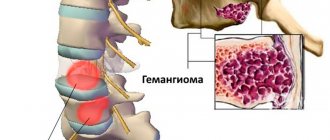
Sacralization of the vertebrae is a pathological process leading to complete atrophy of the intervertebral disc and fusion of the fifth lumbar and first sacral vertebrae. For a long time, sacralization of the spine was considered a congenital disease, a disruption of the process of intrauterine development of the structural parts of the spinal column. However, modern research suggests that the process of fusion of vertebral bodies with each other can occur during the first 30 years of life. With severe degeneration of cartilaginous intervertebral discs, absolutely any vertebrae can fuse together.
In most cases, sacralization of the lumbar spine in an adult is associated with the development of lumbosacral osteochondrosis. This is a degenerative dystrophic disease in which the fibrous ring of the intervertebral disc is destroyed. The process proceeds as follows:
- When a person leads a sedentary lifestyle, the performance of the muscular frame of the back is impaired;
- muscles cannot cope with providing diffuse nutrition to the intervertebral discs (they do not have their own circulatory network and receive fluid, oxygen and nutrients only through diffuse exchange with the surrounding muscles);
- dehydration of the cartilage fibers of the fibrous ring develops, and they lose their ability to withstand increased loads;
- the shape of the intervertebral disc changes - it becomes flatter and extends beyond the vertebral bodies (this stage of osteochondrosis is called protrusion);
- the nucleus pulposus located inside the fibrous ring gives up some of the fluid and loses its shock-absorbing ability;
- with a sharp movement with emphasis on the damaged intervertebral disc, the integrity of the thinned and dehydrated fibrous ring may be disrupted;
- Part of the nucleus pulposus slips into the resulting crack (this condition is called disc herniation).
All these processes lead to the development of dorsopathy, intervertebral discs gradually lose their height and shock-absorbing ability. With a long-term absence of diffuse adequate nutrition, the process of atrophy begins. The bodies of adjacent vertebrae may partially or completely fuse with each other.
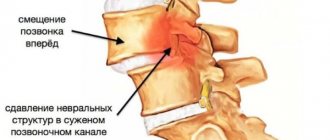
This is a kind of defense mechanism. The spinal canal runs inside the spinal column. It houses the spinal cord, which controls all processes in the human body. This is the central organ of the autonomic nervous system, responsible for vascular tone, the performance of the heart muscle, breathing, and the functions of all internal organs of the thoracic and abdominal cavities without exception. If this type of innervation is disrupted, a person may be paralyzed, his heart may stop, urination may stop, etc. It is very important to ensure the stability of the position of the vertebral bodies and the absence of pressure on the radicular nerves extending from the spinal cord. Therefore, sacralization of the L5 vertebra can be considered a natural process.
Our manual therapy clinic has developed special programs that allow for successful rehabilitation and adaptation of patients with sacralization of the lumbar vertebra. An individually developed course eliminates the risk of developing complications, such as impaired flexibility of the spine, changes in posture, and an increased risk of spreading degenerative dystrophic changes to the intervertebral discs located above.
If you are experiencing recurring pain in the lower back and sacrum, you can schedule a free initial consultation at our manual therapy clinic. An experienced vertebrologist will conduct an examination and examination, make an accurate diagnosis and prescribe individual treatment.
Features of the anomaly
In a healthy person, the spine consists of 24 elements and is divided into three sections, the sacrum and the coccyx. Its development begins at the 8th week of pregnancy and continues until the age of 25. But due to the impact of a number of negative factors on the body of future matter, pathological changes in the spine may occur. The result is sacralization of the vertebra, localized in the lumbar region.
What it is? Fusion of the fifth vertebra with the sacrum. It can be complete or partial. In this case, the total number of segments is reduced by one or, conversely, increased. This process increases pressure on all parts of the lower back that are above the combined area. And if, with normal development, the back is able to cope well with the assigned tasks, then congenital pathology leads to compression of the nerve endings. This provokes severe pain in the area.
Pathology is classified into:
- False. It is distinguished by a low landing of the l5 vertebra in the sacrum, and also maintains the distance, albeit small, between the l5 and s1 vertebrae.
- True. These are all congenital combinations of vertebrae that are diagnosed in people of any age.
Sacralization of the lumbar spine occurs without a single symptom in most patients, and some people learn about it by accident. In other patients, it becomes the cause of osteochondrosis, spondyloarthrosis and other dystrophic, inflammatory processes in the back.
Diagnostics
To diagnose an L5–S1 intervertebral hernia, an in-person examination by a neurologist or vertebrologist is required first. At the first consultation, the doctor collects anamnesis, finds out working conditions, the nature of the symptoms and examines the patient. This suggests the presence of a hernia and prescribe additional studies:
- MRI;
- x-ray of the lumbosacral spine;
- CT;
- myelography.
The most informative method for diagnosing the disease is MRI. The study allows you to accurately determine the presence of a protrusion or hernia of any spinal motion segment and even detect foraminal hernias, which are especially difficult to diagnose. Thanks to MRI, the doctor receives accurate data on the location of the protrusion, its size, and tendency to sequestration, which allows him to prescribe the most effective treatment in each specific case.
Degrees of fusion
Sacralization can be articular, which refers to a mild degree, cartilaginous and bone. In the first case, pits form on the surface of the ilium due to its constant contact with the transverse processes. This provokes neoarthrosis, a pathological joint. Distinctive features are the absence of restriction of movement and minor pain, which appear relatively infrequently.
Cartilaginous sacralization of the vertebral region is the second degree of severity. It is characterized by the formation of a rigid cartilaginous structure (synchondrosis) between the transverse processes, vertebrae and the iliac crest. In this case, the patient has significantly reduced bone mobility, and severe pain is felt when turning.
Bone sacralization is considered the most severe, since this pathology leads to acute pain in the lower back with any movement. The vertebral body and sacrum fuse into one node, thereby immobilizing 15 and s1.
Any of the described degrees of fusion can occur on either side of the vertebra. At the same time, cartilaginous and articular are distinguished by incomplete unification of elements, and bone – by absolute unification.
A visual representation of what vertebral developmental anomalies look like
Classification
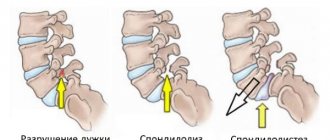
L5 spondylolisthesis can have several types:
- forward displacement – anterolisthesis;
- backward displacement – retrolisthesis;
- displacement to the left or right – laterolisthesis.
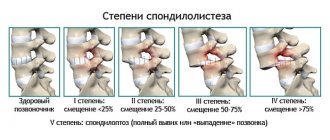
The classification may also relate to the degree of vertebral displacement. There are the following degrees:
- 25% of the vertebra is displaced in relation to the underlying one - the first.
- 50% – second.
- 75% – third.
- 75-100% – fourth.
- Full displacement - fifth.
At the fifth stage, so-called spondyloptosis occurs. This condition can only be treated surgically and is very serious.
Causes
Experts have not fully figured out why the sacralization of the lumbar vertebra occurs, due to the difficulty of tracking changes in a growing organism under the influence of certain factors in the womb. It begins to develop as the embryo grows, and the following contributes to this:
Concrescence of the lumbar vertebrae
- Intrauterine developmental defects.
- Poor nutrition.
- Bad habits (alcohol, smoking, drugs).
- Physical labor or increased stress on the pregnant woman’s body.
- Chemical exposure.
- Constant stress, depression.
- Hypothermia of the body.
- Radioactive exposure.
- Wearing clothes that are too tight or getting abdominal injuries.
Taking a number of medications can have a negative effect on the fetus, especially in the first trimester. It is during this period that the formation of the child’s future organs occurs. In addition, experts note that the anomaly can be triggered by toxins or poisons that enter the bloodstream in small quantities, but trigger irreversible processes.
Sacralization is often combined with other malformations of the spine. When it is detected, a thorough examination is necessary to determine the cause and the presence of complications. For some people it reduces the quality of life, for others it does not cause functional discomfort. It all depends on the individual characteristics of the body.
Most often men suffer from the pathology, but the anomaly is also diagnosed in women. When dealing with severe pain in the lumbar region, sacralization is diagnosed in half of the patients. But for some it can occur in a latent form, without characteristic signs.
In some patients, the anomaly manifests itself as severe pain with increased physical activity.
How to treat pathology
To eliminate congestion, the patient is given a course of physical therapy.
If the radiologist has confirmed the presence of changes characteristic of sacralization, conservative or surgical treatment is prescribed. If the pathology is asymptomatic, monitoring the condition is sufficient.
When pain is present, conservative measures are prescribed:
- taking oral medications from the group of non-steroidal anti-inflammatory and analgesics;
- carrying out blockades with stronger drugs, for example, from the group of glucocorticoids or Novocaine;
- attending physical therapy sessions: electrophoresis with painkillers, ultrasound therapy, magnetic and laser therapy.
To prevent stagnant processes and strengthen the structures of the affected area, therapeutic massage and physical exercise are required. If possible, the patient is sent for treatment to sanitary-resort conditions.
If the results of CT and MRI reveal pathological changes in bone and soft tissues that cause severe back pain that cannot be treated with conservative methods, a planned operation is performed:
- the doctor removes the process that has formed a movable or immobile joint;
- then spinal fusion is performed;
- An artificial disc is installed in place of the formed vertebra.
To accelerate the regeneration of operated tissues, it is recommended to undergo a course of physiotherapeutic procedures. If pain is present, take painkillers.
Symptoms of the disease
Sacralization of the vertebra can be asymptomatic, and many patients learn about it by chance, during an examination for another reason. Typically, such a course is characteristic of a stationary vertebra. If it is active, then the patient experiences pinching of the sciatic nerve. The clinical picture develops rapidly, and with pain in the lumbar region the patient is forced to seek medical help. Typical symptoms include:
- Acute pain syndrome.
- Sensory impairment in the lower extremities.
- Tension in the back after being immobile for a long time.
- Loss of sensory functions in the perineal area.
- Dysfunction of the pelvic organs.
- “Shoots” with increased physical activity.
- Burning or discomfort in the lower back.
- Neurological disorders.
It is difficult for patients to bend over, lift weights, and move freely. In some patients, the anomaly begins to appear as they grow older, during intense physical activity, falling, during jumping or strong lateral bending. The pain syndrome manifests itself only in the lower back, but in some it can radiate to the hip.
No ads 1
What is dangerous about abnormal development of the sacrum?
In most cases, patients with four sacral and six lumbar vertebrae do not notice any pathologies and do not present any complaints, therefore, when lumbarization is accidentally detected, they do not attach due importance to the treatment and the necessary regimen. This approach is dangerous due to the high risk of complications, for example, osteochondrosis, kyphosis, scoliosis, spondylosis and other diseases based on deformation of the anatomical structures of the spine.
Almost 60% of patients with lumbarization have a pronounced curvature of the spine, which becomes noticeable at an early age and is diagnosed when passing a mandatory medical commission before entering a preschool educational institution.
If at this stage no action is taken to correct the pathology, in the future the child may develop severe forms of stoop associated with displacement and deformation of the central axis of the spinal tube. With age, other abnormalities associated with underdevelopment of the sacrum will progress, for example:
- displacement of the closing vertebra l6 during intense physical activity, for example, lifting weights;
- backward deviation of the sacrum and disturbance of the center of gravity (affects posture, tone of the abdominal muscles and the functioning of the pelvic organs);
Radicular syndrome is a complex of pain and neurological symptoms resulting from compression and pinching of the nerve endings of the spinal nerves. The patient feels acute pain (lumbago), which can take a chronic course and last for several months and even years, characterized by alternating remissions and relapses.
In patients with lumbarization of the first sacral vertebra, sciatic syndrome is often diagnosed, caused by compression of the largest and thickest nerve in the human body (sciatic), which passes through the coccyx and sacrum, the pelvic cavity and both limbs. Pain caused by compression of the sciatic nerve is called lumboischialgia.
Important! Severe lumbodynia and lumboischialgia (lumbago with sciatica) can cause a temporary limitation of a person’s ability to work, as well as the ability to move and perform self-care activities. If these pathologies develop against the background of lumbarization of the vertebra at the s1 level, timely measures should be taken to correct the root cause and associated complications (deformation of the vertebrae and intervertebral discs, displacement of the vertebrae, swelling and inflammation of soft tissues, inflammation of the nerve roots).
Diagnostic procedures
It is impossible to visually determine the pathology, so doctors are forced to resort to a variety of diagnostic tests. Since the pain is not specific, if there are complaints of pain in the lower back, the patient is sent for an x-ray. The resulting image is sufficient to determine the pathology and the degree of its development. But additional procedures may be required:
- General blood and urine analysis. To determine the presence of an inflammatory process and concomitant diseases. Usually, with sacralization, all indicators are within normal limits.
- CT scan. The resulting sections provide reliable data regarding the existing pathology, as well as the condition of nearby tissues.
- Magnetic resonance imaging. Another informative technique that allows you to examine all structures of the spine and characterize in detail the damage to ligaments and soft tissues.
The main technique is x-ray due to its ease of implementation and the availability of equipped rooms in each clinic. A photograph is taken in two projections. But they are sometimes not enough to distinguish sacralization from lumbarization, since they can look almost identical.
How does the pathology appear in the image? The transverse processes are enlarged and resemble a fan; complete or partial fusion of the vertebra with the sacrum is noticeable. MRI or CT images are more detailed and allow you to examine in detail changes in the bone tissue of the vertebrae.
[node:field_similarlink]
Anatomy of a disease
In the human spine, the location of the most massive intervertebral disc is between the 5th lumbar and 1st sacral. Thanks to it, the depreciation of the spinal column is reduced ( Pillar (architecture) - a structure in the form of a single vertical rod for support or decorative purposes Pillory Pillar (heraldry) - heraldic figure Pillar (figurative meaning)
) when walking, and it also prevents pinching of the nerve endings in the lower part of the spine. Sacralization of the vertebra leads to an increase in overload to which the overlying sectors of the lumbar region are exposed.
Then the vertebral discs ( "round dish") - a circle (low cylinder) or an object in the form of a circle
) in the lumbar region it becomes difficult to cope with excessive overloads, which results in pinched nerve roots. At the same time, the person begins to experience constant pain in the lower back.
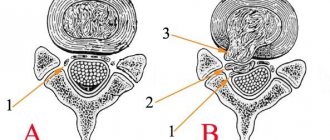
Forms of sacralization l5:
- Full. There is a complete fusion of all structural parts between the two vertebrae.
- Partial. The vertebrae are connected by arches or processes, which significantly reduces their mobility.
- The deepest. It is characterized by the deepest penetration of the l5 vertebra into the region of the sacrum ( the part of the spine of terrestrial vertebrates that ensures its connection with the pelvis
), in which fusion of the vertebrae is not observed.
Also, sacralization l5 is divided into real and false. All of the forms listed above are true sacralization. False is detected when calcium salts are deposited in the ligaments between the same vertebrae. Such a state ( a concept denoting a set of stable values of variable parameters of an object
) can be monitored for ankylosing spondylitis, ankylosing spondylitis.
Given a false form ( can mean: The shape of an object is the relative position of the boundaries (contours) of an object, an object, as well as the relative position of points on a line
) of the disease can manifest itself in older people, since with age, calcium salts are deposited in the spinal ligaments.
We advise you to study - Degenerative-dystrophic changes in the cervical spine
Real and false forms of the disease are distinguished using an X-ray examination of the back. The photographs with real sacralization show complete bone overgrowth of the gap between the vertebrae. In this case, the spinous processes are poorly noticeable or even completely absent.
https://youtube.com/watch?v=G53ksThyeWw
Features of treatment
When there is no pain syndrome, the disease was discovered by chance and in general the patient does not complain of dysfunction in the body or decreased quality of life, specific treatment is not required. The doctor can only recommend wearing a special corset for several hours a day, limiting the load on the spine and doing exercise therapy for preventive purposes. In other cases, you will need to take medications, visit a manual massage room, and undergo physical therapy. Only an integrated approach helps to achieve stable remission and maintain a high quality of life.
Conservative therapy
Taking medications is prescribed only in the presence of pronounced pain. In other cases, the patient needs to do therapeutic exercises and eat right. Complex treatment includes the following groups:
- Painkillers (“Solpadein”, “Analgin”, “Ketanov”). They are aimed at relieving acute pain and helping to alleviate the patient’s condition. In some cases, the pain is so unbearable that a lidocaine blockade is used.
- Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (Diclofenac, Ibuprofen, Nemesil). They can effectively suppress inflammatory processes and relieve swelling in the affected area. Additionally, they enhance the effect of analgesics.
- Chondroprotectors (“Teraflex”, “Dona”, “Arthra”). They protect the intervertebral discs from destruction, and if the process has already begun, they help the tissue regenerate. Therefore, treatment of any spinal pathology cannot be done without these drugs.
- Muscle relaxants (Baclofen, Sirdalud, Tizalud). They eliminate blocks and tightness in the lower back, which are not uncommon during sacralization. They are aimed at relaxing the muscle fiber and thereby eliminating stiffness.
- Multivitamins (“Milgamma”, “Pentovit”). They strengthen bone tissue and improve metabolic processes in the body. They are selected individually, depending on the deficiency of certain substances in the body. During treatment of sacralization, patients often need group B.
This “selection” is considered by many doctors to be universal for any pathological condition of the musculoskeletal system. It allows you to suppress the inflammatory process, alleviate the condition, and protect the intervertebral discs from degenerative diseases.
No ads 2
Physiotherapy
Prescribed physical procedures can enhance the effectiveness of treatment. They are selected by the attending physician based on the age and condition of the patient as a whole. They are carried out only during periods of stable remission. Correct implementation allows you to get rid of pain and improve your overall quality of life. Typically the following sessions are scheduled:
- Electrophoresis with novocaine.
- Ultrasound.
- Paraffin applications.
Paraffin baths are one of the alternative methods of treating pathology
Sanatorium-resort treatment, which is provided in specialized sanatoriums, also helps to cope with the negative manifestation of sacralization. But it is prescribed in the absence of severe pain and the absence of functional disorders in the spine.
Surgery
If conservative treatment does not produce a lasting result, the attending physician recommends surgery. Usually this cannot be avoided when the patient suffers from persistent pain that is practically not relieved by painkillers, as well as when complications rapidly develop. The operation is scheduled as planned and carried out in the vertebrology department.
The operation involves removing the transverse process and fusing the remaining parts using bone grafts. Particular attention is paid to the rehabilitation period, which determines the patient’s recovery rate. Antibiotics are usually prescribed to prevent postoperative complications, as well as painkillers. As healing progresses, it is recommended to engage in exercise therapy and attend physical procedures.
Surgical intervention is used only if there is no result from conservative treatment
The spine is the most important axial part of the human musculoskeletal system
It consists of 33-34 bone segments - vertebrae, connected by cartilaginous intervertebral discs into a single movable structure. Conventionally divided into cervical, thoracic, lumbar and sacral sections. The structural feature of the spinal column allows the human body to perform flexible movements. An equally important function of the spine is to protect the spinal cord from damage.
When the functionality of the spinal column is impaired due to injury or disease, the entire body suffers. A person feels severe, prolonged pain in the back, numbness in the arms and legs, motor activity is limited, and suffers from migraines. Diseases of the spinal column begin in childhood, but the first symptoms appear many years later, when pathological changes have already become irreversible and chronic.
The most common pathologies of the spine today are osteochondrosis, scoliosis and hernias. Doctors explain that these diseases are caused by the realities of modern human life and work activity: low mobility due to sedentary work, or regular injuries to the spinal column due to labor-intensive work with heavy lifting.
We advise you to study - Myositis code according to ICD-10
Also among the main causes are hereditary factors and congenital pathologies. For example, connective tissue dysplasia leads to weakening of the ligaments and tendons of the spine. They acquire a stretched structure and lose stability. The unstable shape of the spine causes poor posture and other disorders of the musculoskeletal system.
Treatment of diseases of the spinal column is carried out with surgical and physiotherapeutic methods, wearing special corsets and physical therapy classes are prescribed.
But the most important goal is to preserve the spine, so the best method is prevention. Posture control, obesity prevention, healthy sleep and nutrition, and daily physical exercise will help keep the spine healthy.
What is sacralization of the l5 vertebra - all the secrets about the spine on NewsForeve.ru
The information published in the article is for informational purposes only.
Share the link and your friends will know that you care about your health and will come to you for advice! Thank youツ
Possible consequences and complications
The congenital anomaly leads to increased stress in the entire lower back, and therefore provokes a variety of negative consequences for the body. The most common of them are:
- Degenerative processes in intervertebral discs (osteochondrosis).
- Curvature of the spine (scoliosis).
- Paralysis.
- Limitation of physical activity.
- Constant unbearable pain.
Due to increased pressure due to sacralization, the bone elements are gradually destroyed, which leads to the need for surgical intervention. Most patients do not have such consequences, and their overall health is not affected, but regular examinations to monitor the dynamics of the disease cannot be neglected.
No ads 3
Preventive actions
Sacralization is a congenital pathology, so there is simply no specific prevention. But you can reduce the risk of such an anomaly in a newborn by observing the following rules for the pregnant woman:
- Quitting bad habits and taking toxic intoxicants.
- Reducing physical activity, giving up exhausting work.
- Avoid exposure to radiation (such as x-rays) unless absolutely necessary.
- Avoid uncontrolled use of medications.
- Prevention of infectious and colds.
- Balanced diet.
- More walks in the fresh air.
- Taking special vitamins prescribed by your doctor.
- Avoid sports activities that are not recommended for pregnant women.
All these measures will not guarantee the absence of spinal abnormalities in a child, but will reduce the likelihood. Therefore, it is worth protecting yourself during pregnancy and eliminating any possible negative effects.
In general, sacralization is considered a pathology with a favorable prognosis, since most patients are not even aware of it, while others do not experience a decrease in quality of life during periodic treatment. Worsening is possible when trying to self-medicate, as well as increased stress on the spinal column. In this case, patients are recommended to undergo surgery to relieve pain and improve their general condition.
Prerequisites for sacralization
Have you been trying to heal your JOINTS for many years?
Head of the Institute for the Treatment of Joints: “You will be amazed at how easy it is to cure your joints by taking the product every day for 147 rubles...
Even old doctors tried to figure out why 2 percent of people experience such a phenomenon as vertebral fusion. No definite answers have been received, other than that this is a congenital pathology. It was also seen that people with such traits are often professional and can have extraordinary capabilities, and therefore sacralization was read as some kind of divine mark, and the word itself was the same root as “sacred,” that is, magical, hidden, incomprehensible.
In general, orthopedists now look at sacralization only through the prism of anatomy and radiology.