The concept of “deposition of salts” in organs and tissues does not apply to medical terminology. This is what people in the vast majority of cases call the formation of osteophytes - growths of the edges of bones in various types of degenerative-destructive pathologies of the musculoskeletal system, accompanied by pain, crunching in the joints, and their deformation. However, an osteophyte is not a deposit of “salt”, but is a newly formed, physiologically inferior tissue that is structurally vaguely reminiscent of bone. The symptoms described may be associated with various diseases that have their own causes of development.
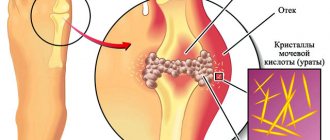
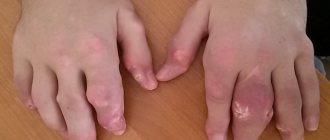
Thus, disturbances in purine metabolism lead to the development of gout, in which crystals of urates (uric acid compounds) are deposited in the joints and periarticular tissues. Being a foreign body, urate provokes the development of an inflammatory process (gouty arthritis) with severe pain and limitation of motor activity. The small joints of the hands and feet are most often affected. In addition, urate deposits in soft tissues and subcutaneous fatty tissue result in the formation of yellow nodules (tophi), which appear in the elbows, ears, extensor surfaces of the forearms, thighs, legs, Achilles tendons, and on the forehead.
Disorders of calcium metabolism with precipitation of calcium salts from the dissolved state and deposition in tissues and organs are characteristic of calcinosis (metabolic, metastatic and dystrophic). Thus, local disturbances in metabolic reactions lead to the deposition of calcium salts in muscles, subcutaneous fat, and skin. Most often the hands, elbows, ears, lower limbs, buttocks, back, and large joints are affected. A high concentration of calcium salts in the blood (hypercalcemia) is fraught with calcification of blood vessels and internal organs. The causes leading to hypercalcemia may be diseases of the parathyroid and thyroid glands, bones, kidneys, intestines, and hypervitaminosis D.
Why does salt deposition occur in the body?
Salt deposition in joints is not a myth, and there are many reasons for this pathology. The problem may be caused by:
- poor diet or excess weight;
- genetic disorders of water-salt metabolism;
- hypothermia;
- injuries;
- diseases of the kidneys or circulatory system;
- endocrine disorders;
- wearing uncomfortable shoes, which leads to microtrauma of the articular surfaces.
Knee injuries often lead to salt deposits in the joint
Physiotherapeutic procedures and exercise therapy
To prolong and enhance the effect of drugs, rheumatologists prescribe 5-10 sessions of physiotherapy to patients. When the pathology worsens, electrophoresis is performed with NSAIDs, analgesics, and glucocorticosteroids. Under the influence of a weak electric current, they penetrate into places where salts are deposited, exhibiting an analgesic, anti-edematous and anti-inflammatory effect. At the stage of remission, the patient is recommended to carry out the following physiotherapeutic manipulations:
- UHF therapy;
- laser therapy;
- magnetic therapy;
- diadynamic currents.
The procedures differ in the mechanisms of action on the diseased foot, but have similar healing properties. Metabolism and regeneration (healing) of damaged cartilage, bone and soft tissues are accelerated. The result of stimulating blood circulation is the removal of uric acid salts, accumulated products of the inflammatory process, from the joints. Some physical procedures can be performed at home during the remission stage. We are not talking about a variety of devices whose therapeutic effectiveness has not been confirmed by any clinical trials. Rheumatologists and orthopedists recommend making medicinal applications at home:
- with bischofite. In pharmacies, the drug is sold in the form of a brown, thick liquid with a specific odor. A sterile napkin is moistened in it and placed on the foot for 2-3 hours. Bishofite is also used for foot baths in a ratio of 1:10;
- with ozokerite or paraffin. These natural substances with a high content of beneficial minerals are packaged in the form of crystals. They are melted in a water bath, cooled slightly and applied with a wide brush or wooden spatula to the foot in several layers. The duration of the procedure is 2-3 hours.
Regular performance of special exercises will help to increase the blood supply to the joints with useful substances. This is a frequent slow flexion of the toes, walking first on the heels, then on the toes. Doctors recommend that patients with gouty arthritis purchase an orthopedic mat. It consists of several sections, each of which imitates a certain natural surface - sand, large and small pebbles. Walking on a mat every day helps strengthen muscles, ligaments and tendons, and prevent blood from pooling in the feet.
Or maybe it's calcification?
Sometimes pathological processes occur in the joints that are directly related to impaired salt metabolism. Calcinosis is the deposition of calcium salts in tissues and organs due to malfunction of the parathyroid glands. Other causes are diseases of the bones, kidneys, hypervitaminosis D.
There are two types of the disease:
- metabolic calcification develops due to a local metabolic disorder in tissues, with salts being deposited in muscles, skin and subcutaneous fat;
- metastatic - caused by a high concentration of salt in the blood (hypercalcemia), so they are deposited on the walls of blood vessels and in the internal organs.
If the concentration of salts in the body is normal, they are dissolved in the liquid and participate in various processes. When oversaturated, they are deposited in organs and tissues, on teeth and in blood vessels, forming growths ranging in size from small peas to formations the size of a walnut. The most common locations are the hands, elbows, lower extremities, ears, back, buttocks and large joints.
Such areas with “salt deposits” are mobile and dense to the touch, and their palpation does not cause pain in a person, with the exception of the shoulder joint. The skin over them stretches and takes on a blue tint, but there is no inflammation. Over time, the formations become softer, whitish grains are released from them - lime, which helps to diagnose “calcinosis”.
Calcification in the shoulder joint is always accompanied by pain
Traditional methods
Bay leaf Among home remedies that even doctors of official medicine can recommend, a decoction of bay leaves is very popular. This simple spice, which every housewife can find, perfectly breaks down salts and removes them from the body. It is necessary to drink a decoction of bay leaves in courses. Take for a week and repeat after a month. Brew a pack of leaves (20g) with a liter of boiling water and leave in a thermos for about half an hour. Drink the infusion throughout the day in small sips in several doses. The product has a strong diuretic property. This must be taken into account to avoid potassium being washed out of the body and causing harm to the cardiovascular system. You can use vitamin complexes high in potassium or eat increased amounts of foods rich in this element. Ointments, compresses and lotions will help relieve inflammation in the foot and reduce pain. You can use burdock leaf, calendula tincture or its leaves, ground with vegetable oil. Poultry-Indian onion Tincture of Indian onion with vodka will help improve blood circulation in the foot, relieve inflammation and reduce pain. Poultry plant tailed is the second name of this indoor plant. All parts of the plant are healing for joint diseases and salt deposits. You can infuse a few leaves of this home remedy with vodka and rub it into the sore area of the foot every day. But it is better to use the plant bulb to prepare a medicinal tincture. The product has virtually no contraindications. An ointment based on pork fat with the addition of cinquefoil, calendula, and golden mustache is easy to prepare and is considered one of the most effective means of combating salt deposits. Melt the fat and add chopped vegetable raw materials. Cool and use instead of massage oil to rub into the affected area of the foot.
Or gout?
With gout, salts are deposited in the joint tissues. This occurs due to a violation of the metabolism of uric acid salts - urates, the concentration of which in the blood increases sharply. Microcrystals of urate settle in the joint capsule and sooner or later lead to inflammation.
Gout happens:
- primary - caused by a genetically incorrect structure of enzymes that are responsible for the exchange of uric acid and urate in the body;
- secondary – develops against the background of psoriasis, chronic renal failure, myeloid leukemia, congenital heart disease or other disease.
Gout manifests itself in acute attacks that occur mainly at night. The metatarsophalangeal joint of the big toe is most often affected. The skin turns red, blue, and the local temperature rises to 39 °C. The inflammation subsides after a few days, but symptoms recur periodically. If the disease is mild, the person experiences minor pain and there is noticeable redness at the joint. In addition to the big toe, gout also occurs in other joints - wrist, elbow, hand.
If the disease is not treated, polyarthritis may develop against its background, and tophi - yellow nodules containing urates - will appear at the site of the lesion. Such formations, which are often confused with “salt deposits,” occur in the area of the elbows, fingers, nasal septum and on the ears.
Gout loves people who lead sedentary lifestyles
Symptoms
Salt deposits in the foot have such varied symptoms that not all doctors are able to identify the pathology the first time, since the first place is not so much the symptoms of salt deposits as the signs of complications that this pathology provokes. Among the leading signs of the disease, doctors note:
Traditional medicine against joint pain
- pain when walking, a feeling of heaviness in the foot, discomfort when stepping on a hard surface;
- swelling of the foot, especially worse in the morning;
- change in skin color at the site of salt deposition, increased vascular pattern;
- feeling of numbness in the foot, the occurrence of cramps;
- crunching in the joints when rotating the foot;
- change in gait as the patient tries to spare the foot;
- if salt deposition accumulates most heavily in the first toe, then inflammatory processes of a wave-like nature, a local increase in temperature, and hyperemia of the phalanx of the toe are characteristic;
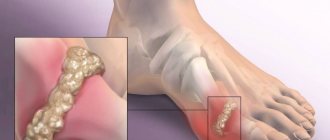
- If salt deposits are predominantly in the heels, then patients develop a heel spur - a disease in which a growth appears in the heel area.
Arthrosis and salt deposition
Very often, people who need treatment for arthrosis or osteoarthritis are convinced that they have a banal salt deposit, especially when it comes to the joints of the first toes. In fact, arthrosis, like the age-related changes in the joints characteristic of it, has nothing to do with this pathology. Joint enlargement is only the growth of subchondral bone.
Cartilage performs two functions - gliding and shock absorption. If it is regularly subjected to impact, the bone in this area thickens. Since mechanical impact is exerted on the joint while walking, certain parts of it are injured. This promotes the growth of cartilage tissue - the formation of spines. The cartilage is no longer able to perform a shock-absorbing function, stops sliding and gradually wears out.
The situation can be corrected through intra-articular injections of a synovial fluid substitute, for example Noltrex. The product evenly fills the joint capsule and pushes the worn cartilaginous surfaces apart. The friction stops and the joint functions are restored.
Arthrosis and salt deposition have nothing in common
Is table salt good for the body or should it be excluded from the diet forever? Opinion of authoritative osteopathic doctor Alexander Evdokimov:
Causes
Salt deposits should not be considered as a separate disease. Rather, these are the consequences of metabolic disorders and various failures of the excretory system. Therefore, it is necessary to get rid of the problem together with treatment of the underlying disease. Salt deposits can be caused by:
- Hormonal imbalance;
- Diabetes;
- Chronic kidney and liver disease;
- Gout;
- Thyroid diseases.
In case of kidney disease, the removal of uric acid from the body is insufficient. This promotes the accumulation of salts.
How to properly treat salt deposits
No competent doctor will undertake to treat “salt deposits” until a diagnosis is established. In any case, you will need to follow a special diet to prevent relapses and speed up the removal of salts from the body. Instead of spicy, fatty, fried foods, patients are shown vegetable and dairy foods. You can rid your body of salt using parsley, dill, melon, watermelon, plums and persimmons.
Drug treatment for salt deposits includes:
- non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs - ointments or tablets;
- hormonal drugs;
- uricosuric medications to lower uric acid levels.
Whatever the cause of the joint pathology - calcification, gout or arthrosis - safe physical activity, such as swimming, will not be superfluous. Sports, like a massage course, will speed up the blood supply to tissues, and with it the removal of salts from the body.
Nutrition
Scientists recognize that food consumed by humans can have a negative impact on health.
But by changing the quality of your diet, it is quite possible to get rid of many diseases. This is especially true for diseases associated with metabolic disorders. If salts are deposited, it is recommended to exclude fatty and spicy foods, limit the consumption of strong tea and coffee, and give up alcoholic beverages. The food should consist of fruits high in pectin. Apples and persimmons will replace a whole complex of pharmacy vitamins. Vegetables and fruits that act as diuretics will help speed up the removal of uric acid and prevent the deposition of salts. It is necessary to exclude heavy foods from the diet, at least for the duration of treatment. Share:
Traditional medicine
Homemade ointments and rubs, infusions and decoctions are used only as an auxiliary method of treatment. Their use is relevant at the stage of remission, when medications have relieved acute pain and inflammation. To improve kidney function and cleanse the entire body of toxic substances, traditional healers recommend using infusions with a weak diuretic effect. To prepare them, pour a heaping tablespoon of dry raw material into a liter of boiling water, leave for 2 hours, filter and drink throughout the day. Diuretic activity is characteristic of the following medicinal plants:
- bear ears;
- corn silk;
- erva woolly.
The localization of the pathology in the foot allows the use of foot baths with warm water in treatment. The procedures improve blood supply to the affected joints with nutritional and bioactive compounds, and help remove salt crystals from them. Infusions of string, St. John's wort, and elecampane are added to the water (3 tablespoons per glass of boiling water). Baths with 4-5 drops of essential oils of eucalyptus, thyme, pine, juniper, oregano, and fir help to cope with morning stiffness. The following folk remedies have proven themselves well in the treatment of gouty arthritis:
- ointment to speed up blood circulation. In a mortar, mix 30 g of petroleum jelly, honey, and pork fat. Gradually add 1 drop of essential oils of thuja, thyme, mint and a tablespoon of cosmetic almond oil into the thick mass. Store in the refrigerator, rub into the foot 2-3 times a day;
- compresses that remove salts from joints. Lightly mash a large young leaf of horseradish, cabbage or burdock, apply a thin layer of thick honey to its surface and place on the foot. Cover with film and thick cloth, secure the compress with an elastic bandage. The treatment procedure lasts from 2 to 5 hours. After removing the compress, small crystals of released salts are noticeable on the dried leaves.
Grind from young fresh horseradish root.
It is not advisable to use rubs containing vodka or alcohol. In the treatment of gouty arthritis, oil extracts with a warming effect are usually used. The most effective is considered to be rubbing from young fresh horseradish root. It is crushed and placed in a dark glass container. Pour in olive, linseed or regular sunflower oil so that it is 1 cm above the plant material. Store in a warm, dark place, shake periodically to improve the extraction of beneficial substances into the oil. The foot rub is ready in 1.5-2 months.
Although the disease cannot be completely cured, if all medical recommendations are followed, the patient can lead an active lifestyle and remain functional. An unfavorable prognosis is typical only when salt deposits in the foot are caused by severe kidney pathologies. To maintain their functional activity, patients are prescribed lifelong medication, and in some cases, surgery.