Diclofenac suppositories are one of the most convenient forms of the drug, which, unlike tablets and injections, has virtually no side effects. They are administered rectally 2-3 times a day. The drug quickly eliminates pain and inhibits inflammatory processes. Admission is allowed to adults and children over 6 years old.
Composition and mechanism of action
Diclofenac is a non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drug. The mechanism of action of the drug is associated with blocking inflammatory mediators, which helps reduce the inflammatory response and helps relieve swelling, pain, and fever. Suppositories have not only a local effect, the therapeutic effect extends to the entire body. Therefore, Diclofenac suppositories are widely used not only in proctology, but also in gynecology, urology, surgery, and nephrology.
Rectal use of Diclofenac accelerates the development of therapeutic effects on the body, since the active components are quickly absorbed into the rectal mucosa.
The maximum analgesic effect when using Diclofenac suppositories occurs after about one hour.
The medicine does not accumulate in the body and is eliminated naturally. The medication is often prescribed to those patients who are contraindicated in taking non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs in tablets. This applies to patients with ulcers and erosions on the mucous membrane of the digestive tract.
Suppositories are widely used to treat bacterial gynecological infections in women. In what cases are Metromicon-neo suppositories prescribed, and what spectrum of action do they have? Read more in the article: “Why is Metromicon Neo prescribed?”
Drug interactions Diclofenac
It should not be used simultaneously with other NSAIDs (including salicylates and pyrazolone drugs), since with such a combination there is a risk of mutual potentiation of toxic effects and a decrease in the effectiveness of one of the drugs. When used simultaneously with anticoagulants, the risk of developing hemorrhagic complications increases significantly. When combined with lithium salts, diclofenac may increase the concentration of lithium in the blood plasma. Co-administration of digoxin with diclofenac after 48–72 hours can lead to a significant increase in the concentration of the glycoside in the blood plasma; after stopping taking diclofenac, digoxin levels return to normal after 48 hours. Diclofenac causes sodium and fluid retention in the body, reducing the effectiveness of antihypertensive and diuretic drugs. When combined with diuretics, potassium levels should be monitored. It is not advisable to prescribe simultaneously with cyclosporines. GCS may potentiate the toxic effects of diclofenac. For patients taking methotrexate, diclofenac is prescribed 24 hours before or after taking methotrexate, since the plasma concentration and toxicity of the latter may increase.
Indications for use
Diclofenac suppositories help with pain and inflammation. Main indications for prescribing the drug:
Advertising:
- inflammatory and degenerative pathologies of the musculoskeletal system - bursitis, arthrosis, spondylitis;
- postoperative, post-traumatic pain, accompanied by an inflammatory reaction;
- rheumatoid arthritis;
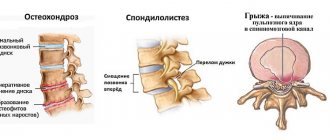
- osteochondrosis;
- radiculitis;
- myalgia;
- inflammatory gynecological diseases - adnexitis, algodismenorrhea;
- migraine.
The medicine is often used for prostatitis. When administered rectally, the active substances quickly penetrate the prostate tissue, relieving inflammation and swelling. Due to this, pain goes away and urination is normalized. Can be used for cystitis, inflammatory diseases of the ENT organs.
Suppositories are also used for hemorrhoids, but only if there are no cracks or tears in the mucous layer in the rectal area.
The duration of use of Diclofenac is on average from 3 to 7 days. The decision to extend the course of therapy should be made by the doctor based on an examination of the patient.
Instructions for use of Diclofenac suppositories
Suppositories are administered rectally (into the anus), starting with a daily dosage of 50-150 mg (for an adult). The maximum amount is 150 mg per 24 hours. It must be divided into 2 or 3 doses (1 candle each).
Children from 6 to 15 years old inclusive determine the daily dosage based on the ratio of 0.2-2 mg of active substance per 1 kg of body weight. If a child is diagnosed with rheumatoid arthritis, the maximum daily amount may be 3 mg per 1 kg of body weight.
Possible side effects, contraindications
Advertising:
Diclofenac in the form of rectal suppositories leads to the development of side effects to a lesser extent compared to the dosage form in the form of tablets and injections. However, after the introduction of this drug, the appearance of:
Antiviral drugs occupy a relatively small niche in the drug market. Among the most popular of them is Acyclovir tablets. Read more in the article: “what acyclovir tablets help with.”
WE RECOMMEND THE ARTICLE!
Ortofen helps with traumatic and non-traumatic pathologies of joints and soft tissues. Read more >>
- abdominal pain, flatulence;
- nausea;
- burning in the rectal area;
- unpleasant taste in the mouth;
- diarrhea, constipation.
The likelihood of developing adverse reactions increases if the recommended dosage is not followed and with prolonged use. Absolute contraindications to the use of Diclofenac in suppositories are:
- hypersensitivity to one or more components of the drug;
- aspirin triad - the appearance of rhinitis, urticaria, asthma attack when using NSAIDs;
- pregnancy (third trimester);
- exacerbation of gastric ulcer and erosive gastritis;
- lupus erythematosus;
- proctitis
Advertising:
Diclofenac suppositories can be prescribed to children only if the child is already 6 years old. The decision to prescribe this drug is made by the doctor.
In the first and second trimester of pregnancy, the medicine is used only if the expected effect from its use is higher than the possible negative effect on the fetus.
It should be used with caution when treating patients with diabetes mellitus, diseases of the gastrointestinal tract, severe changes in liver function, increased blood pressure, and an increased risk of thrombosis.
Diclofenac suppositories
Registration number: P N000061/01
Trade name of the drug: Diclofenac - MFF.
International nonproprietary name: Diclofenac.
Dosage form: Rectal suppositories.
Composition per suppository: Active ingredient:
- Diclofenac sodium – 50 mg
Auxiliary component:
- Solid fat (base for suppositories) - until a suppository weighing 1.50 g is obtained
Description: Suppositories are white or white with a slightly yellowish tint, odorless, torpedo-shaped; an air rod or a funnel-shaped depression is allowed on the cut.
Pharmacotherapeutic group: Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drug.
ATX code: М01АВ05
Pharmacological properties: Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drug, phenylacetic acid derivative; has anti-inflammatory, analgesic and antipyretic effects. By indiscriminately inhibiting cycloxygenase 1 and cycloxygenase 2, it disrupts the metabolism of arachidonic acid and reduces the amount of prostaglandins at the site of inflammation. Most effective for inflammatory pain. Like all non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, the drug has antiplatelet activity.
Pharmacokinetics: The maximum concentration in the blood plasma is created after 30 - 40 minutes and is linearly dependent on the dose used. No changes in the pharmacokinetics of diclofenac are observed during repeated administration and do not accumulate. Communication with plasma proteins is more than 99% (most of it is associated with albumin). Penetrates into synovial fluid. The maximum concentration in synovial fluid is observed 2 - 4 hours later than in plasma. The half-life from synovial fluid is 3 - 6 hours (the concentration of the active substance in synovial fluid 4 - 6 hours after administration of the drug is higher than in plasma, and remains higher for another 12 hours). The relationship between the concentration of the drug in the synovial fluid and the clinical effectiveness of the drug has not been clarified. Metabolism occurs as a result of multiple or single hydroxylation and conjugation with glucuronic acid. The enzyme system P450 CYP2C9 takes part in the metabolism of the drug. The pharmacological activity of the metabolites is lower than that of diclofenac. Systemic clearance is 350 ml/min, volume of distribution is 550 ml/kg. The half-life from plasma is 2 hours. 65% of the administered dose is excreted in the form of metabolites by the kidneys; less than 1% is excreted unchanged, the rest of the dose is excreted as metabolites in the bile. In patients with severe renal failure (creatinine clearance less than 10 ml/min), the excretion of metabolites in bile increases, but no increase in their concentration in the blood is observed. In patients with chronic hepatitis or compensated liver cirrhosis, the pharmacokinetic parameters of diclofenac do not change. Diclofenac passes into breast milk.
Indications for use: Symptomatic treatment of diseases of the musculoskeletal system (rheumatoid arthritis, psoriatic, ankylosing spondylitis; gouty arthritis, rheumatic soft tissue lesions, osteoarthritis of peripheral joints and spine, including radicular syndrome, tenosynovitis, bursitis). Pain syndrome of mild or moderate severity: neuralgia, myalgia, lumboischialgia, post-traumatic pain syndrome accompanied by inflammation, postoperative pain, headache, migraine, algomenorrhea, adnexitis, proctitis, toothache. As part of complex therapy for infectious and inflammatory diseases of the ear, nose and throat with severe pain (pharyngitis, tonsillitis, otitis media).
Contraindications: The period after coronary artery bypass grafting; III trimester of pregnancy, breastfeeding period; Uncompensated heart failure; Hypersensitivity to the active substance or auxiliary components; Anamnestic data on an attack of bronchial obstruction, rhinitis, urticaria after taking acetylsalicylic acid or other NSAIDs (complete or incomplete acetylsalicylic acid intolerance syndrome - rhinosinusitis, urticaria, nasal polyps, asthma); Erosive and ulcerative changes in the mucous membrane of the stomach or duodenum, active gastrointestinal bleeding; Inflammatory bowel diseases (ulcerative colitis, Crohn's disease); Cerebrovascular bleeding or other bleeding and hemostasis disorders; Severe liver failure or active liver disease; Severe renal failure (creatinine clearance less than 30 ml/min), progressive kidney diseases, incl. confirmed hyperkalemia; Children's age (up to 18 years for 100 mg suppositories, up to 15 years for 50 mg suppositories); Rectal bleeding, hemorrhoids, trauma or inflammation of the rectum.
With caution: Anemia, bronchial asthma, cerebrovascular diseases, coronary heart disease, congestive heart failure, arterial hypertension, peripheral arterial disease, edema syndrome, liver or renal failure, dyslipidemia/hyperlipidemia, diabetes mellitus, smoking, inflammatory bowel disease, condition after extensive surgical interventions, inducible porphyria, old age, diverticulitis, systemic connective tissue diseases, creatinine clearance less than 60 ml/min, pregnancy (I-II trimester). Anamnestic data on the development of gastrointestinal ulcers, the presence of Helicobacter pylori infection, long-term use of NSAIDs, frequent alcohol consumption, severe somatic diseases. Concomitant therapy with anticoagulants (for example, warfarin), antiplatelet agents (for example, acetylsalicylic acid, clopidogrel), oral glucocorticosteroids (for example, prednisolone), selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (for example, citalopram, fluoxetine, paroxetine, sertraline).
Method of administration and dosage: Rectally, for adults, the initial dose is 100 mg/day, divided into 2 doses; in mild cases and with long-term therapy - 50 mg/day; in addition to oral administration, the total daily dose (rectal and oral) should not exceed 150 mg. For algodismenorrhea (when the first symptoms appear), the initial dose is 50 - 100 mg / day, which, if necessary, is increased over several menstrual cycles to 150 mg. Migraine attack - 100 mg at the first sign of an attack. If necessary, repeat 100 mg. If it is necessary to continue treatment in subsequent days, the daily dose should not exceed 150 mg over several administrations. For adolescents over 15 years of age - no more than 1 suppository.
Side effects: Often - 1 - 10%; sometimes - 0.1 - 1%; rarely - 0.01 - 0.1%; very rarely - less than 0.001%, including isolated cases. From the digestive system: often - epigastric pain, nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, dyspepsia, flatulence, anorexia, increased aminotransferase activity; rarely - gastritis, proctitis, bleeding from the gastrointestinal tract (vomiting with blood, melena, diarrhea mixed with blood), gastrointestinal ulcers (with or without bleeding or perforation), hepatitis, jaundice, impaired liver function; very rarely - stomatitis, glossitis, damage to the esophagus, diaphragm-like intestinal strictures (nonspecific hemorrhagic colitis, exacerbation of ulcerative colitis or Crohn's disease), constipation, pancreatitis, fulminant hepatitis, exacerbation of hemorrhoids. From the nervous system: often – headache, dizziness; rarely - drowsiness; very rarely - sensory disturbance, incl. paresthesia, memory disorders, tremor, convulsions, anxiety, cerebrovascular disorders, aseptic meningitis, disorientation, depression, insomnia, nightmares, irritability, mental disorders. From the senses: often – vertigo; very rarely - visual impairment (blurred vision, diplopia), hearing impairment, tinnitus, impaired taste. From the urinary system: very rarely - acute renal failure, hematuria, proteinuria, interstitial nephritis, nephrotic syndrome, papillary necrosis. From the hematopoietic organs: very rarely - thrombocytopenia, leukopenia, hemolytic and aplastic anemia, agranulocytosis. Allergic reactions: anaphylactic/anaphylactoid reactions, including severe decrease in blood pressure and shock; very rarely - angioedema (including the face). From the cardiovascular system: very rarely - palpitations, chest pain, increased blood pressure, vasculitis, heart failure, myocardial infarction. From the respiratory system: rarely - bronchial asthma (including shortness of breath); very rarely - pneumonitis. From the skin: often – skin rash; rarely - urticaria; very rarely - bullous rashes, eczema, incl. multiforme and Stevens-Jones syndrome, Lyell's syndrome, exfoliative dermatitis, itching, hair loss, photosensitivity, purpura, incl. allergic. Local reactions when used rectally: irritation of the rectal mucosa, mucous discharge mixed with blood, pain during defecation, rectal bleeding.
Overdose: Symptoms: Dizziness, headache, hyperventilation, clouding of consciousness, in children - myoclonic convulsions, nausea, vomiting, abdominal pain, bleeding, impaired liver and kidney function. Treatment: Activated carbon, symptomatic therapy. Forced diuresis and hemodialysis are not very effective.
Interaction with other drugs: Increases plasma concentrations of digoxin, methotrexate, lithium and cyclosporine. Reduces the effect of diuretics; against the background of potassium-sparing diuretics, the risk of hyperkalemia increases; against the background of anticoagulants, thrombolytic agents (alteplase, streptokinase, urokinase) - the risk of bleeding (usually from the gastrointestinal tract). Reduces the effects of antihypertensive and hypnotic drugs. Increases the likelihood of side effects of other nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs and glucocorticosteroids (bleeding in the gastrointestinal tract), the toxicity of methotrexate and the nephrotoxicity of cyclosporine. Acetylsalicylic acid reduces the concentration of diclofenac in the blood. Concomitant use with paracetamol increases the risk of developing nephrotoxic effects of diclofenac. Reduces the effect of hypoglycemic drugs. Cefamandole, cefoperazone, cefotetan, valproic acid and plicamycin increase the incidence of hypoprothrombinemia. Cyclosporine and gold preparations increase the effect of diclofenac on the synthesis of prostaglandins in the kidneys, which increases nephrotoxicity. Simultaneous administration with ethanol, colchicine, corticotropin, serotonin reuptake inhibitors and St. John's wort preparations increases the risk of bleeding in the gastrointestinal tract. Diclofenac enhances the effect of drugs that cause photosensitivity. Drugs that block tubular secretion increase the plasma concentration of diclofenac, thereby increasing its toxicity. Antibacterial drugs from the quinolone group - the risk of developing seizures. Effect on laboratory test results: diclofenac may affect serum transaminases (if this effect is prolonged or if complications occur, treatment should be discontinued) and may also cause an increase in potassium concentration.
Cautions: Due to the important role of prostaglandins in maintaining renal blood flow, special caution should be exercised when prescribing to patients with cardiac or renal failure, as well as when treating elderly patients taking diuretics, and patients who, for any reason, have a decrease in circulating volume. blood (for example, after major surgery). If diclofenac is prescribed in such cases, monitoring of renal function is recommended as a precaution. In patients with liver failure (chronic hepatitis, compensated cirrhosis of the liver), the kinetics and metabolism do not differ from similar processes in patients with normal liver function. When carrying out long-term therapy, it is necessary to monitor liver function, peripheral blood patterns, and stool analysis for occult blood. During the treatment period, the speed of mental and motor reactions may decrease, so it is necessary to refrain from driving vehicles and engaging in other potentially hazardous activities that require increased concentration and speed of psychomotor reactions.
Release form: Diclofenac-MFF rectal suppositories 50 mg; 5 suppositories per blister pack made of PVC film. Two blister packs together with instructions for medical use are placed in a cardboard pack.
Shelf life: 2 years. Do not use the drug after the expiration date.
Storage conditions: Store at a temperature not exceeding +20 °C. Keep out of the reach of children.
Conditions for dispensing from pharmacies: By doctor's prescription.
Dosage regimen
Diclofenac suppositories are available in packages of 50 and 100 mg. The standard daily dosage is 100 mg, but in some cases it can be increased to 150 mg. Suppositories are placed 2 or 1 time per day. It is better to consult your doctor how many times to put suppositories, since the dosage may also depend on the use of other medications at the time of treatment. When using candles, you should adhere to the following rules:
- before the procedure, it is necessary to empty the intestines naturally or with the help of an enema;
- hands are washed with soap;
- the suppository is removed from the package immediately before administration;
- you need to insert it with the pointed end inward;
- insertion of the suppository is facilitated in a horizontal position on the side or squatting;
- After the procedure, it is advisable to lie down for at least 20 minutes.
Advertising:
After purchase, the medication must be stored where the temperature does not exceed 25 degrees. If the medicine is stored in the refrigerator, then it must be taken out 10-15 minutes before rectal administration.
Exceeding the dosage or using the drug for an excessively long time causes an overdose. Its development is indicated by:
- dizziness;
- tinnitus;
- pain in the epigastrium and head;
- respiratory failure;
- diarrhea;
- clouding of consciousness.
If the above changes occur, Diclofenac should be discontinued; the patient with such symptoms needs medical attention.
[media=
https://youtu.be/8cxsc9bpohE
]
Suppositories with diclofenac: description
The drug is a rectal suppository that contains the substance of the same name - diclofenac sodium at a concentration of 50 or 100 mg per 1 suppository. The medicine belongs to the non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs group. It also has analgesic and antipyretic effects.
Diclofenac sodium suppresses the synthesis of lipids, which provoke inflammation and pain. Absorbed quite quickly and completely absorbed. The product is also available in the form of tablets, gel, ointment, eye drops, and injections for intramuscular administration.
It is recommended to store rectal suppositories in the refrigerator or at room temperature no more than 25 degrees. The place should be protected from direct sunlight. Access for children is excluded. Candles can only be taken within the expiration date, which is 2 years from the date of production.
Drugs with similar therapeutic effects
Advertising:
Diclofenac suppositories cost around 100 rubles per package of 10 suppositories. This drug is not always available in pharmacies, so there is a need to choose an analogue. When selecting drugs with a similar therapeutic effect, one must take into account the indications for their use and all contraindications.
| Drug name | Group of drugs | Compound | Mechanism of action | Release form | Price |
| Voltaren | NVPS | Diclofenac sodium | Analgesic, anti-inflammatory | Rectal suppositories | 330 rubles |
| Naklofen | NVPS | Diclofenac sodium | Analgesic, anti-inflammatory | Rectal suppositories | 100 rubles |
| Buscopan | Antispasmodics | Hyoscine butyl bromide | Relieves spasms, has a weak anti-inflammatory effect | Rectal suppositories, suppositories | 270 rubles |
Good analogues do not have to be too expensive. The effectiveness of their use is determined not only by the composition, but also by compliance with all points of the instructions.
Diclofenac suppositories have several advantages. The medicine is not addictive, does not lead to irritation of the mucous membrane of the digestive organs, acts quickly enough, and has a long-term analgesic effect. Negative reactions when using it rarely occur. However, the use of the drug must be agreed with a doctor, since its therapeutic effect on the body directly depends on the correct determination of the cause of inflammation and pain.