Among pathologies of the musculoskeletal system, dysplasia of the knee joint is more often diagnosed in childhood. But even adults are not immune from the sudden onset of the process of disintegration of hyaline and collagen cartilage. The likelihood of developing this pathology is especially high over the age of 55, when women begin menopause and men experience other signs of menopause.
Hormonal changes in the body can play a cruel joke even in adolescence. During puberty, girls may experience a disturbance in the exchange of female sex hormones. With increased levels of estrogen and progesterone, softening of the cartilage tissue in the large joints of the lower and upper extremities and in the spine is observed. This can be a trigger for the development of dysplasia.
Congenital dysplasia of the knee joint in children is often associated with damage to the hip joint. These two diseases begin to appear quite early - in the first three months after birth. Timely contact with an orthopedist and initiation of treatment allows you to eliminate deformation of the lower extremities and completely restore damaged cartilage tissue.
Sudden onset of knee dysplasia in adults is a reason for a full examination. It is necessary to check the condition of the large intestine, hematopoietic organs, and eliminate calcium deficiency in the daily diet. In adults, dysplasia is often associated with bone degeneration. This may be osteoporosis or osteomalacia. With a deficiency of calcium, phosphorus, and vitamin D, a condition occurs in which bone tissue becomes sparse. The articular endplates lose their ability to provide diffuse nutrition to the lower layers of cartilaginous synovial tissue. She begins to dehydrate and undergo degenerative processes. Thinning of its layer is the primary clinical sign of the development of dysplasia. In the future, the bone tissue may become completely exposed. This causes the development of deforming osteoarthritis.
Translated from Latin, dysplasia means the following: dys - destruction, thinning, plasseo - construction. Thus, this is a process in which the process of building new cells of cartilaginous synovial tissue in the cavity of the knee joint is destroyed. The cellular composition is not renewed and its degeneration (death) gradually begins. The thickness of the cartilage layer decreases until it disappears completely.
With severe dysplasia, there is a violation of the congruence of the heads of the tibia and femur. When they move, they create increased pressure in the joint cavity. The density of synovial wildness and its viscosity increases - this creates difficulties with diffuse nutrition of the preserved cartilaginous layer.
In most clinical cases, the process of dysplasia of the cartilage tissue of large joints begins in the fourth week of intrauterine development of the fetus. In the future, this violation is either compensated or continues to develop. An incorrectly formed cellular structure of cartilage tissue can cause the development of pathology at a more mature age (40–55 years).
Simultaneously with dysplasia of cartilage tissue, degeneration and dystrophy of muscle, ligament and tendon fibers occur. The affected limb may be delayed in growth and development. In adulthood, this is manifested by deformation of the knee and a decrease in the volume of the muscles surrounding it.
When the first clinical signs of the development of dysplasia appear, you should seek medical help. An orthopedist treats such diseases. You can make an appointment with this doctor for a free appointment in Moscow at our manual therapy clinic. Call the administrator and agree on a time convenient for your visit.
Causes of development of knee dysplasia
There are external and internal causes for the development of knee dysplasia. The knee is a complex joint of three bones, between which there are two menisci and several joint capsules. Any violation leads to the destruction of cartilage tissue. This is due to the fact that they do not have their own circulatory network and can only receive nutrition and fluid through diffuse exchange. Therefore, any imbalance causes a chain reaction of gradual destruction of cartilage, bone, and muscle tissue, which ultimately leads to the loss of the ability to walk independently.
Internal risk factors leading to dysplasia:
- genetic disorders, intrauterine pathology of cartilage tissue development, negative family heredity;
- disturbance of calcium and phosphorus metabolism, leading to the formation of osteoporosis and osteomalacia;
- vitamin D deficiency;
- metabolic disorders, microcirculation of blood and lymphatic fluid in the knee area;
- excess body weight;
- incorrect placement of the foot in the form of flat feet or club feet;
- diabetic angiopathy and other serious vascular diseases.
External risk factors can also have a negative impact:
- unfavorable external environment from the point of view of environmental safety;
- taking certain pharmacological drugs without a doctor’s prescription;
- work in hazardous production;
- smoking and drinking alcoholic beverages;
- environmental pollution with salts of heavy metals, which, when entering the human body, primarily destroy cartilage tissue;
- stressful situations, frequent hypothermia of the knees;
- heavy physical labor with prolonged standing;
- wearing compressive clothing that disrupts blood microcirculation in the capillary bed;
- poor daily diet and insufficient consumption of clean drinking water.
Eliminating all potential causes of knee dysplasia is the first step towards recovery. Therefore, during the initial diagnosis, an experienced doctor always carefully collects an anamnesis of the disease. Only after all probable causes of pathological tissue degeneration have been excluded will complex treatment be started.
Causes of occurrence.
Genetic predisposition is the main factor in the development of joint dysplasia. Below are the reasons why this pathology occurs:
- Taking certain medications during pregnancy.
- Tumors, various abnormalities of connective tissue development.
- Infectious diseases of various types in the mother.
- Diseases of the endocrine system.
- Chronic diseases of the pelvic organs.
- Late pregnancy, difficult childbirth, breech position of the fetus.
- Poor nutrition, disruption of daily routine, insufficient fluid intake.
- Vitamin deficiency, mineral deficiency.
- Poor environmental situation in the place of permanent residence.
- Bad habits - drug use, alcohol, smoking.
- Being in an unfavorable environment (working at a chemical plant, etc.).
- Disturbed water-salt balance of the body.
Congenital fibrous dysplasia of the knee joints
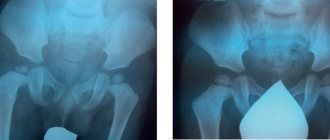
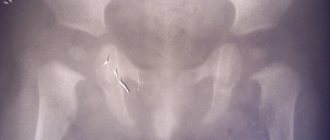
Fibrous dysplasia of the knee joint in children is a common form of this pathology. Its distinctive feature is that fibrous scar tissue is formed at the site of degeneration and destruction of collagen and hyaline cartilage. Gradually it becomes calcified (impregnated with calcium salts). At this stage, fibrous dysplasia of the knee joint is clearly visible on x-rays. These are areas of scar-type deposition of calcium salts in the thickness of the cartilaginous layer of the synovial membrane of the heads of the tibia and femur.
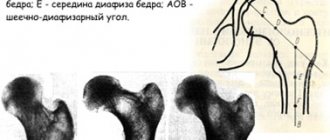
Congenital dysplasia of the knee joints begins to manifest itself during the period when the child begins to stand on his own legs and try to maintain balance. At this age, deviation of the head of the femur towards the internal axis and protrusion of the head of the tibia towards the outer edge will be visible. The deformation of the joint is compensated by incorrect placement of the foot. Children clubbing and try to place their feet on the outside of the sole.
Gradual deformation of the shin bones leads to curvature of the legs. It is necessary to carry out treatment and correction at an early age, as soon as the primary signs of the development of this disease are noticed.
Symptoms.
The most common signs of the disease are as follows:
- 1. 1. “Clicking” symptom. Based on this sign, dysplasia can be diagnosed already in the first week of a baby’s life. This symptom is characterized by the fact that when the legs are bent at the knees, a sound resembling a click is clearly heard. This sound indicates reduction of the hip bone into the acetabulum. When mixing, a similar sound is heard - it indicates the release of the hip bone.
- 2. Difficulty spreading the legs in different directions. This type of diagnosis is also used only in the very early stages of a child's life. Results may be incorrect just a few months after birth.
- 3. Differences in thigh length. It is determined as follows: the patient is placed on the table on his back, with his legs bent at the knees. If one knee is higher than the other, we can talk about pronounced joint dysplasia. This type of diagnosis is not suitable for the initial stages.
- 4. There is asymmetry of the buttock/inguinal folds in the infant. This diagnostic method is used only for children aged two to three months. If dysplasia is present, the folds on one of the legs will be located higher.
- 5. During sleep, external rotation of the hip is observed.
- 6. Lameness. It appears at stages when the pathology is already highly developed.
Knee dysplasia in adolescents
Functional, hormonal or traumatic dysplasia of the knee joints begins to develop spontaneously in adolescents. The first signs appear after serious physical activity:
- increased weakness in the calf muscles;
- pain in the knee area, aggravated by movement and palpation;
- redness of the skin and slight swelling;
- limited knee mobility.
All these primary signs pass quite quickly. In the future, the teenager may complain of increased fatigue of the leg muscles, difficulty standing for long periods of time, and swelling in the lower leg area. If an X-ray examination is performed at this time, a significant narrowing of the joint space will be revealed. Timely treatment will allow you to completely restore the impaired function of the knee joints.
If there is a hormonal imbalance in the process of cartilage tissue regeneration, you will need to consult an endocrinologist. If the etiology of dysplasia is associated with injuries, for example, during strength sports, then these loads must be excluded at least temporarily.
Diagnostics.
Typically, the following methods are used to detect joint dysplasia:
- X-ray examinations (can only be prescribed to children over three months old, since until the child reaches this age, the image will not show cartilage that has not yet passed the stage of ossification).
- Ultrasound of the joint - performed in infancy, one of the safest diagnostic methods.
- Tomography (computer or magnetic resonance imaging) is used if x-rays do not give a clear answer.
- Arthroscopy is a minimally invasive surgical method in which an arthroscope with a camera is inserted into the joint through a small incision.
Signs of knee dysplasia
With the exception of patellar dysplasia of the knee, signs of pathology may include lameness, O-shaped or X-shaped curvature of the lower extremities. With a small degree of dysplasia, external signs will not be characteristic. But with thinning of the cartilage layer, the load on the subchondral end plates will constantly increase. They will undergo a sclerosis process. This will cause a number of negative clinical signs to appear:
- gait disturbance;
- shortening of one limb;
- unsteadiness when walking;
- destruction of associated large joints (ankle and hip);
- cramps in the muscles of the leg and thigh in combination with restless legs syndrome at night;
- pain in the knee area with recurrent secondary forms of arthritis.
All these symptoms are a reason to contact an orthopedist. The doctor will conduct a manual examination, make an accurate diagnosis and give recommendations for treatment. In Moscow, you can visit an orthopedist for free in our manual therapy clinic.
Principles of rehabilitation of patients with connective tissue dysplasia
An important condition for effective rehabilitation of patients with various nosological forms of connective tissue dysplasia (CTD) is the correct choice of medical means: non-drug, medicinal or surgical. Many years of experience in dispensary observation of families of patients with various variants of hereditary connective tissue diseases and CTD, analysis of literature data made it possible to formulate the basic principles of treatment for these patients:
- Non-drug therapy (adequate regimen, diet, physical therapy, massage, physical and electrical treatment, psychotherapy, spa treatment, orthopedic correction, vocational guidance).
- Diet therapy (use of food products enriched with protein, vitamins and microelements).
- Drug symptomatic therapy (treatment of pain, improvement of venous blood flow, taking beta blockers, adaptogens, sedatives, hepatoprotectors, surgical treatment, etc.).
- Pathogenetic therapy (stimulation of collagen formation, correction of disorders in the synthesis and catabolism of glycosaminoglycans, stabilization of mineral and vitamin metabolism, improvement of the bioenergetic state of the body).
An obligatory stage in the management of patients with CTD after a comprehensive examination and diagnosis is a competent conversation between the doctor and the patient before starting rehabilitation therapy. It is necessary to gain the trust of both the patient and his parents in terms of the possibility of significantly improving the quality of life and restoring lost adaptive skills. Experience shows that the doctor should not waste time on this first, extremely important conversation, on which the effectiveness of rehabilitation measures largely depends. It is important to correctly and in an accessible form explain to the sick teenager and his parents:
- what is connective tissue dysplasia;
- what is the role of genetic and environmental factors in its origin;
- what changes in the body it can lead to;
- what lifestyle should be followed;
- how quickly the effect of the therapy occurs and how long it should be carried out;
- how often should instrumental studies be carried out;
- what are the possibilities of surgical and therapeutic correction;
- what are the dangers of playing professional sports and dancing;
- What are the restrictions in professional activities?
If necessary, consultation should be held on the issue of marriage and family, suitability for military service, etc. The purpose of this conversation is to instill the idea of the need for the patient’s active participation in treatment, prevention of complications, and identification of symptoms of disease progression. If possible, the patient should be convinced that the changes in connective tissue observed in him require a special lifestyle, the quality of which is largely determined by his efforts in the desire to help himself. It should be remembered that sufficient knowledge about the disease can help the patient look into the future without fear.
Next, we will allow ourselves to outline in more detail the basic principles of therapy for patients with DST.
Basic principles of non-drug therapy
Daily regime. In the absence of significant functional disorders of leading organs and systems, patients with CTD are shown a general regimen with the correct alternation of work (study) and rest. The exception is patients with osteogenesis imperfecta, who, in order to prevent fractures, need to lead a gentle lifestyle (wear corsets, use crutches, avoid trauma). Patients with osteoarthritis due to DST also require limiting the load on the affected joints. They are not recommended to run, jump, lift and carry heavy objects, squats, fast walking, especially over rough terrain, climbing mountains and walking up stairs. It is advisable to avoid a fixed position, such as prolonged sitting or standing in one position, which impairs blood flow to sore joints. If the joints of the upper extremities are affected, you should limit carrying heavy objects, manually pushing up heavy things, playing musical instruments, and typing on a hard keyboard. The rhythm of optimal motor activity for patients with osteoarthritis due to DST is a reasonable alternation of load (10–15 minutes) with periods of rest (5–10 minutes), during which the joint should be unloaded in a lying or sitting position. To restore blood circulation after exercise in the same positions, you should perform several movements in the joints (flexion, extension, bicycle).
Physical therapy is indicated for all patients with DST. Regular (3-4 times a week, 20-30 minutes) moderate physical training aimed at strengthening the muscles of the back, abdomen, and limbs is recommended. Exercises are carried out in a non-contact static-dynamic mode, in a supine position. Physical exercise should not increase the load on the ligamentous-articular apparatus and increase the mobility of the joints and spine. The method of physical therapy should definitely be discussed with a specialist. In this case, it is necessary to take into account the nature of the pathology, clinical, radiological, and biochemical criteria for damage to the musculoskeletal system. It is useful to prescribe sets of exercises performed while lying on your back or stomach. For most patients, hanging and spinal traction, types of contact sports, isometric training, weightlifting, and carrying large loads are contraindicated. Hydrotherapy and therapeutic swimming, which relieve static load on the spine, have a good effect.
Aerobic training of the cardiovascular system is recommended: dosed walking, skiing, traveling, hiking, jogging, comfortable cycling. Dosed physical activity on exercise machines and exercise bikes, badminton, table tennis, exercises with light dumbbells, and breathing exercises are useful. Systematic physical activity increases the adaptive capabilities of the cardiovascular system. However, if there are signs of its damage - myocardial dystrophy, cardiomyopathy, myxematous degeneration and significant prolapse of the valve leaflets, dilatation of the aortic root - excessive physical or mental stress, participation in any sports competitions is strictly prohibited. All patients with DST should not engage in professional sports and dancing, since excessive loads on functionally defective connective tissue will lead to an extremely rapid onset of its decompensation.
Therapeutic massage - relieves painful muscle spasms, improves blood supply, transmission of nerve impulses, trophism of the trunk muscles and joints. Recently, acupressure with a helium-neon laser beam, which has a biostimulating, analgesic, and sedative effect, has become widespread. Procedures are performed daily or at intervals of one or two days; It is advisable to undergo at least three courses of treatment (15–20 sessions) with an interval of one month. Underwater massage gives favorable results.
Physiotherapeutic treatment is used according to indications. Thus, with osteogenesis imperfecta, to accelerate the healing of fractures, with osteoporosis of various origins, electrophoresis of a 5% calcium chloride solution, 4% magnesium sulfate solution, 2% copper sulfate solution or 2% zinc sulfate solution is recommended on the collar area or locally. In case of vegetative-vascular dystonia syndrome of the vagotonic type, often accompanying DST, a 1% solution of caffeine sodium benzoate, ephedrine hydrochloride or mesatone is used - using the collar method or the ion reflex method according to Shcherbak. To stimulate the function of the adrenal cortex, drug electrophoresis with 1.5% etimizol and DMV is used on the area of the adrenal glands. To normalize vascular tone, water procedures are prescribed that provide “gymnastics” for blood vessels: general carbon dioxide, pine, hydrochloride, hydrogen sulfide and radon baths. At home, douches, rubdowns, contrast showers, salt-pine and foam baths are available. A very useful physiotherapeutic treatment method is a sauna (air temperature - 100 ° C, relative humidity - 10-12%, duration of stay - 30 minutes), course - 25 sessions over 3-4 months. Magnetic, inductive and laser therapy, electrophoresis with Dimexide (dimethyl sulfoxide), and brine are used quite widely to improve the nutrition of cartilage.
In order to soften dense connective tissue formations (for example, postoperative keloid scars), patients with DST undergo phonophoresis. For this purpose, use Collalysin (collagenase), 0.2% solution of hydrocortisone, water-soluble succinate, lidase; fibrinolysin. Electrophoresis using the 4-electrode method of ascorbic acid, sulfur, zinc, copper is widely used; chromotherapy (green, red matrix) according to the general method.
Psychotherapy . The lability of nervous processes inherent in patients with connective tissue pathology, feelings of anxiety and a tendency to affective states require mandatory psychological correction, because neurotic behavior and suspiciousness greatly influence their attitude to treatment and implementation of medical recommendations. The main goal of therapy is to develop a system of adequate attitudes and consolidate a new line of behavior in the patient’s family.
Sanatorium-resort treatment - allows for comprehensive rehabilitation, including the positive effects of therapeutic mud, hydrogen sulfide, radon, iodine-bromine baths, saunas, physiotherapy, massage and physical therapy exercises. It is especially effective if this treatment is carried out for at least three years in a row.
Orthopedic correction is carried out using special devices to reduce the load on the joints and spine. These include orthopedic shoes, instep supports, knee pads that can reduce knee joint laxity and cartilage trauma when walking, and elastic bandaging of hypermobile joints.
Surgical treatment of patients with DST is carried out strictly according to indications. Thus, in case of significant hemodynamic disturbances due to prolapse of the valve leaflets, massive aortic aneurysm, valve replacement and the changed portion of the aorta are performed. In cases of severe functional disorders of the cardiovascular and respiratory systems caused by severe deformation of the chest, thoracoplasty is performed. Progressive pain syndrome in patients with DST with severe grade III–IV scoliosis serves as an indication for surgical treatment. Lens subluxation, complicated by secondary glaucoma, retinal degeneration with the threat of retinal detachment and cataracts are absolute indications for surgical treatment (lens removal). Our practical experience shows that any surgical intervention in patients with pathology of connective tissue metabolism should be carried out only against the background of relative clinical and biochemical remission. After surgical treatment, patients should be under the supervision of specialists and receive, along with traditional therapy, drugs that improve connective tissue metabolism.
Lifestyle. Due to impaired DNA reparative ability, patients with DST The best place to live is the central belt. It is advisable to exclude stressors and sudden changes in professional activity. Weather-dependent patients should avoid professional and psycho-emotional overload on unfavorable days. It is important to prevent hypothermia of the upper and lower extremities. During the cold season, always wear gloves and warm socks. For women, especially when working standing, the use of compression hosiery (anti-varicose tights 50–70 denier) is recommended.
Professional guidance. Specialties associated with high physical and emotional stress, vibration, contact with chemicals and exposure to x-rays should be avoided.
Basic principles of diet therapy. Diet therapy for patients with connective tissue dysplasia is prescribed only after a preliminary examination by a gastroenterologist and (necessarily!) during a period of relative remission of chronic pathology of the gastrointestinal tract, which, according to our data, was observed in 81.6% of patients with DST. Protein-enriched foods are recommended. Additionally, meat, fish, squid, beans, nuts, protein and fatty acids, and foods containing essential amino acids are prescribed. Food products must be enriched with microelements, vitamins, and unsaturated fatty acids.
Patients without gastroenterological pathology are prescribed strong broths, jellied meat and fish dishes containing a significant amount of chondroitin sulfates several times a week. For the rest, it is advisable to take biologically active supplements (BAA) containing combined chondroprotectors 2-3 times a week. For children with excessive growth, food products (soybean, cottonseed oil, sunflower seeds, lard, pork fat, etc.) are recommended from an early age, as well as preparations with a high content of polyunsaturated fatty acids of the Omega class, which have an inhibitory effect on the secretion of somatotropic hormones. hormone.
Products containing B vitamins are shown - B1, B2, B3, B6, which normalize protein metabolism. A significant amount of vitamins of this group is contained in yeast, germs and shells of wheat, oats, buckwheat, peas, as well as bread made from wholemeal flour, liver, and kidneys.
Food products enriched with vitamin C (fresh rose hips, red peppers, black currants, Brussels sprouts, porcini mushrooms, citrus fruits, etc.) and vitamin E (sea buckthorn, spinach, parsley, leeks, chokeberries, peaches, etc.) are extremely important. , necessary for normal collagen synthesis and possessing antioxidant activity.
According to our data, the vast majority of children with connective tissue dysplasia have a decrease in the level of most macro- and microcollagen-specific bioelements. The most common deficiencies were silicon (100%), selenium (95.6%), potassium (83.5%); calcium (64.1%); copper (58.7%); manganese (53.8%), magnesium (47.8%) and iron (46.7%). All of them take an active part in the mineralization of bone tissue, the synthesis and maturation of collagen. In this regard, food enriched with macro- and microelements is recommended. An important point in diet therapy is maintaining optimal ratios in the diet between calcium and phosphorus (1:1.5), as well as calcium and magnesium (1:0.5), which, according to our data, is disturbed in patients with DST. An unbalanced diet can cause a negative balance of calcium and magnesium in the body and lead to even more severe metabolic disorders in the bones. The absorption of calcium is facilitated by the presence of lactose, proteins, and citric acid in food. This process is hampered by phytic acid, which is found in cereals, as well as oxalic acid, phosphates and various fats.
Principles of drug pathogenetic therapy
It is advisable to carry out pathogenetic drug therapy 1–2 times a year, depending on the patient’s condition; Course duration: 4 months.
Stimulation of collagen formation is carried out by prescribing drugs such as Piaskledin 300, Solcoseryl, L-lysine, L-proline, vitreous body in combination with cofactors for collagen synthesis - vitamins (C, E, group B) and microelements (Magnerot, Magne B6, zinc oxide , zinc sulfate, zinc aspartate, zincite, copper sulfate (Cuprum sulfate, 1% solution), zinc, selenium. Our studies revealed increased excretion of collagen breakdown indicators (hydroxyproline, pyrilinx D in daily urine, etc.) in 75% of examined patients with DST.
Chondroprotectors. The most studied are chondroitin sulfate and glucosamine sulfate. Over the past 20 years, dozens of controlled studies have been conducted to study the structure-modifying effects of these drugs. Their participation in the regulation of chondrocyte metabolism (increased synthesis of glycosaminoglycans and proteoglycans) has been proven; suppression of enzyme synthesis and increased resistance of chondrocytes to the effects of enzymes that damage articular cartilage; in the activation of anabolic processes of the cartilage matrix, etc. The drugs of choice are currently combined chondroprotectors (Arthra, Teraflex, Kondronova, Artroflex, etc.). We detected excessive secretion of glycosaminoglycans in daily urine in the majority (81.4%) of the examined patients with DST.
Stabilization of mineral metabolism . To improve the state of mineral metabolism in patients with DST, drugs are used that normalize phosphorus-calcium metabolism: vitamin D2, and, according to indications, its active forms: alfacalcidol (Alpha D3-Teva, Oksidevit), vitamin D3 BON, Bonviva, etc. Along with the above Above, various preparations of calcium, magnesium, and phosphorus are widely used to correct mineral metabolism. When treating with them, it is necessary to monitor the level of calcium, phosphorus in the blood or urine, as well as the activity of alkaline phosphatase in the blood at least once every 3 weeks. It is known that the need for calcium changes at different periods of a person’s life, therefore, when correcting mineral metabolism parameters, it is necessary to take into account the age-related daily need for calcium.
Correction of the bioenergetic state of the body is necessary due to the presence of secondary mitochondrial deficiency in patients with DST. In 80% of the children we examined, a secondary deficiency of total carnitine was detected. Improving the bioenergetic state of the body is facilitated by drugs containing phosphorus compounds: Dimephosphone, Phosphaden, Riboxin, Mildronate, Lecithin, Amber Elixir, Elcar, Carnitene, Coenzyme Q10, Riboflavin, Nicotinamide, etc.
Normalization of peroxidation processes is carried out by prescribing vitamins (C, A, E), Mexidol, citrus bioflavonoids, selenium, glutathione, polyunsaturated fatty acids.
Correction of free amino acid levels in blood serum
In patients with DST, as a rule, there is a decrease in the content of most nonessential and essential amino acids in the blood serum, most often due to impaired absorption through the gastrointestinal tract. Such secondary hypoaminoacidemia cannot but affect their general condition, contributing to a deterioration in the quality of life of patients. We have established a relationship between a decrease in the level of free proline, free leucine and isoleucine, an increase in free hydroxyproline in the blood serum and the severity of the clinical picture. Correction of the level of free amino acids in the blood is carried out through individual selection of diet, amino acid preparations or dietary supplements containing essential amino acids, as well as vitamins and microelements involved in their metabolism. Most often, in our experience, patients with pathologies of connective tissue metabolism require replacement therapy with lysine, proline, taurine, arginine, methionine and its derivatives, tyrosine and tryptophan. Amino acids are prescribed 30–60 minutes before meals. The duration of one course is 4–6 weeks. Repeated course - according to indications, at intervals of 6 months. Today, the doctor has a number of amino acid preparations at his disposal (Methioninum, Glutaminicum acidum, Glycinum, Dibikor and a number of biologically active food supplements.
Approximate treatment regimens for sick children with CTD
Depending on the severity of the clinical condition and the severity of biochemical disorders of connective tissue metabolism, it is recommended to carry out 1–2 courses of metabolite correction throughout the year. The duration of treatment is determined in each case individually, but on average it is 4 months with a break between courses of at least 2–2.5 months. If indicated, in the intervals between courses of drug therapy, physiotherapeutic procedures are performed and psychotherapy is carried out. Patients with DST need to constantly follow a regimen, diet, and engage in physical therapy.
I scheme
- Combined chondroprotector in an age-related dose. Take with meals; drink plenty of water. Duration of treatment is 2–4 months.
- L-proline. Dose for children aged 12 years and older: 500 mg; take 30 minutes before meals; frequency of administration - 1-2 times a day; duration - 1.5 months; according to indications, a complex of amino acids is prescribed (L-proline, L-lysine, L-leucine at the rate of 10–12 mg per kg of body weight, etc.); dosage frequency 1–2 times a day; duration - 2 months.
- Vitamin and mineral complexes such as “Vitrum”, “; dose - depending on age; Duration of treatment: 1 month.
Note: indications for prescribing this treatment regimen are a variety of patient complaints, especially damage to the musculoskeletal system, increased excretion of glycosaminoglycans in daily urine and a decrease in the content of free amino acids in the blood serum.
II scheme
- Combined chondroprotector in an age-related dose. Take with meals; drink plenty of water. Duration of treatment is 2–4 months.
- Ascorbic acid (in the absence of oxaluria and a family history of urolithiasis) in the form of cocktails (with milk, yogurt, jelly, compote, etc.); dose - 0.5–1.0–2.0 g per day, depending on age; Duration of treatment: 3 weeks.
- Amber elixir. Dose depending on age - 1-2 capsules 2 times a day (capsule contains 100 mg of succinic acid); Duration of treatment: 3 weeks.
Note: indications for the use of this regimen may include clinical and instrumental signs of damage to the musculoskeletal system, increased excretion of glycosaminoglycans in daily urine; normal levels of free proline and free lysine in blood serum.
III scheme
- L-lysine. Dose for children aged 12 years and older: 500 mg; take 30 minutes before meals; frequency of administration - 1-2 times a day; according to indications - a complex of amino acids (L-proline, L-lysine, L-leucine), selected individually; frequency of administration - 1-2 times a day; duration - 2 months.
- Vitamin E (preferably the natural form containing alpha-tocopherol or a mixture of tocopherols); dose for children aged 12 years and older and adults - from 400 to 800 IU per day; Duration of treatment: 3 weeks.
Note: the use of this treatment regimen is recommended if there are a variety of patient complaints; clinical and instrumental disorders of organs and systems, a decrease in the content of free amino acids in the blood serum and normal excretion of glycosaminoglycans in daily urine.
The use of the above schemes for individually selected and pathogenetically based correction of identified biochemical disorders in children with CTD is quite possible in an outpatient setting and practically does not require additional material and technical investments. Patients with DST require lifelong clinical observation, constant non-drug therapy and systematic courses of metabolic replacement correction.
T. I. Kadurina*, Doctor of Medical Sciences, Professor L. N. Abbakumova **, Associate Professor
*Medical Academy of Postgraduate Education, **St. Petersburg State Pediatric Medical Academy , St. Petersburg
Contact information for authors for correspondence
Treatment of knee dysplasia
Before treating knee dysplasia, it is necessary to conduct an examination to exclude the effect of destructive factors. The doctor then develops an individual course of treatment for knee dysplasia for each patient.
It may include the following impact options:
- kinesiotherapy – used to restore the amplitude of mobility of the injured limb;
- therapeutic exercises – increases blood supply to the muscles of the leg and thigh, accelerates microcirculation of blood and lymphatic fluid in the affected area;
- osteopathy – restores metabolic processes, triggers impaired diffuse nutrition of cartilaginous tissues;
- massage – improves the condition of all soft tissues, increases their elasticity and firmness;
- laser treatment starts the process of restoration of elastin, collagen and hyaline;
- reflexology speeds up the healing process.
The course of therapy is developed individually. The doctor takes into account the patient’s general condition, his age, weight, type of professional activity, presence of concomitant somatic pathologies, etc.
You can make an appointment right now for a free appointment with an orthopedist in Moscow at our manual therapy clinic. During the examination, the doctor will make an accurate diagnosis and tell you about all the possibilities and prospects for using manual therapy in your clinical case of knee dysplasia.