Ecology of health: Osteoarthritis is a degenerative form of arthritis of the joints; if you have it, then exercise is absolutely necessary...
Osteoarthritis is a degenerative form of joint arthritis characterized by loss of joint cartilage. There is also an inflammatory component to this disease. Osteoarthritis is a common cause of disability among older people.
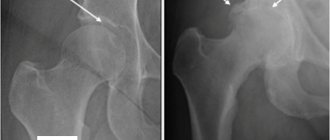
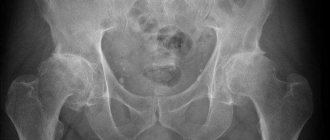
Although osteoarthritis typically affects the distal joints of the fingers and toes, osteoarthritis of the knee and hip joints , the latter of which is the focus of this article.
Contrary to popular belief, if you have osteoarthritis, exercise is absolutely essential to your well-being .
Unfortunately, many people with joint pain avoid exercise. According to previous studies, more than 40 percent of men and 56 percent of women with osteoarthritis do not get even 10 minutes of moderate to vigorous activity per week.
Less than 13 percent of men and less than 8 percent of women meet the recommendation to engage in 150 minutes of moderate-intensity, low-impact physical activity per week.
According to the lead researcher: "The fact that so many people with arthritis are inactive should be a wake-up call to doctors . Indeed, if doctors taught their arthritis patients the importance of exercise, many would benefit greatly.
Diet matters
It's important to pay attention to your diet, both for weight loss and to fight inflammation and promote healthy bones and cartilage.
Homemade bone broth is a great food for arthritis because it contains a number of important nutrients for bones and joints, including minerals, collagen and cartilage components, silicon, glucosamine and chondroitin sulfate.
Two recent studies have confirmed that people who eat processed and fried foods, a lot of sugar and red meat are more likely to develop rheumatoid arthritis (an autoimmune disorder) than those who eat a lot of fresh fruits, vegetables, legumes, poultry and fish .
A number of supplements, including turmeric, hyaluronic acid and astaxanthin , may also be helpful in reducing pain and inflammation associated with arthritis.
What to do if you are diagnosed with osteoarthritis
SOLUTION TO OSTEOARTHROSIS PROBLEMS.
Osteoarthritis is a chronic joint disease that primarily affects the articular cartilage that covers the surfaces of the bones that make up the joint. the cartilage becomes less elastic, less smooth and cracks, and the sliding of the articular surfaces of the bones against each other does not occur as easily as in a healthy person, and pain occurs in the joint, especially when moving.
To choose the right treatment, it is very important that a doctor diagnose osteoarthritis, since there are a number of other joint diseases in the treatment of which there are fundamental differences.
Treatment must be agreed with a doctor. A diagnosis of osteoarthritis is a signal of the need to change existing life stereotypes and correctly use the doctor’s recommendations. At the health school for patients with osteoarthritis, you will be given comprehensive information about the disease, shown physical exercises and explained the possibilities of drug treatment.
How to reduce stress on joints.
Sore joints should be protected from increased stress. If you have arthrosis of the leg joints, it is recommended to exclude such types of physical activity as running, jumping and squats. Fast and long walking, especially on uneven terrain, climbing uphill, and walking up stairs, worsen the condition of the joints and increase pain. In addition, lifting and carrying heavy objects should be avoided. All of these activities place a force on the affected joints that is significantly greater than the body's weight, which is harmful to the already damaged cartilage.
You should also avoid staying in one position for long periods of time, such as sitting or standing for long periods of time, or squatting or bending over when working in the garden. Such postures impair blood flow to diseased joints, as a result of which the nutrition of the cartilage also deteriorates.
If the joints of the hands are affected, you should limit carrying heavy objects, pushing up heavy and bulky laundry with your hands, and any other heavy load on the fingers.
In any case, it is necessary to develop a rhythm of motor activity so that periods of load alternate with periods of rest, during which the joint should be unloaded. Approximate rhythm - 15-20 minutes. load. 5-10 min. rest. You need to unload the leg joints in a lying or sitting position. In the same positions, you can perform several movements in the joints (flexion, extension, bicycle) to restore blood circulation after exercise.
At the same time, despite the presence of a number of limitations, it is necessary to lead an active lifestyle by increasing physical activity, which does not have a negative effect on cartilage. It is necessary to perform special exercises daily, some of which are given below. A common feature of these exercises is that when they are performed, the load on the articular cartilage is minimal, and the muscles surrounding the joint work to a greater extent. This allows you to form a good muscle corset around the joint, maintain normal mobility and sufficient blood circulation in the limb.
If you have osteoarthritis, you must do special exercises every day.
In addition, these exercises strengthen the cartilage itself, which requires movement for normal nutrition. Regular practice of these exercises should turn from an unpleasant chore into a healthy habit, which is the best way to maintain normal joint function.
You need to exercise for less than 30-40 minutes per day, it is better to divide this time into several times a day for 10-15 minutes. A noticeable effect occurs within 2-3 months - pain decreases, vitality increases, hidden reserves of the body are released. Using a cane when walking helps to reduce the load on the joints of the legs. If you are more concerned about your right leg, then the cane should be carried in your left hand and vice versa. If both legs are affected, it may be helpful to walk with two canes at the same time. If you have to walk for a long time, or you expect to have to stand for a long time, you should definitely take a cane with you. This will make your trip more comfortable.
It is very important to choose the right height of the cane. A cane that is too long or too short is equally unsafe for the skeleton. In order to choose the right height of the cane, you need to wear shoes with the same heel that you usually wear. The arms lie freely along the body. The handle of the cane should be located at the level of the base of the first finger of the hand.
Sometimes, in order to reduce pain in the knee joints, the doctor may recommend that you wear special knee pads or special insoles in shoes (instep supports), which allow you to maintain the correct condition of the joints.
Insoles must be selected individually, since everyone’s foot is different and an incorrectly selected insole can be more likely to cause harm.
In case of osteoarthritis of the leg joints, special attention should be paid to shoes. Wearing shoes with low, wide heels and soft elastic soles allows you to absorb the shock that spreads across the limb when the heel touches the ground and injures the cartilage.
It is also important that the shoes are wide enough and that their uppers are soft. In general, most sports shoes meet these requirements.
Useful tips for everyday life
Patients with hand joint damage often find it difficult to open the door with a regular key. This is easier to do if you use a metal pin to increase the lever of the key (see figure). Carry this simple tool in your pocket or purse so that it is always at hand.
If you find it difficult to get up from a sitting position, then take care of your chair. It should be on high legs and have good armrests that protrude forward. When standing up, rest your palms on the edges of the armrests as shown in the figure.
In this case, the body weight will be evenly distributed on strong wrists, and not on the weaker joints of the hand, which often suffer from osteoarthritis. Do not lean on your fingers, this puts a lot of stress on the affected joints of the hand.
You should not sit on your knees. It’s better to kneel down and put a soft cushion
Try to avoid sitting on low chairs or in low armchairs - with sore joints it will be very difficult to get up from them.
When you are about to do your homework, remember everything you will need for this and collect all things together in advance. This will avoid repeated getting up from a chair and unnecessary trips around the house, and therefore reduce the load on the joints. For example, if you plan to start cooking, take out and set out all the food and kitchen tools in advance to protect your feet. It is better to do any work while sitting. If you have to wash the floors, it is better to do it with a mop, and not tilted.
Tips for proper nutrition
Obesity is one of the most important risk factors for osteoarthritis of the leg joints. Extra pounds increase stress on your joints. Sometimes it increases 4-5 times. And, given that the joints are already damaged by the disease, this seriously complicates the prognosis and negatively affects the course of the disease.
Normalizing weight leads to a reduction in the risk of developing the disease and its progression. Thus, losing weight by 5 kg leads to a reduction in the risk of osteoarthritis by 50%. In overweight women, weight loss has also been shown to reduce knee pain and increase physical activity. Changing your eating style and diet should have the goal of gradual but constant weight loss. They must be combined with physical activity.
To lose weight, you should eat less fat. For this, the following rules exist:
Avoid "invisible" fats that can be hidden in confectionery, baked goods, pies, chocolate, sausages and a variety of snacks. To determine the “hidden” fat content of a product, carefully read the information on the labels.
Buy only lean meat. Before you start cooking meat, trim off all visible fat. It is better not to fry the meat, but to cook it on the grill - a significant part of the fat will drain rather than saturate the finished product. If you do fry meat, use a very small amount of oil.
Replace meat with fish and poultry dishes as often as possible. Don't forget that fatty fish is especially healthy. It contains omega-3 fatty acids that your body needs.
Try to use skim milk and dairy products, they are low in fat but high in calcium, which you need.
Eat enough black bread, cereals and cereals. They contain a lot of fiber and practically do not make you fat.
The diet should contain more vegetables, fruits, and berries. The World Health Organization recommends eating at least five fruits a day, as they contain dietary fiber, vitamins and antioxidants that protect our body from harmful effects.
Reduce your sugar intake. Add less of it to cereals, tea, coffee and other drinks. Avoid products with “hidden” sugar: there is a lot of it in soda, ketchup and other sauces. To find such sugar, read food labels carefully.
A combination of diet and exercise therapy is effective in patients with knee osteoarthritis.
Diet and exercise (average weight loss of 5.5 kg) provide improvement in 23-38% of patients.
Exercise (1.5 kg weight loss) improves in 20-25% of patients.
Warm and cold
Cold or heat applied to the joint can significantly reduce pain. It is difficult to predict which will be more effective in your case, so first you need to try both methods and choose the one that helps you better. Cold in the form of finely crushed ice (sometimes frozen peas or others are used), placed in a cloth (towel), is applied to the affected joint for 10-15 minutes (no longer!) every hour. Heat on the joint is especially useful before physical activity. This could be a heating pad, a special lamp, or a bottle of hot water. In general, with osteoarthritis, as with other joint diseases, it is recommended not to overcool the joints and keep them warm.
Exercises for patients with osteoarthritis
For osteoarthritis, physical exercise should be done in a lying or sitting position, when the weight load on the joints is minimized. Exercises should not be done through pain; it is better to start them after barely taking painkillers. The intensity of the exercises and frequency of repetitions are determined by the severity of joint pain. Vigorous movements are contraindicated.
For osteoarthritis, exercise should be done in a lying or sitting position.
There are no age restrictions for physical activities. It should be remembered that in addition to the positive emotional charge, physical activity also helps strengthen the cardiovascular system and bone tissue.
The range of movements should be increased gradually. Vigorous movements are contraindicated.
It is rational to start classes under the guidance of a rehabilitation specialist (physical therapy doctor). After finishing group classes, you should continue to study at home using the skills you have learned.
The main principle is to repeat the exercises frequently throughout the day for several minutes.
Exercises should be performed slowly, smoothly, gradually increasing the range of movements. In this case, it is better to focus on the sore joint, think about how, during movements, blood flows to the joint, bringing with it nutrients that, when the limb relaxes, nourish the cartilage, and during movements are squeezed into the joint cavity, providing good “lubrication” to the joint.
For most patients, these exercises will not cause increased joint pain. If, however, significant pain continues more than 20 minutes after performing the exercises, then you need to reduce the number of repetitions to 5 exercises at a time, then gradually increase their number to 15 when your health allows.
Exercises for the knee joint (complex No. 1)
Do each exercise at least 5 times.
Sitting on the table
1. Sit on the table top. Sit straight. Swing your legs with a moderate range of motion. Do this exercise as often as possible.
2. In the same position. Raise your leg and hold it parallel to the floor for 3 seconds. The foot is at a right angle to the shin. Change leg. When performing this exercise, you need to feel the tension in the muscles of the thigh and lower leg.
3. Standing on the floor, rest your buttocks on the tabletop. The knees are slightly bent and apart. Toes to the sides. Without bending your back, lean forward and go back.
Lying on the floor in a supine position.
4. Legs extended. Bend your knee, while raising your foot slightly above the floor. Hold this for 5 seconds. Change legs. Repeat 5 times.
5. "Small bicycle". Bend both knees, feet on the floor. Bring your right leg to your stomach with your knee, then straighten it and slowly lower it to the floor and bring it back to the second leg. The foot is always at a right angle. Change legs.
6. “Big bike.” Swing your legs like you would when riding a bicycle. Perform slowly at first, then faster, slower - faster. Always pay attention to the tension in the thigh muscles.
7. Bend your leg at the knee, grab your thigh with your hand and pull it towards your stomach. Extend the knee (foot at a right angle, “pull” the heel). Feel the tension in the muscles. Hold this for 5-8 seconds. Lower your heel to the floor, then extend your leg. Change legs one by one. Try not to bend the other leg, which is on the floor.
Lying on your side, with a small pillow under your cheek.
8. Lying on your right side, your right hand is under the pillow, with your left hand you rest on the floor in front of you. The right leg is half bent. The left leg is bent at the knee, brought to the stomach, then pulled back as far as possible. Do the exercise slowly.
9. The position is the same (on the right side), the left leg is bent and the knee rests on the floor. The right leg is extended and lifted off the floor by 25-30 cm.
10. and 11. The same exercises on the left side.
Lying on your stomach
12. Lying on your stomach, bend your knees alternately. Make sure that the pelvis does not come off the floor.
13. In the same position, bend your leg at the knee and hold for 5-10 seconds. Change legs.
Exercises for the knee joint (complex No. 2)
Do each exercise at least 5 times
1. Lying on your back, legs extended, relaxed. On the “one-two” count, the leg bends at the knee joint to the maximum, while the foot slides along the mat. On the count of “three,” the leg is bent at the hip joint and pressed against the body with your hands (do not lift your back from the floor). On the count of four to five, hold your leg. On the count of six, lower your foot to the floor. On the count of “seven-eight” we straighten the leg. The same movement is repeated with the other leg. Repeat 10-15 times.
2. Lying on your back, legs bent. The bent leg is lifted off the floor and pressed to the chest with the help of your hands and held in this position for several seconds, then lowered. The same movement is repeated with the other leg. Repeat 10 times.
3. Lying position on your back. The straightened leg is lifted off the floor to a height of 20-30 cm and held in this position for several seconds, then lowered. The same movement is repeated with the other leg. Repeat 20-30 times.
4. Lying on your back, legs extended. Stretch your arms forward and try to raise your head and upper torso to a height of 20 cm from the floor, then lower them. Repeat 10 times.
5. Lying position on your back. Simulation of cycling. The legs are raised above the mat throughout the entire exercise. Repeat from 20 to 50 times or more. (2nd, 3rd exercises are also useful for the hip joint).
6. Lying position on your stomach. We alternately bend our legs at the knee joints, trying to touch the buttock with the heel. Do not lift your hips off the floor. Can be performed with a load (sandbags or special dumbbells are placed on the feet). Repeat 20 to 50 times.
7. Sitting position on the floor. Legs straightened. We clasp our feet with our hands and lean forward as much as possible, trying to touch our foreheads to our feet. Do not bend your knee joints. Stay in this position as long as possible. Return to starting position. Shake your legs. Repeat 3-5 times.
8. Sitting position on the floor. We bend our leg at the knee joint, grab the table with both hands, lift our leg off the floor and try to straighten it without unclenching our hands. We hold in this position as long as possible. We return to the starting position. We repeat the same with the other leg.
Exercises for the hip joint.
Do each exercise at least 5 times.
1. Lying position on your back. Both legs are bent at the knee joints to the maximum, the feet do not lift off the floor. In this position, the knees are spread apart and brought back again. Try to gradually increase the range of movements. Repeat 10-15 times.
2. Exercise “scissors” - starting position lying on your back, legs straightened. One leg lifts off the floor and moves from side to side with the greatest possible amplitude. At the same time, try not to bend your leg at the knee joint. The same is repeated with the other leg. With good training, you can perform movements with both legs at the same time. Repeat 10 times.
3. Lying position on the back. We lift the straightened leg off the floor to the maximum possible height, then lower the leg. Repeat 10 times with one leg, then change legs.
4. Sitting position on a chair. Try to bend your torso forward to touch your hands and tips of your toes, then straighten up. Repeat 10 times.
5. Starting position: standing, one leg stands on a low stand (step), leaning on the table with your hand. We swing the other leg forward and backward, gradually increasing the amplitude. Later, sideways leg movements are added. Repeat 15 times.
General health activities
Regular wellness activities should be an integral part of any treatment plan. They help reduce pain, improve joint movement and improve overall well-being. Walking on level ground at a moderate pace is a good way to maintain muscle tone. Try to take a 20-30 minute walk every day. The main thing is not to rush, since when walking quickly, the load on the joints begins to exceed body weight by 1.5-2 times. Walking around the shops with heavy bags also does not help improve your physical fitness.
Swimming is an optimal sport for diseases of the musculoskeletal system. In water, maximum range of motion in the joints is possible without weight bearing, which is optimal for articular cartilage.
In addition to its beneficial effect on joints, cycling brings a positive emotional charge. Avoid driving on uneven terrain. Bouncing movements harm your joints and are also dangerous due to falls from your bike. If you have difficulty maintaining balance, weakness, vision problems, or are not very confident in the saddle, then it is better to exercise at home on an exercise bike. It is also important to choose the right bike. You need to choose between a sports and semi-sports type, since they are lighter and faster than road ones.
The most problems arise when the saddle height is set incorrectly. It should be set so that when the pedal is fully pressed in the down position, the leg is fully straightened. If the knee is bent in this pedal position, pain in the joints and muscles occurs. The distance to the steering wheel is also important - your elbows should be slightly bent. A cyclist, unlike a pedestrian, puts stress on other muscles. Therefore, to begin with, a 15-20 minute drive is enough, later, depending on the capabilities, the duration of the trips can be extended to 30-40 minutes.
In winter, skiing is useful, as sliding reduces the weight load.
Useful rehabilitation methods
Massage improves overall well-being, relieves painful muscle spasms, improves blood circulation and transmission of nerve impulses, thereby ensuring improved nutrition of articular cartilage. Massage should be done by an experienced specialist in the absence of exacerbation of arthrosis. The area above the joint is treated with minimal intensity. The spine is treated more intensively, from where the nerves supplying the joint and adjacent muscles emerge. In the absence of contraindications, the massage is repeated 2 times a year. Sanatorium-resort treatment allows for comprehensive rehabilitation, including the positive effects of therapeutic mud, baths, saunas, physiotherapy, massage, and physical therapy exercises. An important role is played by a change of environment, relieving stressors, and being in the fresh air. Sanatorium-resort treatment can be carried out only without exacerbation of the disease. However, it is necessary to realize that the course of treatment at the resort is only a short-term part of the ongoing process of treatment and rehabilitation.
Drug therapy
The goal of drug therapy is usually to alleviate the symptoms of the disease - reducing pain and improving joint mobility. If the pain is not expressed, preference is given to paracetamol tablets. It is also possible to use local medications (creams or gels) that have analgesic and anti-inflammatory effects. They are applied to clean skin over the joint 2-3 times a day. For severe pain, ibuprofen or diclofenac tablets are usually prescribed. However, you should be aware of the adverse reactions that cause medications used internally. Thus, long-term use of paracetamol more than 4 g per day can lead to changes in the liver or an increase in blood pressure. For elderly patients, the dose of paracetamol should not exceed 3.2 g per day. Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs have a negative effect on the gastrointestinal tract, they occur unnoticed by patients (due to the analgesic effect) and are manifested by severe complications. The question of prescribing analgesics and non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs should be decided by the doctor.
Intra-articular administration of drugs
Prescribed by a doctor in exceptional cases to more quickly relieve inflammation in the joint (glucocorticoids) and to relieve severe pain. Patients experience significant improvement after the first intra-articular injection, and therefore sometimes require this procedure in the future, even with slight discomfort. This procedure does not treat arthrosis, but allows you to stop inflammation, and if often unjustified, it is harmful to the joint. In addition, intra-articular injections have a high risk of complications. If traditional treatment is aimed at reducing the symptoms of osteoarthritis, then a completely different result is possible with the use of chondroprotectors or basic agents.
Basic (main) drug therapy
Chondroprotectors are drugs that have a beneficial effect on cartilage, thereby preventing the development of osteoarthritis, and at the same time reducing inflammation in the joint. Currently, the use of the drug Dona from this group has received worldwide recognition, which is based on many years of positive experience, confirmed by serious clinical studies.
The active ingredient of Dona, glucosamine sulfate, is a natural component of articular cartilage, physiologically present in the human body. This explains its ability to stop the destruction of cartilage, strengthen its structure and alleviate the symptoms of the disease.
Currently, there are a number of other drugs containing glucosamine sulfate (or chloride) and chondroitin sulfate.
The methodological recommendation was compiled by the deputy chief physician of the Stupinskaya Central Clinical Hospital V.S. Afanasyev. based on materials from O.M. Lesnyak, head Department of Family Medicine, USMA, Doctor of Medical Sciences, Professor, edited by V.A. Nasonova, chief rheumatologist of the Ministry of Health of Russia, academician of the Russian Academy of Medical Sciences, professor.
What are the benefits of exercise for arthritis?
The idea that exercise is bad for joints is wrong; this belief has no basis. It is a myth that exercise and/or normal activities cause wear and tear on joints such as the knees and hips.
On the contrary, data indicate a positive effect of physical activity on joint tissues. It's important to note that exercise helps reduce joint pain and makes everyday tasks easier .
Additionally, if you exercise enough to lose weight or maintain an ideal weight, you reduce your risk of developing osteoarthritis in the first place.
Obese people are twice as likely to suffer from arthritis as those of normal weight because excess weight puts more pressure on joints. This can not only lead to osteoarthritis, but also significantly worsen the condition.
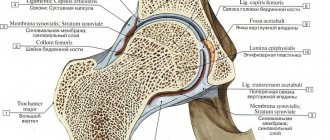
Anatomy of the joints of the spine
Osteoarthritis usually affects people over the age of 50. Statistics show that this degenerative condition is more common in men under 45 and women over 45. In order to identify osteoarthritis of the lumbar spine, the patient must know the anatomy of the joints of the spine.
The lower back can be divided into three main parts:
- lumbar spine; - sacrum; - coccyx.
The structure of the lumbar spine can in turn be divided into five lumbar vertebrae and five intervertebral discs. These vertebrae of the lumbar spine are the largest vertebrae in the human body. They bear the greatest load of the entire body weight. This is the main reason why the vertebrae of the lumbar spine are most likely to cause back pain.
Exercises for hip osteoarthritis
| Flexibility exercises for hip osteoarthritis | |
| Single Knee Pull | Lying on your back, grab your right knee and pull it toward your chest until you feel a stretch. Hold for 20 seconds. Repeat on the left side |
| Double Knee Pull | Lying on your back, grab both knees and pull them towards your chest. Hold for 20 seconds |
| "Cobra Pose" | Lie face down on the floor with your arms parallel to your shoulders. Straighten your arms, lifting your upper body off the floor. You should bend at the lower back, and your pelvis should touch the floor. Hold for 20 seconds, then lower down |
| Hip flexion with adduction | Lying on your back, pull your knee towards your chest. Hold your knee with both hands and rock it from side to side for 20 seconds. Repeat on the other side |
| External rotation of the hip | Lying on your back, pull your right knee toward your chest. Place your right hand on your knee and your left hand on your ankle. Gently pull your right ankle toward your head. Hold for 30 seconds and then repeat with your left leg |
| Hip internal rotation | Lying face down, bend your knees 90 degrees and lower your legs. Hold for 30 seconds |
| Strengthening Exercises for Hip Osteoarthritis | |
| "Sink" | Lie on your side with your feet together and knees slightly bent. Raise your top knee as far as you can and then lower it down. Repeat 15 times, then switch sides |
| Bridge | Lying on your back, press your feet toward the floor and lift your hips toward the ceiling. Stop for a few seconds and lower yourself down. Repeat five times |
| Knee rotation | Lie on your side with your feet together and knees slightly bent. Raise your top knee and foot. Keeping your knee raised, rotate your foot up and down. Repeat 15 times and then switch sides |
| Heel rotation | Lie on your side with your feet together and knees slightly bent. Raise your top knee and foot. Keeping your foot still in the air, move your knee up and down. Repeat 15 times and then switch sides |
Symptoms of arthrosis
Symptoms of osteoarthritis of the lumbar spine can range from mild to severe. Osteoarthritis of the lumbar spine has similar symptoms to intervertebral disc problems. If a patient is concerned about any of the symptoms listed below, this means that he may be suffering from osteoarthritis of the lumbar spine.
Pain in the lower back spreads to the buttocks, legs and back of the knees. Under this condition, there will be no pain in the lower part of the legs in front and in the feet.
Symptoms of osteoarthritis in affected joints:
- numbness and fragility; - muscle spasm; - back pain is reduced in a sitting position compared to a standing position; - swelling of the affected joint; - pain worsens with strenuous exercise; - inflammation increases after a period of rest; - in extreme cases - loss of joint mobility.
How to Exercise Safely with Osteoarthritis
People with arthritis should be careful and avoid activities that aggravate joint pain. Exercises that significantly stretch an unstable joint should be avoided. However, the exercise program should still be as comprehensive as any other. Strength training, high-intensity cardio exercises, stretching and core work can all be incorporated into a workout program tailored to your fitness level.
If you have knee osteoarthritis, be sure to include exercises that strengthen the quadriceps muscle at the front of your thigh. And instead of running or other high-impact exercises, consider non-weight-bearing exercises like swimming and cycling .
If pain persists for an hour after exercise, slow down or try other types of exercise. In addition, assistive devices can help reduce pressure on affected joints during exercise. You may want to see a physical therapist or qualified personal trainer who can help you determine a safe range of exercise for you.
Physical therapy, massage, physiotherapy, manipulation
Session with a physical therapy and sports medicine doctor/rehabilitation specialist (movement therapy/physical therapy/physiotherapy/massage/manual techniques). 60 min. 3 800 Session with a physical therapy and sports medicine doctor/rehabilitation specialist (movement therapy/physical therapy/physiotherapy/massage/manual techniques). 30 min.2 00016 rehabilitation sessions (motor therapy/physical therapy/physiotherapy/massage/manual techniques) - 5% discount57 760Massage session (massage/manual techniques/manual lymphatic drainage/joint mobilizations and other manual techniques)3 600Shock wave therapy (1 zone)2 700 Physiotherapy session (electrical stimulation/ultrasound therapy)2 000Attention! Prices are presented for informational purposes only and are not a public offer!
Korean medicine for arthritis
As noted in an article by Dr. Seo Hyo-seok, director of Pyunkang Hospital of Korean Medicine, arthritis in Korean medicine is associated with decreased kidney function :
“If the kidneys are weak, then in cold weather the circulation of energy and blood is weakened, so residues of various substances are generated and accumulated in the joints... These residues decompose over time and cause arthritis. To regenerate cartilage, you need to improve kidney and lung health...
Modern medicine also recognizes the close connection between the kidneys and bones - it has been found that erythropoietin (a hormone secreted by the kidneys when oxygen levels decrease) signals the bone marrow to increase the production of red blood cells. In addition, the kidneys help regulate and absorb calcium, a key substance for bones...
When people are weakened, they need to strengthen the functions of the organ located above. For the kidneys, therefore, that organ is the lungs, so you can restore fundamental bone health by promoting lung health.”
In Eastern medicine, treating arthritis involves maintaining good circulation and keeping joints warm. Exercise copes with this task, but in Eastern medicine methods such as moxibustion, bloodletting, acupuncture and herbal preparations .
According to Dr. Seo Hyo-seok, six months of treatment with herbal preparations that specifically cleanse the lungs can significantly restore cartilage. By restoring the elasticity of cartilage, even advanced arthritis can be reversed.
Rules for performing exercise therapy for osteoarthritis
Therapeutic physical training is carried out under the strict supervision of a doctor or a special trainer. This is necessary to control and adjust exercises during class. The patient cannot adequately evaluate his actions. Sometimes during training, a person, due to fatigue, tries to reduce the number of approaches, or, on the contrary, tries to increase the pace and number of exercises. Such actions not only turn out to be useless, but also aggravate the situation.
To get the desired result, a person needs to follow several rules:
- Perform any physical exercises strictly during the period of remission. During exacerbation of osteoarthritis, the joints should be completely at rest.
- The first classes are conducted only under the supervision of a specialist. Subsequent classes are allowed to be carried out at home.
- During training, perform only the specified number of exercises, taking into account the correct pace, amplitude and strength of movements.
- Trainings are held daily at a certain time. Exercise for osteoarthritis is also considered an important component of treatment that cannot be ignored.
- If, while performing movements, discomfort, discomfort or pain occurs in the ankle, hip, shoulder, knee, elbow joints or hands, you should abandon this exercise and report the problem to your doctor or trainer.
- A set of exercises for osteoarthritis should be performed at a moderate pace. Haste increases the load on the joints, causing complications.
Following the recommendations will increase the effectiveness of physical exercise, speed up recovery and alleviate the condition of the joints in a short time.
Ozone and laser therapy
Dr. Robert Rowan, one of the leading ozone therapists in the United States, has successfully treated many patients using ozone therapy as an alternative to surgery.
If ozone treatment does not help, it will not cause any harm and you can always have surgery later, but if surgery does not help, then the damage will be irreversible.
Another option worth considering is “cold” infrared laser treatment (also called K-laser ). This is a relatively new therapy that speeds up wound healing by increasing tissue oxygenation and the absorption of photons of light by injured cells.
This particular type of laser has positive effects on muscles, ligaments and even bones, and the K-laser has the ability to penetrate deep into the body, allowing it to be used to treat problems such as arthritis of the knee and hip. It also stimulates mitochondria to produce more ATP and speed up healing.
Benefits of Exercise
The disease is treated with medications, surgery, and therapeutic exercises. Since deforming osteoarthritis cannot be completely cured and occurs chronically over a long period of time, prevention in the early stages is of great importance. Therapeutic gymnastics and special physical education act as retarders of the disease process by improving muscle tone, strengthening them, and improving blood circulation. The legs become more mobile and there is general relief due to a decrease in pain.
Therapeutic gymnastics is prescribed during a period when acute pain is relieved with the help of other treatment methods; exercises strengthen the group of muscles that abduct the leg towards the hip and straighten the knees. The exercises also target the back and abdominal muscles. An important feature that distinguishes physical procedures from the treatment of similar diseases is that the diseased joint is not loaded, the effort is exerted by the healthy leg, or the exercises are carried out in a position on the back or side.
You need to move carefully, exercises should be gentle, and with care and sensitivity you need to develop the muscle complex that helps you walk. Pain during exercise is inappropriate, since this puts stress on the already worn-out cartilage, so gymnastics specifically leads to pain relief and is gentle on the joint, preventing its further atrophy. If you can’t exercise on your own because of pain, you need someone to help, at least at the initial stage.