Intercostal neuralgia is a serious disease characterized by severe painful attacks. The pathology is associated with damage to peripheral nerve endings, which can be caused by a variety of reasons. As a rule, it is treated with conservative methods, including massage. What does massage do for intercostal neuralgia, and can it be done at home?
Massage for intercostal neuralgia
What is intercostal neuralgia
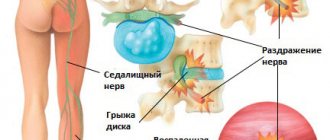
Intercostal neuralgia is pain in the area of the ribs and chest that occurs when the nerve endings are compressed at the exit points of the spine. Depending on the force of compression and the number of affected roots, the pain can be dull, pulling, cutting or burning, localized in one area or encircling. They may be accompanied by muscle spasms and sensory disturbances. Attacks of pain occur when moving the body, sneezing, coughing, when affecting the skin along the spine, on the sternum and in the intercostal spaces, that is, where the nerve roots pass.
Neuralgia in the ribs occurs when the nerve endings are compressed at their exit from the spinal column
Painful attacks due to neuralgia can appear at any time of the day and last from a couple of minutes to several hours. If the lesion is extensive, the pain is felt constantly, only with varying intensity. Often it radiates under the shoulder blade, into the collarbone, around the heart, and prevents you from taking a deep breath. In most cases, the disease develops against the background of pathologies of the spine (in the thoracic region), such as osteochondrosis, spondylitis, and ankylosing spondylitis. This is facilitated by degenerative-dystrophic processes in the vertebrae and intervertebral discs, as a result of which pinched nerves occur.
The most common cause of intercostal neuralgia is degenerative changes in the intervertebral discs and the vertebrae themselves.
There are other causes of intercostal neuralgia:
- hypothermia of the body;
- excessive stress on the back;
- infectious diseases;
- upper body injuries;
- muscle inflammation;
- tumors of the spine and spinal cord.
Neuralgia may be caused by damage to muscle tissue in the upper body
Important! Even severe stress or prolonged nervous strain can provoke the appearance of pain, and in some cases, damage to the peripheral nervous system is caused by hormonal imbalances. Provoking factors also include age-related changes in muscle and bone tissue, since most people with this diagnosis are over 40 years old.
Herpes zoster
Many of us breathe a sigh of relief after chickenpox (common childhood chickenpox). We think that the virus has been defeated and there is nothing to worry about. But this is not entirely true. The virus does not leave the body and under certain conditions can be reactivated. This insidious infection can cause complications in the form of postherpetic neuralgia, which manifests itself as excruciating pain along the peripheral nerves, and herpes zoster.
What is herpes zoster?
After chickenpox, the herpes virus enters the nerve ganglia (nodes) and can exist there for years without causing any symptoms. But with decreased immunity, stress, or in old age, the virus can suddenly become active. According to statistics, this can happen to every fifth of us.
Herpes zoster (shingles) usually begins with a fever and reddened area of the skin on the body, and there may be tingling in the area. Then blisters appear on the skin. The blisters are always located along the nerves, so the rash on the torso looks like a belt. Hence the name of the disease - herpes zoster. Pain may appear before or at the same time as the blisters. However, sometimes it does without skin manifestations.
Postherpetic neuralgia
Many people recover from herpes zoster without consequences. But sometimes the rash goes away, but the pain remains. Or the pain returns a month after recovery. This situation develops in 10–20% of cases and is a complication of herpetic infection.
Excruciating pain occurs at the site of the rash and is called postherpetic neuralgia or “belt of hellish roses.” The pain is burning, pulling, stabbing, quite pronounced, and often interferes with sleep. The slightest touch to the skin, even wearing clothing, can cause unbearable pain. If postherpetic neuralgia is not treated, it may go away on its own within a year after the disease, but more often the pain lasts for years and requires special medications.
At-risk groups
Herpes zoster, as well as its complication - postherpetic neuralgia - is most susceptible to older people. But even in young patients, widespread rashes, especially those that appear after the onset of pain, as well as high fever at the onset of the disease very often lead to postherpetic neuralgia. However, there is always an opportunity to reduce the likelihood of this complication occurring.
The benefits of massage for neuralgia
The main goal of massage for lesions of the nerve roots is to eliminate pain. This is accomplished by relaxing the muscles in the affected area. Tight muscles increase compression of nerve endings and blood vessels, which interferes with normal blood flow and relief of inflammation. With the help of a gentle impact on problem areas, it is possible to relieve muscle tension and reduce pressure on the roots and blood vessels. With the normalization of blood supply, swelling gradually disappears, inflammatory processes in tissues subside, and pain goes away.
Massage helps relax muscles and relieve pain
What else does therapeutic massage provide:
- improves metabolic processes in tissues;
- helps restore the functions of affected nerves;
- relieves stress;
- improves the general condition of the patient.
But a positive result can only be achieved if the massage procedure is carried out correctly and there are no contraindications, otherwise the risk of complications and increased pain attacks increases.
How to distinguish symptoms of the disease from heart pain?
During intercostal neuralgia, the pain is constant and can only be relieved with the help of medications.
Unpleasant sensations become more and more expressive with any movements, especially sudden ones. Heart pains are not so expressive, in addition, they do not intensify during movements. Heart pain affects the patient's pulse and increases blood pressure. Intercostal neuralgia does not affect either pulse or blood pressure.
During the occurrence of both heart pain and pain caused by intercostal neuralgia, self-medication is strictly prohibited.
Indications and contraindications
Therapeutic massage is indicated in cases where intercostal neuralgia is caused by muscle spasms or diseases of the spinal column, and the pain syndrome is moderate. With severe pain, even the lightest touch to the affected areas is painful for the patient, which means there will be no benefit from such a procedure.
Massage is indicated for moderate pain in the rib area.
As for contraindications, in addition to acute pain, these include:
- inflammatory processes in the body;
- the presence of viral and bacterial infections;
- malignant and benign tumors;
- physical exhaustion;
- dermatological diseases, especially purulent ones;
- injuries to the ribs, chest and spine.
For rib injuries, massage is contraindicated.
Also, do not massage if you have high blood pressure or general malaise. To accurately determine the cause of the disease and make sure there are no contraindications, you need to undergo a full examination, and based on its results, the doctor will determine whether a massage can be prescribed.
Important! An experienced, qualified massage therapist should carry out the procedure (at least the first few sessions), and only if there is a lasting improvement and after consultation with a doctor, massage is allowed at home.
Indications for massage
- Massage is indicated for almost all types of neuralgia, manifested in the following symptoms.
- Trigeminal neuralgia often occurs against the background of previous colds and inflammatory diseases or infections. It is expressed by repeated attacks of dull pain in the neck and head.
- Cutaneous neuralgia of the thigh is an unpleasant burning, stabbing pain or numbness in the outer thigh.
- Pterygopalatine neuralgia is constant severe pain in the area of the palate, temples, eyes or neck.
- Intercostal neuralgia - pain during sudden movements, coughing, sneezing.
- Occipital neuralgia is pain between the temples and the back of the head.
Rules for massage
For intercostal neuralgia, it is necessary to massage both the back and chest, regardless of where the pain is localized. To achieve a lasting positive result, a minimum of 10 procedures lasting up to 20 minutes are prescribed. Massage is performed daily or every other day, depending on the patient’s condition and the use of other therapeutic techniques. During treatment, experts recommend adhering to certain rules in order to obtain a high therapeutic effect from the procedures.
- Before a massage, you should not take painkillers or muscle relaxants, as their effect interferes with perception during the procedure. Painful manifestations that occur during massage indicate the specialist to the affected areas, allowing you to choose the right massage technique and force of influence. If the patient does not feel anything, the massage therapist may accidentally touch the damaged nerve and further injure it. So if the pain or spasms are severe enough, massage should be avoided until the pain is relieved.
Do not take painkillers before the massage - It is not recommended to do a massage immediately after eating, since during the procedure you will need to lie on your stomach, and the stomach will be compressed. This negatively affects digestion, gives some discomfort, and makes it difficult for the patient to relax. It is best to conduct a session 1-1.5 hours after a meal or before a meal.
- If the massage is carried out at home, the room should be ventilated, with a comfortable air temperature. For massage, you need a strong, stable couch or a wide chair with a back on which the patient can rest his hands. Often pain due to neuralgia does not allow one to lie normally on the back or stomach, and in such cases it is more convenient to massage while sitting.
Massage can be done while sitting if pain prevents you from taking a lying position - You need to start with light stroking movements aimed at warming up the muscles. The intensity of the effect is increased gradually, and the healthy side of the body is massaged first. If the lesion affects both the right and left sides, first massage where the pain is felt less. In the most painful points, the impact should be minimal, so during the procedure the greatest attention should be paid to the patient's reaction. Exceeding the pain threshold can cause serious health complications.
Important! After completing the session, you should not get up immediately, much less go out into the cold. It is advisable to remain in a lying position for another 5-10 minutes, completely relaxing the muscles. To enhance the therapeutic effect, it is recommended to combine massage with physiotherapy and therapeutic exercises.
Diagnosis of the disease
To get a clear answer about the causes of chest pain, doctors at our clinic conduct diagnostic examinations of the chest.
This is a mandatory requirement for the successful treatment of intercostal neuralgia. It is necessary to exclude diseases with similar symptoms, such as pleurisy or pneumonia. If chest pain occurs on the left side, it is necessary to undergo cardiac electrocardiography to rule out heart disease. It is also necessary to do a general blood test and an x-ray of the spine.
The attending physician may also prescribe an ultrasound examination or MR myelography of the spine to diagnose the condition of the nerve roots.
Massage technique
To perform a massage at home, it is enough to watch how an experienced specialist does it 1-2 times. The massage technique is quite simple and includes standard techniques - stroking with fingertips, kneading, rubbing painful areas.
Table. Stages of performing a massage
| Illustration | Description |
| Step 1 | The patient lies on his stomach and places his hands in front of him. Massage begins on the side where there is no pain or is felt weaker. The fingertips are applied to the skin between the ribs and smoothly moved in the direction from the spine to the abdomen. Stroking is carried out with both hands, alternately running your fingers from top to bottom. |
| Step 2 | After warming up the muscles on the healthy side of the back, move to the sore side. The movements are the same: fingers are placed on the back at an angle of 35-40 degrees, pressed with pads to the skin and passed between the ribs for 2-3 minutes. |
| Step 3 | Switch over to the healthy side again and begin rubbing. The fingers are placed in the same way as before, but now the movements are more intense. For convenience, you can massage with one hand, pressing from above with the palm of your second hand. They rub not only the ribs, but also the area of the shoulder blade. Then repeat in the same way on the sore side of the back. |
| Step 4 | The next stage is kneading. Again, start from the healthy side: place both palms on the ribs, then alternately raise and lower them, grasping the folds of the skin. The movements are intense, quite fast, and involve the area of the ribs and shoulder blade. |
| Step 5 | Move to the sore side of the back. Here you should rub more carefully, but still quite actively. |
| Step 6 | The next technique is called vibration. To do this, grab the skin on the back with your fingers, lift it up and release it, that is, perform frequent pinching throughout the entire area being worked on. Having completed on one side, do the same on the other. |
| Step 7 | After vibration, they again move on to stroking the intercostal space with their fingers. The movements are smooth, with light pressure, in the direction from the spine to the stomach. |
| Step 8 | The patient should roll over onto his back and extend his arms along his body. Begin chest massage with classic stroking: apply palms to the skin and move from the middle of the chest to the back, then to the collarbones and at the same time with both hands from the neck to the stomach. |
| Step 9 | Now stroking is done with the fingertips, moving between the ribs in the direction from the middle of the chest to the back. |
| Step 10 | Start kneading. The movements are fast, active, from the lower line of the ribs to the collarbone. When properly kneaded, the skin should begin to turn red. |
| Step 11 | After kneading, vibration is performed alternately on each side. The pinching should be moderately intense, but not painful. |
| Step 12 | The massage is completed by stroking the entire treated area - from the stomach to the neck. The movements are very light, relaxing, smooth. |
If the patient feels pain in a specific point, it is necessary to work on this area separately. You need to massage carefully, first performing stroking, then rubbing and kneading movements. It is not advisable to use pinches here, so as not to cause suffering to the patient. The duration of such work should not exceed 4-5 minutes. After this, the person should lie quietly for 10 or 20 minutes so that the muscles calm down. Instead of classical massage, cupping and acupressure massage can also be used for intercostal neuralgia.
Types of massage for intercostal neuralgia
Video - Massage for intercostal neuralgia
Massage is also effective for other types of neuralgia, for example, facial or sciatica. Depending on which part of the body is affected, the massage technique has certain differences, but the procedure does not present any particular difficulties. You can read about all the intricacies of massage and related methods of treating neuralgia on our website.
How to treat neuralgia?
During pregnancy, spinal shock wave therapy, therapeutic massage and most medications are prohibited. To alleviate the condition somewhat, a pregnant woman can take the following measures:
- Take a paracetamol tablet. It would be good to coordinate this step with your doctor, however, as a necessary measure, you can take the medicine yourself.
- Take a position in which the pain will be felt minimally. Lying on a hard sofa or rug with a small tight cushion placed under the lower back usually helps to relieve tension and spasm from the intercostal muscles. It is recommended to place a similar smaller cushion under your neck.
- You can ask your spouse to give you a light back massage. The key word here is easy. The movements should be rubbing and stroking. Under no circumstances should you massage anything, much less “straighten” anything.
- Neurologists allow the use of light warming rubs based on natural balms with essential oils in pregnant women. Do not rub the skin “red” or use oils that are contraindicated for pregnant women, for example, wormwood.
- During remission, it is worth paying attention to special gymnastics or yoga for pregnant women. These exercises strengthen the muscle corset and increase the elasticity of the ligaments, thus preventing the next attack of intercostal neuralgia.
It is worth noting that in the vast majority of cases, all pain associated with the musculoskeletal system goes away within a few weeks after childbirth.
Neuralgia - clinics in
Choose among the best clinics based on reviews and the best price and make an appointment
Family
Medical
Moscow, Landyshevaya st., 14, bldg.
1 Pyatnitskoe highway
+7
- Reception from 770
- Manual therapy from 1200
- Neurology from 1200
0 Write your review
Family
Clinic "Your Health Plus"
Moscow, Orekhovy pr., 11, entrance from the yard (from the children's playground)
Shipilovskaya
+7
- Consultation from 1850
- Reflexology from 2000
- Neurology from 500
0 Write your review
Family
Clinic "Cecile"
Moscow, Kalanchevskaya st., 17, building 1
Komsomolskaya (KL)
8
- Reception from 1200
- Neurology from 650
- Shock wave therapy from 5000
0 Write your review
Show all Moscow clinics
Neuralgia - specialists in Moscow
Choose among the best specialists based on reviews and the best price and make an appointment with
Neurologist
Tugutov Alexander Viktorovich
Moscow, prosp. Mira, 79, building 1 (Oriental Medicine Clinic “Sagan Dali”)
+7
0 Write your review
Neurologist
Zhdanov Igor Vyacheslavovich
Moscow, Landyshevaya st., 14, bldg. 1 (Medical)
+7
0 Write your review
Neurologist