The muscular system of the human body is a collection of fibers that are capable of contraction and are combined into bundles - muscles, or are independently part of the internal organs. The muscle corset maintains balance and ensures movement of the body; thanks to the muscles, breathing is carried out, blood supply to organs occurs and food is transported. Therefore, when painful sensations appear, it immediately affects your general well-being. And for any person it is important to find out which doctor diagnoses and treats muscle pain in order to return to normal healthy life as quickly as possible.
Causes
Among the main causes of muscle pain are:
heavy physical activity;- injuries;
- being in a position that impairs blood circulation;
- flat feet or excess weight;
- walking in high heels;
- joint diseases;
- disorders of the musculoskeletal system;
- metabolic disorders;
- inflammatory processes;
- injuries: bruises, sprains, damage to bones and joints;
- bacteria, viruses and parasites as a source of intoxication;
- chronic fatigue;
- lack of vitamins B.
Attention! Qualified specialists from the Kuntsevo Treatment and Rehabilitation Center, which has modern diagnostic equipment, will help you find out the exact causes of persistent aching muscle pain.
Classification of types of muscle pain
Pain associated with injury, such as sprains and tears, rank high on the list of possible causes of pain. In addition to them, there are many types of pain that do not have external influences:
- Cramps . Most often they occur at night or in the morning. The muscle involuntarily contracts and then slowly relaxes, causing severe pain.
- Inflammation (myositis) is characterized by severe pain and muscle weakness. Inflammation of one or a group of muscles at once is a consequence of disruption of metabolic processes and their supply with nerves, through which communication with the central nervous system is ensured. During inflammatory processes in muscle tissue, a person not only feels pain, his mobility is limited and his general condition worsens. If a person regularly has back pain, then there is a possibility that he has myositis of the back muscles.
- Rheumatic diseases affect the muscles or the blood vessels that supply them. The leg (hip area) and shoulder joint are the most common locations of pain in such diseases.
- Metabolic disorders , for example, lack of potassium or enzyme deficiency, can cause not only muscle pain, these conditions often lead to paralysis. Children and young people are at risk after intense physical activity the day before. So pain in the arm is characteristic of metabolic muscle damage.
- Pain caused by genetic diseases or changes in the muscle cells themselves.
Pathologies
Pathological pain in the muscles, requiring a mandatory visit to a specialist, is expressed in the following:
- constant or chronic pain;
- twitching nature of the disease;
- pain appeared after training, but does not go away after rest;
- redness of soft tissues or swelling is observed;
- accompanying symptoms are observed in the form of fever, shortness of breath, rash, and urinary retention.
Important! If at least one of the above conditions occurs, it is recommended to contact a specialist.
Choosing a specialist depending on the cause of pain
After determining the cause of the pain, you can begin to search for a specialist who will prescribe treatment. Since there is no narrow specialization in muscle tissue in medicine, depending on the source of the problem, the following doctors can provide assistance: neurologist, orthopedist, surgeon and therapist, phlebologist and rheumatologist.
Conditions associated with damage to nerve endings: intercostal neuralgia, hernia of the spinal column, pinching, consequences of osteochondrosis are treated by a neurologist.
Muscle pain caused by injuries of varying severity (from sprains to micro-tears of muscle fibers) is the specialty of a traumatologist and surgeon.
If a person has impaired blood circulation in muscle tissue, then he will need to consult an angiosurgeon. As a rule, pain is accompanied by swelling, lameness appears and the nutrition of soft tissues is disrupted.
Timely contact with specialists allows you to avoid serious health problems in the future, such as the transition of the disease to the chronic stage.
Consultations with a doctor online Taking care of your health is a life priority for everyone.
Communicate with doctors online and receive qualified assistance without leaving your home. Try it Please note! The information on this page is provided for informational purposes only. To prescribe treatment, you must consult a doctor.
Which doctor treats
The treatment and diagnosis of such symptoms is carried out by neurologists, rheumatologists or surgeons.
All people experience muscle pain from time to time. If your muscles hurt after playing sports or after a long period of activity, there is nothing strange and there is no need to worry.
IMPORTANT! However, if you notice prolonged aching muscle pain that does not go away over a long period of time, this is a reason to consult a specialist.
Self-medication is not a way out of the situation, because there can be many reasons for the development of symptoms, ranging from injury to chronic inflammatory processes. Make an appointment with a neurologist at our center to understand the causes of your symptoms and choose the right and effective treatment tactics!
Muscle spasm
Probably every person has experienced muscle cramps at some point. In medical parlance, this condition is called “muscle spasm.”
Our muscles are constantly under tension; Thanks to muscles, our body moves, maintains its shape, muscle contractions ensure the functioning of many internal organs and systems of the body. But sometimes muscles contract unnecessarily, involuntarily, and such contraction can be painful. The spasm can affect any skeletal muscle of the musculoskeletal system, but the gastrocnemius muscle (the muscle of the back of the lower leg) and the thigh muscles are most often affected.
The muscle can cramp during increased stress (for example, when playing sports) or at rest (when sitting at a computer or while sleeping).
Lifestyle recommendations
As preventative measures for myalgia of various origins, it is important to avoid heavy physical activity and stress, not to get too cold, to fully treat infectious diseases and to lead a healthy lifestyle.
Aching muscle pain is a fairly common occurrence; sometimes it is harmless and goes away soon, but sometimes it is a consequence of serious diseases that require monitoring and treatment. Highly qualified specialists of the Kuntsevo Medical and Rehabilitation Center are ready to provide timely and high-quality assistance in resolving this issue.
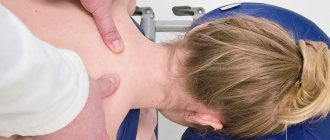
What is therapeutic massage?
Classic massage is a procedure based on the direct impact of the massage therapist’s hands on the body. The specialist rubs, kneads, and stretches the muscles. Human skin has a huge number of receptors, which, in response to exposure, transmit information to the nervous system, which, in turn, helps to relax or tone the muscles.
Stiffness, twisting, and excessive tension are the causes of pain. These factors interfere with the normal recovery of the body after injuries and operations, stressful situations, even after intense physical and mental stress. As a result of the massage, all these clamps are removed, and the body finally gets the opportunity to properly restore its resource.
Typically, therapeutic massage includes a certain number of procedures; for example, a patient may be prescribed 5–10 sessions.
At the same time, classical massage does not aim to find the causes of torsion and stiffness. It works with symptoms and external manifestations, therefore it is often prescribed as part of rehabilitation procedures after various injuries and operations. It is indicated for both athletes who need to regain strength and ordinary healthy people.
With osteopathy it is a completely different matter. It is aimed at eliminating the cause of pain and tension in the muscles, which, as a rule, is not at the level of the myofascial apparatus, and, with rare exceptions, in the muscles and ligaments themselves.
What is the difference between massage and osteopathy?
Fundamental differences between the two areas include:
- an effect on bones and joints that is not found in massage practice, but osteopathy does. An osteopathic doctor can “set” the bones, eliminate displacement, as painlessly and without any discomfort as possible;
- craniosacral therapy - restoration of biological and cranial rhythms of the body. Normalization of cerebrospinal fluid dynamics.
- In osteopathy there are visceral techniques (not to be confused with visceral massage)
- providing a complex effect on the body, inside and out. Osteopathy has this, while massage only has an external effect on the muscles and skin.
- In osteopathy there are techniques for working with muscles, but they are usually performed auxiliary.
- An osteopath is a doctor, a massage therapist is not.
Osteopathy “turns on” the body’s natural recovery mechanisms, helping the body to heal on its own. The only thing osteopathy and massage have in common is that the specialist’s hands “touch” the patient’s body.
And one more thing, ladies and gentlemen. There is no osteopathic massage. This is a lie .
What to choose, classic therapeutic massage or osteopathy? Osteopathy does not dispute the advantages of massage. Massage has existed as long as humans have existed. In some cases (for example: myofascial syndrome) massage is very effective. But, if you want to get rid of the cause of pain and prevent its return after completing the course, then choose osteopathy.
What is osteopathy?
Osteopathy views the human body as a system in which each part is connected to others through innervation, blood supply, lymph flow, hormonal tissue dependence, specific intersystem metabolism, fascia, and muscles. Notice that the muscles are named at the end here. Why? Because the muscular system is reactive, and it reacts to any changes in the body by increasing or decreasing tone, and also serves to maintain postural tone (orientation of the body in space). The reason where the muscle will be the object of close attention of the osteopath is, as a rule, direct mechanical injury. And then the osteopath will treat the muscle directly. In all other cases, the osteopath’s work with muscles is secondary (muscle energy techniques, post-isometric relaxation, isolytic and isokinetic techniques, myofascial release, muscle chain techniques, joint mobilization, etc.). And these techniques have nothing to do with massage.
The body's resource is practically endless, it is capable of self-healing, and the task of an osteopathic doctor is to stimulate this process, working at deep levels.
That is, osteopathic techniques and massage were not even close. These are completely different approaches to healing the body.
Like a massage therapist, an osteopath works with his hands, but the points of application of his hands are different. The manipulations are painless and do not cause discomfort, so they can be shown even to small children and the elderly.
How does osteopathy work as an example? For example, a person complains of constant pain in the form of cardialgia (pain in the heart area), but clinical studies have not found any problems with the heart, but there is pain in the heart area, especially when inhaling, including if you press on the skin in the area of several ribs and muscles of the intercostal spaces. He had already been treated by a neurologist, as there was a suspicion of intercostal neuralgia, but there was no result. And then the osteopath gently performs the “rebound” technique on several vertebrae, eliminates the displacement and torsion of the 5th rib using the muscle energy technique (MET), removes the intraosseous tension of the rib, relaxes the respiratory diaphragm, the coronary ligament of the stomach, etc.... The cause of the pain was the tension of the periosteum of the rib, which very richly innervated due to its twisting. And the pain instantly goes away.
From the point of view of osteopathy, the cause of the disease and its symptoms may be completely unrelated at first glance, and the knowledge of an osteopathic doctor allows us to suggest something that is simply not the task of a therapist or neurologist. Have you noticed how many manipulations the osteopath performed to free the rib?
And where is the massage? And would he help?
Rheumatological complex
Rheumatological diseases in humans are most often associated with joint diseases, although various organs and systems may be affected. How can one suspect a rheumatological disease and what tests need to be taken?
Rheumatological diseases represent a large group of diseases that affect the connective tissue of the body. They are also called autoimmune or systemic diseases. Autoimmune - because the immune system loses the ability to recognize “self or foe” and produces antibodies against its own cells and tissues. Systemic - since connective tissue is contained in all organs and vessels, therefore all body systems are affected to one degree or another. The cause of rheumatological diseases is not completely clear. But the consequences are serious, and early recognition is important for timely treatment and prevention of complications.
How can one suspect a rheumatological disease?
- Severe tiredness, fatigue, general malaise - signs similar to those at the beginning of a cold;
- Muscle and/or joint pain
- Swelling of the joints, changes in the tissue around the joint, up to deformation
- Pain when pressing on a joint or muscle
- Episodes of mild or prolonged fever
- Random detection of elevated ESR in a clinical blood test or C-reactive protein.
The above signs can occur with a number of other diseases, although often they are the only “alarm signals” to start an examination.
In fact, changes often occur in the heart, lungs, kidneys, nervous system and other internal organs, but they do not have clear manifestations. Sometimes you notice signs of skin damage - in the form of various rashes. Redness of the facial skin in the shape of a “butterfly” occurs with systemic lupus erythematosus; thickening of the skin of the fingers with scleroderma.
How is the diagnosis made?
In order to establish a rheumatological disease, the doctor evaluates 2 criteria:
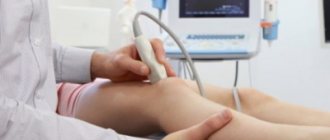
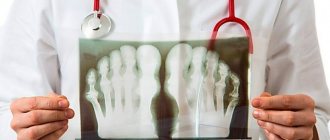
- Manifestations during the collection of complaints, examination and instrumental methods (X-ray, ultrasound, CT). In medical parlance, this is called a “clinical criterion.”
- Laboratory signs
Only on the basis of a joint assessment of clinical and laboratory criteria is it possible to establish a diagnosis of a rheumatological disease and distinguish which disease from the whole group occurs. No criterion is used in isolation!
For your convenience, the main laboratory tests are combined into the “Rheumatological, advanced” complex.
What is included in the complex?
- C-reactive protein is the main indicator of inflammation; in rheumatological diseases it increases significantly, but does not allow us to understand what kind of disease has developed.
- Uric acid increases in the blood and accumulates in the joints during gout.
- Antistreptolysin-O – increases with rheumatism.
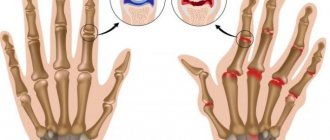
- Rheumatoid factor (total antibodies) and Antibodies to cyclic citrullinated peptide are markers of rheumatoid polyarthritis - the most common rheumatological disease, which mainly affects the small joints of the hands with morning stiffness and rapidly developing deformation of the joints when detected late.
- Antineutrophil cytoplasmic antibodies, IgG (ANCA, Combi 6) - are used to diagnose vasculitis. This is an inflammation of small blood vessels, when the kidneys (glomerulonephritis), lungs and upper respiratory tract are mainly affected.
- Antinuclear antibodies, immunoblot - includes the determination of autoantibodies to 14 different antigens. Depending on the identified antigen, the doctor will be able to understand what disease the patient has: systemic lupus erythematosus, scleroderma, Sjogren's syndrome, polymyositis.
- Antibodies to Chlamydia trachomatis, IgG - their determination is important for assessing immunity to chlamydia and excluding Reiter's syndrome. This is an immunological lesion of the urethra, eye tissue and joints, which develops as a result of a long-standing chlamydial infection.
What do you need to take and how to prepare for the study?
To test for rheumatological complex, venous blood is donated in the morning on an empty stomach or 3 hours after a light meal. It is recommended to give up alcohol the day before.
Rheumatological disease is well treated in the early stages. Pay attention to your health, be attentive to yourself and get examined in a timely manner!