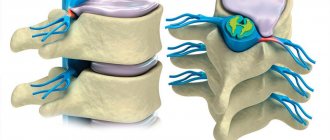
One of the effective operations for removing herniated intervertebral discs is endoscopic discectomy. In this procedure, the herniated disc is removed using microscopic instruments inserted through an endoscope.
Brief history: In 1990, Parvis Kambin described the anatomical safe zone, which caused the endoscopic spine area to evolve into the percutaneous nucleotomy technique (this project uses a needle-like material). This issue gradually led to the development of larger materials, but nowadays in endoscopic discectomy, laser is used to cut the nerves grown in the ruptured disc layer, and this also helps to compress the tears without damaging the disc.
Let's find out what endoscopic discectomy is and how it can help with your treatment.
Key Facts of Transcutaneous Discectomy DISC-FX
- Indications for surgery: painful protrusion of the intervertebral disc
- Progress of the operation: Insertion of a surgical cannula (hollow needle) into the damaged area
- Inpatient treatment: from 2 to 5 days
- Rehabilitation treatment: 14 days outpatient or inpatient
- Discharge from hospital: 7 days after surgery
- Recommended hospital discharge: 21 days after surgery
- Showering is allowed: 1 day after surgery
- Recommended sick leave stay: 28 days
- Driving is not recommended: 14 days
Minimally invasive endoscopic treatment of intervertebral disc
A bulging or herniated disc can put pressure on the spinal cord and nerve roots of the spine, causing a person to experience severe back pain. If this pathology cannot be cured using conservative methods such as physiotherapy and pain therapy, nucleoannuloplasty is performed - a minimally invasive surgical treatment of back pain associated with a displaced intervertebral disc.
medical request
Contraindications and common complications
If the examination reveals that the threat from the operation exceeds its positive consequences, surgery is not performed. There are cases when it is impossible to do without surgery, and here the patient independently decides whether to take the risk or not. Common contraindications to surgery:
- oncological diseases at different stages of development;
- encephalopathy - organic brain damage;
- significant narrowing of the spinal canal;
- post-stroke or post-infarction condition;
- severe heart failure;
- acute stage of nervous disorder;
- infectious process in the spine;
- allergic reaction to anesthesia.
If you ignore at least one of the above contraindications, the operation can lead to negative consequences and serious complications. Complications also arise due to low qualifications or carelessness of a specialist, so you need to choose a surgeon as responsibly as possible. Poor surgical intervention can be accompanied by compression of nerve endings, damage to the spinal cord, dysfunction of the pelvic organs, heavy bleeding, suppuration of bones and tissues of the spine.
Terminology
- Transcutaneous discectomy DISC-FX Combined surgery on the intervertebral disc due to the combination of biophysical effects of several methods of spinal surgery, including mechanical removal of part of the disc and intradiscal electrothermal annuloplasty.
- Intervertebral disc protrusion:
Protrusion of the intervertebral disc, which causes pressure on the nerve roots and spinal cord. - Discogenic pain:
Back pain caused by intervertebral disc material pressing on nerve roots or the spinal cord. - Endoscopic surgery for herniated disc:
seamless surgery on the intervertebral disc using a surgical cannula (hollow needle). - Percutaneous nucleotomy:
A minimally invasive (endoscopic) intervention during which an instrument is installed into the disc through a puncture of the skin in the lumbar region under the control of special equipment and a video camera is inserted, under the control of which the protrusion of the intervertebral disc is removed.
Robotic surgery
Robotic surgery refers to the use of a special robot controlled by a remote control. All operations on the spine are performed by robotic technology under the supervision of a surgeon.
These manipulations are relevant when performing both open and closed operations. The main advantages: maximum precision of movements, minimal risk of accidental damage to nearby tissues and organs, short postoperative recovery time.
Advantages of the Disc-FX method
Radio wave Disc-FX nucleoannuloplasty is an innovation in the field of minimally invasive surgical treatment of the spine. During this intervention, using puncture access through a 2 mm puncture, destruction of nerve endings is carried out quickly and with minimal trauma. Then the surgeon inserts a special needle into the damaged intervertebral disc, after which part of the substance of the intervertebral disc is removed and the nerve is coagulated. As a result, patients experience not only a decrease in pain, but also decompression of the spinal nerve root, as well as restoration of intervertebral disc function.
The Disc-FX method is a combined operation that includes two minimally invasive interventions - on the intervertebral disc and on the spine.
- A thermal process to reduce volume by evaporating intervertebral disc tissue (ablation).
- Removal of hernial protrusion using surgical forceps inserted percutaneously (nucleotomy).
Benefits of endoscopic treatment of intervertebral disc
- A minimally invasive method that does not leave scars in the soft tissue area.
- Fast wound healing.
- No surgical suture.
- Multifunctionality (treatment of protrusion and herniated disc, denervation)
- No pain after surgery.
- No need for inpatient rehabilitation.
- Possibility of performing the procedure under local anesthesia.
- Possibility of treating several intervertebral discs in one session.
Epiduroscopy
The indication for epiduroscopy is a suspicion of an inflammatory process in the spine, as well as ongoing pathological processes. This procedure is aimed at examining the space between the vertebrae and the hard shell of the spinal cord. As a result, the specialist receives an image of anatomical structures - color and volumetric, and determines the signs of inflammatory processes.
During surgery, radiographic control is performed and local anesthesia is used. The endoscope is inserted through a small hole, which saves the patient from the formation of postoperative scars. 100% safety is guaranteed, rehabilitation time is 4-5 days.
Radio wave Disc-FX®-nucleoannuloplasty
Radio wave Disc-FX nucleoannuloplasty is performed under dual X-ray and endoscopic control. This helps the surgeon determine and eliminate the cause of back pain, as well as evaluate the results of the operation at each stage.
Detailed description of the course of transcutaneous discectomy using the Disc-FX system?
- Evaporation of parts of the semi-liquid nucleus pulposus using high-frequency current.
- Reducing the volume of a bulging intervertebral disc and restoring its normal shape.
- The damage to the annulus fibrosus heals and the nucleus pulposus is retracted.
- Reducing the pressure of the intervertebral disc on the nerve roots.
- Complete relief from back pain radiating to the legs (inflammation of the sciatic nerve)
Recovery after spine surgery
There is such a widespread belief that the positive outcome of the operation depends approximately 70% on the correct rehabilitation period and patients’ compliance with the basic rules of recovery. Rehabilitation after spinal surgery is necessary for every patient, even with minor intervention - there are no exceptions in this matter.
The rehabilitation period after spinal surgery depends on the general health of the patient and the nature of the manipulation. Mandatory procedures:
- physical therapy and professional massage;
- training on special simulators and kinesiotherapy;
- wearing orthopedic corsets and bandages;
- reflexology and physiotherapeutic techniques.
The main goals of the rehabilitation period are to reduce pain, prevent complications, restore motor functions, and shorten the time for complete recovery. All actions, their duration and loads must be agreed upon with the attending physician.
Our clinic has been performing such operations successfully for a long time. A high level of professionalism, modern equipment and low prices for spine surgeries are our competitive advantages.
When is the effectiveness of transcutaneous discectomy using the Disc-FX system limited?
Alternative Methods
- Minimally invasive removal of hernial protrusion (nucleotomy)
- Removal and coagulation of tissues Thermal heating of tissues.
In some cases, reducing the volume of the intervertebral disc alone is not enough to treat discogenic back pain: sometimes the strong fibrous ring surrounding the intervertebral disc is simply not able to return to its original position. In the worst case, this may lead to additional complaints, accompanied by shooting pains in the back and legs. When this problem occurs, specialists use an improved principle of the Disc-FX method, namely contraction of the fibrous ring by thermocoagulation.
Reduction of the annulus fibrosus using the Disc-FX method
Using a special probe of the Disc-FX system, in addition to reducing the volume of the nucleus pulposus, specialists have the opportunity to carry out targeted treatment of the fibrous ring.
The thermocoagulation method uses the effect of high temperatures created by a thermal probe on the affected formations of the fibrous ring to interrupt pain impulses, after which a decrease in the volume of the hernia and a decrease in pressure on the nerve roots are observed. Using this thermal method, it is possible to reduce the number of pain receptors in the walls of the intervertebral disc and, thus, get rid of discogenic back pain. The patient feels the positive effect of the operation right in the operating room.
Make an appointment
Radio wave Disc-FX nucleoannuloplasty. Progress of the operation
Anesthesia and patient position
Typically, the patient lies on his side during surgery. In most cases, the intervention is performed under local anesthesia under the supervision of an anesthesiologist.
2.Endoscopic discectomy using the Disc-FX system
After identifying the damaged segment of the intervertebral disc during an X-ray or CT scan, a guide probe is inserted into the intervertebral disc under local anesthesia using a special needle. During the manipulation, a thin probe under X-ray control is inserted directly into the intervertebral disc, after which the fibrous ring is coagulated or folded under the influence of temperature, which helps eliminate compression of the nerve roots and pain.
Due to limited heat generation, the pain fibers of the fibrous ring of the intervertebral disc are removed. Also, this technique allows you to get rid of discogenic pain.
Autologous chondrocyte transplantation
During transcutaneous discectomy using the Disc-FX system, additional manipulations can be performed without the need for additional surgical access. The specialist can insert the necessary instruments through an existing hole in the skin. Then, using an endoscope, the doctor assesses the condition of the nerve roots. Autologous chondrocyte transplantation
During transcutaneous discectomy using the Disc-FX system, additional manipulations can be performed without the need for additional surgical access. The specialist can insert the necessary instruments through an existing hole in the skin. Then, using an endoscope, the doctor assesses the condition of the nerve roots.
In addition, on the same day, intervertebral disc material can be collected for cultivation. After the necessary processing in the laboratory, it is used for the purpose of autologous cell transplantation (ADCT - Autologous intervertebral disc cell transplantation).
What postoperative care is needed?
Activities in general:
- You should only lie on a firm mattress, and never lean on sofas or reclining chairs.
- You can lie on your back or side, but never on your stomach.
- If you are sitting, use only a comfortable, straight-backed chair to provide proper support for no more than half an hour at a time. You can gradually increase your sitting time.
- Obviously no bending, pushing, lifting or straining.
- Avoid housework by exclusively vacuuming and sweeping the house.
- Because of this, you may feel tired after surgery; healthcare professionals suggest that you take 2-3 naps a day.
- You can continue cooking until you lift anything heavier than 10 pounds.
- Consider proper body mechanics to maintain a neutral spine.
- Increasing pain is a red alarm warning you to rest.
- Do not engage in strenuous activity for at least 10 weeks after surgery.
1st week after surgery:
- You may need to use your hands or assistance to climb stairs.
- You can ride in a car as a passenger, but never drive or go on long trips. In addition, it is important that the time in the car is less than 20 minutes.
- Take pain relief supplements as directed, don't try to "get over it." You will heal faster if you feel better.
- Walk around the house on a smooth, level surface. Try spending half a day in ambush.
- Do not lift anything heavier than 10 pounds.
2nd week after surgery:
- Light housework, but still no vacuuming or cleaning.
- You can drive for less than 20 minutes at a time as long as it doesn't make you feel uncomfortable as a passenger.
- Be sure to make your first post-op visit.
- Let your healthcare provider recommend an exercise program at your first visit after endoscopic discectomy.
- Increase walking to 1 mile per day if tolerated.
- Avoid sexual activity during this period of time.
3rd week after surgery:
- It's okay to use a hot tub or spa if you're "scab free."
- Increase your walking time and housework as long as you don't get teased.
- At this point, you can return to your sexual activity if it is relatively painless.
- If you need to lift something, it's still best to be careful not to exceed 25 pounds and use proper body mechanics.
4th week after surgery:
- Increase your driving time as much as possible.
- Return to work will be discussed with your doctor because this issue differs from patient to patient.
- Slowly increase your walking to 1-2 miles per day or as tolerated.
- Increase housework as much as possible.