Causes and pathogenesis of cervical injuries
Injury to the cervical spine can be caused by a blow to the neck area or an extreme extension or flexion movement of the head. Typically, spinal injuries caused by excessive head movement are called "whiplash" in the case of a car accident and "diver's injury" due to hitting the head on the bottom of a body of water. Such spinal injuries are usually accompanied by severe impairment of the spinal cord and can lead to death.
Injuries to the first two cervical vertebrae are considered the most severe and dangerous. The first cervical vertebra, also called the atlas, is often injured as a result of a sudden fall on the head. In this case, the occipital bone of the skull puts strong pressure on it, and the posterior and anterior arches break. The patient complains of acute pain in the neck, back of the head and crown of the head. The second cervical vertebra, called the axis, breaks when the neck is suddenly bent. Complications from this injury range from neck pain to paralysis of the limbs.
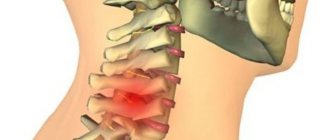
The cervical spine includes seven vertebrae, of which the lower ones are most often damaged - 4, 5 and 6. This usually happens due to sharp flexion of the neck. Signs of a (cervical) injury include severe neck pain, excessive tension in the neck muscles, and limited head rotation.
Diagnostics
When the victim is taken to the hospital, doctors will conduct a physical examination and a complete neurological examination to determine the nature and location of the injury.
Based on the examination data, the patient is prescribed imaging methods that make it possible to determine morphological changes in tissues after injury.
Radiography -
allows you to diagnose fractures and dislocation of the vertebrae.
CT
– this research method is necessary for better visualization of both bone and soft tissues that are damaged during spinal trauma. In addition, CT is a more preferable diagnostic method when the patient’s condition is critical and it is necessary to quickly determine the cause of the condition and prescribe emergency therapy.
MRI.
This method is useful for identifying signs of spinal cord injury, hemorrhages and other morphological changes in soft tissues.
EMG (ENMG) -
allow you to determine nerve damage and the level of damage.
ECG, ultrasound, laboratory methods
studies are prescribed to exclude other consequences of injuries, especially when it comes to combined injuries resulting from accidents/
Densitometry -
necessary if osteoporosis is suspected.
Birth injuries of the cervical spine
During childbirth, the baby is exposed to mechanical stress, which can cause serious spinal injury. Incorrect position of the fetus or its excessive weight, post-term pregnancy and other reasons can lead to subluxation in the joints of the first two vertebrae, displacement of their bodies or damage to the intervertebral discs. Complications of injury may be as follows:
- disruption of the normal functioning of cerebral blood flow,
- violation of venous outflow,
- development of spasms,
- disruption of the functioning of the central nervous system, which is accompanied by a delay in the development of the child.
Due to the injury, the child may later begin to hold his head up, crawl, or walk. In addition to problems with the formation of the musculoskeletal system, he also experiences delayed speech development. Disturbances in the normal functioning of the central nervous system negatively affect memory and concentration. That is why injuries to the cervical spine that occur immediately after the birth of the baby should be treated immediately.
Symptoms indicating a cervical spine injury in a newborn:
- problems with motor development;
- decreased or complete absence of several reflexes;
- problems with self-feeding;
- spasms of the limbs, lack of flexion reflexes;
- digestive disorders (constipation, flatulence, diarrhea);
- headache, loss of consciousness;
- tachycardia occurs periodically;
- the child develops more slowly than his peers - he usually raises his head later, begins to sit down and stand up on his own;
- the speech and mental development of the baby is disrupted;
- the spine is formed incorrectly, which is accompanied by its deformation, different leg lengths, and flat feet.
What are the symptoms of whiplash?
Whiplash is a very insidious disease. It takes a person by surprise, sometimes the collision is immediately forgotten, and the result of the blow can only appear after some time. Signs of what happened are visible in a third of patients almost immediately, in others - within two to three days after the injury. Doctors call this asymptomatic period “light.” In any situation, the consequences of what happened can be equally serious.
The signs of whiplash are varied, but there are leading symptoms.
- Pain
Intense pain appears in the area of the back of the head and shoulders immediately or after a few days. It becomes stronger when raising the arms and limits the mobility of the neck, especially when tilting the head forward or throwing it back. Occasionally, pain radiates to the upper limbs and interscapular area.
- Dizziness
Complaints of dizziness occur in every fourth victim. It comes in different intensities. In this regard, nausea and imbalance may occur, and in severe cases, vomiting.
In addition to the main symptoms, patients often complain of:
- neurological symptoms: facial paresthesia, tinnitus;
- sudden pain in the occipital region, pain radiates to the temples, eyes hurt;
- depression with symptoms of insomnia, anxiety, fatigue;
- inattention, forgetfulness;
- problems with the eyes - the appearance of a veil in front of them, blurred outlines, light bursts, loss of visual fields;
- phenomena of dysphagia - difficulty swallowing
Sometimes whiplash is accompanied by a concussion. Then its symptoms become more pronounced - weakened concentration, decreased memory. Due to damage to the nerve roots, radiculopathy and myelopathy are diagnosed.
Types of whiplash according to severity
First:
With a mild concussion, the victim may not feel anything. Symptoms increase slowly and are minor. After a few days (sometimes weeks), minor pain in the neck may appear. The victim feels nausea, complains of attacks of dizziness, numbness in the fingers. All these complaints can suddenly disappear on their own, so with a minor injury and mild symptoms, patients may not turn to a specialist. This degree of lesion occurs most often.
Second:
In this case, symptoms appear instantly, immediately after the incident. The pain is severe, the neck cannot move, and head mobility is limited. The victims do not put off visiting a specialist and turn to him on the very first day after the injury. The second degree is observed in a third of applicants.
Third:
The third degree is observed in 12% of patients with the conclusion “whiplash injury”. There are already focal neurological signs here. The patient complains of severe dizziness, disturbance, and vomiting. Tendon reflexes may be weakened or absent, there may be paresis, and there may be a loss of sensitivity.
Fourth:
Symptoms appear immediately. The pain affects all parts of the spinal column. The process involves the bones and cartilage of the main human skeleton. There may be dislocations and fractures of the vertebrae, and neurological signs are pronounced. Patients contact a specialist immediately.
Classification of injury by course
- The most acute period is up to four days
- Acute period – from four days to 21 days
- Subacute period - from the 22nd day to 1.5 months.
- Intermediate – from 46 to 180 days
- Chronic – symptoms last more than six months
The longer the complaints persist and the symptoms persist, the worse the prognosis. 8% of victims are diagnosed with “post-whiplash syndrome”
Post-whiplash syndrome clinic.
Post-whiplash syndrome usually appears when recovery is slow, that is, if the recovery process drags on for more than six months. It is characterized by painful movements in the neck and, therefore, limited mobility. The patient complains of visual disturbances, paresthesia of the hands, numbness of the fingers. Others notice the victim's hostility and emotional instability. This situation may persist for years. Typically, this complication is typical for women over 55 years of age who are prone to suspiciousness and depression.
Establishing diagnosis
In case of whiplash injury, in addition to the mandatory questioning and physical examination, the specialist prescribes instrumental examination methods. Only an integrated approach allows a correct diagnosis to be made.
- Survey.
While collecting information, the doctor may ask the following questions:
- when did symptoms appear?
- nature of the accident;
- where the patient was in the car (during a car accident);
- what was the person’s condition at the time of the accident;
- are there any external injuries - abrasions, bruises;
- has your vision changed?
- whether dizziness appeared after the injury;
- whether the patient swallows easily;
- Are there any urinary problems?
- Are there any complaints about memory disorders, have absent-mindedness or irritability appeared;
- are there any difficulties in completing complex tasks;
- whether there have been spinal injuries before;
- Physical examination
During the examination, the doctor pays attention to:
- is there a spasm of the cervical muscles (is the cervical spine straightening);
- how the patient’s head behaves in a calm state, when tilted in different directions, when flexing and extending;
- is there nystagmus;
- whether pain in the shoulder and paravertebral muscles is palpable;
- is there any sensitivity of the skin in the occipital region;
- is there a hematoma or swelling on the surface of the neck;
- hand reflexes are checked;
Instrumental examination
In addition to collecting an anamnesis, finding out all the details of the injury and examining the patient, the doctor prescribes an instrumental examination of the cervical spine, which allows us to identify deeper injuries.
- X-ray. X-rays are carried out immediately after the injury; this examination is the most important, as it gives a general picture of what happened. The examination excludes a fracture of the spine, allows you to determine the presence of spasm in the cervical muscle group - straightening of the cervical lordosis (the main sign of whiplash injury)
- Electromyography (EMG) and measurement of nerve conduction velocity (ENG). These studies make it possible to determine damage to nerve endings and are carried out in cases of persistent pain.
- Discography. The study is prescribed for severe, persistent pain; contrast is injected into the spinal disc and the resulting picture is analyzed.
- Magnetic resonance imaging and CT scans determine the presence of ligament ruptures, hemarthrosis and cartilage damage.
- Diagnostic analysis of the musculoskeletal system - DIERS 4D MOTION - this innovative technology allows you to identify the slightest deviation in the structure of the spinal segments and is an excellent alternative to x-rays.
If necessary, the patient is examined by an ophthalmologist and a neurologist. Only after a thorough examination and history can a diagnosis of whiplash injury be made and the optimal treatment prescribed.
The European Center for Orthopedics and Pain Therapy presents a wide range of the most modern equipment, which provides a high percentage of reliability. New technologies are absolutely harmless, informative and have a number of advantages over classical examinations.
Treatment of birth cervical injury
Injury to the cervical spine almost always provokes serious health complications for the child. That is why its treatment should begin from the first days of a newborn’s life. The most suitable treatment methods are considered osteopathic, which allow you to gently and delicately eliminate the problem. During the examination of the baby, the doctor identifies tension in different layers of tissue, then creates tension and a fulcrum, thereby allowing the tissues to straighten.
Particular attention is paid to the tissues of the head, since it is in them that blood vessels pass and part of the cerebrospinal fluid flows out. It is worth noting that even during a safe and normal birth, the baby’s head (especially the occipital bone) experiences severe stress as it makes its way through the birth canal. The neck rests on the base of the skull, and the base of the head consists of a large number of cartilages. During childbirth, these cartilages may shift, which leads to pinching of cranial vessels and nerves.
Osteopathic techniques for treating a newborn are selected individually. Their use allows you to relax muscles and eliminate pain, activate blood circulation, which will promote rapid healing. The main preventive method of birth trauma is considered to be regular monitoring of the pregnant woman by the attending physician and timely elimination of health problems.
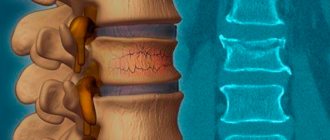
Vertebral body fracture
Vertebral body fracture
The cause of such an injury is strong compression (squeezing) of this area or a strong spontaneous blow.
Characterized by the following symptoms:
- with a fracture of 1 vertebra (atlas), pain is felt at the site of injury, and also spreads to the back of the head and parietal region;
- Damage to the 2nd vertebra is characterized by discomfort when turning the head from side to side. Numbness of the fingers or temporary paralysis are possible;
- injury to the 3rd vertebra leads to pain and severe limitation of movement;
- the muscles in the area of the fracture often swell, become hard and swollen.
- in rare cases, breathing difficulties, headaches, increased heart rate and dizziness may occur.
The most complex fracture is the one with splinters. In this case, touching the head, pulling or turning is prohibited. The victim should be placed on a hard, horizontal surface. Fix the neck in the position in which the head is located. You can put a collar-type cushion under your neck.
Principles of treatment of cervical injuries
Treatment of cervical spine injury should begin with diagnosing the injury. The patient must receive emergency first aid aimed at maintaining normal blood circulation and breathing. It is important to correctly immobilize the spinal injury—the patient should be placed in a neutral position and splinted. When moving the patient, his head should also occupy a neutral position - rotation, flexion and extension of the neck should be avoided in every possible way.
Conservative treatment of neck injuries involves the use of immobilizing bandages and cervical orthoses. As soon as possible after injury (the first few hours), a procedure of closed reposition of the cervical spine should be performed, aimed at restoring the correct anatomy of the spine. In severe cases, surgical intervention is prescribed. Indications for surgery are uncomplicated dislocations and subluxations, compression of the spinal cord due to displacement of the vertebral bodies and its fragments, and chronic dislocations of the cervical vertebrae.