophic-inflammatory processes leading to gradual destruction of the joint. More and more experts believe that the causes of arthrosis and osteoarthrosis, the mechanisms of their development are the same, that is, in fact, they are the same disease.
According to statistics, from 10 to 20% of the population suffers from arthrosis in different countries. By the age of 80, almost everyone has age-related disorders in the musculoskeletal system. At the same time, patients do not always consult a doctor on time and take a long time to treat themselves, which leads to disability. Whereas the right treatment can relieve suffering and stop the progression of the disease. Arthrosis codes according to ICD 10: M15-M19.
What causes lead to knee arthrosis?
To identify the causes of arthrosis of the knee joint, it was necessary to conduct a large number of studies. Many years of examinations of patients and a thorough study of the clinical picture of the pathology allowed specialists to come to the conclusion that the influence of a number of negative factors is the root cause of the destruction of joint tissue, causing severe pain and inflammation.
Among the main reasons leading to degenerative-dystrophic processes, it is worth highlighting:
- previous injuries - a bruise, dislocation or fracture of the knee automatically classifies a person as a risk group and can cause the development of the disease. Damage to the joint presupposes its fixation, and long-term immobility is a direct path to the formation of arthrosis;
- strong physical activity - intense stress on the knees (especially in older people) leads to microtraumas, which also leads to the development of negative pathological processes;
- insufficiently strong ligamentous apparatus - abnormal joint mobility also negatively affects their condition, which manifests itself mainly in old age;
- excess body weight - extra pounds can cause irreparable damage to the knee joints, because the likelihood of meniscus injuries in this case is incredibly high. If a lot of weight is accompanied by varicose veins, then there is a high probability of developing severe forms of arthrosis of the joints of the lower extremities;
- metabolic disorders - a failure in the exchange of nutrients and elements in the body provokes the development of various kinds of diseases, which is caused by insufficient supply of various tissues, in particular bone and cartilage;
- increased levels of stress - worries and worries negatively affect not only people’s mood, but also the level of physical well-being.
Treatment of arthrosis 2 degrees
Treatment methods can be divided into 2 types - conservative and radical. Conservative therapy also involves the use of non-drug treatment methods aimed at restoring the functionality of the limb. If the situation is advanced, as with end-stage arthrosis, surgical intervention is prescribed. During surgical treatment, endoprosthetics is performed - this is the replacement of a joint with an artificial implant.
Drug treatment used for grade II arthrosis
Drugs in the treatment of degenerative joint damage can be divided into disease-modifying and symptomatic. Symptomatic treatment is carried out during the period of exacerbation, using short-term medications to eliminate pain and inflammation.
What medications are most effective for exacerbation:
- NSAIDs. Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs have a complex effect, remove inflammation, pain and reduce elevated body temperature. With short-term use, in most cases they do not cause unwanted side effects, so when using them for up to 5-7 days, there are no consequences. If, after the specified time, the exacerbation with the help of NSAIDs is not eliminated, then the treatment tactics need to be changed. Examples of medications are Diclofenac, Airtal, Nimesil, Movalis.
- Corticosteroids. For arthrosis, they are not used systemically, but are prescribed with caution in the form of intra-articular injections to suppress severe inflammation. Often, intra-articular blockades with corticosteroids are not recommended, as they negatively affect the structure of cartilage tissue. Typically, long-acting drugs are used to suppress inflammation for a long time if it is chronic. More often, injections of Diprospan or Kenalog are prescribed. Less commonly, Dexamethasone or Hydrocortisone.
- Muscle relaxants. They do not affect the joint, but relax rigid muscles that tense in response to inflammation, which in turn increases pain in the affected area. It is possible to treat osteoarthritis with the help of muscle relaxants by increasing the effectiveness of NSAIDs, because these medications potentiate the effect on each other. In case of defarthrosis during the period of exacerbation, it is necessary to relax the muscles so that the inflammation does not increase even more. The average duration of taking relaxing drugs is two to three weeks. Examples of products are Baclofen, Mydocalm, Sirdalud.
- Chondroprotectors. With long-term use of these drugs, a therapeutic effect often appears. These medications help relieve pain. Many medical studies confirm the presence of improvements when taking this group of medications, but their use does not lead to quick results. To evaluate the result in terms of reducing discomfort in ligaments and joints, it is necessary to take chondroprotectors for six months or more. These drugs will not help with severe pain, but they effectively support the functions of joints and bones, and improve well-being in the presence of chronic discomfort. An example of substances is Dona, Chondroguard, Teraflex.
- Hyaluronic acid injections. This drug is injected into the joint. Such manipulations are performed in special institutions under close medical supervision. When performing an injection, control is carried out through an ultrasound machine or x-ray so that the needle does not touch the surface of the bones. This medication serves as a synovial fluid replacement that helps temporarily improve range of motion when bending your legs or arms. Such medications are administered 1-2 times a year into each joint.
- Vitamins, minerals. One of the ways to correct the condition of deforming osteoarthritis is to correct the patient’s diet with the help of nutritional supplements. Not all patients can afford a diet that is maximally rich in minerals and varied, so it is necessary to enrich the menu with nutritional supplements. This approach to therapy is based on the fact that when osteophytes grow, calcium is actively consumed from the bones. If the patient has polyarthrosis (more than 3 joints are affected), secondary osteoporosis may occur against the background of ankylosis. To prevent this condition, calcium and cholecalciferol preparations should be prescribed. The duration of the appointment is determined by the doctor based on laboratory tests. Examples - Calcemin Advance, Aquadetrim, Detrimax.
For external use, ointments and gels with NSAIDs and muscle relaxants are prescribed. If there are no signs of inflammation, it is permissible to use warming agents that improve mobility in the joint.
How to treat using non-drug methods
Non-drug therapy is based on the use of physiotherapeutic correction methods, the use of massage techniques and regular exercises that develop joints. It is worth understanding that during the period of active exacerbation these treatment methods are prohibited. Non-drug correction is supportive, effectively helping a patient with osteoarthritis during remission. There are several effective recovery methods to consider.
What physiotherapeutic procedures help fight chronic inflammation:
- Electrophoresis. The method is based on the effect of a weak electric current on the affected tissue. Additionally, NSAIDs, hormones or vitamins are prescribed in the form of injection solutions, but they are not used parenterally, but are applied to the skin, after which the device is connected. In this method, medications enter transdermally and affect the focus of chronic inflammation. As a result, the patient feels better after several sessions. The advantage of the method is quick results without side effects on the entire body. Using electrophoresis, it is possible to remove chronic pain, inflammation and swelling.
- Magnetic therapy. The essence of the method is similar to electrophoresis, but with one difference - medications are administered through the skin using a weak magnetic field. This method also helps relieve chronic inflammation and pain. After several sessions of magnetic therapy, the patient begins to feel much better, stiffness and chronic discomfort disappear.
- Shock wave therapy. Using this method of therapy, it is possible to adjust the rate of development of osteoarthritis, slowing down its progression. Hardware radiation effectively affects the chronic source of inflammation and destroys bone growths - osteophytes. It is recommended to undergo several sessions to experience a significant effect from this procedure.
Massage techniques are also effective. When there are no longer signs of inflammation, it is recommended to gently massage the limb, which will help mechanically relax the rigid muscle tissue. As a result, the muscles become softer and more pliable, which leads to significant improvements in the patient's condition.
How to relieve pain from arthrosis
One of the key points of recovery is exercise therapy. Physical therapy effectively helps to develop a manually constrained joint. It is recommended to select a set of exercises individually with a rehabilitation therapist. After the specialist shows the correct execution of the exercises, and the patient learns to do them independently without mistakes, you can carry out physical education at home. The key to treatment with gymnastics is patience.
To achieve the effect, you need to carry out physical therapy daily, at least once a day. This point is especially relevant for people leading a sedentary lifestyle. Exercise therapy allows you to work out your muscles and helps strengthen them. Strong muscles relieve stress from the affected joint, after which the patient feels better. If the patient does not perform the exercises every day, but from time to time, then such treatment is ineffective.
To avoid exacerbations, it is important to adhere to a gentle lifestyle. The patient must normalize his diet and life schedule. If the patient works in difficult labor conditions, he needs to change his professional activity. It is important to wear orthopedic shoes with anatomical insoles, sleep on a hard mattress and avoid physical inactivity.
Characteristic symptoms of arthrosis of the knee joint
The symptomatic manifestation of the disease allows timely tracking of the onset and development of pathological processes, which gives each patient the opportunity to recover.
Before determining who to turn to for help and how to treat arthrosis of the knee joint, it is important to become familiar with the symptoms of the disease.
Only a specialist competent in this matter can identify the presence and confirm the diagnosis by prescribing treatment for knee arthrosis. However, every patient should know the main symptoms of knee osteoarthritis, among which are usually identified:
- pain - discomfort that gradually develops into painful sensations does not appear immediately. Their slight manifestation in the knees can bother a person for many years, but at some point they may become stronger, and they will not stop in a calm state;
- crunch – “clicks” when flexing/extending a joint are an alarm bell, which manifests itself already in the second and third stages of the disease;
- synovitis is an inflammation of the joint membrane, in which fluid accumulates, which leads to local swelling;
- deformation is a characteristic feature that appears in the last stages of the disease, accompanied by pronounced inflammation and swelling.
Symptoms of deforming arthrosis
Symptoms in the presence of this disease are not specific and in the initial stages may seem vague. If arthrosis is in the first stage of development, then slight pulling sensations or stiffness can be confused with signs of overload. As the pathology progresses with the subsequent growth of osteophytes, the discomfort intensifies. At first, pain is felt only during periods of physical activity, but as the clinical picture worsens, discomfort begins to bother you even during periods of rest.
Symptoms are directly related to the stage of development of the disease. At the initial stage, discomfort rarely occurs. If discomfort occurs, it is associated with fatigue during prolonged walking or running. They are often periodic in nature and immediately subside during the rest period. The crunch occurs rarely and is not accompanied by discomfort. A person can calmly go about his daily activities for years, because arthrosis develops very slowly.
What symptoms occur with arthrosis?
Vivid symptoms that force you to go to the hospital more often appear with the development of stage 2 of deforming arthrosis of the knee joint. The patient begins to feel severe pain, which worsens during periods of exercise and subsides slightly during rest. A characteristic symptom of the disease, in addition to constant crunching, is the occurrence of night or morning stiffness in the area of the affected knee. After waking up, a person needs some time to eliminate the stiffness in the knee, otherwise it will not bend normally. If you do exercise therapy, the stiffness will go away. During exacerbations, the joint may swell and become red. Pain is effectively relieved by the use of NSAIDs.
With further development of the pathology, the pain becomes severe and constant. The patient experiences discomfort even during periods of complete rest. Typically, this condition indicates complete neglect of the disease, which requires urgent treatment to the hospital. If the stage of development of the pathology is late, then the knee stops hurting, but can no longer bend or straighten, since the cartilage has completely worn out, and instead of them a large number of osteophytes have grown, which do not allow normal movement. External signs of deformation are also detected at a late stage of the disease.
Diagnosis of arthrosis of the knee joint
Diagnosis and treatment of arthrosis of the knee joint is carried out by an orthopedist or rheumatologist. If you wish to undergo a diagnostic examination, each patient can contact a therapist, who will give a referral to a specialist or independently take a voucher to one of them.
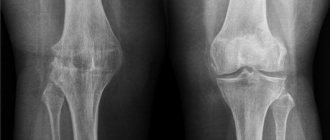
The main diagnostic tool of specialists is, of course, an X-ray machine. Thanks to the image taken, you can track not only the presence of pathology, but also the degree of its development.
It is important to note that x-rays can exclude the possibility of the presence of other diseases of the musculoskeletal system.
X-ray examination opens up the opportunity for a specialist to:
- track the narrowing of the joint space;
- detect compaction in joint tissues.
The combination of clinical symptoms and information obtained from the image provides high-quality diagnosis and diagnosis, with the determination of further treatment for osteoarthritis of the knee joint.
Establishing diagnosis
An orthopedic surgeon can make a diagnosis of arthrosis of the knee joint after movement tests and medical history. The following procedures are usually prescribed as additions to diagnostics:
- Relating to laboratory tests, such as a biochemical blood test and bacterial microflora, smear, puncture of joint fluid and/or bone marrow, serological analysis, that is, a study for the presence of antibodies and antigens contained in the blood serum.
- Instrumental studies, which may include ultrasound, magnetic resonance imaging, densitometry and others.
- Examination of the internal joint capsule using an arthroscope - a device for a minimally invasive procedure for penetrating the cavity through an incision. Most often, this method is used after damage to the meniscus or with cracks and severe wear of the cartilage tissue, as well as to restore the anterior cruciate ligaments. Although recently the anthroscope has rarely been used as a diagnostic tool, it has been successfully replaced by a completely non-invasive diagnostic method using MRI.
- Just “by ear” - with a 3rd degree articular lesion, extraneous sounds in the form of creaks, rustles, and clicks are clearly audible in the joint.
The information obtained is brought together into a general history, and only on the basis of it can full and effective treatment begin.
Degrees of osteoarthritis of the knee joint
Modern medicine divides knee arthrosis into several degrees, in accordance with the nature of the development of pathological processes.
To begin with, it is worth noting that according to observations, the disease can have a different nature:
- unilateral (right-sided/left-sided);
- bilateral.
In addition, the pathological process has three stages of development, each of which has its own clinical picture.
1st degree arthrosis of the knee joint
The initial stage of the development of pathology, the successful diagnosis of which is an incredible success not only for the patient, but also for the attending physician.
The peculiarity of the degree of development of arthrosis at this stage is the absence of clinical signs and clear symptoms. Identification of the disease can be carried out during medical examination or during the study of another disease.
Evidence of grade 1 arthrosis of the knee joint may be:
- local discomfort in the knee area during long walking;
- mild pain that disappears with rest.
It is important to note the fact that pain can be felt in one or both joints of the lower extremities.
It is interesting to note that left-sided gonarthrosis is often diagnosed in left-handed people, while right-sided gonarthrosis is typical for people involved in various sports.
2nd degree arthrosis of the knee joint
Symptoms of the second degree of development of pathology are accompanied by an expansion of signs, which are usually included:
- pronounced pain syndrome;
- stiffness and severe discomfort in the knee joint;
- atrophy of the muscles located near the knee joint, which is caused by tissue damage;
- increased pain;
- visually noticeable deformation of the joint;
- limitation of mobility.
Expanding the symptoms simplifies the diagnostic process. Changes characteristic of grade 2 arthrosis of the knee joint are easy to track during palpation. When undergoing a clinical examination, a specialist can easily detect an abnormal formation in the knee area.
3rd degree arthrosis of the knee joint
It is almost impossible not to notice the third degree pathology, because the patient faces constant pain. In addition, the progress of the disease reaches a critical point, which is manifested by severe deformation of the joint, in which the limb completely loses the ability to flex/extend.
The lack of proper treatment leads to complete destruction of the cartilage and, as a consequence, the development of ankylosis (fusion of articular bones).
The only solution for the final stage of development of the disease is an expensive surgical intervention, involving the removal of remnants of cartilage tissue or joint replacement.
Degrees and stages of development of gonarthrosis
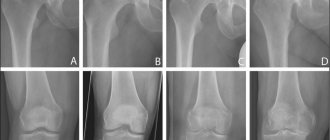
The division of the disease into stages is arbitrary, since the disease progresses over time. Depending on the symptoms and data from instrumental examination methods, four stages of osteoarthritis are distinguished.
Arthrosis stage 1
The initial stage is associated with a deterioration in the quality and decrease in the quantity of biologically active substances in the synovial fluid (articular fluid, provides nutrition to cartilage, has shock-absorbing properties, and promotes the sliding of articular surfaces). Malnutrition leads to wear and degradation of cartilage tissue, pain and inflammation. At the initial stage, movements are not impaired, in full. Patients experience slight pain, discomfort, tingling, and crunching in the joints when moving. Pain occurs during physical activity, long walking or after it. At the initial stages of gonarthrosis, external changes in the knee joint are not noticeable, there are no differences from a healthy one. More details>>
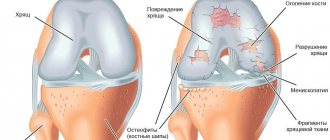
Osteoarthritis stage 2
It is characterized by the following symptoms: thinning of the cartilage up to 1.5-2.0 mm (normal 2.5-3.0 mm), slight narrowing of the joint space (no more than 10-20% of the norm), small single bone growths (osteophytes) appear. up to 5mm, the articular surfaces begin to deform. The inflammatory process is wavy in nature, with periods of emission and exacerbation. Grade 1-2 gonarthrosis is characterized by: pain with minor exertion, when the weather changes, after walking you feel tired, moderate swelling, and weakness of the thigh muscles. Limitations of mobility are insignificant, morning stiffness and sometimes crunching or clicking are disturbing. It is at this stage that patients most often consult a doctor. More details>>
Stages of development of osteoarthritis (see text for description)
Gonarthrosis stage 3
Pathological changes are caused by further progression of the disease, external deformation of the joint and surrounding tissues becomes noticeable, the axis of the limb is curved (varus or O-shaped deformity). At the third stage, the cartilage tissue is severely damaged, thinned to 1-1.5 mm, and exposed bone is visible in places. Bone growths and bone deformities can be easily felt under the skin, and the range of motion of the affected joint is significantly reduced. At 2-3 degrees of osteoarthritis, an even greater narrowing of the joint space occurs, movements are limited, accompanied by pain, crunching, morning stiffness and lameness are characteristic, and contracture develops in the joint. I am bothered by aching and sometimes sharp pain in the knee, even at rest. Due to severe pain, patients often suffer from insomnia due to the fact that they cannot take a comfortable position and react to weather changes. More details>>
Stage 4 gonarthrosis
This is the last stage of the disease, characterized by clinical signs: complete destruction of the articular surfaces, exposed bone is visible, the cartilage is represented by rare “islands”. There is a noticeable significant narrowing of the joint space throughout, a pronounced O-shaped deformity of the lower extremities, and swelling. Mobility is almost completely lost. Treatment with non-surgical methods at this stage is ineffective, and recovery is not possible; help is of a multilateral nature. At this stage, it is recommended to replace the joint with an endoprosthesis. More details>>
Commented by orthopedic doctor Ph.D. Litvinenko Andrey Sergeevich:
To accurately determine the stage of osteoarthritis, in addition to examining the patient, it is extremely important to conduct an instrumental examination: ultrasound, radiography, computed tomography (CT) or magnetic resonance imaging (MRI). Bilateral gonarthrosis is common, so before treatment it is recommended to examine the left and right joints simultaneously. This will help you choose the optimal tactics, and therefore prevent further progression of the disease.
How to treat arthrosis of the knee joint?
The level of modern medicine is at a fairly high level, which ensures successful treatment of various types of diseases. Osteoarthritis of the knees is no exception.
Today, there are a large number of methods for treating arthrosis of the knee joint.
At the initial stages of pathology development, predominantly conservative treatment methods are used. Conservative therapy includes:
- physiotherapeutic procedures;
- physical therapy (physical therapy);
- visiting various massages.
Progressive methods of treating osteoarthritis of the knee joint are also actively used. Among the modern effective ways to combat dangerous pathologies are the following:
- Ozone therapy is a local effect of ozone on the affected joint tissues. Helps reduce pain and stop inflammatory processes. Improves blood circulation in the problem area;
- kinesitherapy is a set of exercises for arthrosis of the knee joint, aimed at increasing its mobility and increasing blood flow.
Treatment of knee arthrosis with physiotherapy
Physiotherapy is one of the most popular methods of treating knee osteoarthritis.
Methods of physical influence, subject to a certain number of conditions, have the most positive effect on the area of localization of pathologies of various types.
Physiotherapy includes procedures such as:
- electrophoresis;
- ultraphonophoresis;
- irradiation with laser/infrared radiation;
- pulsed magnetic therapy.
The effectiveness of the procedures is individual and depends on the quality of the patient’s basic treatment plan.
Massage as a treatment for osteoarthritis of the knee joint
Massage is a useful addition to the treatment strategy for knee arthrosis.
Most experts around the world are of the opinion that massage is a mandatory component of the treatment of symptoms of arthrosis of the knee joint, which has a beneficial effect on metabolic processes and helps speed up recovery.
Knee massage can be performed both at home and within the walls of a hospital. The main thing during massage is preliminary high-quality warming up of the joint and compliance with the optimal duration of the process (from 10-15 minutes).
Treatment of osteoarthritis of the knee joint with massage should include techniques such as stroking, rubbing and kneading.
Gymnastics and exercise therapy for arthrosis of the knee joint
Exercises for arthrosis of the knee joint are an effective way to eliminate unpleasant symptoms and treat the disease.
The process of treating knee arthrosis is a rather complex and lengthy process, and physical therapy is an excellent assistant in achieving the desired result.
The type of exercise therapy and exercises for arthrosis of the knee joint are selected by a specialist individually, depending on the degree of development of the pathology and the general state of the patient’s physical fitness.
The main principle of gymnastics for arthrosis of the knee joint sounds like this: no increased loads on the affected joint, only rational, calm actions.
Endoprosthetics
Advanced arthrosis sooner or later requires joint replacement. This is the main treatment method for such patients. Millions of such operations are performed annually around the world. They are becoming more and more effective and safe.
The essence of the operation is that the person’s own joint is removed. An artificial endoprosthesis is installed in its place. It has sufficient functionality for a person to lead a physically active lifestyle. Even operations carried out over decades were mostly successful. Today their effectiveness is even higher because:
Drugs for the treatment of osteoarthritis of the knee joint
Drug treatment for arthrosis of the knee joint is used to relieve symptoms such as pain and swelling, as well as to activate regenerative processes.
Drugs for the treatment of arthrosis of the knee joint can come in different forms (ointments/gels, tablets or injections, patches).
IMPORTANT! Any medication must be prescribed by a specialist as part of an existing treatment plan developed taking into account the symptoms of knee arthrosis.
Self-medication is unacceptable and can lead to extremely negative consequences, in particular, paralysis of the lower limbs and disability.
Painkillers for arthrosis of the knee joint
Used to eliminate symptoms of arthrosis of the knee joint.
Painkillers play an important role in the treatment of arthrosis of the knee joint, because their use improves the patient’s well-being and gives him the opportunity to get a good night’s rest.
Relief of pain is achieved through the action of active substances. The most effective tablets for pain in arthrosis of the knee joint are considered to be “Ketanol” and “Nimesulide”.
Antispasmodics for osteoarthritis of the knee
Prescribed as active assistance. A key area of focus is the fight against spasms.
The active substances included in the preparations help relax the muscle frame and provide pain relief.
Among the frequently prescribed ones, it is worth highlighting Mydocalm.
Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs)
Treatment of arthrosis of the knee joint with drugs of this type not only eliminates pain, but also slows down and completely eliminates the progress of pathological processes.
Regular use of medications allows you to observe a constant concentration of active components, which guarantees a positive effect.
Artradol is considered to be the most effective NSAID.
Chondroprotectors for arthrosis of the knee joint
The main assistants in the treatment of arthrosis of the knee joint are chonroprotectors.
The active effect of chondroprotectors for arthrosis of the knee joint is aimed at restoring motor ability, which is due to the microelements included in the composition, which are an integral component in the process of building cartilage tissue.
The peculiarity of the principle of action of drugs involves a rather long, but at the same time effective process of getting rid of osteoarthritis of the knee joint.
Among the most effective and affordable drugs, it is worth highlighting Artracam, Structum and Chondroxide.
Knee pain - causes
With age, the vast majority of people face the acute question of how to treat arthrosis of the knee joint, with the typical symptoms inherent in this disease at its different stages. This includes the appearance of swelling in the knee area, redness around these swellings, creaking and rustling, clearly audible in silence when the knee moves, especially during squats, and a distinct pain syndrome of varying degrees of intensity. Pain can appear immediately after normal, everyday physical activity or after physical exercise that is inappropriate for age in duration and intensity. When touching on the underlying causes of this pain, we must keep in mind that its appearance can also be the result of:
- Inflammatory process in the knee joint. That is, be a consequence of arthritis. It occurs as an independent pathology or as a complication from other diseases.
- Arthrosis is a degenerative process during which the tissues of the joint are destroyed, it loses mobility, and if the course of arthrosis has been prolonged, it also causes deformation of the joint.
- Injuries. Most often it occurs from a fall, a blow to the knee, or a blow to the knee on a hard surface. The joint may become deformed.
- Ligament damage. Ligaments hold the joint in the correct position, preventing it from moving. But when they are damaged (stretched, displaced, ruptured), the joint also suffers - with severe pain and the appearance of a tumor. In order not to aggravate the injury, in such cases, urgent medical attention and rest for the injured leg are needed.
- Damage to the meniscus of the kneecap. This protruding, round, movable cartilage in the knee can be injured even when squatting or turning sharply. It is not always detected visually due to swelling of the knee joint that often occurs in such cases. Accurate diagnosis is made using ultrasound, x-rays, and palpation by an experienced specialist.
- Popliteal cyst (Becker's cyst). As a result of inflammation, fluid is formed in the joint, which accumulates in the inner side of the popliteal fossa, in the area of the tendons.
- Inflammation of ligaments and tendons (tendinitis). They cause unpleasant, painful sensations localized along the ligaments and are accompanied by swelling. The pain intensifies when the knee is used (flexion and extension), radiates to the area along the muscles along the ligaments and nerves, above the knee, into the femoral ligaments and muscles, and below - into the lower leg.
- Ischemic pain, from impaired blood circulation in the knee joints. They can appear from a sudden change in weather, severe hypothermia for a long time. Examples are sailors who work for a long time in high (arctic) latitudes. In most cases, the localization of pain is symmetrical, equally intense, and at the first stage does not affect joint mobility.
The most serious mistake in such cases would be to ignore the pain and hope that if you just rest, “everything will go away on its own.” Only a specialist can give recommendations for treatment and make a correct diagnosis, therefore treatment of arthrosis of the knee joint is unacceptable at home only on the basis of advice from “knowledgeable people”, and even purely using traditional medicine. Effective treatment is possible only with a combination of medications in the form of tablets, rubbing, ointments, and the use of physiotherapy. Sometimes, in severe or advanced cases, surgery cannot be avoided.
Diet and general nutritional recommendations for arthrosis of the knee joint
A diet for arthrosis of the knee joint is necessary for patients with excess body weight. A low calorie diet and a wealth of nutrients will ensure weight loss and accelerate the recovery process of affected joints.
Nutrition for arthrosis of the knee joint should first of all be balanced. The daily diet should contain dishes enriched with beneficial vitamins and microelements necessary for the regeneration of joint tissues and maintaining the balance of the entire body.
It is recommended to give up not only bad habits (alcohol abuse and smoking), but also such dishes as:
- store-bought semi-finished products;
- fatty, spicy and overly salty foods;
- sweet carbonated drinks.
For convenience and competent planning of the diet, when treating knee arthrosis, it is recommended to keep a food diary, which disciplines and helps facilitate the process of restructuring the usual lifestyle.
Causes of arthrosis
- Destruction of the joint due to natural wear and tear (aging of the body).
- Hormonal disorders (menopause, endocrine diseases).
- Congenital defects of the musculoskeletal system.
- Injuries, surgery on the knee joint.
- Professional sports.
- Monotonous physical work with increased load on the knee joints.
- Excess body weight.
- Genetic predisposition.
- Autoimmune diseases.
Reasons leading to the development of gonarthrosis
The main cause of the development of the disease is considered to be age-related changes caused by the natural aging of the body, and the disruption of metabolism and blood circulation. Other factors that can provoke the development of the disease include:
- obesity;
- injuries;
- congenital anomalies;
- hereditary tendency to joint diseases;
- rheumatoid arthritis;
- work associated with heavy physical activity.
The risk group includes professional weightlifters.
Arthrosis
Symptoms of arthrosis | Causes of arthrosis | Degrees of arthrosis | Treatment of arthrosis | Is it possible to completely cure arthrosis?
Arthrosis is the destruction of a joint due to a number of reasons. Doctors say: degenerative-dystrophic changes in joints. Arthrosis can affect all joint tissues, including cartilage. In advanced cases of arthrosis, the joint becomes noticeably deformed and this becomes visible to the naked eye. With severe arthrosis of the joints, the patient may lose ability to work and become disabled.
Sign up
SYMPTOMS OF ARTHROSIS
The most obvious symptom of arthrosis is pain with the slightest movement, and sometimes even at rest. However, this is an extreme degree of development of arthrosis. At first, the disease manifests itself more delicately. And it is important not to miss these alarm bells: stiffness, stiffness, difficulties in working the joint to its full amplitude. For example, it is not possible to bend and straighten the knee to the end.
Also, the development of arthrosis is reported by muscle tension, a characteristic crunch when moving, and swelling in the area of the affected joint. For example, with shoulder arthrosis, you can see swelling on the side of the affected shoulder. The symptom of arthrosis in the final stages is difficult to hide. The joint becomes deformed, loses its functionality, and anatomical changes are already evident!
CAUSES OF ARTHROSIS
Many factors can provoke arthrosis of the joints:
- Diseases of the musculoskeletal system, pathologies of the immune, endocrine and lymphatic systems. These diseases lead to metabolic disorders. Destructive phenomena begin if the joint does not receive enough nutrients for the structure of its own tissues.
- Diseases of the genitourinary system also lead to the appearance of arthrosis. The kidneys do little to cleanse the blood. Chronic inflammation appears. In patients with diseased kidneys, arthrosis of the hip and knee joints is diagnosed mainly.
- Increased physical activity. For example, athletes, general workers. In such cases, shoulder arthrosis often appears.
According to the provoking factor, arthrosis occurs:
- idiopathic or primary. This diagnosis is made when it is difficult to determine for certain the cause that provoked the disease.
- secondary. In this case, the cause of arthrosis is clearly determined, and the underlying disease can be established. The doctor should focus efforts not only on relieving symptoms, but also adjust metabolic processes, carry out rehabilitation after joint injuries, and take measures to maintain the endocrine and immune systems.
- if the disease affects several joints at once, it is polyarthrosis. Also called a disease in which joint deformation reaches a high degree. Usually paired joints are affected: knee (gonarthrosis) or hip (coxarthrosis).
Osteochondrosis is perhaps the most common cause of arthrosis. When the vertebrae are displaced and the intervertebral discs do not absorb the shock well, the joints compensate for the load. Increased pressure on the joints does not go away without leaving a trace. The hip joints are the first to fail. In this case, it makes sense to treat arthrosis, starting with the spine. At the Doctor Ost Medical Center, vertebrae are carefully returned to the anatomically correct position by DRX robots, which have no analogues.
Joint arthrosis is diagnosed more often in older patients, when, due to the appearance of various diseases, there is an accumulation of negative factors. In particular, in women during menopause, hormonal imbalance is added. In addition, the body experiences a lack of nutrients, vitamins and microelements. Against this background, various joint disorders arise. The aging body can no longer cope with overexertion and accumulated injuries. As a result, arthrosis appears.
Excess weight plays a significant role in the development of arthrosis. Excess body weight places excessive stress on the spine and joints, which wears them out prematurely.
Ask a Question
At the Doctor Ost MC, in the treatment of arthrosis caused by excess weight, biothreads are prescribed for weight loss. They are carried out under the supervision of a doctor and help you lose extra pounds without dieting or training. For older patients with sore joints and patients with endocrine disorders, this is perhaps the only opportunity to get rid of excess fat without resorting to plastic surgery.
DEGREES OF ARTHROSIS
At the first stage
Arthrosis pain appears only after noticeable physical tests that are not typical for ordinary life. Externally, the joints look healthy. In the second degree of arthrosis of the joints, more intense attacks of pain in the joint and spasms in the limbs are characteristic, limiting movement.
For arthrosis of the joints, degree 2
An x-ray will show depletion of cartilage tissue, and on the surface - osteophytes - bone growths in the affected area. Just when stage 2 arthrosis of the joints occurs, the patient first thinks about the need to visit a doctor. Fortunately, at this stage, arthrosis can be effectively treated!
In the third degree
arthrosis, the pain becomes chronic: it does not subside with movement and at rest. The third degree of arthrosis no longer requires additional research; the deformation of the joint is already noticeable to the naked eye. With this form of arthrosis there is a risk of complete loss of joint mobility. Usually, implantation of a prosthesis is prescribed to replace the destroyed joint.
TREATMENT OF ARTHROSIS
When starting treatment for arthrosis, it is important to make sure of the true origin of joint pain and the correct diagnosis.
For example, arthritis and arthrosis have a very similar clinical picture. With arthritis, as with arthrosis, limited movements and painful sensations are a concern. But each disease requires a fundamentally different approach!
Arthritis (unlike arthrosis) is not dystrophic, but inflammatory in nature. Various types of heating are effective in the treatment of arthrosis, but for arthritis they are strictly contraindicated!
Arthrosis and arthritis require constant attention from a doctor! If you think that knowing your diagnosis is enough, you are mistaken. You cannot rely on the advice of a pharmacist, much less on advertising. The dosage of medications should be controlled by the attending physician.
Remember! Taking medications without observing the dosage and duration, without tracking the dynamics and monitoring the general condition of the body can damage the kidneys and aggravate the course of arthrosis.
Doctor Ost MC gives preference to modern hardware technologies that operate without side effects. For example, a super-intense laser can relieve even acute pain in just one session.
It is not necessary to take medications for years or put blockades or painkillers every six months. Arthrosis, even in severe form, is treated according to the author’s scheme without prostheses and operations at the Doctor Ost MC. We are ready to help patients with arthrosis at any age and with diseases of varying severity.
“When I tried to raise my left arm, I was seized by wild pain. It turned out that I had arthrosis and ligament rupture. They couldn’t help me at the city hospital, but they could at Doctor Ost, the pain disappeared, and the mobility of my arm returned! "" Read full review
Make no mistake! Pharmaceutical drugs for arthrosis will not bring the desired effect. Over time, the dosage will need to be increased. It is necessary to correct systemic disorders in the body.
Treatment of arthrosis should be aimed at stimulating regenerative processes, the growth of new healthy cells in worn-out cartilage, and replenishing synovial fluid in the joint. This task is perfectly accomplished at Doctor Ost by intra-articular injection of stromal cells (SVF) and the latest regenerative medicine technique - Plasmogel injection. This is the only way to return the joint to working form. And the pain will go away naturally.
IS IT POSSIBLE TO COMPLETELY CURE ARTHROSIS?
It is certainly easier to stop the destructive process in the joints in the initial stages of arthrosis development. Therefore, it is important to rush to the doctor at the first symptoms! If the degenerative process has deeply affected the joint, longer comprehensive treatment of arthrosis will be required. Otherwise, arthrosis will constantly remind you of itself.
The Doctor Ost Spine and Joint Treatment Center has advanced non-surgical methods for treating arthrosis. They are ready to help even with severe forms of spondyloarthrosis and gonarthrosis, in which they are usually referred to a surgeon for prosthetics. However, is it worth waiting for such a severe exacerbation? Don't tolerate joint pain. Make an appointment with a neurologist at Doctor Ost MC today.
how much does it cost? Treatment of arthrosis at Doctor Ost is carried out by a rheumatologist and orthopedist. The cost of consultation with a specialist is indicated in the “Consultative appointment” section of our price list. Follow the promotions, don't miss out on the best price!