Treatment of joint diseases with salt
Saline solution is an excellent absorbent. In medicine, this product is one of the most affordable and accessible means that has a therapeutic effect. Using salt, you can make various products that are widely used for self-treatment at home. Salt compresses and bandages are often used to relieve joint pain.
Treatment of joints is the most common trend in medicine. Among elderly people, the percentage suffering from joint pain reaches almost 100. However, many researchers note that this type of disease has recently become “younger”. More and more girls and boys are facing this problem, mainly due to the sedentary lifestyle that prevails in our time.
There are quite a lot of diseases associated with joints, and it would seem that each one requires its own approach, a bunch of medications and preventive medications, consultations with specialists, and so on. However, there are many traditional methods that are widely and effectively used in the treatment of many types of joint diseases.
Among them:
- arthritis is an inflammatory disease of the joints;
- the appearance of gout is a metabolic disorder that is accompanied by the deposition of uric acid in the joints;
- bursitis - inflammation of the periarticular bursa;
- rheumatism is a disease that affects connective tissue;
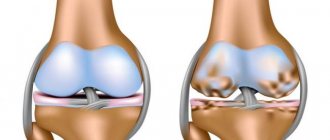
- arthrosis is a disease of the joint that leads to its immobility
- Osteochondrosis is a type of arthrosis, which is accompanied by the destruction of articular cartilage. This disease is incurable, but pain relief is possible;
- joint dysplasia is a disorder in the development of joint structure.
Useful tips for sea salt therapy
For high effectiveness of therapy with the component, it is necessary to remember a number of features of using salt:
- treatment should be started with small doses;
- in case of high blood pressure, heart problems, improper kidney function or dysfunction of metabolic processes, treatment with salt must be agreed with a doctor;
- in case of violations of the integrity of the skin, it is necessary to exclude salt compresses, bandages and baths;
- Only the recommended solution saturation should be used;
- with high saturation of the salt substance in the solution, the result of the therapeutic effect will be the opposite.
Treating joints with salt requires care and following instructions. Joint pain decreases little by little.
Many useful reviews about sea salt treatment give hope to those who suffer from systematic or recurrent joint pain. To achieve results, you must listen to the following tips:
- treatment with a ten percent saline solution will show a positive result, as it has absorbent and anti-inflammatory properties;
- regular treatment with salt will allow the affected organ to suppress the development of pathogenic organisms, reduce and gradually eliminate the source of inflammation;
- therapeutic bandaging on large joints relieves inflammation, pain and swelling;
- when making a saline solution, table or sea salt is used, the main thing is that the addition of aromatic oils and aromatic additives is excluded;
- It is forbidden to use purified, “killed” water for the solution;
- the water should not be colder than sixty degrees;
- Only natural materials should be used for the bandage.
The use of salt is not a guarantee of healing from a disease, but only an additional therapeutic method for a comprehensive effect on the disease. You should not engage in self-medication and prescribe medications, dosage and duration of salt treatment yourself.
Methods of using salt in medical procedures
Salt is widely used in the manufacture of compresses, bandages, as well as in warm foot baths and when rubbing joints with saline solution.
When a bandage is applied directly to a sore joint, a reaction begins between the skin and the salt. Fluid is “pulled out” from the upper skin. Then tissue fluid is “pulled up” from the lower layers. Together with it, harmful substances residing in tissues, muscles, and joints are removed.
Rubbing increases the supply to the affected joint, thus improving the oxygen supply to its tissues.
Salt baths can be very helpful in treating hand or ankle joints.
Salt baths have demonstrated anti-inflammatory and analgesic properties. Very effective in the initial stages of polyarthritis of the fingers and osteochondrosis. The physical effect of salt baths depends on the level of intensity of the salt solution. During the procedure, salt settles on the skin, irritates receptors, generating reflex interactions in the functional systems of the body. This helps to dilate blood vessels, improve blood supply to muscles, and increase tissue oxygen consumption.
Balneotherapy in the treatment of diseases of the spine and joints
Balneotherapy is classified as a branch of alternative medicine or one of the areas of naturopathy, which involves treatment with mineral water.
Despite its alternative nature, hydrotherapy is widely used in classical medicine for physiotherapeutic procedures. This can include various showers, bathing, dousing, wraps, baths, washing, as well as inhalations, oral administration, irrigation, intestinal lavage and other procedures related to water. In the treatment of diseases of the musculoskeletal system and joints, mineral water is used mainly externally.
Unlike conventional hydrotherapy, balneotherapy uses mineral water, often of natural origin or thermal water. Mineral waters are considered to be waters that contain a high concentration of mineral (less often organic) chemical elements or gases and have some physical properties. Thermal – medicinal waters, the temperature of which ranges from 37°C to 42°C.
Of course, the benefits of mineral waters and hydrotherapy in general in the treatment of diseases of the spine and skeleton have long been proven. With the correct selection of the chemical components of water, a favorable climate, adequate physical activity, appropriate regimen and diet, the recovery of patients is much more intense and faster.
At the same time, balneotherapy, like mud therapy, for example, requires constant medical supervision. Gases, salts, chemical elements and other components of mineral waters can irritate the skin, stimulate or calm the central nervous system, increase lymph flow and blood circulation, and, therefore, increase the load on the heart. Therefore, to avoid unwanted reactions or exacerbation of the condition, short breaks may be taken during the course of hydrotherapy.
Thermal hydrotherapy
Hydrotherapy, unlike other types of treatment, is characterized by simplicity, accessibility to the general public (it is offered not only by sanatoriums and resorts, but also by many regular medical institutions), safety and the absence of side effects.
Depending on the temperature, water procedures and activities are divided into:
- cold or cryoprocedures, the temperature of which is below 20°C;
- cool (temperature range 21-33oC);
- indifferent (34-36oC);
- warm (37-39oC);
- hot (over 40°C).
Warm and hot hydrotherapy is useful for gout, various arthrosis, gastroenterological diseases, chronic inflammatory processes, in the post-traumatic period for the speedy restoration of soft tissues, elimination of contractures and for the development of joints. Cold procedures relieve swelling and inflammation, activate metabolic processes and the immune system, and tone regulatory systems.
Hydrotherapy is usually represented by:
- showers (Charcot, circular, ascending, Scottish, underwater massage, etc.);
- baths (radon, turpentine, hydrogen sulfide, nitrogen, etc.);
- wraps, applications, rubdowns, douses, etc.
The duration and type of water procedures are determined by the attending physician individually for each patient, based on the location, degree and type of skeletal damage, age, and general health. As a rule, the course consists of 10-15 daily procedures; if necessary, a break of 1-2 days can be taken for better adaptation of the body to balneotherapy.
External use of mineral waters
The physiological and therapeutic effects of balneotherapy in the treatment of spinal diseases are based on a combination of factors:
- thermal (temperature) effect of water on the body;
- mechanical impact (pressure, underwater flows, waves);
- chemical composition of mineral waters.
Temperature changes in water when taking external baths have a much greater impact on the human body than fluctuations in air temperature. For example, it is much easier for a person to tolerate being in cold air than in a bathroom of the same temperature.
Cold baths, when immersed in them, initially irritate the blood vessels and nerves located in the skin, and the greater the difference between the patient’s body temperature and the water, the greater the irritation. This “shock” entails oversaturation of internal organs with blood, increased pressure in the walls of arterial vessels (their narrowing and tone), increased heart rate, increased metabolism and an automatic increase in body temperature.
After some time, a reverse reaction occurs: the vessels located in the skin dilate, blood flow to them increases, the heart rate calms down and becomes less frequent, metabolic processes slow down, and the internal body temperature gradually decreases.
During cold baths, the nervous system is toned and refreshed, the skin, muscles and ligaments are strengthened. Cryoprocedures can be used as a powerful antipyretic, as a means of activating blood circulation, restoring tissue sensitivity and the passage of nerve impulses along nerve fibers.
Warm and hot water procedures help relax tissues, dilate blood vessels in the skin, fill them with blood, body temperature rises, and the speed of metabolic processes increases. Pulse, heart contractions, breathing increase, blood pressure decreases, the nervous system becomes irritated and excited. Thermal effects have a relaxing, analgesic and anticonvulsant effect, promote the removal of toxins from the body in case of gout, rheumatoid arthritis, scrofula, inflammatory exudates, etc.
The mechanical effect of water during hydrotherapy is often combined with temperature influence. Mechanical indicators depend on the type of procedures (filling a bath or pool, the presence of waves or underwater hydromassage), on the strength and pressure of the water, and on the pattern of its movement. Thus, the therapeutic effect is achieved due to the movement of water or the patient in it, the resumption of the movement of water flows, the direction and height of the fall of the jets, constant contact with the skin or dosed exposure.
The pressure of the water column causes the tone of the chest and abdominal muscles, and the activation of the internal organs. The skin and the vessels located in them also experience pressure, blood is forced out of them, blood pressure rises, and the work of the heart increases.
The chemical effect of mineral waters is mainly through the skin and inhalation, and only volatile substances and gases are absorbed in full. Non-volatile compounds, salts, iodine, radon, hydrogen sulfide and other elements saturate the skin and then spread throughout the body.
Many studies have been carried out on the electrical charge of mineral medicinal waters, but there is no reliable information about the usefulness of such procedures in the treatment of osteochondrosis and other skeletal diseases.
Types of mineral waters and baths
For a long time, balneologists could not reach agreement regarding individual medicinal mineral waters. Some of them, when environmental conditions change, change their chemical composition and properties, and sometimes form very unstable compounds.
Today, according to the content of salts and gases, mineral waters are divided into alkaline, sodium, iron, sulfur, calcareous, indifferent, iodine-bromine and nitrogen-radon.
Alkaline water contains carbonic acid, sodium carbonate and sodium sulfate as the main elements, and table salt in a smaller amount.
- Internal consumption of carbonated water improves the peristalsis of the stomach and intestines, the secretion of gastric juice and bile, quenches thirst and has a diuretic effect. Low-temperature baths with carbon dioxide water are prescribed for chronic rheumatism, for the treatment of various types of neuralgia, paresis and paralysis of the limbs.
- Alkaline carbon dioxide water has a mild laxative effect, thins and removes mucus from the respiratory tract, activates metabolic processes, and breaks down fats. It is used externally to treat obesity; when warm, it is used to eliminate spasms and inflammation of muscle tissue.
- Alkaline salt water is prescribed to improve appetite and better absorption of nutrients. In the form of baths it helps to activate tissue trophism, with exhaustion of the body and anemia.
- Alkaline Glauber water has a laxative effect, dilutes and removes bile and gallstones, and enhances metabolism. Externally recommended for the treatment of excess weight, arthritis and various arthrosis, gout and diabetes.
Waters containing table salt consist in significant quantities of sodium chloride and also contain calcium, potassium, magnesium, iodine, bromine, lithium and other trace elements. Salt baths irritate the blood vessels and nerves passing through the skin, restore reflex reactions, improve blood circulation, breathing and other physiological functions of the body. By regulating the temperature of the baths, various therapeutic effects are achieved in the treatment of diseases of the musculoskeletal system.
Iron waters are usually prescribed for internal use, since iron is not absorbed through the skin. They are used to improve metabolism, sluggish digestion, dyspepsia, anemia, blood stagnation in the portal vein, etc.
Sulfur mineral waters contain significant quantities of hydrogen sulfide or hydrogen compounds with any metals, and penetrate into the human body through the stomach, breath or skin.
When taken orally, they enhance the activity of the gastrointestinal tract, the secretion of bile, cleanse the portal vein, remove toxins, heavy metals and salts, and improve the activity of the cardiovascular system. Inhalations help in the treatment of respiratory diseases. Externally used to treat rheumatism, osteochondrosis, arthrosis, skin rashes, neuroses and neuralgia. They relieve inflammation and pain well, and stimulate the immune system.
Calcareous or earthy water consists of carbonic or sulphate chalk and gypsum. It neutralizes acids, improves metabolism, and is used in the form of baths for softening and necrosis of bone tissue, osteoporosis, caries, rheumatic pain, inflammation of the joints, and gout.
Artificial or natural indifferent waters have a rather poor chemical composition (mainly sodium carbonate, nitrogen and oxygen predominate). Their main therapeutic aspect is the temperature effect on the patient’s body.
Warm baths are recommended to be taken after debilitating illnesses, prolonged immobilization, diseases of the nervous system, hysteria, headaches, cerebrovascular accidents, muscle weakness or convulsions, paralysis, paresis, and various skin lesions.
Hot water procedures are used to develop joints after injuries, for rheumatism, to eliminate contractures, infiltrates and inflammation of soft tissues and internal organs, to restore damage to the central and peripheral nervous system, to treat sciatic neuralgia, etc.
Iodine and bromine are halogens and are poorly soluble in water, but form quite stable compounds in saline solutions. Therefore, iodine-bromine baths must be combined with salt baths and are indicated for calming the nervous system, treating degenerative diseases and joint damage.
Nitrogen and radon waters are saturated with the corresponding gases and are often combined with underwater hydromassage or resemble a jacuzzi. Indicated to normalize blood circulation and blood pressure, relieve inflammation and pain, muscle spasms, and have a beneficial effect on joints and bones.
Contraindications to balneotherapy
Hydrotherapy with mineral waters of different temperatures is contraindicated in the following cases:
- the presence of tumors of various etiologies in the body, especially in the stage of active growth;
- acute or chronic inflammatory processes;
- after recent heart attacks, strokes or operations on the cardiovascular system;
- heart failure, angina pectoris, hypertension, vascular atherosclerosis, thrombosis, thrombophlebitis of large vessels, especially with trophic skin lesions, etc.;
- active tuberculosis;
- epilepsy and some diseases of the nervous system;
- skin lesions or allergic reaction to components of mineral water;
- poor blood clotting and predisposition to bleeding.
Author: K.M.N., Academician of the Russian Academy of Medical Sciences M.A. Bobyr
Which salt should you choose?
One of the frequently asked questions is which salt to choose to achieve the best effect: table salt or sea salt?
Scientists have long proven that the composition of these two types of salt is not so different. The only thing is that sea salt is more natural, since it was formed only under the influence of natural factors. In practice, this does not play a big role, since the results will be the same. But here it is worth noting that sea salt can have an stimulating effect on the body (for the nervous system), so you should not use it at night. It is preferable to use sea salt for dystrophic and inflammatory lesions.
When to take a sodium chloride sea salt bath
- For the following diseases of the cardiovascular system: atherosclerosis (initial manifestations), rheumatic heart defects in the 1st degree of activity in adults and children with circulatory failure of the 1st and 2nd degrees, myocardiosclerosis and myocardial dystrophy, arterial hypertension of the 1st degree, hypertension stages I-IIA, arterial hypotension, hypotension, cardioneurosis, vegetative-vascular dystonia, coronary heart disease (coronary insufficiency without heart failure)
- For the following vascular diseases: thrombophlebitis (post-thrombophlebic syndrome), varicose veins
- For the following diseases and consequences of injuries of the central and peripheral nervous system: neurosis, dystonia, neurasthenia with insomnia and irritability, consequences of polio and polyradiculoneuritis, neuropathy, radiculitis, plexitis
- For the following diseases of the musculoskeletal system: ankylosing spondylosis, consequences of muscle and tendon injuries, arthritis and polyarthritis of non-tuberculous origin, spinal diseases
- For inflammatory diseases of female and male genital organs
- For the following skin diseases: neurodermatitis, psoriasis, eczema
How to make bandages and compresses
Let's consider the use of salt dressings and compresses for various diseases:
| Bandages and compresses | |||||
| Name | How to cook | How to do | Proportions | For what diseases | How long to keep |
| Bandage | The ingredients are mixed, and gauze folded in several layers is lowered into the resulting solution (you can also use cotton fabric). | Gauze is applied to the affected joint and secured tightly with a bandage or other cloth. | 2 teaspoons salt per 100 ml warm water | Bursitis, arthritis, rheumatism | 9-10 hours |
| Salt based compress | The salt must be heated to 60-69 degrees. Put it in a tight bag. | The compress is wrapped in film and applied to the sore joint until it cools completely. | 100 grams of salt | Gout, rheumatism, arthrosis of the fingers | 15-40 minutes |
| Saline compress | The solution is heated to room temperature (it is important to remember that it should not be higher than human temperature) | Any available breathable fabric, for example, a gauze bandage, is folded into 4-5 layers and lowered into the solution. Gauze is applied to the sore joint. | 100 grams of salt per 1 liter of water | Rheumatism, pain in the knee joint | Until completely dry |
Salt baths
A salt bath is one of the most pain-relieving remedies for treating joints. In this case, it is preferable to use sea salt.
- Water heated to 37-42 degrees is poured into the prepared container.
- Salt is added at a ratio of 1:10. After the salt has dissolved, immerse your hands (feet) in the water for about 15 minutes. At the end, the remaining salt is washed off in fresh water.
Saline baths have a number of useful components and properties that have a beneficial effect on the human body.
Taking salt baths is preferable for osteochondrosis, arthritis, bursitis, gout and, conversely, it is undesirable during pregnancy, skin damage, and diseases associated with the endocrine system.
Full body bath with sea salt:
- 1-2 kg of salt is dissolved in hot water, essential oils are added according to personal preference;
- The water should cool to body temperature;
- Take a bath for no more than 20 minutes, go by your personal feelings. After the procedure, you should wipe your body with a towel.
Baths for osteochondrosis: Water is heated in the range of 40-60 degrees, depending on the doctor’s recommendations. Then 1-2 kg of salt is added and thoroughly dissolved. Duration – no more than 20 minutes. At the same time, it is undesirable for the water to touch the heart area while in the bathroom.
How to take a salt bath
In order for the procedure to bring maximum benefit, you must follow simple rules. Before the procedure, take a warm shower and, if necessary, cleanse your body with a scrub to remove dead skin particles and open the pores for the free penetration of minerals.
- If you are taking a bath in a course, the water temperature for the first procedures should be about 36°C. Then gradually raise it to 38–39°C and, by the end of the course, reduce it again to 36°C.
- If you take salt baths as needed, for example to relieve stress after a long flight or to improve the condition of your skin before an important event, choose a temperature that is comfortable for you.
- If you want a morning energizing bath that will energize you throughout the day, the water temperature can be lowered to 30°C or lower.
- Do not eat 1.5 hours before the bath, but drink a glass of water 15 minutes before the bath, which will cover the loss of fluid in the body.
- How long to take a bath with salt: adults - 20-30 minutes, children under 12 years old - 5-15 minutes.
- The amount of water should be such that it reaches only the heart line. In the process, you can drench your shoulders and plunge your head in several times.
- After the bath, do not wash off the salt, just pat your skin dry with a towel and put on soft, loose clothing. The “salt cloak” should remain on the body for 1.5–2 hours. Spend this time in a relaxed state - drink a cup of herbal tea, freshly squeezed juice or water with lemon. Lie in bed with a book, watch a movie.
- Now you can rinse off in a warm shower to wash off any remaining salt and sweat. Don't forget to apply moisturizing milk, cream or lotion to your body.
How often can you take a salt bath? To achieve a stable result, the course includes 10–15 procedures, which are carried out every other day. You can repeat it after two to three months.
Taking baths with natural salt is not only beneficial for adults; experts also recommend bathing children in a salt bath.
How much salt do you need for one bath?
Standard dosages are usually indicated on the packaging. On average, 500 g is enough for one bath to achieve a general strengthening and calming effect. This concentration is enough to reduce muscle pain, eliminate swelling, prevent vascular diseases, and improve skin health for psoriasis, eczema and atopic dermatitis.
Increase the concentration to 2-4 kg per bath if you want to speed up metabolism, quickly cure a cough or prevent the development of an incipient cold. The same baths are indicated for rheumatism, pathologies of the spine and joints - in the salt solution the body completely relaxes due to the absence of stress.
Higher concentrations are used when organizing floating, when there is up to 10 kg of salt per bath. Due to the increased load on the heart, a sharp increase in blood circulation and lymph flow, the procedure is carried out under the supervision of a medical professional. It's better not to do it at home.
What can you add to a salt bath?
- Lavender - essential oil, extract or petals. It has a relaxing and calming effect, helps cope with stress and irritability, and normalizes sleep. Peppermint, valerian and St. John's wort act similarly.
- Nettle extract perfectly tones and improves blood circulation.
- Tea tree essential oil acts as an antiseptic, restores skin after sunburn, relieves burning and redness after multiple insect bites.
- Essential oil of eucalyptus or fir is an excellent remedy for the prevention and treatment of acute respiratory infections and diseases of the upper respiratory tract. When you breathe in the fumes of a saline solution mixed with phytoncides, you disinfect the bronchi and lungs.
- A mixture of juniper and geranium essential oils added to a bath with Epsom salts will clear the skin of redness, irritation, and acne.
- Orange essential oil enhances the lifting effect of a salt bath and allows you to quickly get rid of cellulite.
- Tea rose petals with essential oils of grapefruit and bergamot will help moisturize the skin and give it a delicate sensual aroma.
- Oak bark decoction is a proven remedy for excessive sweating, ideal for hot summer days.
- Neroli, patchouli, geranium, ylang-ylang, and nutmeg oils are suitable as an aphrodisiac.
Choose the herbal extract, infusion or essential oil that suits you. If you are using the product for the first time, check if you have any allergies. To do this, apply a small amount of product to a small area of skin, such as the crook of your elbow or wrist. Is your skin red, itchy, or small pimples appearing on it? This remedy is not suitable for you.
Sometimes a situation may arise when there is no allergy to individual products, but there is an allergy to their combination. This indicates an overabundance of certain ingredients. Therefore, to begin with, we recommend taking a bath only with salt and gradually adding additional products to it, so that it is immediately clear what exactly caused the negative reaction of the body. If you are using essential oil, start with 6 drops and gradually work up to 10, but no more.
Contraindications
When using salt as the main ingredient for self-medication (at home), the following contraindications must be taken into account:
- Allergic reactions to components or intolerance to them.
- Heart failure, vegetative-vascular diseases, atherosclerosis, hypertension, hypertension.
- Pregnancy.
- There are malignant tumors or skin diseases that are infectious in nature.
To avoid any serious consequences for health and the body as a whole, you should definitely consult a doctor before treatment.
Who should not take salt baths and when?
If you have no health problems, you can take a bath with any type of salt: sea, Epsom, pink Himalayan.
If you have chronic diseases, ask your doctor how to take a salt bath, what concentration to choose and how long to spend on the procedure. Diagnoses for which it is worth obtaining preliminary consultation:
- Cardiovascular diseases, including heart rhythm disturbances, hypotension, hypertension, congenital pathologies
- Diabetes
- Benign and malignant tumors
- Acute infectious diseases
- Thrombophlebitis - aseptic and progressive
- Open wounds and cuts
- Burns
- Bleeding
- Blood diseases
- Weeping eczema
- Progressive glaucoma
Children can definitely take salt baths once they reach 6 months of age. If you want to give an Epsom salt bath to improve sleep in a baby under six months old, talk to your pediatrician.
In the absence of uterine tone and other problems, pregnant women can take a salt bath. Water temperature - no higher than 37°C. Be attentive to your well-being. If you experience the slightest discomfort, complete the procedure and rinse the saline solution from your body with warm water.