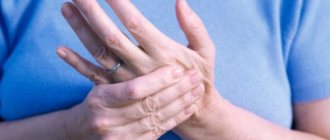
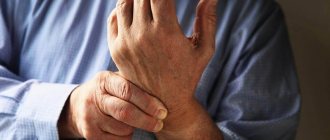
Syndactyly - a congenital anomaly of the development of fingers or toes, which is a complete or partial fusion of two or more fingers. Sometimes the disease is complicated by their deformation and underdevelopment (the nail bed or phalanx may be absent).
The cause of syndactyly is an anomaly in the embryonic period of bone formation during pregnancy. The disease is diagnosed in one baby out of 2,500 newborns, and boys suffer from this disease almost twice as often as girls. Every second baby with syndactyly is diagnosed with additional skeletal developmental anomalies (hypoplasia of the fingers, flat feet, foot deformity, etc.).
The main consequence of syndactyly is a cosmetic defect that can be eliminated in the only way - surgical separation of the fingers. In this case, it is possible to perform partial plastic surgery to restore missing tissue.
Lack of timely treatment for syndactyly can cause irreversible consequences in the development of the child’s limbs, his mental and intellectual development.
General information about pathology
Fused toes are a congenital malformation of the lower extremities. This deviation is characterized by incomplete or complete fusion of two or more fingers. In medical practice, fused toes have a special name - syndactyly.
With this pathology, a person may experience fusion of both deformed and underdeveloped fingers and correctly developed ones. The consequence of syndactyly is a functional and cosmetic defect of the lower limb.
A child with such a deviation should definitely be consulted by a geneticist and an orthopedic surgeon. To determine the type of syndactyly, an x-ray of the foot should be taken. Treatment of this defect is carried out only by surgery. In this case, the two fused toes are separated, and if urgently necessary, plastic closure of the defect is used.
Diagnostics
The disease is usually diagnosed in the maternity hospital, immediately after the birth of the child. The pathology is visible to the naked eye, so it is not difficult for a neonatologist to identify the disorder. The little patient and his mother are sent for a consultation with a geneticist to check the child for the presence of chromosomal pathologies. Next, the child will have to be constantly monitored by an orthopedist and surgeon. Doctors send the child for x-rays and ultrasound to identify the type of fusion in order to select the correct treatment tactics. Research will help to see the condition of bones and joints and prevent their destruction in the future.
Some statistics
Syndactyly is the abnormal development of the fingers, which is the result of a violation of their correct separation. As a rule, this occurs in the embryonic period.
Fused toes in a newborn child occur with a frequency of 1 in 3000. It should be noted that syndactyly accounts for approximately half of all congenital anomalies. This foot pathology can be either an independent deviation or combined with other defects (for example, hypoplasia of the fingers, polydactyly and polyphalanxy, ectrodactyly, brachydactyly, brachioradial synostosis, cleft hand, ulnar or radial clubhand, etc.).
Approximately 60% of children who have fused toes (a photo of the defect is presented in this article) have concomitant congenital abnormalities in the musculoskeletal system (for example, pseudarthrosis, clubfoot, pathological alignment of the feet, etc.).
Surgery for syndactyly in Moscow
The Department of Pediatric Surgery at CELT invites you to undergo surgery for syndactyly of fingers and toes in Moscow. We have been working in the domestic market of paid medical services for more than twenty-five years and provide treatment and diagnostics in accordance with international standards.
Your child will be cared for by experienced pediatric surgeons with the highest qualification category. They have decades of experience and hundreds of successfully completed operations behind them. Good knowledge of child psychology allows them to quickly find a common language with young patients. The correct attitude of the baby plays an important role, as it affects the outcome of the operation.
Surgery for syndactyly of the legs and arms is preceded by a thorough diagnosis. Our multidisciplinary clinic has a powerful diagnostic base that allows us to conduct comprehensive studies, identify contraindications, determine the scope of intervention and draw up a plan. The process uses special anesthetic drugs designed specifically for the child’s body. They do not harm it, but at the same time provide the desired effect, eliminating any pain or discomfort.
The cost of surgery for syndactyly is calculated individually, taking into account the complexity of the case and the technique used. You can find out the exact numbers from your doctor after consultation and diagnosis. Preliminary figures are presented in the “Services and Prices” tab in this section of our official website. We regularly update price lists, although in order to avoid misunderstandings, we still ask you to check the numbers with our operators: +7 (495) 788-33-88.
Causes of the defect
Why do children develop such a defect as fused toes? The reasons for this deviation may vary. Experts believe that in 20% of cases this is due to a hereditary factor. In other words, the autosomal dominant type of inheritance is to blame.
If syndactyly is absent in the family history, then it should be assumed that disturbances in the differentiation and formation of the lower extremities of the fetus occurred during embryogenesis. This usually happens if there is exposure to various unfavorable factors.
Symptoms of deformation of the 5th finger
Tailor's foot can cause significant discomfort to patients and cause significant difficulties both in professional activities and at home. It is characterized by:
- irritating, often throbbing pain that occurs and intensifies while walking or playing sports (can become painful and force a person to reduce physical activity);
- aching pain of mild or moderate intensity, present even during rest and night sleep;
- discomfort in the foot due to the expansion of its transverse arch;
- difficulties with choosing shoes, since in the later stages of development the formed callus, especially in combination with the presence of the same, but mirrored on the big toe, does not allow wearing ordinary shoes;
- pain, swelling, redness of soft tissues in the projection of the inflamed joints of the foot;
- dropsy and wounds in the area of the protruding bone on the lateral surface of the foot due to rubbing with shoes;
- the formation of calluses and corns on the plantar part of the foot, which is caused by the transverse flatness of the foot.
How does the defect develop?
Why do the toes have fused toes, and how can we explain this development of the limbs? The formation of the unborn child’s foot occurs in the 5th week of intrauterine development. It is at this time that the fetus can develop physiological syndactyly.
In the absence of a defect, fingers are formed already in the 7th week. This occurs due to the growth of the digital rays and the slowing down of the development of the interdigital spaces. If the reduction of the interdigital septa is impaired, then the phalanges do not separate, that is, syndactyly occurs.
Causes
There is a fairly long list of factors that can cause the formation of Taylor deformity. These include:
- Congenital structural features of the feet or a hereditarily determined tendency to develop certain orthopedic disorders, in particular flat feet, an atypical type of fixation of the muscle responsible for abduction and spread of the toes, cavus foot, etc.
- Anomalies of the structure of the fifth toe, including dumbbell-shaped, hammertoe little toes, the presence of additional bones, abnormal bending, etc.
- The habit of sitting for a long time in a cross-legged position “Turkish style”.
- Prolonged wearing of uncomfortable, tight, small shoes, as well as with too high heels or platforms.
- Flat feet, especially those that remain undiagnosed for a long time and therefore cannot be corrected.
- Neoplasms in the foot in the area of the 5th metatarsal bone.
- Neurological diseases, especially cerebral palsy, meningitis, Lederhosen contracture, etc.
- Fractures of the little toe that healed incorrectly, injuries that led to weakening of the muscle-ligamentous structures, overstretching of tendons and other disorders that negatively affect the anatomy of the foot.
Possible causes of pathological development
Fused toes in a child can be observed due to toxic effects on the body of a pregnant woman. In most cases, this occurs when taking medications, alcoholic beverages, as well as due to unfavorable ecology, occupational characteristics, X-ray exposure and infectious diseases (for example, influenza, syphilis, tuberculosis, etc.).
Often the reasons for the birth of a baby with syndactyly remain unclear.
Fused toes are a frequently observed defect that is part of the structure of chromosomal and gene syndromes.
By the way, acquired syndactyly occurs very rarely in people. As a rule, this pathology occurs after foot burns (chemical or thermal).
2. Reasons
Acquired syndactyly is possible only as a result of a burn or chemical “fusion” - and is much less common than congenital forms. The main etiological cause of congenital syndactyly is heredity, burdened by the same or other similar anomalies. However, one cannot discount reliably established and confirmed risk factors, which provide alarming dynamics in the incidence of congenital defects of limb development:
- environmental hazards, incl. mother's work in hazardous industries;
- intoxication during the gestational period: alcohol, smoking, taking medications, etc.;
- radiation injuries.
Visit our Microsurgery page
Fused toes - what does this pathology mean?
Many people who are actively interested in mysticism believe that such pathology develops for a reason. There is an opinion that this type of mutation is diabolical. Indeed, fused toes quite closely resemble a hoof.
However, doctors say that there is nothing strange or scary in this development of the foot. This is just an anomaly of the limb, which is quite easy to get rid of, especially in the early stages of a child’s life.
Therefore, there is no need to worry too much if you have fused toes. What this means, only a doctor can tell you, and not lovers of devilish marks.
Rehabilitation and specialist forecasts
After finger separation surgery, there is a recovery period. During rehabilitation, wearing a plaster splint is indicated. This measure is necessary to fix the foot in the correct position. Gel inserts are placed between the fingers. After 3-4 months, the child will be able to remove the structure and freely rest on his leg. At the same time, the surgeon observing the child will be able to assess the success of the operation. The doctor will evaluate joint mobility, muscle function and sensitivity of the fingers.
Rehabilitation measures begin 14 days after surgery. Physiotherapy methods will help restore the functioning of the limb.
- Ultraphonophoresis. Using ultrasound, special substances are injected under the skin to improve metabolism and blood circulation. After eliminating syndactyly, lidase is used.
- Electrical stimulation. Due to the influence of electric current pulses, active muscle contraction is provoked, which speeds up the recovery process.
- Foot massage. Stroking and rubbing movements improve blood circulation and nutrition of the soft tissues of the foot.
- Physiotherapy. Performing a set of exercises improves coordination of the toes after surgery.
- Ozocerite applications. When carrying out the manipulation, heated rock is used. This reduces the likelihood of developing inflammatory processes.
- Paraffin baths. Such warming has a beneficial effect on the condition of the joints.
If the child complains of pain after separating the fingers, the doctor will prescribe a safe analgesic.
You may need to take anti-inflammatory drugs. In some cases, fused fingers are a cosmetic defect. Thus, with the membranous form of syndactyly, there are no direct indications for surgical intervention. Surgeries to eliminate pathology are also performed on adults. Most often this is necessary to restore the aesthetic appearance of the foot.
Defect classification
In orthopedics, syndactyly is classified taking into account the length, type of fusion, and the condition of the fingers.
Currently there are:
- bone shape (if bone adhesion occurs);
- soft tissue form (sometimes membranous and skin).
Classification of the defect by length depends on the number of fused phalanges and the length of the fusion.
As for the condition of fused fingers, syndactyly can be complex or simple. In the latter case, fusion of normal fingers occurs, and in the first case, with anomalies of the bone, articular, tendon or ligamentous apparatus.
Indications for surgery for syndactyly of the toes and hands
A patient with syndactyly of the upper limbs experiences psychological discomfort due to a cosmetic defect. He may complain of feeling inferior, experience a lack of communication and self-confidence. In addition, the disease limits normal movements not only of the fingers, but of the entire limb. As a result, the child lags behind in development, his psychomotor, intellectual, and speech abilities are inhibited, which impedes learning and does not allow normal self-realization in the future.
As for syndactyly of the legs, there is discomfort here too. Although the defect can be hidden with shoes, there are a number of areas in which sufferers of this disease feel inferior. They refuse to visit gyms and swimming pools, saunas and beaches. At the same time, an abnormality of the toes is quite rarely complicated by functional disorders, so most often the reason for visiting a doctor is the patient’s desire to eliminate a cosmetic defect.
In a simple form, surgery is indicated at the age of one to two years, in a complex form - from five months to one year. Such an earlier procedure will eliminate the lag in general development and the development of complications in the form of secondary deformities.
Genetic types
Syndactyly is also classified according to genetic types:
- The first type is zygodactyly. Partial or complete fusion (webbed) of the 2nd and 3rd toes. Webbing between other fingers is also possible.
- The second type is synpolydactyly. Fusion of the 4th and 5th toes with duplication of the 5th. This pathology is characterized by: disturbances in the relief of the skin of the soles and hypoplasia of the middle phalanges.
- Third type. Bilateral complete syndactyly of the 4th and 5th fingers. In this case, the feet are not affected.
- The fourth type is Gaza syndactyly. Complete bilateral cutaneous syndactyly of the hand. In this case, there is no damage to the feet.
- Fifth type. Fusion of the metatarsal and metacarpal bones. On the hands, fusion of 3-4 fingers is more common, and on the feet – 2 and 3.
FRONT FINGERS OR SYNDACTYLY: ALL ABOUT THE IMPORTANT
Today we’ll talk about a disease called syndactyly.
WHAT IS SYNDACTYLY? Syndactyly is a congenital fusion of two or more fingers on the hands or feet. The key feature of this pathology is that the fingers or toes become fused. The disease can be present on one or several limbs. In addition, syndactyly of the arm or leg may be accompanied by other deformities of the limb associated with improper development of the joints. STATISTICS Syndactyly accounts for about 50% of congenital anomalies of the upper limbs. According to statistics, pathology occurs in 10% of newborns. In girls, the pathology is less common than in boys, since very often the mutating gene is transmitted through the male line. WHEN DOES PATHOLOGY APPEAR? The pathology manifests itself at 4-8 weeks of pregnancy, when the embryo begins to lay and form the hand. This developmental defect accounts for more than half of all anomalies of the hands and feet. TYPES OF SYNDACTYLY Syndactyly on the legs, as well as on the arms, is of two types depending on the type of fusion:
- Soft tissue form
, in which only soft tissues grow together, while the bones can fully develop. - Bone form
, in which the fusion of the fingers of the bone form is complicated by the fact that there is a partial or complete fusion of the bones of the phalanges.
WHAT ARE THE CAUSES OF THE DISEASE? The main cause of syndactyly is a hereditary factor that is transmitted in an autosomal dominant manner. However, if there were no cases of syndactyly in the family, then the cause of the anomaly lies in the unfavorable course of pregnancy, provoked by negative factors, such as:
- taking medications,
- alcohol,
- ecology,
- work in hazardous industries,
- x-ray irradiation,
- infectious diseases during pregnancy.
Very often, the reasons for the formation of syndactyly remain unclear. SYMPTOMATICS OF SYNDACTYLY The main symptom of syndactyly is the presence of fused fingers, which is obvious at the first examination of a newborn child. The shape and type of fusion can be different, depending on whether the fusion is soft tissue or bone, complete or incomplete, with deformation of the fused fingers or not. With bilateral syndactyly, as a rule, symmetrical fusion is observed. With soft tissue fusion, the functions of the hand are practically not impaired, which allows children with this type of pathology to perform a fairly wide range of actions. But still, limitations in performing various actions with the fingers can hinder the harmonious development of the child, complicate the learning process and inhibit psychomotor, mental and speech development. WHAT ARE THE METHODS FOR DIAGNOSIS OF THIS PATHOLOGY? The diagnosis of syndactyly is established immediately after birth based on an external examination of the child. To accurately determine the form of the defect and select the most appropriate treatment tactics, a number of studies are carried out:
- Doppler ultrasound;
- radiography;
- rheovasography;
- angiography;
- electrothermometry.
Also, to exclude chromosomal and gene abnormalities, consultation with a geneticist is recommended. WHAT DOCTOR TREATS THIS DISEASE? Treatment of syndactyly is usually carried out: at the diagnostic stage - by a neonatologist, at the treatment stage - by a surgeon and pediatric orthopedist. TYPES OF SYNDACTYLY Typification of syndactyly is carried out: by form and structure.
In particular,
according to the form of the disease, 5 types of syndactyly are distinguished:
- Type 1 (zygodactyly): complete or partial membranous fusion of the middle and ring fingers, or the second and third toes. Possible webbing between other fingers;
- Type 2 (synpolydactyly): fusion of the middle and ring fingers and simultaneous doubling of the ring finger; fusion of the fourth and fifth toes with duplication of the little toe;
- Type 3: complete bilateral fusion of the ring finger and little finger, shortening of the little finger due to an undeveloped or absent middle phalanx;
- type 4 (Haas type): complete bilateral skin fusion, as a result of which the hand becomes spoon-shaped;
- Type 5 is characterized by the complication of syndactyly by synostosis of the metacarpal and metatarsal bones, mainly observed between the ring and middle fingers of the hand, and on the legs - between the second and third.
Based on their structure, there are 4 types of syndactyly:
- bone, in which there are bone adhesions of the fingers;
- cutaneous syndactyly - the connection of the fingers with a soft membrane, often running along the entire length;
- terminal, in which the ends of the phalanges of the fingers are fused;
- cutaneous membranous syndactyly - the connection of the fingers by a small skin bridge.
TREATMENT OF SYNDACTYLY Treatment of syndactyly is carried out through surgery. In cases of fusion of the toes, surgery is performed only if the pathology interferes with walking. The method that will be used to perform the operation and the time of its implementation are determined depending on the form of the pathology and its nature. The most suitable age for surgery is 4-5 years. In cases with terminal syndactyly, surgery is performed between 6 and 12 months of age to prevent uneven growth and secondary deformation of the fingers. METHODS OF OPERATION There are five methods of operation, the most complex of which is a multi-stage intervention, in which, in addition to separation, bone, muscle, tendon and skin plastic surgery is performed. The simplest intervention is to separate the membrane, which does not require plastic surgery. For 3-4 months after surgery, a removable plaster splint is applied to the hand. Two weeks after the operation, physiotherapeutic procedures begin:
- physiotherapy;
- massage;
- ultraphonophoresis;
- ozokerite, paraffin or mud applications.
It is important to note that in the vast majority of cases, the simple (cutaneous) form of toe syndactyly does not cause functional problems. The main indication for surgery is aesthetic dissatisfaction with the appearance of the foot. Which naturally prevails in female patients, since in women the foot, like the hand and face, is an aesthetically significant part of the body, which is often not covered by clothes or shoes. Therefore, the main issue that must be resolved by the patient before choosing to undergo surgery or refuse it is the issue of quality of life. FOLK SIGNS Our ancestors believed that any deformation of the foot is a sign. The signs of fused toes were also noticeable. Moreover, they had two completely opposite interpretations on this matter.
- Because in ancient times, any deformation of the foot was considered an ominous sign, bringing misfortune not only to the patient and his loved ones, but also to the entire environment. It was believed that such people sow spiritual and emotional destruction around themselves. For a boy, fused toes on the right foot were considered a particularly unlucky sign, and for a girl, on the left. If the phenomenon was observed on both limbs, then everyone was sure that the child was possessed by evil spirits.
- Another interpretation, on the contrary, endowed people with fused fingers with extraordinary mystical abilities and special protection from higher powers. It was believed that children with such characteristics have special talents in many areas from the exact sciences to various types of arts.
FAMOUS PEOPLE WITH SYNDACTYLY Among the people suffering from this disease, there are famous personalities. For example, Stalin's second and third toes on his left foot were fused from birth. American actor Ashton Kutcher also suffers from this disease, who is not at all embarrassed by it, and even periodically shows off his fused fingers on camera. If you or your child suffers from this disease, our clinic will be happy to help you solve this problem and live a full life! Your Ladisten Clinic.
Symptoms of the defect
With syndactyly on the feet, a child most often experiences fusion of the 2nd and 3rd toes. In this case, undivided phalanges can be either underdeveloped or normally developed. In some cases, there is a decrease in the number of fingers due to their amniotic amputation.
Unlike children with syndactyly on the hands, children with syndactyly on the feet develop quite normally. They have no problem performing a wide range of activities. At the same time, functional inferiority of the foot does not in any way complicate studies, and almost never limits the choice of a future profession.
Forecast
With timely treatment, the prognosis is quite favorable.
If necessary, a surgical operation is prescribed during which the function of the foot is completely restored and in adulthood the child no longer remembers the problem, nothing bothers him. If syndactyly in a particular case does not pose a danger and does not impair the function of the foot, then the operation may not be performed. In this case, no violations are observed other than a cosmetic defect. If the operation was not performed, but there is a dysfunction of the foot, the consequences can be dire. At an older age, a change in gait is observed, the child limps, the legs constantly hurt, flat feet occur, which causes the ankle, knee and hip joints to suffer in adulthood. To avoid serious complications, the child should be shown to an orthopedic surgeon while still a small child and treated according to the plan drawn up by the doctor. It is possible that no operation will be needed at all, but you must make sure of this by taking tests. Share:
How is it diagnosed?
How are fused toes diagnosed (a sign of what this defect is, was described just above)? Syndactyly is detected by a neonatologist immediately after the birth of the baby. Further observation of the child is carried out by a pediatric orthopedist or surgeon. To exclude chromosomal and gene abnormalities, a geneticist can also be involved.
Despite the fact that such a diagnosis is established after a visual examination, to clarify the type of defect, as well as to develop treatment tactics, an instrumental study should be carried out.
Radiography of the feet in two projections allows specialists to assess bone density, the condition of the joints, the extent and presence of bone fusion. To identify the characteristics of blood circulation and the vascular network in the fingers, ultrasound, rheovasography, angiography and electrothermometry are performed.
Sign up for a free consultation:
Does this autograft always survive?
On the hands, almost one hundred percent engraftment usually occurs; on the legs, the probability of complete engraftment is less, since immobilization of the feet is often difficult: the patient needs to move around and come for dressings. This area is constantly in motion and inevitably gets injured, even though we apply special bandages that press the flap to the surface of the wound. There may even be a situation where, due to sweating under this bandage, the flap begins to macerate. Maceration of this flap leads to its partial and sometimes complete necrosis. In the literature, there is data on the use of materials of artificial origin or allografts, but we traditionally work with autoskin - this material is always available, does not require additional costs, and the percentage of engraftment of one’s own tissues is very high
What are artificial materials?
Artificial leather, Alloderm and others. But, I repeat, one’s own tissues – free autograft, transferred flaps from the back of the hand – are the “gold standard” of hand surgery. All the publications that I came across on the use of synthetic or allomaterials were of a research and not practical nature.
Will the patient walk with this artificial material all his life?
If we are talking about a classic transplant, it is always an autotransplantation of an epidermal skin flap. Therefore, surgery for cutaneous syndactyly involves a lot of nuances and is not as simple a correction as it seems at first glance.
As for bone syndactyly, this is work for orthopedists and traumatologists. Plastic surgeons, as a rule, do not do this. There are also many correction options here. These could be reconstructive bone surgeries; the fused bone can be split, creating two bone blocks... But orthopedists and traumatologists will tell you better about this.
Will the function of finger flexion after surgery be good or conditional?
With cutaneous syndactyly, the function of flexing the fingers does not suffer at all, the only difference is that the fused fingers bend together, but the tendons of the flexor and extensor muscles of such fingers are their own. After surgery, they will also bend. But since we create a scar deformation, and the scar tissue stretches worse, the flexion may be a little worse at first. The fingers need to be developed, first passively, and then actively, then the scar will not pull. There are isolated cases when hypertrophic scars form, but in most cases everything ends well.
How long after correction of cutaneous syndactyly should one begin to develop the operated fingers?
Development can begin 2-4 weeks after surgery. At first, passively, to prevent the scar from shrinking during the ripening process and to prevent . The scar takes up to six months to form, and all this time you need to work with a brush. After about another 2 weeks, you can already actively develop, for example, using rubber balls or hand expanders. We also quite often use special silicone gels or dressings to prevent severe scarring. How does bone syndactyly behave in terms of flexion?
Bone form of syndactyly
– this is the most surgically complex type of this pathology. The flexion-extension function can be significantly hampered, since the finger bones, joints, and tendons can be significantly deformed. When dividing bone syndactyly, speaking about the results of the operation, one must take into account, first of all, functional aspects. It is not always possible to obtain a satisfactory result.
Syndactyly also occurs in stars. Ashton Kutcher, for example, has zygodactyly - fusion of the second and third toes. This, by the way, is the most common variant of the anomaly. The actor did not undergo surgery, as he considers it not a flaw, but a highlight.
Let's talk more about the operation. What are the nuances of surgical correction? What anesthesia is used?
Correction of cutaneous syndactyly can be done under local and regional anesthesia, but it is not worth it, because in this case it is often necessary to do anesthesia in two places: on the fingers and where we will take the flap. These are additional negative sensations for the patient. It is better to perform this operation under conduction anesthesia, under spinal or epidural anesthesia with an additional intravenous component, that is, with sedation, or under general anesthesia with an inhalation component. This is ideal because the operation can last 2-2.5 hours.
The difficulty of the operation is not in dividing the syndactyly and removing the fibrous cord, but in not damaging the vascular and nervous structures, in transplanting the skin flap, and in the correct pattern of the Z-shaped flap. A straight cut should not be made on the fingers to avoid scar contracture, which will not allow the fingers to move fully. The incision lines must be planned in a certain way so that the edges of the skin do not become necrotic and at the same time are mobile enough for suturing the wound defect.
A Z-shaped scar stretches better than a straight scar. And autodermal flaps are also cut out to fit the resulting z-shaped wound surface. We sew these flaps with special thin threads, and then the flap is additionally fixed with a pressure bandage, which presses it to the entire wound surface. Without this, the flap cannot take root completely. At first, the nutrition of the flap occurs diffusely, then a capillary network begins to form.
Treatment of pathology
Is it possible to cure fused toes? An operation to separate the phalanges is the only possible solution. However, it should be noted that surgical intervention is used only for syndactyly of the fingers. As for fused phalanges of the feet, in this case surgery is not indicated. If such a pathology interferes with normal walking, then the intervention is still carried out.
Postoperative period
Immediately after recovery from anesthesia, the surgeon applies a removable plaster splint designed to immobilize the fingers on the operated limb. You need to wear it for 2-4 months.
In special cases, it may be necessary to additionally wear a finger spacer to prevent re-fusion of the sutures.
In the first few days after surgery, the baby requires special care (regular changes of bandages, application of healing ointments to the wound) and medications (antibiotics, painkillers).
4 weeks after surgery, after the wound has healed, you can begin a course of restorative treatment aimed at normalizing the functioning of the limb:
- massage of the limb by a specialist to improve tone;
- Exercise therapy with a trainer;
- ultraphonophoresis;
- electrical stimulation of muscles;
- applications on limbs of mud, paraffin, ozokerite.
Surgical approaches
The following surgical approaches may be used during surgery:
- separation of fused fingers with skin grafting using local tissues;
- separation of the membranous fusion without skin grafting;
- separation of fused fingers, which is complemented by combined skin grafting using free autografts and local tissues;
- separation of fused fingers, which is complemented by free skin grafting with a full-thickness or split skin flap;
- multi-stage interventions with tendon-muscular, skin and bone plastics.
Result of the operation
Treatment methods for syndactyly used in modern surgery provide good cosmetic and functional results. With timely intervention, not only the normal structure, but also the functions of the hand and foot are completely restored.
The operation to eliminate syndactyly was successful if the patient has no constricting scars and lateral deformation of the fingers, and also has a full range of motion in the interphalangeal joints (adduction, abduction, extension and flexion), grasping function (in the case of the hand), good sensitivity and natural shape spaces between fingers.
If it is decided not to treat syndactyly, this may have a negative impact on the development and growth of the baby’s limb.
Treatment
The disease can only be treated surgically; no ointments or folk remedies can get rid of finger fusion; there is absolutely no point in using them. If a child has fusion of the fingers, it is necessary to visit an orthopedist and undergo an examination, and if necessary, the doctor will prescribe surgery. The following types of surgical intervention exist:
- Separation of fingers without plastic surgery;
- Separation with plastic surgery in which a skin graft may be used.
- Separation with plastic surgery in which only local skin is used.
- It is also possible to have an operation that combines all types of surgical interventions at once.
Usually only the fingers are separated, as they create an obvious cosmetic defect. In most cases, toes are not operated on if they do not have a negative impact on the child’s development, he walks normally, and there are no delays. In cases where syndactyly on the legs has a negative impact on the development of the child, surgical intervention is indicated. The purpose of the operation is not only to eliminate the cosmetic defect, but also to restore the function of the foot in order to prevent its further deformation. The age of the operation depends on the type of pathology; as a rule, the appointment is made by a doctor. The most optimal age for surgical treatment of fused fingers is 5 years, but when the extreme phalanges are fused, such a delay will certainly lead to secondary deformation, because the fingers grow unevenly. For this reason, surgery is prescribed before the age of one year. If you don't separate your fingers in time, the consequences will be sad. The patient will begin to experience constant pain when walking, lameness, and will constantly have to wear ugly and unfashionable orthopedic shoes in order to slightly normalize the gait and alleviate the condition.
Rehabilitation
After the operation, a rehabilitation period begins, the fingers are immobilized, and special silicone gaskets are inserted between them so that the fingers do not grow together again. The duration of immobilization can be up to 3 months.
After surgery In the first days after surgery, severe pain is observed, so the patient is prescribed painkillers. To prevent infection after surgery, antibiotics are indicated, which the doctor prescribes individually, taking into account the patient’s age. After 2 weeks, when the wounds have healed, the doctor prescribes physiotherapeutic treatment. This includes the following procedures:
- exercise therapy;
- Massage;
- Electrophoresis;
- Ultrasound treatment;
- Compresses with medicines, etc.
The patient is most often discharged from the hospital on the same day or the next day after surgery, if no complications arise. The child spends the rehabilitation course at home, during which time parents must follow all the specialist’s recommendations and give the child the necessary medications. Despite the child's complaints, it is forbidden to remove the finger separators, even at night, as the fingers may grow back together. In addition, for the first month after the operation you need to remain calm and not disturb the sore leg again. The fused leg must be taken care of, especially after surgery. It is allowed to begin active movements and physical therapy when the wounds have completely healed and the pain has passed.