About the method
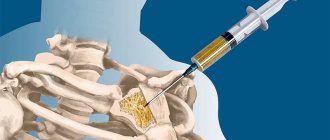
A bone biopsy is the procedure of removing a piece of bone tissue for examination. It is carried out if the use of other diagnostic methods does not allow an accurate diagnosis to be made.
The procedure is carried out in the following cases:
- The need to distinguish between benign and malignant tumors;
- In order to evaluate previously prescribed therapy;
- To determine the exact characteristics of oncology.
The procedure is complex, but capable of yielding maximum information about the tumor. It is no coincidence that it is called the most informative diagnostic procedure in oncology.
Having received a sample of the affected bone tissue as a result of a biopsy and examined it in the laboratory, the doctor can get a complete picture of all the characteristics of the tumor and, based on this knowledge, formulate the optimal tactics for subsequent treatment.
Anatomy of education
Content:
- Anatomy of education
- Indications for use
- The essence of the operation
- Patient preparation
- Procedure technique
- Complications of the procedure
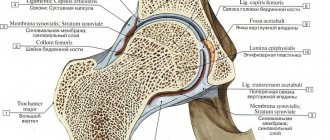
The hip joint is a spherical synovial joint: its structure includes the femoral head and acetabulum. The hip joint is the articulation of the pelvis with the femur, which connects the axial skeleton to the lower limb. In adults, the hip bone is formed by the fusion of several other bones, which occurs towards the end of adolescence. The 2 bones of the femur form the bony pelvis together with the sacrum and coccyx and are united anteriorly by the pubic symphysis. The hip joint is a synovial joint between the femoral head and the acetabulum of the pelvis.
The vertical head is formed by the three bones of the pelvis. Between them is a Y-shaped cartilaginous growth plate (cartilage), which usually fuses between 14 and 16 years of age for a high degree of mobility. The acetabular labrum increases joint depth, thereby increasing joint stability, but causes decreased joint motion. Compared to the shoulder joint, it allows a smaller range of motion due to increased depth and contact area, but exhibits much greater stability.
The joint is surrounded by a fibrous capsule that attaches to the acetabulum and then attaches to the proximal femur. The processes of this capsule make up the ileofemoral, ischeofemoral and pubofemoral ligaments.
Indications for use
As mentioned above, bone biopsy as an independent procedure is performed in cases where other diagnostic methods - radiography, CT, MRI - do not provide the doctor with the required information about the disease.
Indications for:
- Tumors;
- Chronic osteomyelitis;
- Brody's abscess;
- Tuberculosis of bone;
- Bone destruction of unknown etiology;
- Bone diseases that cannot be cured.
In most cases, the procedure is indicated for patients in whom a primary bone tumor is suspected.
The procedure is indicated before or during surgery. This is important to understand the nature of the tumor, because this is what affects the extent of the operation. If we are talking about an infectious lesion, then a biopsy makes it possible to determine the sensitivity of bacteria to therapeutic drugs.
Methods
There are two methods of bone biopsy - open and closed.
The open method is a surgical intervention that is performed with direct access to the bone.
The main advantages of the method:
- Excellent visibility of the study area;
- Easy collection of the required amount of biopsy material.
There are risks:
- Infection;
- Poor tolerance to anesthesia;
- Bone damage with cancer can affect the spread of mutated cells throughout the body.
In the future, such an intervention may complicate surgical treatment of the disease and pose a threat to radical removal of the bone tumor.
In addition, when taking a biopsy using the open method, it is necessary to incise significant amounts of soft tissue, and this, in turn, lengthens the recovery period.
The open method is applicable during the operation, as well as in cases where it is difficult or impossible for a needle to get closer to the lesion.
The closed method is usually used using:
- Punctures;
- Aspiration;
- Trepanobiopsy.
The puncture method is very popular. The tissues are pierced with a special needle and the liquid contents are removed for laboratory study.
The procedure is performed to examine the bone marrow, and also if there is a fluid-filled lesion that can be reached by a needle.
Trephine biopsy is performed in almost all other cases with a special needle for any localization of the pathological process. For greater accuracy, tomographic control is used.
Diagnostic
Puncture of articular structures is carried out to study the intra-articular fluid component. The puncture helps:
- Determine, even without conducting an analysis, whether there is pus or blood in the synovial fluid, and consider the nature of these impurities.
- A biochemical study of the synovial fluid component allows you to find out whether there is an inflammatory process in the articular joint.
- Also, by puncturing and injecting air into the joint capsule, you can determine whether there are foreign bodies in the hip joint. This study is carried out for fractures to determine the presence of cartilage or bone fragments inside the joint.
The puncture is also performed when preparing the patient for an MRI. Injecting air or a contrast agent into the articular structure for better viewing of the articular area on the monitor.
Bone biopsy technique
When performing an intraoperative biopsy, samples obtained during the operation are transferred to specialists for further research.
At the same time, the duration of anesthesia and rehabilitation periods are influenced by the nature of the operation performed.
As a DIY procedure, a bone biopsy involves removing the necessary material using needles, either thin or thick, through the skin.
This biopsy method is called puncture. And depending on the choice of needle, it can be fine-needle or thick-needle.
For a puncture biopsy, local anesthesia is used. Ultrasound or CT can also be used to monitor the movement of the needle in the bone tissue.
The choice of method of carrying out the procedure is the prerogative of the doctor.
To conduct a bone biopsy at the Onco.Rehab integrative oncology clinic, you will have to consult with a doctor who, taking into account your wishes, as well as the necessary factors, will choose the optimal method.
Medical
Puncture of the hip joint for therapeutic purposes There are two types of indications for puncture for therapeutic purposes. In the first case, pathological tissues and contents are removed from the joint structure, in the second case, medications are injected into the joint. Depending on what ailment was diagnosed in the patient, the following procedures are performed:
- The synovial fluid component, blood or purulent clots are removed with a syringe.
- Hormonal therapy is carried out by injecting hormonal and enzyme preparations into the joint cavity when diagnosing arthrosis.
- Anesthetizes the joint structure in case of dislocation or fracture.
- Oxygen is administered under pressure to fuse joint tissues when they are deformed or destroyed.
Risks
The procedure, carried out taking into account the necessary requirements, does not pose a danger to the patient, and complications are also minimal.
However, there are still risks:
- Bleeding;
- Hematoma;
- Nerve fiber damage;
- Damage to the vessel;
- Infection;
- Vein thrombosis and some others.
Skin biopsy
A negative reaction to a local anesthetic is also possible:
- Dizziness;
- Tremor of the limbs;
- Swelling;
- Itching;
- Reduction of heart beats;
- Reduced blood pressure, some others.
To minimize the risk of complications, doctors recommend:
- Make a preliminary diagnosis of the area where the procedure will be performed;
- Select the required size trephine in advance;
- Understand the course of blood vessels and nerves in the surgical area;
- If you suspect cancer, determine exactly where the wound will go;
- Maintain complete sterility;
- Prepare means for emergency leveling of possible bleeding;
- Use radiography and CT for deep localization of the lesion.
Technique
Scheme of puncture of the hip joint The general technique for performing a puncture is the same for all articular joints. Despite the fact that the procedure may seem simple to many, it should only be performed in a medical facility, entrusting the puncture to an experienced specialist. When performing a puncture, the surgeon uses exclusively sterile material. He prepares a syringe and other instruments, then treats the surgical field with an antiseptic. If necessary, excess vegetation is shaved off the puncture area and treated first with an iodine solution and then several more times with alcohol. Next, using a thin needle, the puncture area is anesthetized with novocaine injections. After the preparation has been carried out, the doctor takes a twenty-milliliter syringe with a thick needle and moves the skin to the side at the puncture site. This procedure is carried out to prevent air and pathogenic microorganisms from entering the joint. Then a puncture is made and the needle is advanced into the intraarticular cavity. Next, the specialist either administers the medicine or takes the punctuation for analysis. When the procedure is completed, he quickly removes the needle, seals the wound with a plaster and applies a bandage to the limb. Due to the fact that there are some anatomical differences in the articular joints, the puncture in each case is carried out taking these nuances into account. Various methods of inserting the needle and guiding it along the joint are also used. The only thing that is common in the technique is that all procedures are performed in the extensor part of the joints or places where there are no nerve endings and large vascular network. When performing a puncture of the hip joint, the specialist asks the patient to lie on his back. If the patient is thin, then the puncture is performed using a needle used for intramuscular injections, but if the patient is overweight, a thick and long needle is used for the procedure. The needle is inserted perpendicular to the skin, at the same time, retreating two fingers under the inguinal fold in the area of the point where the pulsating femoral artery passes. The needle is carefully advanced deep into the articular structure until it touches the head of the femoral bone tissue, after which the specialist makes an indentation of two centimeters and injects the medicine or takes the synovial fluid component. If the needle is in the cavity of the articular structure, then the drug is administered without resistance, and punctuation is collected easily and quickly.
After the procedure
After the procedure, painkillers are needed for two to three days, for example, Panadol, Ketonal. Sometimes the pain lasts up to two weeks.
The patient covers the wound with a bandage until it heals (about two days). The wound should not be wetted; after removing the bandage, lubricate it with iodine until complete healing occurs. Physical activity should be avoided.
If there is swelling, severe pain, redness, increased body temperature, or discharge from the wound, you should consult a doctor.
Oncology centers - partners of the Onco.Rehab Integrative Oncology Clinic will provide you with highly qualified diagnostics for subsequent treatment.
Recovery period
After a therapeutic or diagnostic procedure, the patient will need time to recover. After taking a small amount of fluid, as a rule, there are no complaints and the patient will be able to walk in 10-15 minutes.
With significant hemarthrosis or arthritis with a large amount of exudate, after puncture the patient experiences a decrease in the severity of symptoms. Swelling and redness decrease almost immediately after the fluid is removed.
In state medical institutions, puncture is included in the list of surgical procedures for a number of pathologies. If indicated, this manipulation is performed in such hospitals free of charge for both diagnostic and therapeutic purposes.
In commercial clinics, the price for this diagnostic and treatment technique depends on the technology of the equipment and the range of laboratory tests performed. The cost of the puncture will also be affected by medications that are used for pain relief, treatment of inflammation and protection of the ligamentous apparatus. The minimum price in private clinics and medical centers is 1000-1200 rubles per procedure.