Neurologist
Chudinskaya
Galina Nikolaevna
Experience 29 years
Neurologist, member of the Association of Interdisciplinary Medicine
Make an appointment
If a person does the same job for a long time, for example, sits at a computer for a long time, pain may appear in his hands. This will be tunnel syndrome. This problem can occur not only to those people who work at the computer, but also to drivers, since their hands are in one position for a long time.
Tunnel syndrome occurs when the tissue around the tendon swells, putting pressure on the nerve. This leads to the patient beginning to feel tingling in the hands and numbness in the fingers. The muscles become weak and swelling may appear on the fingers.
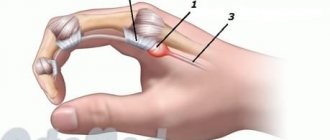
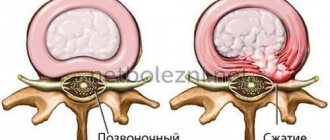
Carpal tunnel syndrome is associated with the tunnel that runs between the transverse ligament and the bones of the wrist. In the middle of the carpal tunnel there is the median nerve. Any diseases, injuries, or pathologies lead to a narrowing of the canal, and this affects the nerve, which causes the syndrome.
Causes
Tunnel nerve syndrome is both a congenital anomaly and a disease associated with a person’s activity and lifestyle.
Among the main causes of carpal tunnel syndrome are:
- maintaining an uncomfortable hand position for a long time (this may be associated with professional activities, for example, working at a machine);
- genetic predisposition;
- hormonal imbalances caused by pregnancy, menopause;
- inflammatory processes;
- benign, malignant tumor in the canal area.
The causes of tunnel syndrome include diseases such as arthrosis, diabetes, arthritis, and thyroid diseases. Patients may encounter this problem due to metabolic disorders, after fractures, frequent injuries, or bruises.
Differential diagnosis
Carpal tunnel syndrome should be differentiated from arthritis of the carpo-metacarpal joint of the thumb, cervical radiculopathy, and diabetic polyneuropathy. Patients with arthritis will show characteristic bone changes on x-rays. In cervical radiculopathy, reflex, sensory and motor changes will be associated with neck pain, while in carpal tunnel syndrome these changes are limited to distal manifestations. Diabetic polyneuropathy is usually a bilateral, symmetrical process involving other nerves (not just the median nerve). At the same time, a combination of polyneuropathy and carpal tunnel syndrome in diabetes mellitus cannot be ruled out.
Kinds
There are more than 30 types of carpal tunnel syndrome, among the main and most common ones we should highlight:
- carpal tunnel syndrome;
- cubital tunnel syndrome;
- elbow;
- peroneal tunnel syndrome;
- tarsal.
Most often, patients experience carpal tunnel syndrome (1.5% of the world's population). The arms suffer more from neuropathy than the lower extremities. Even less often, doctors are consulted with tunnel neuropathy of the trunk.
Causes of ulnar nerve syndrome
Ulnar nerve tunnel syndrome causes neuropathy and muscle weakness, which leads to impaired motor activity of the upper limb. Many functions are affected, including performance and self-care. Excessive pressure on the ulnar nerve can be caused by the following pathogenic factors:
- inflammation of an aseptic nature, provoked by ischemia or compression;
- inflammation of infectious origin when the infection spreads through the blood and lymphatic fluid or when the pathogen penetrates through a violation of the integrity of the skin (for example, with abrasions and scratches);
- ischemia – a violation of the trophism of nerve fiber tissue due to compression or hypothermia;
- swelling of the soft tissues at the site of the ulnar nerve;
- spread of pathology in an ascending or descending manner;
- damage to the nerve fiber at the site where the radicular nerve exits the foramen in the lateral surface of the vertebral body.
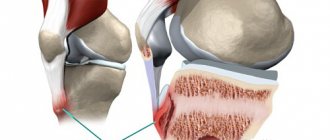
Ulnar nerve syndrome is most likely to develop in individuals who repeatedly apply pressure to the cubital tunnel area. This usually happens when a person is sitting at a table and leans on its hard surface with his arm bent at the elbow.
Elbow tunnel syndrome can occur when talking on the phone for a long time. But only if the phone is held with the same hand, which is bent for a long time. This disrupts the microcirculation of blood and lymphatic fluid in the elbow area. Ischemia of the nerve fiber begins. This can cause pain, numbness, and weakening of muscle effort.
The risk group includes people who lead an active lifestyle and are fond of team sports. Any activity that involves the risk of injury to the elbow joint is a potential pathogen.
Ulnar nerve compression syndrome can occur for the following reasons:
- cervical osteochondrosis with radicular syndrome and impaired innervation of the upper limb;
- plexitis of the brachial nerve plexus, including that caused by inflammation of the axillary lymph nodes;
- deforming osteoarthritis of the shoulder, elbow and wrist joints;
- damage to the ligaments and tendons in any of the joints of the upper limb;
- arthritis of any etiology;
- articular form of ankylosing spondylitis or systemic lupus erythematosus;
- injuries of the upper limb, such as dislocation of the elbow joint, sprains or ruptures of ligaments, tendons and muscles, fractures of the ulna and radius;
- tumor processes of a malignant and benign nature (most often patients are worried about the so-called “fat tumors” - lipomas, which have a strong compressive effect on the ulnar nerve);
- tumors affecting bone tissue (sarcoma, osteoma, etc.);
- any inflammatory processes associated with hematomas and bruises.
For complete treatment, it is necessary to try to eliminate as many potential negative influence factors as possible.
Symptoms and signs
The working arm often suffers from the disease; pain is especially disturbing in the morning and at night. The main symptoms of carpal tunnel syndrome include:
- colic, stabbing pain;
- weakness in the arms;
- decreased sensitivity;
- limbs become less active and mobile.
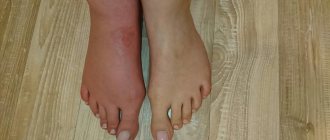
Patients experience a sensation as if goosebumps are running over their palms, a feeling of shooting pain, and numbness. It will become difficult for a person to control and control his hand; when clenching his palm into a fist, unpleasant sensations will arise, and in the later stages, pain.
Take into account! The disease affects all fingers except the little fingers.
Are you experiencing symptoms of carpal tunnel syndrome?
Only a doctor can accurately diagnose the disease. Don't delay your consultation - call
Ulnar (cubital) and radial tunnel syndromes
- if you regularly rest your joint on any hard objects (for example, using a phone, tablet, laptop, lying on your stomach, or incorrect body position while sleeping).
- if you hold your hand in an unnaturally bent position for a long time (again, an example is your mobile companion during long-term communication).
- playing certain sports (for example, basketball, in which the elbow area is under constant tension), in which the nerve can be damaged, which will cause ulnar neuropathy (one of the names of the syndrome).
If you see a doctor on time, you may avoid many unpleasant sensations. The initial symptoms of this disease are acute pain and loss of sensation in the limb, as well as tingling in the hand, especially in the little finger and ring finger. If you missed this point, then no less unpleasant symptoms may develop later:
- change in the shape of the hand and general weakness of the hand (in particular the two fingers above)
- loss of ability to fully move fingers
- death of muscle tissue
The final diagnosis can be made only after a detailed examination, or using various methods that check the presence of an impulse in certain areas of the nerve fiber.
Symptoms of Radial Tunnel Syndrome (RTS)
The cause of RTS is the same pinched nerve. But this nerve runs much deeper - in the bones and muscles of the forearm. The beginning of the problem can be any of the following situations:
- bone tumors
- inflammation of external tissues
- all kinds of fractures and dislocations
The main symptom of RTS is muscle pain in the forearm and part of the hand, mainly from the palm. The pain is especially aggravated when trying to straighten the arm. Tingling sensations are not as common as ulnar neuropathy.
As in the case of the previous example, it is possible to draw a correct conclusion only with a comprehensive examination of the limb that has disturbed you.
Treatment
The difficulty of treating LTS is determined by the pressure on the nerve. If it is not strong enough, then the use of surgical interventions is not required; it is quite possible to get by with preventive measures and a little effort. Such measures may include avoiding situations in which the elbow joint experiences stress when placed on hard surfaces under the slightest pressure, as well as wearing various orthopedic devices, such as cuts during activity and splints during sleep to prevent excessive flexion of the arm. You should try to avoid sitting for a long time at a personal computer, preferably sleep in a supine position, and do not rest your elbows on the table while eating. Sports and active recreation will also have to be excluded for a while.
If these measures do not help, then an unpleasant but reliable surgical intervention comes to the rescue, in which most patients are satisfied with the result. The main method in this case is to shift the nerve to another area that is freer from compression. But in rare cases, the complexity of the operation is an order of magnitude higher and boils down to the fact that space is freed up near the nerve without moving it by cutting off part of the tissue. The postoperative period is several months. At this time, as after almost any operation, any physical activity on the operated limb is not recommended, otherwise the entire treatment may be useless and will have to be repeated.
In the case of RTS, various intramuscular drugs are often used to reduce inflammation and swelling. Splints and other orthopedic devices may also be used. As a preventative measure, special exercises are prescribed to improve the supply of tissue cells with necessary microelements. In addition, physical therapy procedures such as ultrasound and other types of electromagnetic waves may be prescribed.
But here, too, if the ineffectiveness of the treatment is realized (as a rule, it comes after 2-3 months), they resort to surgical intervention.
In this case, again, various methods are used to reduce pressure on the nerve (both changing its position and changing its environment). But, in any case, operating on a limb is a last resort, and it is used when the doctor and patient realize the hopelessness of the situation. This is usually caused by severe weakness in the hand and elbow, as a result of pain and ailments, as well as sagging of the wrist and the inability to bend the limb. Author: K.M.N., Academician of the Russian Academy of Medical Sciences M.A. Bobyr
When to see a doctor
Do not expect that everything will go away on its own; if you do not consult a doctor in a timely manner, atrophy of the limbs may begin to develop. If your profession involves working at a computer, you stand at a machine for a long time, or you work as a driver, you are at increased risk. When the first symptoms appear (nighttime, vegetative, pain), you need to consult a specialist.
Neurologists at JSC Meditsina (clinic of Academician Roitberg) have extensive experience in treating such problems. Our clinic is located in the center of Moscow, within walking distance are the Mayakovskaya, Belorusskaya, Novoslobodskaya, Tverskaya, and Chekhovskaya metro stations.
Radial nerve compression syndrome
Three variants of compression damage to the radial nerve can be distinguished: 1. Compression in the armpit area.
Rarely seen. It occurs as a result of the use of a crutch (“crutch paralysis”), and paralysis of the extensors of the forearm, hand, main phalanges of the fingers, abductor pollicis muscle, and supinator develops. The flexion of the forearm is weakened, the reflex from the triceps muscle fades. Sensitivity is lost on the dorsal surface of the shoulder, forearm, and partly the hand and fingers. 2. Compression at the level of the middle third of the shoulder (spiral canal syndrome, “Saturday night paralysis”, “park bench”, “bench” syndrome). It occurs much more often. The radial nerve, emerging from the axillary region, bends around the humerus, where it is located in the bony spiral groove (groove), which becomes the musculoskeletal tunnel, since the two heads of the triceps muscle are attached to this groove. During the period of contraction of this muscle, the nerve is displaced along the humerus and as a result can be injured during forced repeated movements in the shoulder and elbow joints. But most often, compression occurs due to compression of the nerve on the outer-posterior surface of the shoulder. This usually occurs during deep sleep (deep sleep often occurs after drinking alcohol, which is why it is called “Saturday night syndrome”), in the absence of a soft bed (“park bench syndrome”). Pressure on the nerve may be due to the location of the partner's head on the outer surface of the shoulder. 3. Compressive neuropathy of the deep (posterior) branch of the radial nerve in the subulnar region (supinator syndrome, Froese syndrome, Thomson-Kopell syndrome, “tennis elbow” syndrome). Tennis elbow, tennis elbow, or epicondyllitis of the lateral epicondyle of the humerus is a chronic disease caused by a degenerative process in the area of muscle attachment to the lateral epicondyle of the humerus. Compression syndrome of the posterior (deep) branch of the radial nerve under the aponeurotic edge of the short extensor carpi radialis or in the tunnel between the superficial and deep bundles of the supinator muscle of the forearm can be caused by muscle overload with the development of myofasciopathies or pathological changes in perineural tissues. It manifests itself as pain in the extensor muscles of the forearm, their weakness and hypotrophy. Dorsal flexion and supination of the hand, active extension of the fingers against resistance provoke pain. Active extension of the third finger while pressing it and simultaneously straightening the arm at the elbow joint causes intense pain in the elbow and upper forearm. Treatment includes general etiotropic therapy and local effects. Take into account the possible connection of tunnel syndrome with rheumatism, brucellosis, arthrosis of metabolic origin, hormonal disorders and other conditions that contribute to compression of the nerve by surrounding tissues. Anesthetics and glucocorticoids are injected locally into the area of the pinched nerve. Complex treatment includes physical therapy, the prescription of vasoactive, decongestant and nootropic drugs, antihypoxants and antioxidants, muscle relaxants, ganglion blockers, etc. Surgical decompression with dissection of the tissues compressing the nerve is indicated if conservative treatment is unsuccessful. Thus, hand tunnel syndromes are a type of damage to the peripheral nervous system caused by both endogenous and exogenous influences. The outcome depends on the timeliness and adequacy of treatment, correct preventive recommendations, and the patient’s orientation in choosing or changing a profession that predisposes to the development of tunnel neuropathy.
The article uses drawings from the book by S. Waldman. Atlas of commom pain syndromes. – Saunders Elsevier. – 2008.
Diagnostics
To correctly diagnose the disease, the doctor communicates with the patient and takes into account his complaints. Afterwards, the limbs are examined, tests and instrumental examination are prescribed.
The main tests include:
- Tinnel;
- Vest;
- Fallena.
The patient is also prescribed an ultrasound, computed tomography, and MRI, which makes it possible to determine (or refute) the presence of tumors. Before prescribing treatment, the specialist is faced with the task of determining how affected the nerve is. For this purpose, electroneuromyography is prescribed.
Pronator teres syndrome (Seyfarth syndrome)
Entrapment of the median nerve in the proximal part of the forearm between the pronator teres fascicles is called pronator syndrome.
This syndrome usually begins to appear after significant muscle activity over many hours involving the pronator and flexor digitorum muscles. Such types of activities are often found among musicians (pianists, violinists, flutists, and especially often among guitarists), dentists, and athletes [Zhulev N.M., 2005]. Long-term tissue compression is of great importance in the development of pronator teres syndrome. This can happen, for example, during deep sleep when the newlywed’s head is positioned for a long time on the partner’s forearm or shoulder. In this case, the median nerve in the pronator snuffbox is compressed, or the radial nerve in the spiral canal is compressed when the partner’s head is located on the outer surface of the shoulder (see radial nerve compression syndrome at the level of the middle third of the shoulder). In this regard, to designate this syndrome in foreign literature, the terms “honeymoon paralysis” (honeymoon paralysis, newlywed paralysis) and “lovers paralysis” (lovers paralysis) have been adopted. Pronator teres syndrome sometimes occurs in nursing mothers. In them, compression of the nerve in the area of the pronator teres occurs when the baby’s head lies on the forearm, he is breastfed, lulled to sleep, and the sleeping person is left in this position for a long time.
Treatment
Your doctor will tell you how to treat carpal tunnel syndrome. Do not self-medicate; painkillers will temporarily eliminate the pain, but the cause will remain, which gives rise to new symptoms.
Treatment depends on symptoms and causes. In case of a mild form of the disease, a massage is prescribed; a specialist may also prescribe wearing an orthosis - it will reduce pain at night and simplify the work process during the day. The massage can be performed either by a clinic specialist or by the patient at home; the doctor will introduce you to the technique and movements. Medications may also be prescribed to help restore blood circulation. For severe pain, painkillers are prescribed. At the initial stage, conservative treatment, for example, physical therapy, will help. In the later stages, it is necessary to cut the retaining ligament and eliminate the pinched nerve.
Clinical manifestations
With the development of pronator teres syndrome, the patient complains of pain and burning 4–5 cm below the elbow joint, along the anterior surface of the forearm and pain radiating to the 1st–4th fingers and palm.
Tinel's syndrome. In case of pronator teres syndrome, Tinel's sign will be positive when tapping with a neurological hammer in the area of the pronator snuff box (on the inside of the forearm). Pronator-flexor test. Pronating the forearm with a tightly clenched fist while creating resistance to this movement (counteraction) leads to increased pain. Increased pain can also be observed when writing (prototype of this test). When examining sensitivity, a sensitivity disorder is revealed, involving the palmar surface of the first three and a half fingers and the palm. The sensory branch of the median nerve, innervating the palmar surface of the hand, usually passes above the transverse carpal ligament. The occurrence of sensory disturbances on the palmar surface of the first finger, the dorsal and palmar surfaces of the second and fourth fingers, with preservation of sensitivity in the palm, allows one to confidently differentiate carpal tunnel syndrome from pronator teres syndrome. Thenar atrophy in pronator teres syndrome is usually not as severe as in progressive carpal tunnel syndromes.