When should you go to the hospital?
To prevent the occurrence of the above diseases, you need to consult a specialist in time. Here are additional symptoms after which you must go to a neurologist:
- The back pain has been going on for 2 weeks now and is getting worse.
- After discomfort in the back, my legs began to hurt in the knee area.
- Severe attacks appear suddenly without much stress.
- The pain began after a certain injury related to the back.
- During attacks, breathing becomes difficult.
- The pain is accompanied by fever and weakness.
- Spasms appear in the stomach and chest.
Does your back hurt? Check your urine
Many people are familiar with aching pain in the lower back firsthand. And, for the most part, this is the result of muscle overstrain. However, the same pain is a sign of a much more serious problem, for which “warming” ointment is already contraindicated.
Down up
The lumbar region, as is known, corresponds to the projection of several organs at once, and the pain that occurs here can be the result of:
- muscle strain,
- diseases of the spine and pelvic bones,
- ovaries and uterus,
- intestines,
- kidney
At the same time, distinguishing one pathology from another only by the nature of the pain is most often quite problematic. Therefore, the clinician's attention is directed to the history, examination and associated signs.
So, if lower back pain was preceded by symptoms of cystitis, the kidneys immediately come under suspicion.
The fact is that pyelonephritis (or bacterial inflammation of the kidneys), in most cases, is of an ascending nature. And it starts with the “classic” signs of a urinary infection:
- frequent urination
- and false urges to “go to the toilet”,
- pain in the groin area
- and/or when urinating,
- burning in the urethral area
- and a significant deterioration in general well-being.
It is also noteworthy that such symptoms can be both bright and faded, mild in nature. They strongly depend on the individual characteristics of immunity. And they require examination even in case of minor “inconveniences”.
Without treatment, a urinary infection quite quickly “moves” to the level of the kidneys, which provokes the appearance of a dull, aching pain in the lower back, which can easily be confused, for example, with “sciatica.”
However, the latter is never accompanied by fever, while with pyelonephritis the body temperature reaches 40 degrees and above.
It is characteristic that such a temperature “reacts” rather weakly to antipyretic drugs. And without antibiotics, the situation can end in sepsis, the formation of large purulent foci (carbuncles) and purulent melting of the kidney, requiring surgical intervention. .
Who's at risk
The main culprits of pyelonephritis, as well as urinary infections in general, are bacteria:
- coli,
- Proteus,
- staphylococcus
However, inflammation can also be caused by other types of bacteria, as well as fungi of the genus Candida.
Therefore, people at increased risk for pyelonephritis include:
- existing chronic diseases of the urinary and reproductive systems (urethritis, cystitis, vaginitis and others), which serve as a source of infection;
- diseases that cause urinary stagnation:
- urolithiasis disease,
- BPH,
- tumors of the bladder and uterus
- and some others;
- and reduced immunity (chronic stress, hypothermia, vitamin deficiency, postoperative period and others).
And women, due to the wide and short urethra, and children under 7 years of age are especially susceptible to pyelonephritis.
Analyzes
When the first symptoms of a urinary infection appear, you must test:
- General blood test with leukocyte formula (1.0.D2.202)
- and urinalysis (6.1.D1.401).
It is true that it is important to note that an increase in blood leukocytes, characteristic of all inflammatory processes, may not occur with pyelonephritis.
Whereas in the urine, an increase in leukocytes, bacteria and nitrites is a mandatory sign.
However, a general urine test can confirm, but not indicate, the level of spread of urinary infection. And for this you should undergo an ultrasound of the kidneys.
A feature of pyelonephritis is often unilateral kidney damage, which is visible from ultrasound results. True, you shouldn’t “delude yourself” too much here, because in some cases the inflammation can be atypical in nature, and then on an ultrasound the kidneys can look “quite decent”, despite all the signs of existing inflammation.
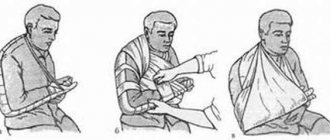
How to act in case of severe pain?
- Drink your painkiller right away.
- Contact your doctor immediately.
- Lie down immediately and try to relax as much as possible. Do not get up until the pain subsides.
- You should not sit or lean forward during attacks of pain.
Prevention of back pain
To prevent the development of the disease and attacks of pain, it is enough to follow some recommendations:
- Train yourself to exercise daily. It should not put a lot of stress on the spine. It is enough to twist your body, pull yourself up and twist. Repeat the warm-up every morning and during periods of prolonged sitting.
- Buy a special orthopedic mattress and small pillows. Quality sleep affects the health of your back.
- Don't burden yourself with weights. Try to distribute any weight between two hands. It is best to purchase a backpack in which you can carry heavy things without harm to your health.
- Forget about sudden movements. Perform any action slowly and calmly.
- Train yourself to get up at least every hour after working at the computer for a long time. It is enough to take a break for 5 minutes and do a short warm-up.
- If you lift heavy things from the floor, be sure to bend your knees when doing so. Straight legs put a lot of stress on the spine.
- Pay attention to your posture, walk straight and don't slouch.
Diagnostics
Primary diagnosis is carried out by a traumatologist-orthopedist. If there are neurological symptoms, the patient is examined by a neurologist. The doctor interviews the patient and carries out an objective examination. According to indications, consultations with a surgeon, rheumatologist, urologist, and other specialists are prescribed. The diagnostic program may include:
- Neurological examination.
During the examination, the specialist evaluates reflexes, muscle strength, coordination of movements, deep and superficial sensitivity. - X-ray.
X-rays of the lumbar region show fractures, decreased height of intervertebral discs, other degenerative changes, space-occupying formations, signs of inflammatory processes, and spondylolisthesis. If necessary, standard radiographs are supplemented with functional studies. - Other neuroimaging techniques
. MRI is also used to clarify radiographic data. When performing a computed tomography, the structure of hard structures is studied in detail, and the condition of ligaments and intervertebral discs is examined using MRI. To exclude stenosis, myelography is performed. - Functional Research
. The condition of muscles and nerve conduction is assessed using electromyography, electroneurography, and evoked potential studies. - Lab tests
. To confirm the infectious nature of the disease and determine the pathogen, blood tests and microbiological examinations are performed. Serological tests are used to detect neuroinfections.
According to indications, ultrasound of the kidneys, prostate, pelvic organs, urine tests, ultrasound of the abdominal aorta, and other studies are performed.
Manual therapy
Severe back pain
Let's take a closer look at diseases that cause sharp and severe pain:
- Radiculitis. Painful sensations are accompanied by slight tingling and burning. Discomfort radiates to the leg and buttock. The pain gets worse when you start walking or coughing heavily.
- Osteochondrosis. The attack intensifies as soon as you lift something heavy. Sometimes pain occurs near the heart. In this case, you have thoracic osteochondrosis.
- Intervertebral hernia. Pain appears not only in the back, but also in one of the legs. It becomes harder to make side turns and normal bends.
Symptoms of coronavirus COVID-19
Coronavirus
COVID-19
71667 January 27
IMPORTANT!
The information in this section cannot be used for self-diagnosis and self-treatment. In case of pain or other exacerbation of the disease, diagnostic tests should be prescribed only by the attending physician. To make a diagnosis and properly prescribe treatment, you should contact your doctor. Definition
The SARS-CoV-2 virus spreads in microscopic particles of fluid released by a sick person during coughing, sneezing, talking, singing or heavy breathing and gets onto the mucous membranes of the nose, mouth or eyes of another person.
In addition, the virus can also spread through household contact, when particles with the virus located on surfaces or objects enter the mucous membranes of the respiratory tract through the hands.
Aerosol transmission occurs in closed, crowded and poorly ventilated areas.
The airborne dust (aerosol) transmission route is realized through the spread of aerosols (droplet nuclei) suspended in the air, the size of which is <5 microns. Due to their small size, aerosols can be transported over long distances and remain in the air for several hours. It must be remembered that aerosol-producing devices (nebulizers, halochambers, etc.) are prohibited for use in healthcare institutions during the COVID-19 pandemic.
Symptoms of mild COVID-19
Most common symptoms
- The main symptom (80-90%) is any increase in body temperature (even low-grade - 37-37.5°C).
- The cough is dry or with a small amount of sputum (60-80%).
- Increased fatigue (40-50%).
Less common symptoms
- Sudden loss of smell and/or taste (60-80%).
- Nasal congestion or mild rhinorrhea (5%).
- Conjunctivitis or redness of the eyes (1-2%).
- Sore throat (14%).
- Headaches, dizziness (8-14%). Immediately after the end of the incubation period, migraines of varying severity may appear.
- Pain in joints and muscles (11-15%).
- Skin rashes (8%).
- Diarrhea, nausea, vomiting (up to 20%).
- Chills (11-13%).
Those who have had a mild form of COVID-19 infection compare the sensations with the course of a common respiratory disease.
Symptoms of COVID-19 in severe and moderate forms of the disease
Most common symptoms
- Shortness of breath, rapid breathing (55%).
- Increased cough, appearance of sputum (30-35%).
- Hemoptysis (5%).
- Loss of appetite (20%).
- Confusion (9%).
- Sensation of constriction and congestion in the chest (> 20%).
- Body temperature above 38°C (80%) for more than 5 days.
- Blood oxygen saturation according to pulse oximetry (SpO2) ≤ 95% (up to 20%).
Less common symptoms
- tachycardia,
- vitamin D deficiency,
- irritability,
- convulsions,
- anxiety,
- depressed state
- sleep disorders.
Important! Symptoms may not be detected during the incubation period of COVID-19 or may appear in any combination (for example, without fever). The exact diagnosis is determined by the doctor based on the results of examinations.
Patients over 65 years of age may experience an atypical picture of the disease, which includes delirium (cloudedness of consciousness), speech impairment, movement disorders, as well as more severe and rare neurological complications - stroke, inflammatory brain damage, and others.
The majority (about 80%) of patients who develop symptoms recover without hospitalization. Approximately 15% of patients develop a severe form of the disease that requires oxygen therapy, and 5% develop an extremely severe form that requires treatment in an intensive care unit.
Differences between the new coronavirus disease COVID-19 and ARVI and influenza
COVID-19 also refers to ARVI - acute respiratory viral infections characterized by similar symptoms: cough, runny nose, fever, headache, sore throat and sore throat. The most clearly defined clinical picture is caused by influenza viruses, parainfluenza, and adenoviruses. Coronavirus can be more severe than other acute respiratory viral infections, leading to complications and even death. That is why it is extremely important to distinguish the new type of coronavirus from a relatively harmless cold.
What is the difference between coronavirus and ARVI?
- Longer incubation period. For ARVI, 2-3 days are enough to go into the acute phase, but coronavirus takes up to 2 weeks.
- Unlike other acute respiratory diseases, coronavirus causes a low body temperature of 37-37.5°C, which can last a relatively long time (up to 7 days).
- A cough when infected with coronavirus is often long-lasting, dry, painful and may be accompanied by chest pain.
- Coronavirus infection can cause digestive upset (diarrhea, nausea, vomiting); such phenomena are rare with ARVI in adults.
- ARVI is usually cured in 7-10 days, and COVID-19 on the 7-8th day in a certain percentage of people can move to the next stage, when shortness of breath and respiratory failure appear.
Only a laboratory test will help you accurately name the type of pathogen and establish the disease (coronavirus, ARVI, influenza).
What is the difference between coronavirus and flu
It should be noted that COVID-19 and influenza have much in common:
- transmitted by airborne droplets and contact;
- may manifest as aching joints, headache, severe weakness and a general feeling of weakness;
- Intestinal disorders may occur.
Main differences:
- The flu begins acutely with an increase in temperature immediately to febrile values (39-40⁰C). Symptoms of general intoxication come to the fore: headache, weakness, pain in muscles and joints, lacrimation, pain in the eyes.
- Coronavirus develops gradually - from general malaise in the first days to severe symptoms, including a significant increase in body temperature after a week.
It is important that a doctor determine the difference between coronavirus and influenza, since both diseases can lead to dangerous complications, including pneumonia.
If a person has the flu and not coronavirus, he also needs medical care and treatment under the supervision of a therapist. Other diseases with similar symptoms
Pneumonia, including atypical.
Allergies. Shortness of breath, problems with smell, and other symptoms may occur as a result of exposure to allergens. The problem is solved by antihistamines, which are ineffective for viral infections.
Bronchial asthma, which also makes itself felt by difficulty breathing and a painful cough, but is non-infectious in nature.
Are symptoms different in children and adults?
Children make up only about 2% of all COVID-19 cases. At the same time, they tolerate coronavirus infection more easily and are often asymptomatic carriers.
The course of COVID-19 in children of different ages:
From 1 year to 3 years
The infection usually manifests itself as a mild illness. There are no characteristic symptoms of COVID-19. Sometimes there is a loss of appetite, which goes away after 2-3 days and does not affect the baby’s general well-being.
From 3 to 7 years
Children at this age are sick for about seven days and recover without complications. They may experience hoarseness and mild nasal congestion. There is no cough, occasional sneezing is possible.
From 7 to 17 years old
Primary schoolchildren and adolescents may experience a slight increase in body temperature and mild malaise. A dry cough is possible, and even less often - a headache.
According to Rospotrebnadzor, a mild form of the disease is usually due to the patient’s strong immunity.
The immune system of children and adolescents is usually well prepared to fight viruses. They can become infected, but their disease is milder or completely asymptomatic.
Stages of disease development taking into account symptoms
Symptoms of coronavirus in an adult by day
1-3 days. The disease begins with mild malaise, a slight increase in temperature, nasal congestion and muscle pain, as with ARVI or influenza.
3-5th day. Body temperature rises, and a mild, superficial cough is possible. The sense of smell may disappear, and taste sensations may change greatly. Digestive disorders occur, including diarrhea. This period is considered the culmination of a mild form of COVID-19.
5-10th day. An important period for determining the severity of coronavirus infection. 80% of people sick with COVID-19 experience improvements, which can lead to a full recovery in a few days. The second scenario involves a worsening of the condition, which is manifested by an increase in the number and severity of symptoms. With this development of events, the patient develops a severe runny nose, debilitating cough, chills, body pain, and shortness of breath.
10-12th day. This period is characterized by severe shortness of breath, chest pain, progression of weakness, and pallor, which indicates the development of pneumonia. Damage to the lungs leads to oxygen starvation. Hospitalization required. This condition is considered moderate.
12-14th day. With COVID-19, 75% of patients with viral pneumonia begin to recover on average 2 weeks from the onset of the disease. However, those who develop severe disease may require mechanical ventilation.
14-30th day. It takes on average up to two weeks from the onset of a serious complication to recover from a severe form of pneumonia caused by coronavirus.
But even after complete recovery, mild shortness of breath may persist, weakness and malaise may appear for a long time (up to several months).
Clinical variants and manifestations of COVID-19
- Affects only the upper respiratory tract.
- Pneumonia without respiratory failure.
- Acute respiratory distress syndrome (pneumonia with acute respiratory failure).
- Sepsis, septic (infectious-toxic) shock.
- Syndrome of disseminated intravascular coagulation, thrombosis and thromboembolism.
- Blood oxygen saturation is less than 88%.
Patients with critical COVID-19 develop vascular endothelial dysfunction, bleeding disorders, thrombosis, and thrombotic microangiopathy.
A cytokine storm in COVID-19 is the body’s response to an inflammatory process, leading to immune cells attacking not only the virus, but also the tissues of the body’s own. The consequence of this can be the destruction of tissues and organs, and, as a consequence, the death of the body.
It is very important that sometimes COVID-19 is dangerous not only because of pneumonia and its complications, but also because it has a negative effect on blood vessels, the brain and the heart, which increases the risk of stroke. In such cases, the patient experiences dizziness, fainting may occur, the face turns blue and the muscles become numb.
Symptoms indicating the healing process
Attention!
The time intervals for the course of the disease are arbitrary; they depend on the individual characteristics of the organism. COVID-19 in mild form usually lasts no more than 14 days. But only an antibody test can confirm final recovery. Given the severity of the disease, the recovery process can take place in different ways. The criterion for recovery is if two consecutive tests for coronavirus using the PCR method gave a negative result.
Acute back pain
It occurs in the case of such diseases:
- Lung diseases. If the attack is felt in the shoulder blades and chest. The temperature rises sharply and weakness appears throughout the body.
- Lumbago. People who engage in physical labor every day are susceptible to illness. If you stop exercising, the pain will go away on its own within a week.
- Diseases of the genitourinary system. In addition to back pain, the stomach begins to ache and the temperature rises.
- Disc displacement in the spine. Appears after dislocations and severe fractures. May occur when lifting heavy objects.
- Renal colic. Sharp pain in the abdomen that radiates to the genitals.
Other types of pain
- Chronic pain. Occurs with spondylosis. Pain not only in the back, but also in the back of the head and neck. Weakness appears in the legs, sometimes severe numbness.
- Leg pain. This is a sign of inflammation of the sciatic nerve. The pain is not only in the back and legs, but also in the buttocks, lower back and foot.
- It's a dull pain. Appears with myositis. The pain is not severe, however, it lasts quite a long time. The disease appears after severe hypothermia and stress on the back.
Diagnosis of back pain
To determine which of the above diseases is beginning to develop, the doctor must refer you for diagnostics.
- Ultrasound diagnostics.
- Laboratory research and testing.
- MRI – magnetic resonance imaging.
- ECG – electrocardiogram.
Treatment of back pain
An experienced specialist will prescribe a set of procedures to completely relieve back pain. Here are the most common treatment methods:
- Back massage . Thanks to the correct impact on the back muscles, posture improves, tension and pain go away.
- Mud treatment . Therapeutic mud is applied to the back and a wrap is made. It nourishes tissues with minerals and nutrients and removes harmful toxins. After the procedure, the pain goes away.
- Spinal block . If inflammation occurs in a certain area of the spinal discs, a blockade can relieve it. The doctor injects the drug with a syringe into the area of inflammation. This method allows you to get rid of severe pain in a few minutes and has a therapeutic effect.
Causes and danger of increased body temperature with osteochondrosis
People suffering from osteochondrosis try to collect as much information as possible about it in order to know exactly the symptoms of its manifestation and methods of treatment. Some people have a completely reasonable question: is elevated body temperature one of the symptoms or signs characterizing the disease? It turns out that yes, this phenomenon does occur.
For what reasons can the temperature rise?
Fever can be a consequence of too intense stress and overwork, resulting in a complication of osteochondrosis - protrusion, which is also called a harbinger of the development of an intervertebral hernia. By massaging the entire spinal column with light movements, you can accurately determine the location of painful sensations. If this is successful, then we can assume that the cause is back pain.
The spine is constantly under severe stress. If it exceeds the permissible limit, then it is quite logical that microcracks form on the spinal column. They may be the reason for the occurrence of an inflammatory process, the symptoms of which are as follows:
- Feeling of weakness throughout the body;
- Aching pain that does not go away;
- Feeling of numbness in the limbs.
These signs are also characteristic of any disease that is inflammatory in nature. Therefore, it is important not to confuse them with this complication and start taking measures in time.
Temperature that appears with osteochondrosis of the thoracic or cervical spine
The temperature with cervical osteochondrosis may not rise at all. But the patient will feel pain in the neck, which can spread to the shoulder girdle and head. If you notice such symptoms, you should definitely consult a doctor so that he makes the correct diagnosis and selects the correct treatment for the spine. In this case, even at high temperatures, you should not use drugs that lower it, no matter whether they are medicinal or traditional.
Osteochondrosis of the spine in the thoracic region can be characterized by pain under the shoulder blades. High temperature in this case may be a manifestation of another inflammatory process or disease. It is worth seeking medical help to rule out pneumonia or heart problems, including a heart attack.
Recommended examinations
If the patient has already been diagnosed with osteochondrosis, but the temperature is 37 degrees or higher, and the condition is worsening, then it is worth conducting an MRI of the spinal column. The doctor also prescribes blood tests: biochemical and general. This is done to identify the process of inflammation in the body. The results will reveal the causes of the temperature, exclude or confirm an infectious disease or tuberculosis.
X-rays will help identify infectious foci in the spine.
Other reasons for increased temperature in osteochondrosis
Body temperature can rise for a variety of reasons. It doesn't have to be a disease. For example:
- Neurology.
- Pathologies inside the skull.
If a patient has several diseases at once, should the increase in temperature be attributed to osteochondrosis? This is quite likely, especially given the combination of diagnoses and circumstances.
Neurology can manifest itself with the following symptoms:
- Regular stress;
- Anxiety, fear of anything;
- Discomfort with loud sounds;
- Cardiopalmus;
- High sweating.
Before attributing a fever to osteochondrosis, you need to analyze the accompanying diagnoses.
The temperature of a person suffering from osteochondrosis may increase if there are additional factors:
- Increased body weight;
- Smoking;
- Inactivity;
- Hard labour.
Preventive measures
It is necessary to undergo regular medical examination, at least twice a year.
In addition, of course, comprehensive measures coupled with medications, massage and exercises will help alleviate the condition. Author: K.M.N., Academician of the Russian Academy of Medical Sciences M.A. Bobyr
Treatment of lower back pain
Pre-hospital assistance
In case of traumatic injury to the spine, the patient must be placed on a backboard and immediately taken to a medical facility. For non-traumatic pain, you should reduce the load on your back and optimize your body position during work and rest. Acute pain syndrome is an indication for consultation with a neurologist.
Before being examined by a specialist, a single dose of analgesics is possible. For lumbago and lumboischialgia caused by previously diagnosed degenerative diseases of the spine, the use of warming and local anesthetic drugs is allowed. If an infectious process is suspected, local remedies are not indicated.
Conservative therapy
The basis of treatment is physiotherapeutic measures and drug therapy. The patient is prescribed a protective regimen. The following methods are used:
- NSAIDs
. Effective for acute and chronic pain in muscles and spine. Used in the form of tablets and topical agents. - Neurotropic vitamins
. Patients are administered B vitamins, which enhance the effect of drugs from other groups and help reduce pain. - Local anesthetics
. For persistent and acute pain, therapeutic blockades with anesthetics are performed. To improve the treatment outcome, painkillers are combined with glucocorticosteroids. - Physiotherapy
. Ultrasound, magnetic therapy, transcutaneous electrical stimulation, laser therapy, and medicinal electrophoresis are used. It is possible to prescribe massage, manual therapy, acupuncture.
Surgery
Taking into account the characteristics of the pathology, the following surgical interventions are performed:
- Instability: interbody fusion, transpedicular fixation, plate fixation.
- Tumors, osteoporosis, osteomyelitis, tuberculosis: sequestrectomy, vertebroplasty, kyphoplasty, corpectomy.
- Intervertebral hernias: discectomy, microdiscectomy, nucleoplasty.
- Narrowing of the spinal canal: laminectomy, facetectomy, puncture decompression of the disc.
In the postoperative period, analgesics and antibiotics are prescribed. Rehabilitation measures include exercise therapy, massage, physiotherapy.