Causes of aches and pain in the joints during menopause
Menopause, postmenopause and menopause are 3 conditions that follow each other starting at the age of 45 years. Characterized by a total restructuring of the body. First of all, the production of sex hormones decreases. These substances are responsible not only for the condition and functioning of the reproductive system. They regulate many processes in the body, so their deficiency leads to a number of changes. This affects the physical condition of the woman. And it often manifests itself as painful sensations in the joints. Joints may hurt during menopause and menopause for the following reasons:
- Excess weight - an increase in body fat - is the body's response to stopping the production of estrogen. Excess body weight is an additional load on the joints of the lower extremities, especially the knees.
- Poor blood circulation in soft tissues is associated with a decrease in the concentration of substances such as elastin and collagen. This leads to a decrease in muscle tone.
- Changes in the functioning of the central nervous system are the cause of frequent cramps and joint pain.
Joint pain during menopause can be the body’s response to diseases that develop as a result of physiological changes:
- osteochondrosis;
- osteoporosis;
- rheumatoid arthritis;
- arthrosis
These pathologies can develop as a result of menopause, when bone and cartilage tissues lose useful substances. Often, a woman already has such diseases of the musculoskeletal system, but before menopause they occur in a latent form, without pronounced symptoms. Their exacerbation is associated with hormonal changes.
Headaches during menopause in women
To the question whether a headache can occur during menopause, the answer is clear. This is a constant companion of menopausal syndrome. Painful sensations are caused by various reasons, including physical dysfunctions of certain systems and psycho-emotional disorders.
Headaches are an inevitable accompaniment of menopause. There are a number of reasons for their occurrence.
Localization of pain can be in the occipital, temporal, frontal and parietal regions. Depending on this, the doctor may suspect the following reasons:
- Increased blood or intracranial pressure. It is especially common in older people. Associated with blockage of blood vessels by fatty formations - cholesterol plaques.
- Dysfunction of cerebral vessels. Depletion of the walls, chronic diseases lead to frequent spasms or excessive dilation of blood vessels. After 45 years of age, the risk of migraine attacks increases.
- Neuralgia of nerve endings in the neck and head. Hormonal imbalance can lead to irritation of these structures.
- Injuries. Previously received head and neck injuries provoke chronic pain of varying strength.
- Excessive tension in the cervical and shoulder regions. Staying in the same position for a long time, low mobility, and large loads of the same type lead to spasms.
Depression and unstable emotional state lead to severe headaches. The woman constantly feels overwhelmed. Night hot flashes also have a negative effect on your well-being. Sleep disturbances, constant depression of the nervous system, and autonomic disorders have characteristic consequences.
If a woman suffered from severe headaches or migraines, their frequency and intensity increases by 50-60%.
Diagnostic methods
Pain in the back, knees and spine, which occurs in the morning and intensifies after prolonged exercise, for example after long walks, are generalized symptoms. It is not possible to make a diagnosis and prescribe treatment only by the presence of such signs.
A thorough diagnosis is required, including:
- laboratory blood test for hormones;
- radiography - shows changes in bone and cartilage tissues that occur during the development of osteoporosis;
- osteodensitometry - the study reveals how thin the bone tissue is.
Based on the results, treatment is selected individually.
Menopausal arthritis: symptoms
Menopausal arthritis, the symptoms and treatment of which cause a lot of inconvenience for a woman, can have acute and chronic forms. The success of therapy depends on timely consultation with a doctor, so it is important to know what signs you should pay attention to:
- Stiffness and lack of joint mobility that appears in the morning. After a few hours this goes away.
- Pain, numbness, tingling, which may worsen at night or after heavy physical activity. These symptoms of menopausal arthritis affect the neck, wrists, fingers, and knees.
- The appearance of swelling around the joint affected by inflammation. It can erase joint contours.
- Bone deformation. Indicates a neglected form. Thinning cartilage tissue leads to curvature of bones, for example, fingers, hands, etc.
In the absence of adequate treatment, destruction of cartilage and bone tissue occurs.
Diagnostic methods
To differentiate this type of arthritis from other diseases, several hardware and laboratory methods are used. First of all, an ultrasound of the joint is performed to assess the condition of the tissues. An X-ray examination is also carried out.
A blood test is required. It is used to determine the amount of calcium as the main building material and the concentration of estrogen. It is the insufficient level of hormones that allows a final diagnosis to be made.
Before prescribing therapy, you need to undergo a comprehensive diagnosis, which will allow you to make an accurate diagnosis.
Drug treatment
Comprehensive drug therapy. It is important not only to eliminate pain in the joints, but also to stop the further development of the pathological process.
Hormone replacement therapy
Menopausal arthritis or osteoporosis cannot be completely cured. But with the right treatment, the disease will be stopped. Considering the fact that most pathologies of the musculoskeletal system during menopause are caused by hormonal changes, the main treatment will be aimed at supporting hormonal levels. Prescribed drugs:
- Premarin;
- Atarax;
- Angelique;
- Divina;
- Cliogest;
- Vagifen.
Hormone therapy helps stop the process of calcium loss from bone tissue. The treatment helps restore metabolic processes. Thanks to this mechanism of action of hormonal drugs on the body, joint pain goes away and their normal functioning is restored.
- How to cope with joint pain during menopause?
When a woman has contraindications to hormonal therapy, these medications will be replaced with homeopathic medicines - Klimaksan, Remens, Klimadinon, Qi-Klim.
Taking calcium supplements
Lack of calcium in bone tissue is the main cause of joint pain. Acute calcium deficiency especially occurs in women during menopause. To restore the concentration of the microelement, strengthen the joints and improve their normal functioning, medications containing calcium are prescribed:
- Vigantol;
- Osteo-Vit;
- Alfacalcidol;
- Aquadetrim.
In addition to calcium preparations, products are prescribed that contain minerals in high concentrations - Nycomed, Natekal, Kaltsinova, Doppelhertz active Menopause.
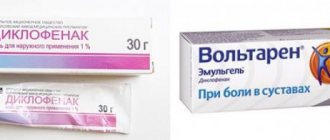
NSAIDs
Joint pain during menopause is often a sign of the development of an inflammatory process in them. To eliminate them, you need to take non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs:
- Xefocam - in addition to relieving inflammation, the drug effectively fights painful symptoms.
- Movalis - removes inflammation, feeling of internal heat and pain. The advantage of the medication is the ability to take it for a long period.
- Celecoxib helps with many joint pathologies and has analgesic and anti-inflammatory effects.
- Nimesulide - helps relieve pain and restores mobility in joints.
The listed NSAIDs belong to a new generation of drugs; they are well tolerated and have minimal risks of side symptoms.
Chondroprotectors
Drugs of this pharmacological group are required to be taken for diseases and pathologies of joint tissue. Chondroprotectors help restore cartilage. Menopause medications:
- Arteparon;
- Artron;
- Rumalon;
- Traumeel.
During therapy with chondroprotectors, it is necessary to avoid physical activity.
Painkillers
Joint pain is a sign that negatively affects a woman’s quality of life. To restore mobility and not experience constant discomfort, pain-relieving medications are taken:
- No-shpa;
- Voltaren;
- Novocaine;
- Papaverine.
Painkillers additionally relieve muscle spasms.
- What to do if joints and muscles hurt during menopause
Physiotherapy and exercise therapy
In addition to drug therapy, it is recommended to use physiotherapeutic procedures in the treatment of joints during menopause.
Recommended methods:
- mud treatment;
- phonophoresis;
- UHF therapy;
- electrophoresis;
- paraffin applications.
Physiotherapeutic procedures relieve pain and reduce inflammation, and improve metabolic processes in joint and cartilage tissues.
Despite the fact that many women experience an increase in pain intensity due to physical activity, a passive lifestyle also negatively affects their well-being. During menopause, it is recommended to regularly perform physical therapy exercises. Simple movements will help develop joints, restore metabolic processes in them, relieve pain and improve the general condition of a woman.
If pain or discomfort in the joints occurs during physical exercise, it is prohibited to exercise with force, as this can lead to damage to the joints.
In addition to exercise therapy, it is recommended to visit the swimming pool. Swimming is the best form of physical activity for joints. Recommended exercise therapy exercises:
- flexion and extension of arms;
- bending the legs, performing shallow squats at a slow pace;
- swings of the upper and lower limbs;
- rotation of the limbs in the joints clockwise and counterclockwise.
Before performing exercises, the body needs to be well warmed up. In addition to exercise, it is recommended to massage or rub joints with ointments that have a warming effect.
Problematic features of menopause in women: symptoms and treatment
In some cases, the manifestations of menopause cause a woman such a severe deterioration in her quality of life that she has to seek medical help to reduce them. Below you will find general information regarding the treatment of menopausal symptoms, but remember that treatment should be prescribed by a specialist.
Self-medication can lead to new health problems and worsening symptoms of menopause.
Treatment of hot flashes during menopause
For frequent and intense hot flashes that cause physical and emotional discomfort to a woman, menopausal hormone therapy (MHT) medications may be prescribed. They contain analogues of sex hormones - both plant and synthetic origin. More often it is a combined drug based on estrogen and progesterone, which has a protective effect on the uterus (endometrium) and mammary glands.
To achieve the best results, it is advisable to start taking hormone replacement drugs at the very beginning of menopause, when its first symptoms appear. The dosage and regimen should be drawn up by a doctor, taking into account the woman’s general health, medical history, age, TSH, FSH levels.
Despite the fact that menopausal hormone therapy can reduce the unpleasant symptoms of menopause, in some cases its prescription is impossible. We are talking about absolute contraindications to taking MHT - such as heart attack (Infarctus) and/or stroke (Insultus), deep vein thrombosis, renal or liver failure, hormone-dependent oncological diseases, autoimmune diseases.
Preparations based on phytoestrogens, for example, Climafemin Ginocomfort, act as an effective alternative to MHT. This is a dietary supplement that contains the phytoestrogen genistein, an organic substance that helps reduce hot flashes and sweating, normalizes metabolism and hormonal levels, and improves sleep quality. In addition to genistein, the product contains active ingredients such as vitamin E, coenzyme Q10 and grape seed extract. All of them have a beneficial effect on a woman’s body, helping to preserve youth and normal well-being.
Treatment of hypertension during menopause
If the symptoms of menopause are accompanied by increased blood pressure, treatment may also include taking antihypertensive drugs (diuretics and diuretics).
Normalization of psycho-emotional state
If during menopause a woman experiences serious emotional instability, even to the point of developing depressive states, she may be recommended sedatives, and in especially severe cases, antidepressants.
Therapy for osteoporosis during menopause
To combat such a symptom of menopause in women as osteoporosis, they are prescribed to take bisphosphonates, calcitonin, strontium preparations, fluoride salts, vitamin-mineral complexes and food supplements containing boron, calcium, vitamins K1 and D. During menopause, it is recommended to include foods in the diet foods rich in calcium and vitamin D (milk, hard cheese, poppy and sesame seeds, soy, nuts, fresh herbs, fish; beef and pork liver, egg yolks, fish oil, cod and halibut liver, butter).
To reduce the manifestations of osteoporosis during menopause, it is necessary to stop smoking, since tobacco helps remove calcium from the body.
Combating vaginal dryness during menopause
To solve the problem of vaginal dryness caused by the onset of menopause, you can use special intimate gels. For example, you can use the Gynocomfort moisturizing gel, which provides relief from natural vaginal secretions and eliminates itching, dryness, burning and irritation in the vagina.
This product was tested during clinical studies conducted at the Department of Dermatovenereology with the clinic of St. Petersburg State Medical University, under the leadership of Ignatovsky A.V. and Sokolovsky E.V. Clinical studies have shown that due to the components included in the gel, the use of the product helps to achieve good hydration.
Neurologist Dmitry Shubin and the appearance of menopause. Live healthy!
The mucus-like consistency of mallow extract, which is part of the product, envelops and moisturizes the mucous membrane of the vulva, has a mild soothing and anti-inflammatory effect on it. Chamomile extract has a beneficial effect on existing microcracks, promoting their speedy regeneration. Panthenol and bisabolol eliminate irritation and have antibacterial properties. Moisturizing gel "Ginocomfort" was developed by specialists from a pharmaceutical company and has the necessary certificates of conformity.
Also, during menopause, a gynecologist may recommend the use of vaginal suppositories containing herbal or synthetic analogues of sex hormones. Some folk remedies for treating crisis symptoms can also be extremely effective. But it is better to coordinate everything with your doctor.
The use of such products helps to normalize the thickness of the mucous membrane during its atrophy, enhance the formation of vaginal secretions, and maintain an optimal level of acidity.
Traditional medicine recipes
Decoctions and tinctures based on medicinal herbs give a good effect in the treatment of joints. But such prescriptions must necessarily be combined with traditional drug therapy. To make the pain go away quickly, use a herbal decoction.
Mix coltsfoot, fragrant woodruff and Chernobyl in equal proportions (1 tsp each). Pour the herbal mixture into 500 ml of boiling water. Cover the container with a lid and leave for 1 hour. Take a decoction of ¼ cup 2 times a day.
A universal folk recipe that will help eliminate unpleasant symptoms of arthrosis and rheumatoid disease. Ingredients:
- Why joint pain occurs during pregnancy and how to get rid of it
- cinquefoil root - 200 g;
- galangal root - 100 g.
Pour the ingredients into a 3-liter jar and fill them to the top with high-quality vodka. It can be replaced with 70% alcohol. Cover the container with a lid. Keep the tincture for 21 days. The jar needs to be shaken every day. After the required time has passed, strain the tincture through gauze folded in several layers. The result should be approximately 2 liters of tincture. Take 1 tbsp. or 50 ml three times a day. The tincture is taken 30 minutes before meals.
If the pain is intense and constantly present, during an exacerbation you can take 1 glass or 2 tbsp. l. tinctures. The drug shows itself well as a local spectrum of action. It is recommended to apply the substance in a small amount to the joint and rub in a circular motion.
The roots of cinquefoil and galangal are used to prepare ointments. They need to be finely chopped and mixed together. Melt the vegetable and butter oils in a water bath, add the chopped roots to the resulting mixture. Mix all ingredients thoroughly until the mixture becomes homogeneous. Only a wooden spoon is suitable for stirring. Before use, the ointment needs to be warmed up a little so that it is better absorbed. Apply a small amount of the substance to the joint, rub until completely absorbed. The course of using the ointment is 30 days. If it is necessary to continue treatment, you need to take a break of 10 days. To get a good effect, you will need 2 to 3 courses.
To maintain healthy joints, it is recommended to take decoctions based on rosemary and sage. They are prepared according to the same recipe: 1 tbsp. pour boiling water over the crushed ingredient. Leave for 30–40 minutes or until the broth has cooled completely. Strain. Take ½ glass 2 times a day.
Popular questions
Hello, hot flashes have begun, mood changes have begun, (menopause) the uterus has been removed due to mime.
What can you take in combination with vitamins to reduce this condition? You can start taking Ginocomfort climafemin 1t once a day for 3 months to relieve vegetative storms.
Hello, burning sensation in the vagina, menopause, the doctor prescribed Levomekol ointment, what else can I use?
Hello! In your case, you can use Ginocomfort gel with mallow extract, 1 dose 1 time per day for 10 days, and then 2 times a week for a long time. This product contains herbal components, bisabolol and panthenol, which will moisturize and restore the mucous membranes of the genital tract. In the absence of contraindications, it is possible to use estriol-containing drugs, for example Ornion cream, which will be etiotropic therapy.
Hello! Surgical menopause, breast cancer in 2011. I suffer from vaginal dryness, periodic cystitis and constant vaginitis after each sexual intercourse. What prevention methods are possible? After every contact?
During menopause, you can use products that do not contain hormonal components. In the Gynocomfort line, this requirement is met by a gel with mallow extract. This will help not only moisturize the mucous membranes, but also restore elasticity and aid in regeneration. The gel can be used both before contact and as needed without a time limit.
Hello, I’m 47 years old, menopause has been going on for 5 years now, at 42 it ended and that’s it, at first I didn’t take anything, the condition worsened, hot flashes and mood swings, poor sleep. 3 years ago, on the doctor’s recommendation, I took Femoston 1/5 for a year. I took it for 1 year, felt good, stopped taking it, after all, it’s hormones, now I feel bad again. hot flashes, increased blood pressure, palpitations, poor sleep, hot flashes mainly at night and depression, tell me Ginocomfort Klimafemin could help me or should I take Femoston again?
Hello!
At this stage, you can start by taking Gynocomfort climafemin. This will improve your well-being and you will have time to conduct additional examinations before resuming menopausal hormone therapy, if necessary: pelvic ultrasound, mammography, lipid spectrum, general blood test, TSH level, consultation with a therapist and obstetrician-gynecologist, smears for flora and oncocytology. For an accurate diagnosis, contact a specialist
Prevention of joint diseases during menopause
Joint pain does not occur spontaneously during menopause. Deviations in the condition and structure of bone tissue occur in the presence of concomitant diseases, if they are not treated in a timely manner. Menopause, accompanied by hormonal changes in the body, is only a provoking factor. Therefore, prevention plays an important role in preventing the occurrence of joint pain.
Vitamin complexes
Every woman from the moment of menopause should begin to regularly take vitamin and mineral complexes. When choosing drugs, you need to focus on their composition. Vitamin D must be present in the complexes. Without this substance, calcium cannot be fully absorbed by bone tissue. Vitamin complexes:
- Miacalcic;
- Lady's Formula;
- Menopace.
Vitamin B6, or pyridoxine, is recommended for menopause. This substance helps restore the normal state and functioning of the nerve roots. Vitamin B6 takes part in the synthesis of female hormones.
Proper nutrition
In addition to drug treatment, a woman during menopause must follow proper nutrition. A properly formulated diet, which includes only healthy foods enriched with vitamins and minerals, is the best prevention of joint pathologies and the appearance of pain in them.
There is no need to follow a special diet. The main thing is that the diet is balanced and correct. Starting from menopause, it is necessary to exclude fatty and fried foods, smoked meats and marinades, pickles and hot spices from the menu. The daily diet should contain foods that contain minerals necessary for cartilage tissue:
- oats, apples and soy are sources of phytoestrogens;
- legumes, prunes and pumpkin - contain a high concentration of potassium;
- seafood, nuts, yeast and bran - enriched with calcium;
- Strawberries and garlic, asparagus and peaches are sources of magnesium.
It is recommended to completely avoid salt. If this cannot be done, it is necessary to limit its quantity and frequency of use. Salt not only negatively affects joints, but also has a better effect on the functioning of the heart muscle and vascular system. Salt slows down metabolic processes and interferes with the full absorption of mineral elements.
What is menopausal syndrome, its symptoms and characteristic signs
There inevitably comes a time in every woman's life when her body begins to age. This period is called menopause. It begins after 45 years and lasts for several years. At this time, certain changes occur, the result of which is the complete extinction of reproductive function. Menopause has 3 stages:
- Premenopause. During this period, the frequency of the menstrual cycle changes, it may become longer (in some cases it becomes more frequent). A woman experiences symptoms such as hot flashes, sleep disturbances, depression and irritability, sudden weight gain with the appearance of a “beer belly.”
- Menopause. The shortest stage, which lasts only 12 months. It begins after the end of the last menstruation. The onset of this stage is indicated by a reduced level of FSH (follicle-stimulating hormone). Only it can be reliable evidence of menopause.
- Postmenopause. After 1 year of absence of menstruation, the final stage of restructuring of the female body begins. Childbearing function completely fades away.
Can there be pain during menopause?
Most women experience the following characteristic symptoms of menopause:
- Tides. This is a sharp, sudden sensation of heat. It lasts from a few seconds to 5-6 minutes. They also end abruptly, the woman feels chills and breaks out in sweat.
- Sleep disorders. Their causes may be hot flashes, depressive states, and other psycho-emotional disorders.
- Dryness of the mucous membranes, their thinning. As a result, intimacy causes discomfort; a woman may feel a burning sensation, pain (and not only during sex).
- Predisposition to fractures, pain in legs, back.
- Increased blood pressure. Occurs due to the accumulation of cholesterol in the body. Plaques complicate the normal flow of blood in the vessels.
- Gynecological diseases. After 45 years, the risk of developing uterine fibroids, endometriosis, and mastopathy increases.
The listed symptoms can cause such unpleasant consequences as various pains. Any system can suffer, thus signaling possible problems. Therefore, complaints of headaches, muscle or joint pain, and characteristic pain manifestations in the mammary gland can also be considered satellites of menopausal syndrome.
Causes of pain
Menopause is caused by a decrease in the amount of the female sex hormone estrogen. It is produced by the ovaries. This substance takes part in a large number of processes, including: maturation of eggs, ensuring normal pregnancy, absorption of calcium, potassium, magnesium and much more.
A decrease in the concentration of this hormone leads to the following consequences:
- Poor absorption of calcium provokes thinning of bone tissue. As a result, bone fragility increases.
- Estrogen is synthesized in small quantities by fat cells. Therefore, rapid weight gain is possible; a woman notices that her belly is growing.
- The appearance of cholesterol plaques. As a result, blood pressure increases and cardiovascular diseases develop.
- Problems with the pelvic organs. The genital area suffers first. Hormonal imbalance leads to pathological growth of the endometrium, the appearance of malignant and benign neoplasms.
- Changes in the levels of prolactin, estrogen and progesterone lead to chest pain. As a result, fibrous tissue grows, mastopathy and neoplasms develop.
The second common cause is psychological problems. Depressive states and neuroses lead to vascular spasms, causing various dysfunctions of a neurological and physical nature.
Consequences and complications
Painful sensations in the joints that appear from the beginning of menopause and menopause will not go away on their own. It is important to understand that without proper treatment the situation will only get worse. Many women do not pay due attention to this sign, thinking that it is just fatigue from physical activity. A common mistake in treatment is taking only painkillers. But they do not cure, but only eliminate the symptom, while the pathology develops further.
Due to age-related changes in the body and due to hormonal changes, beneficial macro- and microelements are actively washed out of the body. Their lack leads to the gradual destruction of the bone tissue that makes up the joint. Parts of the joints begin to rub against each other, this leads to their damage.
If you do not recognize the cause of joint pain during menopause in time and do not undergo appropriate treatment, the consequences can be very disastrous. The woman will begin to develop diseases such as rheumatism and osteoarthritis.
Constant pain has a negative impact on a woman’s general condition. The functioning of the central nervous system is disrupted, insomnia appears, and the psycho-emotional background changes. The woman becomes nervous and irritable.
Calculate your strength
Arthrosis develops due to the fact that with age, the metabolism in the cartilage tissue of the joint is disrupted - its natural recovery slows down, and destruction accelerates. However, although this is the main, but not the only cause of the disease. Arthrosis occurs more often and is more severe in those who regularly overload their joints during work or sports. This leads to microtraumas of the cartilage, which take a long time to heal, because regeneration is difficult. If this happens constantly, there is a high probability that the cartilage tissue will begin to quickly deteriorate.
Therefore, it is very important to alternate work and rest and select an adequate load. Heavy lifting, jumping, fast running, and any activity involving shaking are especially dangerous for joints. In youth, such activity should be reasonably limited, and after 50–60 years it should be eliminated if possible.
What are the dangers of arthritis and arthrosis?
Observe safety precautions
Not only regular microtraumas to the joints, but also immediate major injuries - bone fractures, sprains of ligaments and tendons, dislocations, meniscus tears - can become an impetus for the development of arthrosis. Of course, no one is safe from them, but they happen especially often to those who do not follow safety precautions.
Related articleDoes your shoulder hurt? 6 exercises against arthrosis
If you decide to try a new sport, the first lesson should be with an instructor who will tell you how to perform the movements correctly, and most importantly, how to fall. In everyday life, choose stable and comfortable shoes; in winter they should not slip. And, of course, remember that any industrial safety rules are written for a reason; they cannot be neglected.
In your free time, go for a walk instead of sitting in front of the TV
With a lack of physical activity, the blood supply to the joints and their nutrition deteriorate. In addition, the muscles located around the joints and providing their stability are not trained and lose tone. All this leads to the fact that the cartilage can hardly withstand even a small load and can be damaged.
Just 30–40 minutes of ordinary walking a day can reduce these risks. There is no need to set records - walk at a pace that is comfortable for you. Or sign up for swimming: it is very good for your joints because it exercises them without overloading them. You can limit activity as much as possible only in one case - if you have an exacerbation of arthrosis. And even then you need to do special exercises, which the doctor will prescribe.
What joints love. Lifestyle with arthrosis
Lower abdominal pain during menopause
Pain in the lower abdomen during menopause is associated in most cases with gynecological problems.
Menopause is a blow to the reproductive system. Lack of estrogen provokes a large number of different abnormalities. The appearance of pain in the lower abdomen is a reason to immediately consult a doctor. It may indicate the development of the following diseases:
- Fibroids (fibroids) of the uterus. This is a benign neoplasm that occurs as a result of an excess of estrogen levels over progesterone (an imbalance). It is often diagnosed in women whose menopause began after 50 years of age (late menopause). In addition to nagging or sharp pain, it may be accompanied by bleeding.
- Endometriosis. Refers to estrogen-dependent diseases, manifested in the form of proliferation of endometrial cells. This process is quite unpredictable; its localization can extend to the vagina, cervix, intestines, and bladder. In addition to pain when the lower abdomen is pulled, a woman sometimes observes the appearance of bloody discharge and discomfort in the back.
- Chronic salpingitis. This is a disease that affects the fallopian tube. Often it begins to develop before the onset of menopause, being asymptomatic. But due to low estrogen levels, inflammatory processes intensify. The localization of the pain is on the side with a downward impact, and the temperature also rises.
- Uterine synechiae. Inhibition of the synthesis of female sex hormones leads to atrophy of the ovaries, uterus, and the appearance of adhesions. The process can occur on its own without obvious symptoms; the appearance of pain indicates a possible accumulation of fluid in the cavity. If you ignore this symptom, severe inflammation develops, accompanied by painful attacks that are difficult to bear.
- Malignant tumors. In the early stages, minor aching sensations may occur. Severe pain appears only in the later stages.
In some cases, lower abdominal pain is associated with cardiovascular diseases, such as myocardial infarction.
Bloating is a sign of intestinal problems. They appear as a result of decreased metabolism. Food is digested worse; many foods are too “heavy” for the female body during menopause. It hurts in the upper part of the abdominal cavity due to problems with the liver, gall bladder, and pancreas.
Other types of pain during menopause
Chest pain is a common occurrence during menopause. There may be several reasons for this:
- Breast dysfunction. Lack of hormones leads to tissue replacement with fibrous and fatty tissue. Mastopathy, other benign and malignant tumors.
- Problems with intervertebral discs. Their wear and tear causes the space between the vertebrae to expand and hernias to form.
- Cardiovascular diseases. These are frequent companions of menopause.
In some cases, so-called goose bumps appear. This is the result of a lack of hormones and vitamins, low collagen levels.
Don't overeat
Excess weight is one of the most important risk factors for damage to the knee, hip, and big toe joints. Due to excess kilograms, the load on them increases, so their cartilage tissue wears out faster.
Article on the topicFrom two of us. What diseases may leg problems indicate?
Overweight people often say that they have a “slow metabolism” or “such a bad constitution.” However, most often this is not the case at all. According to the observations of nutritionists and endocrinologists, only in 5% of cases does excess weight appear due to illness or hormonal disorders. The remaining 95% is due to overeating. Therefore, first of all, you need to reconsider your diet: eat less sweets and fatty foods, more vegetables, fruits, and high-protein foods. And also adequately evaluate the portions and not put too much on the plate.
Don't go on strict diets
Nutrients are needed for the natural restoration of cartilage tissue. If we eat too little, we don't have enough of them, and this increases the risk of arthrosis. Mono-diets (eating only one product) and diets with extremely low calorie content (less than 1200 kcal) are especially harmful.
If you want to keep your joints healthy, your diet should be varied and nutritious. It is imperative to get all vitamins and minerals from food (sulfur, calcium, and selenium are especially important). The diet should have enough protein and healthy unsaturated fat, which is found in fish and vegetable oils.
Arthrosis of the shoulder. What are the first symptoms of the disease?
Preventive measures
To maintain the integrity and strength of bones, as well as prevent calcium leaching, you should follow some recommendations:
- lead a healthy lifestyle. It is worth giving up bad habits, in particular smoking and alcoholic beverages;
- follow a proper diet. If you balance your diet at a young age, this will help prevent shortages of important substances in adulthood;
- stay in the sun more often. Vitamin D is produced under the influence of sunlight;
- track the amount of vitamins and calcium you receive;
- do physical activity every day. This can be walking at a brisk pace, running, exercising in the gym, which will make the bones strong;
- do not forget about the clinical examination. If you identify diseases and problems in the early stages, you can prevent their development into more complex forms.
See a doctor if you feel unwell
Article on the topic: When your knees hurt. What is kinesitherapy and how does it help with arthrosis Arthrosis is an irreversible disease: if the cartilage tissue is worn out, it is impossible to restore it to its previous healthy state. However, today there are drugs that can stop the destruction of cartilage. They are called chondroprotectors and include glucosamine and chondroitin sulfate. These components nourish the cartilage, moisturize it, but most importantly, block the work of enzymes that contribute to its destruction.
The drugs give the greatest effect at the first and second stages of arthrosis, when the cartilage is partially worn out. The doctor can prescribe them at the third stage, when the damage is already more pronounced. But on the fourth, the use of medications no longer makes sense, because there is virtually no cartilage tissue left. Therefore, it is important not to start the disease. You cannot endure pain in the joint area, hoping that it will disappear on its own, or attributing the ailment to fatigue. You need to see a doctor at the moment when the first symptoms of arthrosis appear. And, contrary to popular belief, this is not a painful sensation at all, but a feeling of stiffness in the joint in the morning, which goes away after about half an hour, as soon as it goes away.
Next material
You may also be interested
Menopause (synonym: menopause) is a physiological condition that is characterized by the extinction of sexual functions in women and the occurrence of diseases of various etiologies. In this article we will look at joint pain during menopause.
Climax
Attention! In the International Classification of Diseases, 10th revision (ICD), menopausal disorders are designated by code N95.
Changes in the body during menopause
Both ovaries contain several million follicles at birth. This number decreases during puberty to approximately 100,000-250,000 and then with each ovulation. Although only one oocyte leaves the ovaries at each monthly ovulation, several follicles mature each month and are lost after ovulation.
At an average age of 50, a woman's ovaries no longer contain vesicles that can grow into a follicle capable of ovulation. Follicles produce estrogens, which are classified as “female” sex hormones. The fewer follicles a woman has, the less estrogen is synthesized. As a result, menstrual bleeding disappears and menopause occurs.
The synthesis of hormones in the brain also changes with the onset of menopause: as the ovaries produce less and less estrogen during menopause, the brain releases more gonadotropins, that is, sex hormones. In particular, the so-called follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH) is released: although, for example, the concentration of a specific estrogen called estradiol decreases to approximately 1/6, the concentration of FSH increases on average by more than 6 times. This hormone imbalance can lead to various symptoms:
- fatigue;
- local hyperemia;
- outbursts of anger;
- joint pain;
- tachycardia.
FSH
The most important group of female hormones is estrogens. Sex hormones also include gonadotropins and progestogens.
Functions of estrogen:
- stimulation of female breast growth;
- female voice;
- stimulation of the growth of subcutaneous adipose tissue;
- stabilization of the endometrial structure during the menstrual cycle;
- growth of uterine muscles;
- opening of the cervix before ovulation;
- stimulating the synthesis of bone-forming cells and therefore increasing bone stability.
Gonadotropins, which form at the onset of menopause, are a group of sex hormones that form in the brain. Gonadotropins include luteinizing hormone (LH) and follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH). LH and FSH together promote the formation of estrogens in the ovaries.
Functions of gonadotropins:
- LH: The brain releases LH to stimulate ovulation. LH also promotes the formation of the so-called corpus luteum.
- FSH: accelerates follicle maturation.
Within the menstrual cycle, the interaction of estrogens, LH and FSH results in ovulation once a month.
Progestogens are also known as “corpus luteum hormones” because they are synthesized by the corpus luteum. During menopause, the ovaries gradually stop producing progestogens. The most important progestogen is progesterone. Other progestogens are prepanediol and pregnenolone.
LH
Even the female body produces a certain amount of male hormones (androgens). The most important one is testosterone. While estrogen levels decrease during menopause, the proportion of male hormones remains unchanged. This excess can lead to “masculinization.” Some people start to grow a mustache or develop belly fat.
Risk factors appear to be related to lifestyle and diet: coffee and alcohol, spicy foods and hard-to-digest foods worsen the condition in women. Excess weight, stress and too much sexual activity are risk factors that affect females less.
About a third of women have no pathological symptoms during menopause. About a third of women experience complaints so severe that they are unable to lead a normal life.
Development of osteoporosis during menopause
In order to prevent sudden fractures, special preventive measures are taken.
Menopause or menopause is an age-related biological period in a woman’s life, which is characterized by involution, decline in the functionality of the reproductive system, and the inability to have a child. The gradual and natural process of aging is accompanied by hormonal changes in the body (decreased activity of the ovaries and adrenal glands, as well as a decrease in the production of certain hormones).
One of the most negative consequences of menopause is the possibility of developing osteoporotic bone disease. In this case, bone loss occurs, the architecture of the bones and their mineral balance are disrupted, which makes them very fragile and brittle. As a result, the risk of sudden fractures, even with minor loads, increases significantly, and with a femoral neck fracture in old age, death.
Climax
Menopause occupies a fairly long period of time in a woman’s life cycle. On average, it begins at the age of 45-50 years and lasts until 65-70. Of course, the main changes occur in the reproductive and hormonal systems, and they, in turn, trigger secondary processes in the body.
Female sex hormones (estrogen and progesterone) are mainly produced in the ovaries (where egg development occurs) and in small quantities in the adrenal cortex. At the beginning of menopause, the development of germ cells (eggs) stops, which affects the possibility of conception and childbearing. Next, the amount of hormones produced changes, which is expressed in a violation of the regularity, abundance and gradual cessation of menstrual discharge.
The complete cessation of the synthesis of sex hormones is characterized not only by the absence of menstrual cycles, but is also reflected in almost all organs.
Most sensitive to estrogen background:
- skin (wrinkles appear, it loses elasticity and firmness);
- hair becomes less beautiful, pale, gray hair appears;
- the mammary glands lose their attractiveness, the figure changes, excess weight appears;
- liver (not able to completely cleanse the volume of blood pumped through it);
- genitourinary system (decreased libido, the occurrence of chronic diseases);
- brain and cardiovascular system (development of atherosclerosis, stroke, heart attacks, coronary heart disease, varicose veins, thrombophlebitis, etc.);
- muscles, joints, bones (a significant loss of muscle tissue affects the nutrition of the joints and their performance, then the bones are involved in the process, osteoporosis develops);
- the immune system.
Typically, menopause is accompanied by the following symptoms and manifestations:
- hot flashes to the face and whole body, excessive sweating;
- instability of blood pressure, pulse and heartbeat;
- increased sensitivity, nervous excitability and frequent causeless mood swings;
- sleep disturbances, poor health, fatigue and general weakness;
- headaches, dizziness, nausea, memory disorders, absent-mindedness, etc.
Osteoporosis
The processes of bone formation in the human body continue almost until old age and two types of cells take part in them: osteoblasts and osteoclasts.
Osteoblasts are young bone tissue cells that are responsible for the synthesis of intercellular substance (matrix) or for the formation of bone, as well as for the accumulation of calcium salts in the matrix. The matrix mainly consists of collagen fibers enriched with layers of calcium and phosphorus.
Osteoclasts are large multinucleated bone cells that contribute to the dissolution of their mineral components and the destruction of collagen, which entails resorption (destruction, removal) of bone matter.
The qualitative indicators of human bone tissue and the volume of bone mass are not constant values. They can change throughout life and depend on external and internal factors (physical activity, quality of nutrition, bad habits, environmental conditions, hormonal levels, etc.).
Bone mass density and volume peak at approximately 25–30 years of age, and gradually begin to decline after age 40. In women, the quality of bone tissue deteriorates sharply (in the first 3-5 years) after the cessation of ovarian function, i.e. in the menopausal period, resorption processes prevail over bone formation - osteopenia develops.
Usually the disease is practically asymptomatic, does not bother anyone except aching back pain after physical activity, and is detected in the later stages or completely by accident. The diagnosis of postmenopausal osteoporosis is already made when there is a significant loss of bone mass, when compression fractures of the vertebral bodies occur or fractures of the bones of the extremities with a slight axial load.
Other signs of osteoporosis may include:
- sudden stoop;
- decreased growth;
- change in gait;
- the appearance of skin folds on the sides;
- back pain in the morning after sleeping or staying in a static position for a long time.
In old age, osteoporosis can lead to hip fractures, prolonged bed rest, death, or disability. Only 17-20% of women manage to return to normal or satisfactory physical activity.
Diagnostics
Conventional radiography for osteoporosis is not always sufficiently effective. It visually shows changes in bone tissue (they become more transparent) only when bone loss is 25-30% or more. Of course, an x-ray can show compression fractures of the vertebral bodies, but they are not always associated with osteoporosis or menopause.
Therefore, densitometry or DEXA scanning is used to detect osteopenia and osteoporosis in the early stages. This study refers to x-ray methods, but can detect loss of bone density at 3-5%.
Dual-energy X-ray absorptiometry machines can be portable peripheral units that measure bone density and mineralization in the wrist, finger, or heel bones. Stationary devices allow for examination of large skeletal bones (spine, hip bones, etc.).
Densitometry is recommended for all women at risk at the beginning of menopause 1-2 times a year. If the loss of bone mass is small, then it is sufficient to perform the study once every 2 years.
In some cases, to exclude cancerous tumors in the bones and metastases, patients may be prescribed a tomographic examination, ultrasound or radioisotope scanning.
Treatment and prevention of menopausal osteoporosis
Therapy for postmenopausal osteoporosis mainly consists of:
- prescribing hormonal medications (sex hormone replacement therapy): calcitonin, parathyroid hormone, androgens;
- bisphosphonates - drugs that prevent bone loss;
- fluorine and calcium salts;
- vitamin D, other vitamins and microelements.
At the beginning of the last century, the life expectancy of women was quite short (on average up to 60 years) and the problem of osteopenia practically did not affect them. Today, this figure has increased to 80 years and osteoporosis has become a common cause of premature death, disability, or simply suffering and bed rest.
In order to somehow avoid these disastrous consequences or postpone them to a later date, it is recommended to take special preventive measures.
Prevention of menopausal osteoporosis:
- high-quality and balanced diet containing sufficient amounts of calcium, fresh fruits and vegetables;
- maintaining age-appropriate physical activity, which will help maintain the normal state of muscle, cartilage and bone tissue;
- giving up bad habits (alcohol and smoking), limited consumption of coffee and dark chocolate;
- timely detection of endocrine system diseases;
- sufficient time in the fresh air, sunbathing, active recreation.
Author: K.M.N., Academician of the Russian Academy of Medical Sciences M.A. Bobyr
Associated symptoms
Many people ask: can joints hurt during menopause? Most common symptoms:
- tachycardia, hyperemia and sweating. There is often a slight pressure in the head and a feeling of discomfort, then a heat wave begins to spread across the face, neck and upper body. Women's faces turn red and they sweat. Some women suffer from such attacks several times a day. Often hyperemia is accompanied by a strong heartbeat;
- sleep disturbances and insomnia, fatigue and decreased productivity: more than half of menopausal women suffer from sleep disturbances. Many women have problems falling asleep. They wake up more often during the night. At the same time, the depth of sleep may decrease, which affects the overall quality of sleep. Many women feel exhausted during the day and their productivity suffers;
- mood swings – nervousness, irritability, depressed mood. Some women go through shorter and longer periods of severe mental imbalance during menopause;
- Dry mucous membranes and vaginal infections: The mucous membranes of the vagina dry out and become vulnerable over time. Women suffer from itching or burning. They often feel pain during intercourse;
- changes in sexual behavior: many patients change sexual preferences. There are women who lose sexual interest and arousal, while others experience increased sexual pleasure. Therefore, researchers believe that hormonal changes do not always reduce the quality of sexual life;
- discomfort in the urethra: the mucous membranes of the bladder and urinary tract suffer from circulatory disorders during menopause. Therefore, there are women who are more likely to suffer from infections and inflammation of the urethra. Also, the pelvic floor muscles relax, which in rare cases leads to urinary incontinence.
More rare symptoms during menopause:
- dizziness;
- high blood pressure;
- pain in muscles and joints;
- headaches that occur mainly in particularly sensitive women.
However, not all researchers agree that such symptoms are caused by hormonal changes.
Drug therapy
Patients are interested in: what to do if joints and muscles hurt? The most common treatment for severe menopausal symptoms is hormone replacement therapy (HRT). In this case, either only one estrogen (estradiol, estriol, prometra) is administered as monotherapy or a combination of estrogen and progestogen (Cyproterone acetate, Dydrogesterone, Norethisterone Acetate). The goal of therapy is not to return the body to its pre-menopausal state, but to eliminate or at least alleviate the symptoms caused by estrogen deficiency. Treatment should be carried out under strict medical supervision.
Estradiol
Medicines for the treatment of inflamed joints should not be taken without consulting a doctor, as there is a risk of adverse effects. Medicines (medicines) are dispensed in pharmacies strictly according to prescription.
Pharmacies sell tablets, patches, gels, suppositories, creams, injections and sprays. The advantage of hormone therapy is that it virtually eliminates all symptoms and also prevents osteoporosis. However, HRT has some side effects:
- the risk of breast cancer increases;
- there is a risk of developing a stroke or heart attack;
- the risk of thrombosis and other diseases increases.
The risk of developing certain types of cancer or high blood pressure also increases. An alternative to estrogens and progestins is the artificially produced hormone tibolone, which is administered in tablet form.
In 1 in every 100 women, the ovaries stop working between the ages of 35 and 40 (primary ovarian failure). Doctors in this case talk about premature menopause (Climacterium praecox). The causes are various diseases: thyroid disease and diabetes. The cause may be chemotherapy, genetic abnormalities and genetic predisposition.
Causes and symptoms of pathological menopause
Factors that provoke the pathological course of menopause include:
- diseases of the reproductive organs;
- surgery to remove the uterus or ovaries;
- the presence of chronic diseases (for example, the thyroid gland);
- vitamin deficiency caused by dietary errors;
- stressful situations;
- hereditary predisposition.
The main symptoms of pathological menopause are hot flashes, accompanied by increased sweating, attacks of dizziness and migraines, tachycardia, vaginal dryness, and weight gain. Pathological changes also occur in the emotional sphere. The woman becomes more irritable, anxious, and prone to sudden mood swings.