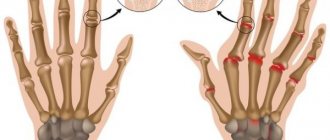
When a joint is destroyed - complete or partial - a person suffers unbearable pain. The organ loses its functional features, which can lead to disability. For some time, the patient can use painkillers and physiotherapeutic procedures, but only prosthetics can radically change the situation.
Medicine is trying to restore joint function using conservative methods, but serious changes are not amenable to such treatment. If there is damage to bone tissue or completely worn out cartilage, no medicine will correct the situation.
Endoprosthetics of hand joints is most often in demand among elderly people. It allows you to move actively and feel good. Thanks to such operations, the patient returns to his normal life without pain.
Prosthetics, like any operation, has risks. They are defined:
- health status;
- the severity of the problem;
- type of prosthetics.
Before the operation, a thorough examination is carried out to identify indications and contraindications for this action.
Indications for prosthetics
- joint deformation after injury;
- long-standing dislocation;
- chronic joint inflammation;
- pain that cannot be relieved.
FINGER PROSTHETICS in ISRAEL
Prosthetics of toes and hands in the Israeli prosthetic center is performed in the shortest possible time: 2-4 weeks.
Advanced technologies, modern materials and components are used in prosthetics. The range of prosthetics products is very wide and is designed for people of all age categories, amputation levels and varying degrees of physical activity: elderly people, people leading an active lifestyle, athletes, etc. Each amputation case is unique. Each case of prosthetics has special requirements. We offer a wide range of field-tested products and services to provide a wide range of prosthetic options for lower-limb amputees. Masters develop new technologies and methods of prosthetics based on a thorough study of the characteristics of the musculoskeletal system and strive to provide their patients with the highest possible mobility and quality of life.
The prosthetics program includes:
- A consultation with a prosthetist, at which possible options for prosthetics for the patient are discussed, and testing of his physical and physiological capabilities is carried out.
- Prosthetics;
- Training in using a prosthesis;
- Warranty service;
- Possibility of purchasing aids designed to ensure comfort when using the prosthesis, such as: stump care products, stump covers made of high-quality materials, liners for any level of amputation, sanitary equipment, walkers, wheelchairs, crutches, canes, bandages , corsets, orthoses, etc.
- Full support in Russian.
On the 1st day, a consultation with a prosthetist is held:
- A prosthesis model is selected and its dimensions are determined;
- The required model is made, taking into account the correct location of the functional units and is first tried on;
- A model of the prosthesis is produced in accordance with the individual characteristics of the receiving cavity;
- The patient is taught how to properly use the artificial limb.
In case of complete loss of a finger, prostheses are usually not used, since the latter are mainly cosmetic, while functional models, as a rule, are applicable only when one or two phalanges are lost; they are put on the remaining stump of the finger. If a person loses several fingers, he can undergo both cosmetic prosthetics and functional prosthetics with restoration of grip function.
Cosmetic prosthetic finger made of silicone, connected to the hand using vacuum and/or body glue.
Cost: 1705 USD
After all measurements have been taken, the process of making the prosthesis begins. Production time: up to 30 days.
You can fly home and wait for the prosthesis to be ready at home. When the prosthesis is ready, you arrive at the medical center and test the prosthesis for two to three days.
If you are satisfied with the result and everything suits you, we confirm the order.
If the prosthesis is sent for revision, if there are additional changes, then everything is repeated again. That is, the prosthesis will be remade for you; as soon as it is ready, you will again need to try it on and test it. When the final prosthesis is ready, there is no need to come to us again. We will be able to send it via courier services.
(495) 506-61-01 – where is the best place to get prosthetic limbs?
Limb prosthetics in Moscow
The Rehabilitation and Orthopedic Center in Moscow has been engaged in lower limb prosthetics for the last ten years. The REC produces a wide range of modern modular prostheses using high-tech modules from Icelandic and German Otto Bock. In addition, the center’s specialists use well-proven modules from the Russian company Metiz to produce low-cost prosthetics. More details
Intelligent prosthetic leg C-leg
The microprocessor-controlled lower limb prosthesis C-Leg uses a pneumatic drive to provide its wearer with sensations similar to those of walking on both legs. The pressure sensor (strain gauge) measures the load on the prosthesis fifty times per second, and thanks to this, the process of bending the artificial knee and ankle is carried out properly. According to users, walking with the C-Leg is much easier than walking on conventional “non-intelligent” prostheses: you can go down the stairs without any problems, whereas previously you had to avoid this, etc. More details
Biocybernetic neural interfaces – BrainGate2
Thanks to this device, for the first time in the history of mankind, a completely paralyzed person was able to independently drink coffee from a bottle, using the electrical activity of his brain and controlling a robotic manipulator that looks like a hand with the power of thoughts. To do this, a 58-year-old patient named Kate had a special neurochip implanted into the motor area of the cerebral cortex, consisting of ninety-six gold contacts and allowing the signals of neurons to be converted into commands for an artificial hand. More details
Types of modern prostheses
Modern prosthetic companies produce a wide variety of devices designed to replace lost limbs for people. All of them differ according to one or another criteria: method of fastening, principle of operation. To restore simple and basic functional abilities of the hand, it is necessary to apply a working model of the upper limb. To overcome complex movements, an active functional prosthesis is most often used. Such mechanisms are quite complex and more expensive.
There are two large types of prostheses:
- Functional (active) - allowing you to perform any actions
- Cosmetic (passive) – performing only a decorative function
Functional prostheses are controlled through various mechanisms. Depending on the operating principle, they are divided into bionic (the most modern), working, and active mechanical. Such devices may have a cosmetic shell that imitates the appearance of a hand, or a modern technological design.
The prosthetics itself does not take much time. The most important thing is choosing the right device. It must be not only convenient, but also reliable, since it is used every day and in a wide variety of conditions.
To protect the moving mechanisms of prostheses from wear, corrosion and other unpleasant aspects, special service materials are used during their assembly and maintenance.
Modern high-tech coatings significantly improve the characteristics of prosthetic hands without causing any harm to the health of their wearers.
Today, such materials are produced not only abroad, but also in our country, which is increasingly developing in the field of prosthetics.
Coatings form a thin but durable composite layer on parts that levels the surfaces, thereby increasing their supporting area and load-bearing capacity.
Among the most popular coatings used in the production and maintenance of prostheses is MODENGY 1014. The material based on molybdenum disulfide and polytetrafluoroethylene reduces wear of contacting surfaces, protects parts from water ingress and corrosion.
Unlike conventional lubricants, the cured coating leaves no traces and does not emit harmful fumes, so the wearer of the prosthesis feels as comfortable as possible.
Coatings are used in the production of the most modern functional prosthetic models. Read below about the types of limb replacement devices.
Why do you need a prosthetic toe?
In addition to the fact that prosthetics guarantee an aesthetic appearance, the functionality of the foot, which was reduced after amputation, improves. Interestingly, prosthetic toes were practiced in ancient Egypt. During the excavations, a mummy was discovered; a prosthetic big toe was clearly noticeable on her foot; at that time it was made of wood and was secured to the foot with leather straps. Now technology has gone far ahead and a person can use modern prostheses that are easy to use.
X-Fingers prosthesis
This prosthesis was invented in America, and at the moment this solution remains the most popular. Dan Diedrick's company produces hundreds of unique prosthetics every year. This takes everything into account:
- Finger thickness.
- Its length.
- Methods of integration with the stump.
- Other important nuances.
These prostheses have the necessary flexibility and significant motor activity. Here are just a few examples: with such a prosthetic finger, fastening buttons, looking for change in a wallet, even tying shoelaces will not be a problem.
Features of prosthetics
At the moment, various manufacturers offer prostheses made of high-quality silicone, which do not cause allergic reactions, and they also look aesthetically pleasing. A person with such a prosthesis will not feel inferior.
There are different types of prostheses, which differ in price and their functional load. Among the options:
- Working prostheses are simple products that will follow the shape of the foot and fingers. Often these are used as a method of getting the stump used to a permanent prosthesis. The period of wearing this before installing a permanent one is 2-6 months.
- Active/passive functional - this product is more complex in its structure. Often used for permanent finger prosthetics. They have joint modules and movements are regulated using micromotors and rods. The sensors in them react to micropulses that occur when you try to bend your finger.
- Cosmetic functional prostheses are the most modern option, at the same time they are the most complex in their structure. In addition to having a special module that allows finger movements, it is covered with a synthetic material that is very similar to real leather. These prosthetics are so perfect. That they can be used constantly, they do not need to be removed even when visiting the shower or swimming pool.
Which prosthesis to choose?
Modern companies that manufacture prosthetic fingers are actively improving. New developments are constantly appearing, but not all of them are successful. You should select a prosthesis together with an orthopedist; the main criteria in this case will be:
- Type of prosthesis. It depends on which finger needs to be replaced. The specifics of replacing a particular finger are described in the types of prostheses.
- Finger amputation technique, condition of the stump. This influences the option of attaching the prosthesis and the choice of socket. Today, vacuum fastening is most often practiced, when the transition from the prosthesis to the stump is almost imperceptible.
- Cosmetic similarity of the prosthesis to a finger. In this case, the more realistic it is, the better. The ability to manufacture prostheses from silicone allows them to be made very natural, both to the touch and when looking at the prosthesis.
- The patient’s financial capabilities – the more money he is able to spend, the better and more functional the prosthesis will be.
- Manufacturer's choice. In this case, there is no need to chase cheapness; it is better to choose a product from a well-known brand that has proven itself.
Conclusion. The choice of a particular prosthesis is made together with an orthopedic surgeon. Among the features of prosthetic fingers is their miniature size with great significance for a person’s everyday life.
Prosthetic fingernails
The need to do this arises quite often. After all, nails are the natural protection of the toes from mechanical damage. The lower extremities are often exposed to it. The specificity of such prosthetics is that it is impossible to carry it out using gels, as is done when extending the nail plate on the hands.
This procedure is carried out only in a specialized institution. The peculiarity of the materials is that it is necessary to achieve flexibility, which will help prevent injury to the finger as a result of wearing shoes. For this purpose, fiberglass and other similar plasticizers are used; it is they that provide flexibility.
Bionic prostheses
Bionic (bioelectric, myotonic) prostheses are one of the most modern and advanced upper limb replacements. According to the classification of the Ministry of Labor of the Russian Federation, they are called prostheses with an external energy source.
Such devices are controlled by signals generated during muscle contraction. Myodensors built into the prosthetic socket capture them and transmit them to the microprocessor of the hand. Through computer algorithms, information is converted into motor commands - as a result, the prosthesis performs a certain gesture or grip.
Simple bionic devices use only 2 muscle sensors, which record the activity of the two largest muscles. This is associated with some inconveniences when using such prostheses: sometimes, in order to perform one movement, you need to send a whole series of similar, repeating commands. Only after this does a kind of switching of modes occur.
However, today not only simple but also high-tech bionic devices are produced that are suitable for restoring various parts of the hand (fingers, hands, forearms) and the entire limb.
The most modern bioelectric prostheses resemble mini-computers: they have built-in mini-bank tags, with which you can pay for purchases and services with one touch, flexible displays that allow you to track the time, date, battery level, prosthesis control mode, and other parameters. Some devices are equipped with GSM modules for remote status monitoring, fault detection and firmware updates.
Research continues on how to control a prosthesis using human neural activity (the user’s concentration must be captured by a special cap).
The latest models of bionic prostheses also make it possible to sense heat and pressure through sensors, the signal from which enters the skin of the stump.
Treatment regimen
In order for prosthetics to be successful, the first step is to undergo a series of examinations. Among them: tests, x-rays, electromyography. It is also necessary to undergo an examination by an orthopedist and, together with the doctor, select a suitable prosthesis that will be easy to use and affordable.
Next comes the manufacture and installation of the prosthesis. You need to get used to it, so there will be an adaptation process. Clinics give recommendations on how to make the addiction process go faster. This process is naturally monitored.
Benefits of treatment with ServiceMed:
- Creation of high-quality silicone prostheses according to individual parameters
- Optimal program for patient adaptation to the prosthesis
- Advisory assistance from specialists on all issues related to prosthetics
- Excellent prospects for sanatorium-resort restoration
- Support on accommodation and travel arrangements around the country
Functional and comfortable prosthetic toes will give you the opportunity to walk, run, play sports and get rid of your inhibitions forever!
Finger prosthetics in Israel with the support of ServiceMed is the right decision for everyone.
LEARN ALL ABOUT THE FEATURES OF PROSTHETICS IN ISRAEL
Dr. Botzer Itamar , chief physician of the arthroscopy department at the Tell Hashomer clinic, specialist at ServiceMed
The doctor's scientific and practical activities are known far beyond the borders of Israel - he is the author of research and articles. Specializes in sports orthopedics. He performed many operations on joints.
Would you like to consult Dr. Botser Itamar?
No
Please fill out all fields of the form and we will contact you shortly
Receive a treatment plan and prices for free by filling out the form Specialists in the field
- BiographyOnline consultation
Dr. Arbel Ron Orthopedics. Traumatology. Orthopedic surgery - BiographyOnline consultation
Dr. Rosenblatt Ishai Orthopedics. Orthopedic surgery
- BiographyOnline consultation
Prof. Jacob Bickels Orthopedics. Oncology. Orthopedic surgery
Questions that concern a person before prosthetics
- The need for a prosthesis. If there are any doubts about whether a prosthesis is needed at all, the doctor will dispel them during the first consultation. Even the amputation of one toe affects gait, especially if it is the big toe. In addition to the fact that this causes discomfort when walking, it can be accompanied by pain in the lower leg and thigh. Plus, over time, deformation of the foot will occur.
- Preparation before prosthetics. Preparation is needed not just before prosthetics, but during the adaptation period after amputation. Particular attention should be paid to exercises that will help maintain the flexibility and functionality of the remaining fingers. Since the center of gravity shifts after the loss of one or more fingers. It is necessary to adapt the leg muscles to the new balancing conditions. In clinics, after amputation, the patient is prescribed a course of exercise therapy with specially designed exercises.
- Durability of the prosthesis. Most prosthetics today are silicone. With proper use and care, this material can retain its appearance for 1-2 years. In order to extend its service life, the prosthesis must be regularly wiped with a disinfectant and removed every day.
Conclusion. Prosthetic toes will help you feel like a full-fledged person again. You will be able to forget about the problems and discomfort caused by the amputation of one or more fingers.
Prosthesis: what is it and what are they?
Prosthetics
- replacement of lost or irreversibly damaged body parts with artificial substitutes -
prostheses
. The word came into Russian from the French prothese, which in turn came from the Greek. prosthesis – accession, attachment.
The first mention of prosthetics in history is the escape from captivity of the Greek Hegazistratus, who lived approximately 500 BC. e. Chained, he was forced to saw off his leg and then ask a carpenter he knew to make him a prosthesis. This prosthesis was like two peas in a pod to the well-known wooden prostheses of quite a late time. The Roman writer Plinius Major mentions a general who lost an arm during the Punic War (218-201 BC). An iron hand was made for him with which he could hold a shield. After the development of mechanics, closer to modern times, more advanced types of prostheses began to appear, well simulating the lost part of the body or even capable of moving due to built-in mechanisms.
Bionic hands: history, future and reality
The loss of any limb or any organ is a big problem for a person. In some cases, you have to put up with it, but sometimes modern prosthetics can turn a person with “disabilities” into a person with “augmented capabilities,” as representatives of some companies in this industry put it. In this article we will talk about hand prosthetics. Here we will not touch on the topic of teeth, eyes, ears, face, internal human organs and even legs. And let's start with the Middle Ages, when amputation was one of the most effective ways to fight infections. The topic will continue with devices from the Victorian era and modern bionic prosthetics, and at the end we will discuss the future of this area.
Steel hands of knights
This prosthetic arm, made of steel, dates back to the 16th century. It has double fingers and a thumb that can be held in specific positions. Control took place using a button on the back of the hand. This device is one of three prosthetics of the Chevalier Götz von Berlichingen. The device made it possible to pick up objects and, perhaps, even write with a pen.
This is another knight's hand.
This iron hand, made in the 17th century, had a mechanism inside it that allowed the flexion of the remaining arm to control the clenching of the fist. This was apparently the prototype of modern traction prostheses.
This wooden prosthesis is believed to have been made in 1800.
Another wooden prosthesis was supposedly controlled by a cable. The artificial hand is on display at the Smithsonian Museum.
Source: invention.smithsonian.org
Less wealthy people could use prosthetic hooks like this early 19th century device. When I took up this article, I was sure that only such prostheses existed before the 20th century.
The elbow, wrist and fingers of this prosthetic, made between 1850 and 1910, can move. A glove was probably put on this iron hand. Although the device looks very interesting.
In 2013, a post about a miracle prosthesis from Holland was downvoted on Habrahabr. The post contained a scan from the Journal of the Ministry of Public Instruction No. 7 of 1837, which described "a mechanical arm of a new device, which can completely replace the loss of these precious members." Two such hands, which can be used to wave, move fingers and pick up objects, were given to two servicemen. Judging by previous examples of prosthetics, which are stored in various museums and described by historians and scientists, this article may not have been a hoax, as users thought.
The photo below is a veteran of the American Civil War of 1861-1865.
The palm of this 19th-century female artificial hand shows holes that may have been used to attach a hook or other devices to make life easier.
Source: collectmedicalantiques.com
XX century
The prosthesis in the photo below was made for a 16-year-old girl who lost her arm below the elbow. The prosthesis is made of wood, leather and fabric. It should be noted that they thought about both the appearance of the device and its functionality: the wrist rotates, the fingers change position, and a hook is added to the palm - so that you can, for example, carry a bag. The prosthesis is on display at the Science Museum in London.
This is what dentures looked like in the 19th and 20th centuries. Presented at the Science Museum.
In this photo, a German soldier works in a workshop using a prosthetic left arm. The photograph is housed at the National World War I Museum in Kansas.
This is a Swiss prosthesis. In the best traditions - with different replaceable attachments.
This prosthesis is on display at the Science Museum in London. It was made for a 17-year-old boy in 1959.
Source: sciencemuseum.org.uk
Military personnel were among the first recipients of prosthetics. In this case, a Brooklyn-based prosthetics manufacturer said in a promotional poster that it was proud to work with the US military.
As you can see, prostheses of this type have not changed much over several decades.
Modern bionic prostheses
Let's first understand what “bionic prostheses” are.
Bionics is an applied science that combines biology and technology. Wildlife helps scientists find solutions for technical devices. There are biological bionics, which studies processes in biological systems, theoretical, which builds mathematical models of these processes, and technical. What is important to us now is technical bionics: it applies models of theoretical bionics to solve engineering problems, as in the case of prosthetics. Previously, experts meant by “bionic” prostheses such devices that are similar to the part of the body that they replace. From the point of view of modern concepts, these prostheses are those that are controlled by electronics and biocurrents, that is, they use myography or an encephalogram.
The British company RSLSteeper, which currently has about 90 years of experience in prosthetics, introduced the BeBionic bionic hand prosthesis to the international market in 2010. At that time, an artificial hand for an adult had only four functional grips, but it already allowed eating, drinking, typing, turning a key in a lock, using an ATM and holding small objects. Using the device, the user can break eggs and hold a disposable cup in his hand - because even the pressing force is regulated by commands received by sensors from the muscles.
The lack of mass demand and low competition is the main reason why bionic prostheses are very expensive. In 2013, a prosthetic palm cost up to one hundred thousand dollars.
How to reduce the cost of a prosthesis? We need to make it cheaper to produce. In 2013, a crowdfunding campaign on IndieGoGo was successfully completed to create an open and affordable prosthetic palm, most of the parts for which can be 3D printed. The device has independent actuators for each finger, haptic feedback, and reads signals through the skin for control. In the palm of the device there are electric drives and a control board on Arduino.
» width='600″ alt=“image”/>
Model of a child’s version of Dextrus, stylized as Iron Man’s arm.
Another project, Limbitless Solutions, which makes inexpensive prosthetics, arranged for Robert Downey Jr. and a seven-year-old boy, Alex, to meet in 2015 to give the child a bionic prosthesis in the shape of the arm of his favorite character's costume.
And what is very important is that thanks to printing on a 3D printer, the cost of this prosthesis was only $350. The project itself makes these prosthetics mainly for children whose families cannot afford to spend 30-100 thousand dollars on a bionic arm.
» width='600″ alt=“image”/>
In 2014, Johns Hopkins University Hospital developed a double-arm prosthesis and tested it on a man who had lost both arms from the shoulder down. To control the prosthesis, the system read signals from the pectoral muscles.
One of the most serious players in the hand prosthetic market in the world is Bebionic. The media often say that it was this company that made the first bionic prosthesis. This video shows a demonstration of the capabilities of the BeBionic 3 myoelectric prosthesis from Nigel Ackland, a well-known cyborg in Russia and the world.
In June 2021, the first British woman received a Bebionic Small hand, a realistic prosthetic hand that, due to its small size, is suitable for women and teenagers. Nicky Ashwell, 29, from London, was born without a right arm and spent her entire life using a cosmetic prosthesis that had no functionality. Judging by the photos, Nicki decided not to wear a glove that imitates human skin.
The Bebionic Small prosthesis weighs 390 grams, can hold up to 45 kilograms and has 14 grips.
» width='600″ alt=“image”/>
In May 2021, 26-year-old James Young received a prosthetic arm made to resemble the arm of Solid Snake, the hero of the Metal Gear Solid game series. James lost his left arm, injured his left leg and suffered other injuries when he was hit by a train, and after hospital was given standard prosthetics, which he described as "ugly." Now he is “testing” another prototype of an artificial hand.
Photo: dailymail.co.uk
Metal Gear Solid 5
As can be seen from the examples above, modern bionic prostheses have sufficient functionality for various everyday activities. But there is something else that scientists are working on: the sensitivity of prosthetics. It is important for a person’s hand to understand how tightly to squeeze something, what exactly can be taken in the hand, and what cannot. It’s the same with an artificial brush - the ability to feel it will greatly improve it.
In 2013, a team from the Cleveland Veterans Affairs Medical Center and Case Western Reserve University developed a prosthesis whose sensors are directly connected to the nerve endings of the remaining limb. In this case, the impulses from the sensors do not differ from the impulses transmitted by one’s own hand. The first volunteer who tested the device said that he began to feel in his “fingers,” palm, and back of his hand. In the video below, a volunteer tries to pick a twig from a cherry - first with the artificial hand's sensitivity function turned off, then with it on. In the second case, he copes with this task better.
DARPA also introduced a feedback prosthesis in mid-2013 as part of the RE-NET (Reliable Neural-Interface Technology) program. The agency planned to work on this project until 2016.
In 2015, a 28-year-old paralyzed patient, using a prosthetic device connected to the brain, began to touch various objects, including touching each finger. This was done as part of another program - Revolutionizing Prosthetics.
In 2014, Dennis Aabo Sørensen, who lost an arm due to careless handling of pyrotechnic “toys,” volunteered to test a feedback prosthesis. The electrodes of the prosthesis were connected to the human nervous system. The strength of the signal is calculated by a computer, and Dennis began to sense the size, shape and texture of the object.
Bionic prostheses in Russia
There are virtually no players on the Russian market who have introduced bionic prosthetic hands into commercial use.
The development is being carried out by the Motorika startup, known for introducing traction prostheses for children into the federal program for providing disabled people with technical means of rehabilitation - thanks to this company, children receive traction prostheses at state expense. This video shows tests of the fourth prototype of the Stradivary artificial hand, which the team plans to begin producing and installing in Russia in October-November 2021. The Stradivary prosthesis is myoelectric. No surgery is required to install it. Surface myodensors are built into the receiving sleeve, touch certain places on the skin in the muscle area, capture the potential during muscle contraction and transmit a signal to open or close the hand.
The main problem encountered when installing this type of prosthesis is poorly developed forearm muscles. To avoid this problem, “Motorika” makes traction mechanical prostheses for children - such prostheses not only help perform various functions of the hand, but also serve as a simulator.
According to Ilya Chekh, founder of Motorika, there are now two directions for the development of bionic prostheses.
The first is sensation, that is, feedback that allows the owner of the prosthesis to receive information about the qualities of the object he touches with the device.
The second is the implantation of all elements, including the frame and sensor. One of the problems with James Young's Metal Gear Solid-like prosthetic arm is the need to remove it to sleep or shower. In the future, prosthetics will more closely resemble the hand of the main character in the film “I, Robot,” played by Will Smith. Not in terms of matching your own limb, but in terms of the absence of the need for additional care.
Nowadays, inexpensive printing in prosthetics is very popular in the world. The availability and proliferation of 3D printers has led to this. There are various projects that help you get free traction prostheses, and diagrams that you can use to modify and print a myoelectric prosthetic arm. Ilya Chekh considers this trend to be temporary: it will be popular for the next 10-12 years while implantable technologies develop and scale. 3D printing now offers a lower cost, but significantly loses in quality. And it will most likely never provide better quality compared to traditional technologies. It will always be cheaper and better quality to laser cut sheet metal than to print with polymers using a printer. At least this will be the case if you think in the existing paradigm of the development of printing, and do not fantasize about the molecular construction of objects. The printing was created to minimize the time and cost of prototyping and R&D.
How do you see the future of human arm prosthetics? What installation and control methods do you think will be most in demand in 20-30 years?
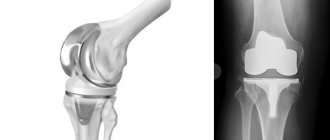
Endoprostheses of finger joints
Many bone pathologies lead to loss of motor function in the fingers or hand. Sometimes an excellent solution to such problems is endoprosthetics of the joints of the hand. The procedure allows you to completely restore normal mobility of the damaged joint. The operation requires certain preparation and rehabilitation measures. There are also contraindications to prosthetics.
Indications for the procedure
Endoprosthetics is an operation in which damaged joints are replaced with implants.
This technique is widely used all over the world and makes it possible to implant not only large joints, such as knee or hip joints, but also finger joints. Only high-quality materials are used for prosthetics: metal alloy, polyethylene and ceramics. The average lifespan of an endoprosthesis is 15 years. As a rule, prosthetics are recommended for the following pathologies:
- chronic inflammation of cartilage tissue;
- dislocation and subluxation;
- joint deformation due to injury;
- severe pain that does not respond to painkillers.
Return to contents
Preparation for endoprosthetics of fingers
The decision to use prosthetics is made by the doctor. Before surgery, the patient is given a detailed description of the course of the operation, the duration and features of rehabilitation, possible consequences and complications. In addition, the patient must undergo a series of instrumental and laboratory tests. As a rule, the following tests are prescribed:
- General clinical tests of urine and blood. They provide information about the patient’s health status, the presence of inflammatory processes and individual characteristics.
- MRI. Layer-by-layer images show the condition of the cartilage and muscle tissue and allow you to accurately select the size of the prosthesis.
Return to contents
Contraindications
There are no absolute contraindications for penile prosthetics. However, in some cases the operation may be postponed to a later date:
- somatic diseases in the stage of decompensation;
- foci of infection;
- voluntary painful erections (priapism);
- inflammatory processes in the surgical field area.
Senile age is not a contraindication, but requires a more thorough examination before surgery with the involvement of related specialists.
How is the operation performed?
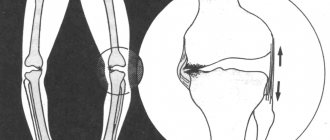
Endoprosthetics of hand joints is a complex surgical procedure that is carried out in two stages. First, it is necessary to eliminate visible damage: scars, crooked fingers, correct a dislocation. For this purpose, external devices and plastic surgery are used. When replacing the finger joints of the hand, the surgeon makes two incisions: one on the dorsolateral side of the phalanx, the second - directly on the articular capsule. The affected cartilage is removed, and an endoprosthesis is inserted in its place - into the spinal canals. The replacement is performed under local anesthesia or general anesthesia. After the operation, the patient is in the hospital. It is necessary to wear a cast on the hand for some time. The doctor prescribes pain relief and anti-inflammatory therapy.
A prerequisite for the successful outcome of finger joint replacement is the performance of therapeutic exercises.
Penile prosthetic methods
In modern medical practice, several types of prostheses are used, introduced into the cavernous bodies of the penis and differing in their operating principle:
- elastic non-hydraulic - reliable and simple silicone paired rods, with the help of which the genital organ is constantly in a state of erection;
- plastic non-hydraulic - double metal spiral or polyethylene rods, with good ability to plastic deformation;
- hydraulic - fluid flows into the implanted cylinders through tubes under the action of a pump from the reservoir, stretching the organ to the desired size.
The latter are 2-component (the pump and reservoir are combined and placed under the skin of the scrotum) and 3-component (the pump is located in the scrotum, the reservoir is behind the womb). The cost of hydraulic prostheses is higher, but they have a more natural appearance. The incision is made in the area of the folds, the stitches are almost invisible after healing.
The question of which penile prosthesis to choose is decided together with the patient. The technique of the operation is determined by the doctor taking into account clinical indications. In some cases, plastic reconstruction is performed. For significant defects and curvature of the penis, flap corporoplasty and Nesbit surgery are performed.
Contraindications and consequences
Endoprostheses cannot be installed in the following pathologies:
If there is muscle atrophy on the sore finger, surgery is not performed.
- acute inflammatory diseases;
- atrophy of the muscles of the affected finger;
- circulatory disorders of the limb;
- destruction of bone tissue, which prevents proper attachment of the implant;
- refusal to follow doctor's orders;
- open areas of bone growth.
Prosthetics of small joints in the hands is fraught with possible complications, such as:
- Wear of the endoprosthesis. Occurs as a result of the use of low quality materials, improper installation, or after 15-20 years. In this case, the prosthesis is replaced.
- Infection. It is caused by improper care of the postoperative suture. Typically, patients receive anti-inflammatory therapy after surgery, so the chance of infectious inflammation is negligible.
- Bone cysts. Formed when blood circulation is impaired.
The patient needs to understand that endoprosthetics is a common operation, and the incidence of complications is very small. With proper examination before surgery and proper care after prosthetics, the possibility of side effects is reduced to zero. The main task of the patient is to strictly follow the recommendations of the attending physician.