Osteochondrosis is a disease of the musculoskeletal system, it affects the cartilage tissue of bones, and there are four stages of severity. It is more common in older people, but can also occur in younger people.
Most often, osteochondrosis, with which a person lives in his usual rhythm and only feels discomfort from time to time, is not taken into account by the draft board. However, its more serious stages can become a valid reason for both deferment and ineligibility for military service. Let's look at each type of disease.
Types of osteochondrosis
Features of development and symptoms of osteochondrosis
Before finding out whether people with spinal osteochondrosis are recruited into the army , it is important to understand the origin of this disease. It is characterized by serious pathological changes, as a result of which the structure and function of the intervertebral discs are gradually disrupted in the patient.
According to statistics, the average age of patients with this diagnosis is 30-40 years, but the likelihood of progression of this disease in young men is also possible.
Most often, lumbar osteochondrosis and other types of dystrophic lesions develop due to uneven load on the spine. For example, carrying heavy weights in one hand or incorrect posture while sitting can give impetus to the gradual progression of the disease.
Additional provoking factors for the development of osteochondrosis are:
- excess weight;
- incorrectly selected pillow;
- using inappropriate shoes;
- previous back injuries;
- existing severe joint damage, leading to uneven load on the back while walking;
- scoliosis;
- sedentary lifestyle and absence of any stress on the back;
- physical strain associated with work;
- acute lack of vitamins;
- metabolic disorders;
- smoking.
It is important to note that it will be much more difficult for conscripts with osteochondrosis (especially in advanced forms of the disease) to serve in the army, since in such a condition they can observe the following signs of the disease:
- disruption of myocardial function;
- hypotension;
- spasm;
- pain in the back and neck, lower back;
- feeling of stiffness in the body;
- migraine;
- dizziness.
As a rule, signs of spinal damage largely depend on the location of the degenerative process. Thus, with thoracic osteochondrosis, the patient may suffer from shortness of breath, pain in the area of the shoulder blades and tingling in the heart.
Osteochondrosis of the cervical spine provokes “floaters” before the eyes, tinnitus and chronic migraines.
Damage to the lumbar region can lead to problems in the reproductive system, as well as pain radiating to the lower extremities.
Prevention of osteochondrosis
To keep your back healthy, follow these recommendations:
- Your nutrition should be complete.
- You need regular physical activity. If you have chronic diseases, consult your doctor and ask them to recommend a suitable gymnastics complex.
- Maintain a normal weight - this will help prevent not only osteochondrosis, but also many other “sores”.
- If you have a sedentary job, take breaks more often to walk and stretch.
- Lift weights correctly. Don't bend at the waist. Keep your back straight - your legs should do the work.
Do not wait for complications of osteochondrosis. Visit a neurologist and get examined. You can make an appointment with us around the clock by calling +7 (495) 230-00-01.
Get a consultation with a doctor
Message sent!
expect a call, we will contact you shortly
Osteochondrosis belongs to a group of diseases that are scientifically called “degenerative pathologies.” In other words, these are diseases in which the vertebrae, intervertebral discs and joints themselves prematurely “wear out”, “age” (this is not an entirely accurate explanation, but in general it helps to roughly imagine what is happening to the spinal column). But what causes this premature wear and tear?
Categories of suitability for the army
After receiving the summons, conscripts must go through a special military commission. It is she who will decide whether the young man is fit for service or not.
Doctors on such a commission pay attention to all acute and chronic diseases that can prevent a man from joining the army.
There are 5 categories of eligibility for conscripts:
- "A" . In this case, the man is completely healthy and fit for service. He has no health restrictions or contraindications to physical activity.
- "B" . Category “B” is assigned to a man who is fit for the army, but with certain restrictions. For example, such conscripts may have mild types of illnesses that do not interfere with service (minor vision problems).
- "IN". Such conscripts are sent into reserve due to some health problems.
- "G" . This category is assigned to those men who receive a short-term health deferment in order to undergo the necessary treatment and fully recover. After this, the person will need to undergo a second commission.
- "D" . Men who receive this category can count on complete exemption from the army. In addition to osteochondrosis, this category is established for asthma, advanced forms of allergies or hypertension with complications.
When is osteochondrosis a limitation?
With such a diagnosis as osteochondrosis, those conscripts who were assigned categories “B” and “D” during the process of the military medical commission were not allowed into military service.
According to fitness category “B”, the conscript has significant health problems. People with this category are not allowed into the army in peacetime. A person can achieve this category in two ways.
In the event that a conscript has limited deforming spondylosis, it is necessary to confirm that the disorder affected 3 vertebrae. This category is also given to conscripts with intervertebral chondrosis - in this case, up to three discs are affected, and the person has pronounced pain in case of physical activity, or the deformation is visually visible.
Law company Povestok.Net®
We have been protecting the rights and interests of conscripts since 2015.
Services for conscripts ›
In addition, this category can be obtained by those conscripts who are diagnosed with deforming spondylosis and intervertebral chondrosis with a large number of beak-type growths. They appear in the area of the intervertebral parts and such growths are characterized by chronic pain.
In order to receive the “D” fitness category, we recall that with it the conscript receives a complete exemption from military service and cannot be drafted even during the war period, it is necessary to have confirmation of a significantly pronounced degree of osteochondrosis. Thus, it is almost impossible to achieve a delay in osteochondrosis in this category.
This category is assigned to those conscripts who have an unstable nature of the disease in the thoracic and lumbar spine. In addition, confirmation of the presence of significant paraparesis and tetraparesis, amyotrophic lateral sclerosis syndrome is necessary.
This category is also given to conscripts who have significant pain syndrome or static-dynamic disorders. According to the conditions, the conscript must undergo at least 3 months of hospital treatment annually without significant improvement.
Any changes in the diagnosis or incorrect formulation during additional examination may affect the change in category. A detailed description of the correct wording can be found in the Schedule of Diseases.
Degrees of osteochondrosis
Before passing the commission, it is important for a man to understand that the initial diagnosis of “osteochondrosis” is not a significant indication for release from service. In fact, the consequences that the disease provokes play a much larger role (there may be problems with the heart, respiratory system, neurological disorders, etc.).
Medical board doctors at the military registration and enlistment office also pay attention to the following factors:
- availability of documents that confirm the diagnosis;
- extracts and certificates from doctors about recorded cases of exacerbation of the disease;
- diagnosed consequences of the disease and chronic pathologies that arose in a person against the background of osteochondrosis.
Moreover, no less attention is paid to the degree of neglect of the disease. There are only 4 stages of osteochondrosis, each of which is characterized by its own characteristics:
- The first degree of the disease provokes pathological changes in the vertebrae. As a rule, patients do not experience any characteristic symptoms, as a result of which they may not even be aware of the pathology. Osteochondrosis of the 1st degree is usually detected randomly when performing an MRI. Conscripts with this diagnosis are fit for service.
- The second stage provokes changes in cartilage tissue, as well as the appearance of instability of the spine. The first signs of such a disease will be prolonged pain in the neck and back, which may be periodic. Patients often do not pay attention to such manifestations of pathology, which leads to the development of 2nd degree osteochondrosis.
- The third stage provokes the formation of hernias, severe pain and various neurological disorders. Conscripts in this condition may be assigned fitness category B.
- The fourth stage of osteochondrosis leads to secondary pathological changes. Such patients often experience spondylosis, hernia and other complications. Young men with this diagnosis should be assigned a fitness category D, which deems the person unfit for service.
Osteochondrosis of the spine - does such a diagnosis exist?
In English-speaking medicine, this term denotes a completely different group of diseases that have nothing to do with our “native” osteochondrosis. In the International Classification of Diseases, a book that all neurologists should refer to when indicating a diagnosis, there are terms such as “spinal osteochondrosis in adults,” “juvenile spinal osteochondrosis,” and “unspecified spinal osteochondrosis.”
However, sometimes this diagnosis is not made entirely justifiably, when the doctor actually cannot fully understand what is happening to the patient. This term may cover diseases such as:
- Myofascial pain syndrome is a condition in which spasm occurs repeatedly in the same muscles.
- Muscle injuries. After an injury, pain begins to bother you, and after a while it goes away on its own.
- Otolithiasis is a condition in which calcium salt crystals accumulate in the inner ear. They lead to dizziness - sometimes they are mistaken for a manifestation of spinal diseases.
- Headache. They are also often associated with degenerative changes in the cervical spine. In fact, more often they have other reasons.
Visit the neurological center International Clinic Medica24. We can understand the causes of your symptoms and recommend treatment to help manage them.
Take care of yourself, book a consultation now
Message sent!
expect a call, we will contact you shortly
Intervertebral osteochondrosis
Intervertebral osteochondrosis is a form of the disease during which serious changes in fibrous tissue are observed. A conscript’s condition is considered serious in the following cases:
- observation of long-term pain that occurs during physical activity;
- pronounced degree of curvature of the spine;
- damage to the intervertebral discs, which led to the formation of hernias.
Most often, conscripts with this diagnosis are assigned category G or D.
What happens to the spine during osteochondrosis?
The development of osteochondrosis is primarily based on the “wear and tear” of the intervertebral disc. Its structure changes at the molecular level. At first, the intervertebral disc swells, then “dries out,” its height decreases, it begins to protrude beyond the vertebral body, and cracks and tears appear in its outer part. Through them, vessels grow inside, the disc becomes denser, and calcification begins in it. The vertebra becomes loose.
Next, the degenerative process spreads to the vertebrae themselves and intervertebral joints. The muscles surrounding the affected part of the spine are constantly under tension, and compactions appear in them.
In order to compensate for the increased load on the vertebrae, bone outgrowths (osteophytes) appear on them, increasing their surface.
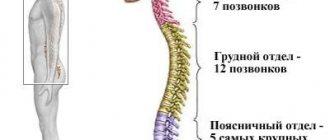
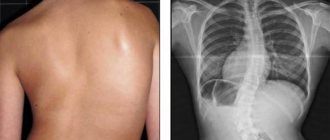
Depending on where the pathological changes occur, cervical, thoracic and lumbar osteochondrosis are distinguished. Two or all three sections may be affected at once.
Medical Center International Clinic Medica24 is a place where they know how to help you. We employ highly qualified neurologists, we use the most modern diagnostic equipment, and adhere to the principles of evidence-based medicine. Appointments can be made 24 hours a day by calling +7 (495) 230-00-01.
The material was prepared by Natalya Yurievna, a neurologist at the international clinic Medica24, Candidate of Medical Sciences Lasch.
Diagnostic measures
To identify osteochondrosis, an examination by an orthopedist and therapist is not enough. In such a condition, the patient should perform the following diagnostic tests:
- MRI of the cervical spine or other affected areas;
- radiography in two projections;
- neurological examination of the sensitivity of the limbs.
You will also need an examination by a neurologist who will identify salts, see the distance between the vertebrae and give an understanding of the degree of neglect of the pathology.
Neurological examination in the diagnosis of osteochondrosis: how is the appointment in the neurologist’s office?
During your appointment, your doctor will ask you some questions:
- What complaints bother you?
- Where does pain usually occur?
- How long does the pain last? How strong is she?
- What is the nature of the pain: are they stabbing, shooting, aching, pulling?
- When do your symptoms usually occur? What provokes them?
- When and after what do you feel better?
Then the doctor will conduct a neurological examination, checking the sensitivity of your skin, muscle strength and tone, reflexes, sense of balance, and coordination of movements. The neurologist can press on specific points near your spine to determine pain. After this, to clarify the diagnosis, you will be prescribed an examination program.
Our neurologists work according to the same standards: they will examine you carefully, won’t miss anything, and will prescribe all the necessary tests.
Lumbar osteochondrosis and the army
Each type of osteochondrosis is dangerous for humans, but the most severe consequences are characterized by the lumbar form of this lesion.
This is due to the fact that in such a condition the patient often experiences drying out of the discs, their protrusion and subsequent complete destruction.
Due to severely pinched nerves, patients may experience severe shooting pain, difficulty urinating, deterioration of erection, and even paralysis of the legs. These are dangerous complications, the occurrence of which is a prerequisite for urgent surgical intervention.
Of course, a conscript can take a deferment for medical therapy, but if the disease is advanced, there is a high risk that he will not be able to serve in the future.
Are they allowed into the army with osteochondrosis - category “B”
Category “B” assigned by the military registration and enlistment office means that the young man need not be afraid of summonses in peacetime. This category implies the presence of serious diseases:
- an intervertebral hernia discovered in a conscript;
- severe pain in a young man during intense physical activity;
- significant deformation of the spinal column, recorded during radiography.
Read more about whether people with a hernia are accepted into the army on our website.
Destruction of tissue in the area of 3 or more vertebral discs, accompanied by sharp pain during movement and increased load, will be a contraindication for military service.
A conscript soldier performs many duties, including marching, physical training. preparations that can cause significant harm to the damaged spine.
We must not forget that it will not be possible to obtain a non-conscription category for patients of military age who are awaiting a summons to the army and who are interested in whether they are recruited for service with osteochondrosis without documentary evidence:
- extracts from the outpatient card;
- certificates from a neurologist, therapist;
- radiography, which clearly shows the deformation.
If the guy fails to prove that he has serious problems with his spine, he will be sent to the troops along with other recruits.
Read more about what diseases will not allow you to be drafted into the army.
Is it possible to wait for release from service?
According to the law, men with the following manifestations of osteochondrosis and its complications are exempt from conscription into the army:
- The patient has complications in the form of motor abnormalities.
- Detection of spondylosis.
- Obvious manifestations of spinal deformity.
- Severe curvature of the thoracic region, which provokes scoliosis and impaired respiratory function.
Categories of suitability for military service
The suitability of a young man of conscription age for military service is determined by a military medical commission held within the walls of the military registration and enlistment office. When examining a conscript, before making a final decision about his health, if there are complaints on his part and suspicions of various pathologies, he is sent for additional research and for consultation with specialists of a narrow profile. As a result of their conclusion, all conscripts are assigned a category corresponding to their state of health, namely:
- Category A - confirms full suitability for combat service in the army in any branch of the military;
- Category B – determines partial suitability;
- Category B – fitness for service in wartime;
- Category G – a young man is considered temporarily unfit for service;
- Category D – completely exempts from the army, without further confirmation.
Doctors believe that the disease itself with osteochondrosis is not a good reason for exemption from conscription, since this disease requires confirmation, which is not always possible to obtain with infrequent exacerbations. For this reason, it is impossible to fully hope to receive a deferment or recognition of unfitness for service with the assignment of categories B or D, even in the presence of scoliosis or osteochondrosis.
In practice, situations often arise when doctors, as a result of an examination, for some reason, cannot make the correct diagnosis. Most often, this happens in the presence of a polysegmental form of osteochondrosis, which in its early stages of development can be perceived as other pathological conditions of internal organs. This poses a certain danger, since the difficulty of making a final diagnosis in such cases threatens the further progression of irreversible changes and disability.
How to prove osteochondrosis
must have the following documents with him when undergoing a military medical examination
- conclusion of the attending physician with a diagnosis of osteochondrosis;
- documents that will confirm the limitation of spinal functions;
- MRI and radiography results;
- a doctor’s report with identified complications from this spinal lesion.
Reviews
Dear readers, you can leave your review about whether people with osteochondrosis of 1st, 2nd, 3rd degrees are accepted into the army in the comments, your opinion will be useful to other users of the site!
Oleg:
When I passed the draft commission, it took me a long time to prove that I had osteochondrosis, and they didn’t really listen to me. And nothing, I served the required term and now I can get any job without restrictions.
Valentin:
There are many cases where liberation from the army makes future life much more difficult. You can no longer get a job in special structures somewhere.
Service and osteochondrosis
Conscripts need to know that they should not hide osteochondrosis. This is especially true for those young people who take analgesics to hide back pain.
In such a condition, painkillers will only mask the problem, instead of eliminating the cause of the lesion.
As a rule, this disease has a chronic form with gradual progression. Excessive physical activity, hypothermia, stress, and poor nutrition can aggravate the patient’s condition. For this reason, men with advanced forms of spinal lesions are not recommended to enlist.
Treatment of spinal osteochondrosis
The standard set of treatment measures for exacerbation of the disease looks like this:
- Anti-inflammatory and painkillers. The doctor may prescribe Voltaren, Movalis, ibuprofen and other drugs.
- If the pain is very severe and does not go away , novocaine blockades are used. The doctor, armed with a needle and syringe, injects the anesthetic into special places where it blocks the transmission of pain nerve impulses.
- Physiotherapy procedures help: medicinal electrophoresis with novocaine, ultrasound, ultraviolet irradiation, diadynamic currents.
- If pain forces you to constantly be in nervous tension, medications are prescribed to help you calm down.
- to the area of pain .
- In order to unload the spine, different types of traction are used. The patient can be placed on a special bed with a raised headboard and secured with rings by the armpits. Underwater traction in the pool is also used.
- Your doctor may recommend that you visit a chiropractor or acupuncture sessions.
- During an exacerbation , special orthopedic devices are worn that help relieve the muscles and support the spine - corsets, Shants collar.
When the exacerbation passes, you need to take measures to help prevent a new one. Therapeutic exercises and massage help strengthen the muscles that support the spine. Physiotherapy courses are prescribed. Swimming is good for you. All treatment methods for osteochondrosis have contraindications, they must be used wisely, so self-medication is not the best choice. Visit your doctor.
Sometimes the symptoms of the disease, despite treatment, continue to increase, and the patient’s condition worsens. In this case, the neurologist may raise the question of surgical treatment.
Why should you visit a doctor soon? Firstly, “real” osteochondrosis is not such a harmless disease. Over time, it can make a person disabled if left untreated. Secondly, the symptoms can be caused by the same myofascial pain syndrome - a neurologist will be able to quickly detect the cause of the pain and eliminate it. Visit a specialist at the medical center International Clinic Medica24 - call to make an appointment at any time of the day: +7 (495) 230-00-01.
Take care of yourself, book a consultation now
Message sent!
expect a call, we will contact you shortly
Back pain is a symptom that, according to statistics, more than 90% of people experience at least once in their lives. Most often it is attributed to osteochondrosis. Not all people experiencing pain in the spine go to doctors. Many people treat themselves with medications that can be obtained without a prescription at the pharmacy, or with folk remedies. Sometimes such “treatment” brings temporary relief - but in the meantime the disease can continue to progress and, perhaps, next time the back or lower back will “twist” much more strongly.
An experienced neurologist will be able to correctly assess the symptoms of osteochondrosis, understand their causes and prescribe the correct treatment for osteochondrosis.
Pain, the main manifestation of osteochondrosis, can be more or less successfully combated for a long time with the help of painkillers and anti-inflammatory drugs, and some folk remedies. But this does not solve the main problem; pathological changes in the spine continue to increase. Over time, this is fraught with compression of the spinal cord and the arteries that supply it, and the development of serious neurological complications: severe weakening, even complete loss, of movements and sensitivity, loss of control over the bladder and rectum.
Will conscripts with cervical and lumbar osteochondrosis be accepted to serve in 2021?
Lesions of the spine in the neck and lower back are observed quite often in young people, but the pathology is not always considered a contraindication for the army.
Significant deformation, severe pain, displacement, destruction of at least 3 discs may become the basis for receiving category “B”.
When undergoing a medical examination, the degree, dynamics of pathology, and concomitant diseases are taken into account.
Often, guys with osteochondrosis cannot provide a sufficient number of arguments confirming their inability to serve, so they join the army.
According to statistics, young men with this disease receive category “D” extremely rarely. There are more opportunities to become the owner of the letter “B”, but for this you will have to collect in advance the necessary package of documents confirming the established diagnosis.
It is not easy to carry out a difficult program for recruits, to adhere to the army regimen, having problems with the spine. Conscripts who are not prepared for the difficulties ahead should take care of their future in advance.
Not every potential recruit can prepare certificates or develop tactics for behavior at the military registration and enlistment office, so it is worth turning to time-tested specialists.
Sedentary work is one of the causes of cervical osteochondrosis.
Cervical osteochondrosis is a serious disease, the symptoms of which are not limited to pain in the cervical region when moving the head. In the absence of treatment, as the disease develops, the patient faces numerous complications that cause significant discomfort and can cause various dysfunctions of the body.
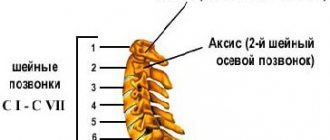
Cervical osteochondrosis is a disease of the intervertebral discs in the cervical spine (usually C5, C6 and C7), which is degenerative in nature and characterized by the proliferation of bone tissue in the cervical spine. Osteophytes formed on the vertebrae irritate the muscles, which leads to their reflex compression and increased pressure on the vertebrae. As a result, the intervertebral discs are compressed and their thickness decreases, which also contributes to compression of the vertebral artery and pinching of nerve endings when turning the head. The blood supply to the brain is disrupted, which provokes oxygen starvation of parts of the brain with possible complications. Artery entrapment, which occurs due to the fact that the vertebrae are deformed and brought closer together, leads to the so-called vertebrobasilar syndrome. Insufficient blood flow to the brain causes imbalance, dizziness, regular or constant blurred vision, tinnitus, fainting and loss of consciousness. Depending on the degree of compression of the artery of the cervical spine and the general characteristics of the body, the consequences can manifest themselves in varying degrees of severity and be combined with each other.
Infringement of the occipital nerve in cervical osteochondrosis causes constant headaches radiating to the neck and temple. The most dangerous is infringement of the spinal cord and its nerve processes. In this case, serious dysfunctions may be observed, consisting of impaired coordination of the limbs, decreased sensitivity, and loss of strength. The patient may also experience difficulty controlling the bladder and bowels, and spastic, uncontrolled leg movements are common.
CAUSES OF OSTEOCHONDROSIS OF THE CERVICAL SPINE
- Poor posture . Scoliosis, stoop, round back, kyphosis and other postural disorders, even if they are minor, cause serious imbalance in the spinal column. As a result, the load on the intervertebral discs is distributed unevenly, which provokes their deformation and increased wear. The vertebrae begin to come closer together, causing pinching of the nerve processes, and cervical osteochondrosis develops quite quickly. Posture disorders caused by changes in the natural position of the ribs have similar consequences.
- Muscle spasms . Spasmodic reactions of the muscles of the neck, back, chest, and abs can lead to certain areas of the body becoming very tense. As a result, the overall equilibrium position of the body is disrupted, causing a change in the position of the spine. Deformations can affect the cervical region or other parts of the spinal column, causing osteochondrosis of the thoracic, cervical, and lumbar regions.
- Impaired blood supply . Since the vertebral discs do not have a direct connection with the circulatory system, they receive nutrition from surrounding tissues. Impaired blood supply to the cervical spine leads to the fact that the discs do not receive enough fluid to rehydrate (restore their shape by absorbing moisture) and renew cartilage tissue. As a result, their wear accelerates, and a decrease in the distances between the cervical vertebrae is observed, leading to osteochondrosis.
- Violation of innervation . A decrease in the sensitivity of the nerve roots leads to pathological changes in their structure, as a result of which the displacement and deformation of the cervical vertebrae goes unnoticed by the patient. After all, there is no pain due to sensory disturbances.
- Diseases of internal organs . Incorrect position of internal organs, their displacement and lowering due to various dysfunctions leads to disruption of the overall balance in the body. As a result, this acutely affects the position of the spinal column - the cervical and lumbar vertebrae are displaced and deformed, leading to the corresponding types of osteochondrosis.
SIGNS OF CERVICAL OSTEOCHONDROSIS
Depending on which vertebrae are affected by cervical osteochondrosis, symptoms may manifest differently. But if you have at least one, you should suspect osteochondrosis of the cervical spine, so it makes sense to contact a specialist for a comprehensive examination and diagnosis. The main signs of osteochondrosis of the cervical spine:
- Painful sensations . The first symptom is pain, which in the early stages only appears when turning or tilting the head. Unpleasant sensations are usually localized in the right or left part of the cervical region, sometimes symptoms also affect nearby areas. With the development of cervical osteochondrosis, the pain radiates to the occipital and frontal parts of the head and takes on the character of a migraine.
- Deterioration of the senses. Mostly, vision problems begin to occur. Vivid symptoms are cloudiness, double vision, darkening of the eyes, which is regular, and tinnitus is often observed.
- Dizziness. Almost always, osteochondrosis of the cervical spine is accompanied by characteristic dizziness that occurs with sudden movement or turning of the head, bending, or changing posture. This may cause nausea and vomiting.
- Fainting. Semi-fainting and loss of consciousness are a common symptom of the late stages of cervical osteochondrosis. In some patients, these signs may also be observed during the initial development of the disease;
- Cardialgia. Along with other symptoms, sensations characteristic of angina attacks are often observed;
- Sensory disturbances. Depending on which vertebrae are affected by cervical osteochondrosis, a sign of the presence of the disease is partial loss of sensitivity in the occipital and parietal regions of the head, in the glenohumeral region, and forearm. In some cases, numbness may spread from the neck along the arm up to the little finger or thumb, respectively, along the outer or outer side of the limb;
- Speech impairment. It is not a very common symptom and occurs due to loss of control of the tongue due to compression of the C3 and C4 nerve roots. There may also be difficulty breathing.
At the first signs, it is recommended to consult a specialist for whom cervical osteochondrosis, symptoms and treatment is one of the areas of professional activity.
TREATMENT METHOD:
- Manual therapy is performed
- Acupuncture
- Electrical stimulation techniques
- Physiotherapy
- Gymnastics
- Swimming.
We offer several exercises that will help you defeat osteochondrosis and preserve your health . 1. Lower your chin to your neck. Turn your head first 5 times to the right and then 5 times to the left. 2. Raise your chin a little. Again turn your head to the right 5 times, then to the left 5 times. 3. Tilt your head to the right, trying to reach your shoulder with your ear - 5 times, then to the left 5 times.
4. Head straight. Overcoming the resistance of tense neck muscles, press your chin to the jugular fossa. The top of the head stretches upward. 5. Press your forehead into your palm and tense your neck muscles. Perform the exercise 3 times for 7 seconds. 6. Straining your neck muscles, press your left temple onto your left palm (3 times for 7 seconds). Now press your right temple onto your right palm (3 times for 7 seconds). 7. Chin straight, hands on the back of your head. Press the back of your head onto your hands 3 times for 7 seconds. 8. Place your hands, joined at the fingers, under your chin. Press your chin onto your hands 3 times for 7 seconds.