Pathologies of the lower extremities, resulting from disturbances in the formation of the musculoskeletal system in the prenatal and postnatal periods of child development, are diagnosed in 2-12% of babies. Congenital inferiority of the movable joints of the legs is a treatable ailment, the treatment of which involves massage, physiotherapy, casting and orthopedic devices. Soft and hard spacers for hip dysplasia restore the functionality of the joints and help avoid complications of the disease.
Symptoms and causes of hip dysplasia in infants
Causes
Today, science identifies several causes of dysplasia.
However, the following is considered the most logical and reasonable of all. In preparation for childbirth, the female body secretes the hormone relaxin. Its main task is to relax the hip ligaments and muscles and prepare the birth canal. However, this hormone cannot determine which specific joints it needs to influence and which it does not, so it affects both mother’s and children’s. Of course, the risk of a mother having a dislocated hip bone is minimal, but in a newborn it is quite high, since all the bones are still soft and fragile. In addition, babies do not yet have ligaments that help the bone return to its place.
Other factors that increase the chance of having a baby with dysplasia include:
- First delivery. The body of a young mother tries to facilitate the process as much as possible, and therefore produces the hormone relaxin in huge quantities.
- Big fruit. The larger the newborn, the more pressure it puts on the hip joints.
- You are waiting for the princess. For some reason, nature has it that girls are much more likely to suffer from this complication than young gentlemen.
- Breech presentation of the fetus. In this case, it is not the child’s head that comes out first, but the butt. Of course, in this case the pressure on the joints is colossal, and if the femur jumps out of the joint, then it does not always have enough strength to return to its place.
- Heredity through the female line. If someone in your family suffered from such a problem, then most likely it can happen again with your baby.
Of course, you can try to outwit nature: if doctors predict you two or more of the above-described scenarios for the development of the situation, you may also be offered to have an operation—caesarean section—. In this case, the hormone relaxin will not begin to act, and you will be able to give birth to an absolutely healthy baby.
Symptoms
But how do you know if your newborn has this complication? Of course, there are symptoms by which only a doctor can determine the presence of a problem, but there are also those that should raise a seed of doubt in you and prompt you to make an appointment with a specialist. So, let's look at what symptoms you can see and what should alert you:
Asymmetry of folds, namely: place the newborn on his stomach or back and carefully straighten his legs. Now take a closer look: the folds that are located under the butt, in the groin and on the hips should be the same, that is, at approximately the same angle on each leg.
A newborn's knees are of different heights. If you lay your baby on his back and bend his knees, you should see that they are approximately at the same level, but if this is not the case, then the cause may be imperfection of the hip joints.
When the legs are spread to the side, the joints have different amplitudes. Most often, this manipulation is performed by pediatricians when they come to meet you for the first time. It's very simple: you put the baby on his back, raise his legs, bend his knees and spread him to the side. As a rule, children of this age are very flexible, and the legs should practically lie on the surface, but under no circumstances use force if you feel that somewhere the baby is not comfortable and the leg will not lie down further. If this manipulation is difficult for a newborn and, moreover, you hear a crunch in the joint, this is also a reason to consult with an orthopedist or at least a pediatrician.
As for older children, the following should alert you: if you observe in a child older than 6 months the habit of standing up or walking on his toes, clubfoot, toes turned inward or outward, as well as severe curvature of the spine, especially in the lumbar region, or gait like a duck's.
This disease is treatable, but it will be most effective if you manage to apply measures in the early stages.
Symptoms
The pathology of joint development in the normal position of the legs does not cause any discomfort or pain in the baby. Because of this, it is difficult for parents to notice underdevelopment of joints in the early stages.
The first manifestations of pathology may appear when the child begins to walk. With DTS, swaying when walking or the so-called “duck walk” is observed on both sides. If one or both joints are underdeveloped, the child may limp and walk “on tiptoe” (do not step on the heels).
At the slightest suspicion, you should consult a doctor who can determine the diagnosis not only through examination, but also through special manipulations. With DTS, the following symptoms are identified:
- different lengths of the lower limbs, shortening of the thigh;
- asymmetry of folds on the inner surface of the thighs (non-specific symptom, can also be observed in healthy children);
- pain (the child reacts by crying) or restriction of movements when trying to spread the bent legs to the sides (normally, in infants, the legs are spread up to 90°);
- the head of the femur easily (with a click) moves out of the acetabulum and returns to it: this indicates increased elasticity of the joint;
- excessive mobility in the hip joints: the baby may unnaturally turn his legs outward or inward.
Differences in treatment tactics for dysplasia in infants and older children
Therapy for diseases identified in children under one year of age includes wearing splints, using physical therapy exercises, and engaging the services of a massage therapist and physiotherapist.
If not detected in a timely manner, the anomaly actively progresses; To stop the disease, more complex methods are required - plaster casting, surgery.
The last of these methods includes:
- Closed reduction. The surgical technique involves forcing the femoral head back to its natural position. Stabilization of the elements is achieved using plaster casts.
- Tenotomy is the lengthening of the terminal structures of the striated muscles.
- Rotational osteotomy. It is carried out in several stages. Among them are exposure of the bone segment, destruction of the hip, changing the position of the joint structures to the desired configuration with further fastening with metal plates.
- Open reduction - movement of the caput femoris with simultaneous lengthening and separation of the tendons.
- Pelvic osteotomy, or reconstruction of the acetabulum affected by pathology.
Long-term restriction of mobility in older age may be accompanied by a disturbance in the patient’s psycho-emotional state and the development of complications.
DTS detected in a child is not a death sentence. Timely treatment and compliance with all medical recommendations during the rehabilitation period allow the patient to achieve full recovery.
Diagnostics
A specialist examines the baby’s hips while still in the maternity hospital
. To make a correct diagnosis, the doctor finds out whether the newborn is at risk: whether the pregnant woman suffered an infectious disease or intoxication, what environmental situation she lived in, whether there is a family history, etc.
Next, the specialist examines the baby’s hips. Such an examination is carried out within the walls of the maternity hospital: after physiological muscle hypertonicity sets in, diagnosis will be difficult.
To confirm the diagnosis, instrumental diagnostic measures are prescribed.
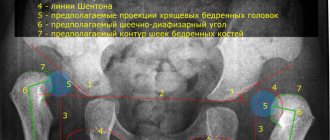
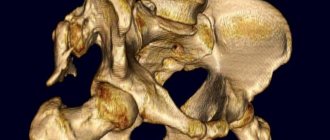
Ultrasound examination of the hip is a mandatory method to help identify dysplasia. Ultrasound is mandatory for children under 3 months of age who show signs of pathology. The manipulation is completely safe and quite informative. Examining the deformed area, the doctor checks the condition of the bone as a whole, the cartilaginous protrusion, and the angle of inclination of the acetabulum.
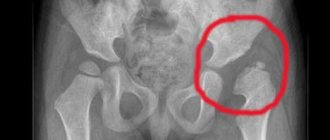
X-rays will be informative in identifying pathology in babies over 7 months of age. Until 7 months, most of the acetabulum and the head of the bone are covered with cartilage tissue, and it will not be visible on an x-ray.
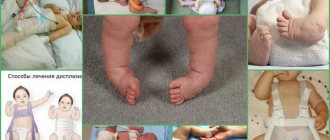
Devices for infants with mild dysplasia
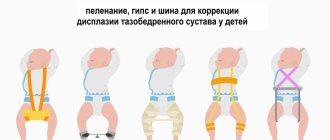
If the subluxation is not too serious, doctors suggest using simple devices that do not create much discomfort. Some of them are allowed even for newborns.
| Method of therapy | How to use | Suitable age | approximate cost |
| Wide swaddling diaper | An ordinary soft diaper 15–20 cm wide is folded several times and placed between the baby’s legs, bent at a right angle, which helps to abduct the hips. | From birth to 3 months. | 200 rubles. |
| Freyka's pillow | An improved version of the previous method is a fabric roller with straps. It also helps to spread the baby's legs. | From birth to 3 months. | 900 rubles. |
| Becker's pants | Briefs with a rigid insert on a felt or metal gusset. This detail prevents the thighs from closing. | From one to nine months. | 1000 rubles. |
Another popular device is Pavlik stirrups. Suitable for children 2–12 months old with moderate dysplasia. It looks like a bandage made of delicate textiles with straps that holds the legs in the correct position, but does not interfere with movement. Such stirrups are prescribed for straightening and rehabilitation after reduction of a dislocation. They need to be worn for about six months. The price of the device is from 1300 rubles.
Treatment methods
Therapy is aimed at the correct further formation of the hip joint in newborns. Only an integrated approach is used using all conservative methods of treating dysplasia. They complement each other, enhance and prolong the therapeutic effect.
Plastering
If dysplasia of high severity is detected, treatment is carried out by simultaneous reduction of the dislocation with further immobilization of the limb by casting. Orthopedists perform such manipulation only when the child reaches 2 years of age. Treatment can also be supplemented with skeletal traction.
Orthopedic devices
Orthopedic correction is the most effective method of treating underdevelopment of the hip joint of any severity. Long-term, often constant use of devices contributes to the correct formation of the hip joint, a gradual increase in range of motion, and restoration of all its functions.
Pavlik stirrups
Pavlik stirrups are the first soft orthopedic structure that began to be used in the treatment of pathology. It is still in demand today, as it does not unduly restrict freedom of movement in the hip joints. Pavlik stirrups consist of a chest bandage attached to the body with straps, small soft pads on the knees and straps connecting all parts of the product into one. Depending on the severity of the pathology, the device is worn for a period of 2 to 12 hours a day.
Freyka's pillow
Freika's pillow is a soft orthopedic product that fixes and holds children's legs bent at the knees in an extended position. Its design includes a thick knee roller, straps and fasteners for securely attaching the device to the child’s body. Freyka's pillow can be used in the treatment of dysplasia from 1 month. It is usually worn during the day and removed before bed. But with congenital dislocation, round-the-clock wearing is often indicated.
Vilensky tire
The Vilensky splint is an orthopedic device in the form of a leg spacer, equipped with fixing straps and lacing. The design also includes a regulator, with which the doctor adjusts the angle of hip abduction. The Vilensky splint is more often used in the treatment of severe underdevelopment of the hip joint. The device is designed to be worn around the clock for 3-6 months.
Tübinger tire
The Tübinger splint is an abductor orthopedic mechanism for the treatment of dysplasia in infants from birth to 1 year. The main components of the device are soft shoulder pads, hip pads, an adjustable spacer, white and red fasteners, and threads with beads. The Tübinger splint is used for continuous wear with short breaks for hygiene procedures.
Tire Volkova
The Volkov splint is an orthopedic product made of polyethylene, consisting of a bed for the back, an upper part that fits on the stomach and side elements that fix the legs and hips. The wearing regimen is determined individually depending on the severity of the pathology and the age of the child. The Volkov splint has recently been almost never used due to the lack of a regulating mechanism in the design and severe limitation of movements.
Gymnastic and massage techniques
Therapeutic gymnastics is used from the first days of therapy. Regular exercises help strengthen the muscles, ligamentous-tendon apparatus, and maintain the femoral head in the acetabulum. When choosing exercises, the doctor takes into account the child’s age, his general health, as well as the current stage of therapy - leg extension, hip joint stabilization or rehabilitation. A referral to a professional massage therapist specializing in the treatment of dysplasia to treat the gluteal muscles is required.
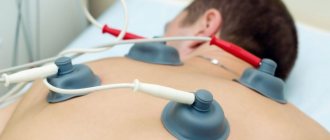
Physiotherapy
Throughout the treatment of dysplasia in newborns, physiotherapeutic procedures are carried out - magnetic therapy, laser therapy, hyperbaric oxygenation, amplipulse therapy, ultrasound therapy. Under the influence of physical activity, the blood supply to tissues with nutrients necessary for the proper formation of bone and cartilaginous structures of the hip joint improves.
Surgery
If conservative therapy is ineffective and there is severe deformation of the hip joint elements, surgical treatment is indicated. More often, open reduction of the dislocation is performed - dissection of the articular capsule followed by installation of the femoral head in the acetabulum. Surgical methods for treating dysplasia also include osteotomy, which is performed to give the proximal end of the femur the correct configuration.
How to choose the correct Vilensky tire size?
The size of the brace is selected strictly by an orthopedic surgeon. They are produced by specialized enterprises in 3 standard sizes:
- Small – for newborns and children up to 4 months. The child's legs are spread 16-23 cm, the length of the cuffs is 12-16 cm.
- Medium - for children under 1 year, with a separation of 21-33 cm and cuffs of 16-22 cm.
- Large - for children over one year old, with a separation of 30-50 cm and cuffs of 22-28 cm.
To determine the size of the Vilensky splint, the doctor takes into account not only age, but also the nature of the anomaly, the severity of bone changes and the general activity of the child. An incorrectly selected tire not only does not improve the functional condition, but can also worsen it.
Causes
The true cause of pathological development or underdevelopment of the joint is not fully known.
Predisposing factors are:
- genetic predisposition (usually in the female line);
- female gender of the baby (80% of all cases of dysplasia);
- hormonal levels: excess progesterone in a woman before childbirth can contribute to underdevelopment of the ligamentous-muscular system;
- incorrect position of the fetus in the uterine cavity, limiting the normal mobility of the child;
- large size of the fetus, which limits its movement and prevents the development of the joint;
- harmful factors, especially in the early stages of pregnancy (ecology, toxicosis, maternal illness, vitamin deficiency, etc.);
- prematurity: fetal tissue does not have time to mature.
How to recognize hip dysplasia in newborns?
dislocations in newbornsSigns of dysplasia in newborns
- The clicking symptom is one of the most reliable signs of dysplasia. It is detected during the first week and can persist for up to 3 months. The essence of the method: the child lies on his back, legs bent at the hip and knee joints at a right angle. The specialist’s hands lie on the knee joints: the thumbs cover the inner surface of the joint, the rest lie on the outer surface of the thigh. The knees are brought to the midline. The doctor slowly moves them apart, and a click is felt and sometimes heard on the painful side - this is the femoral head taking its place. The next stage: the doctor brings the child’s hips together, at this stage a click is felt again - this is the femoral head leaving the acetabulum. The click is explained by the slipping of the lumbosacral muscle from the anterior surface of the femoral head if there is a dislocation and the head does not fit into the acetabulum.
- Shortening one leg. The child lies on his back, his legs are bent at the knees and placed on his feet. If one knee is higher than the other, then there is a high probability of congenital hip dislocation.
- Asymmetrical arrangement of skin folds, their increased number. The child's folds are checked with the legs straightened in front and behind.
- Limitation of hip abduction. However, in some children this symptom does not develop until the 3rd or 4th week. In healthy children, the knees can be placed on the table surface without effort until the age of 4 months.
after feeding in a warm room, Indirect symptoms
- Torticollis;
- Softness of the skull bones (craniotabes);
- Polydactyly – more than normal number of fingers;
- Flat feet and displacement of the axis of the foot;
- Violation of reflexes characteristic of newborns (searching, sucking, cervical).
within 3 weeks
- The acetabulum becomes flatter and is unable to support the head of the femur;
- The roof is behind in development;
- Stretching of the joint capsule.
Briefly about the anatomy of the hip joint
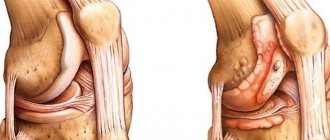
The hip joint is the connection point between the pelvic and femur bones. The joint is formed by the insertion of the head of the femur into the cup-shaped acetabulum of the pelvic bone, which makes it multiaxial, that is, capable of movement in many directions at once, including the possibility of circular rotation.
In the human body, the main function of the hip joint is to ensure motor activity such as walking, running, jumping, etc. With congenital underdevelopment (inferiority) of this joint, motor activity is limited to the point of complete impossibility of independent movement.
Causes
Various factors can lead to the development of the disease. Large joints, including the hip, begin to form and form in utero. If certain disturbances occur during pregnancy, this leads to the development of anatomical abnormalities in the structure of the musculoskeletal system.
The most common causes leading to dysplasia include:
Genetic predisposition. In families in which close relatives have manifestations of the disease, there is a higher likelihood of having a child with this disease. It is more than 30%.
- Violation of the formation of the baby’s joints during pregnancy as a result of an unfavorable environmental situation or exposure to toxic substances on the body of the expectant mother.
- High hormone levels during pregnancy. Oxytocin, which is produced in the body of the expectant mother, causes an improvement in the mobility of the ligamentous apparatus. This property is necessary before childbirth. Oxytocin also improves the mobility of all joints, including further provoking an excessive range of motion. The hip joints are most susceptible to this effect.
- Tight swaddling. Excessive tightening of the legs during this daily procedure leads to the formation of dysplasia. Changing the type of swaddling leads to improved joint functioning and prevents the development of the disease. This is also confirmed by numerous studies conducted in Japan.
- Birth of a child over 35 years of age.
- The baby's weight at birth is more than 4 kilograms.
- Prematurity.
- Gluteal.
- Close placement of the fetus. This usually occurs when the uterus is narrow or small. If, then it can fit quite tightly to the walls of the uterus and practically not move.
Payment
Terms of payment for delivery of goods in Moscow and Moscow Region
Cash payment
The Buyer or his authorized representative pays for the goods in cash in rubles to the courier upon receipt of the goods after checking the integrity of the packaging, appearance, completeness of the goods and fitting (if the goods are subject to fitting).
Cashless payments
Payment is made by invoice.
- To issue an invoice to a private person, the order must indicate the last name, first name, patronymic without abbreviations, exact address with zip code, contact phone number and email address.
- To issue an invoice to a legal entity, the organization's details are required.
After prepayment and receipt of funds for settlement by our organization, an order is formed and transferred to the courier service for further delivery to the Buyer.
Terms of payment for delivery of goods in Russia
The goods are dispatched only after full prepayment of the goods and services of the transport company (if payment for the services of the transport company is not possible upon receipt of the goods.)
Cashless payments
Payment is made by invoice.
- To issue an invoice to a private person, the order must indicate the last name, first name, patronymic without abbreviations, exact address with zip code, contact phone number and email address.
- To issue an invoice to a legal entity, the organization's details are required.
After prepayment and receipt of funds for settlement by our organization, an order is formed and transferred to the courier service or transport company for further delivery to the Buyer.
Full terms and conditions are available on the Payment page.
How to recognize dysplasia
Parents of newborns should immediately show their child to an orthopedic doctor if:
- the baby's legs are of different lengths;
- asymmetrical folds on the buttocks;
- there is an extra fold on the thigh;
- the legs are retracted asymmetrically;
- the baby’s knees do not touch the surface of the table when the legs are abducted, they cannot be fully abducted;
- The child’s hip joint moves easily, with a characteristic click (you can hear the head of the femur popping out of the acetabulum).
Diagnosis of dysplasia
When the baby has already begun to walk independently, or is over a year old, parents should be alert to:
- “duck walk”, the little one sways in different directions when walking;
- the child's habit of walking on his toes.
The earlier the disease is detected, the better for health. Medical practice shows that in 90% of newborns with initial type dysplasia, the disease goes away by the age of six months, provided they undergo treatment and follow doctor’s instructions.
If the disease is diagnosed after six months, treatment in children takes a long period, the result will be worse (surgical intervention is possible). If a diagnosis of “dysplasia” is made to a child who has already learned to walk, unfortunately, one cannot count on a full recovery. Treatment of dysplasia diagnosed after 12 years of age can last for decades. The consequences are unpredictable, so newborn pathologies should be treated on time and visits to the clinic should not be missed.
Types of hip dysplasia
Doctors differentiate the disease into several groups. The classifications are based on the degree of development and area of localization of the disease.
Taking into account the affected area in which dysplasia progresses, the following are distinguished:
- Acetabular DTS, which disrupts the formation of the acetabulum. The modified joint segment is distinguished by a flatter (compared to normally developing structures) shape and smaller size. The progression of this type of disease causes wear of the cartilage and stretching of the capsule of the movable joint.
- Rotational type of pathology. Dysplasia affects the configuration of intermittent joints in horizontal projection. During the examination, the doctor identifies violations of the natural position of the femoral head.
- Epiphyseal DTS, characterized by ossification of cartilaginous tissue. The lack of proper flexibility in the connecting structure leads to limited movements and deformities of the legs.
Depending on the area of localization, the disease is also differentiated into right-, left-, and bilateral.
Stages of development of the pathological condition
To indicate the severity of the disease, orthopedists use a step-by-step systematization. This classification distinguishes 4 degrees of dysplasia; the main characteristics of each are shown in the table below.
| Stages | Peculiarities |
| Zero - borderline state, immaturity of joint tissues | Inferiority of the joint with unchanged configuration. Identified by using instrumental examination methods. |
| The first is pre-dislocation of the hip joint | Accompanied by stretching of the capsule of the intermittent connection. It is characterized by the absence of pain and does not affect the child’s activity. |
| The second is hip subluxation. | Upon examination, a change in the position of the head of the largest tubular bone (displacement upward, outward) and tension in the ligaments is diagnosed. There is a clicking symptom. |
| Third - dislocation of the joint | Complete violation of the natural configuration of the element. The head of the hip joint moves beyond the acetabulum; part of the cartilaginous rim of the latter is bent inside the joint. The ligaments are tense. |
The earlier the disease is diagnosed, the faster the child’s recovery. Severe stages of the pathology are treated with surgery and long-term therapy, which takes more than a year.
How to prevent hip dysplasia?
Early diagnosis is aimed at identifying congenital pathologies. Examination by an orthopedist in the maternity hospital; All girls who were in a pelvic or breech presentation are recommended to have an ultrasound scan at 6 weeks after birth; Ultrasound is also performed for children who have other predisposing factors (clicking in the joint, dysplasia in relatives, birth weight over 4 kg, congenital torticollis and foot deformities, maternal age over 35 years); An x-ray is performed if necessary for monitoring at the age of 4 months and older. Free swaddling. Avoid tight swaddling, in which the baby's legs are straightened and pressed together. It is necessary that after swaddling the baby’s legs remain in the same position as after birth - bent at the hips and knees, and spread apart. Carrying a baby in a sling on its side or in a “rider” position on the mother’s back. Such positions, when his legs embrace the mother’s waist, are the most physiological. It is for this reason that Africans have the lowest percentage of children with dysplasia. When the child's legs are spread, the capsule of the hip joint contracts, which ensures its reliable fixation in the future. Diapers are 1-2 sizes larger. The diapers prevent the baby's legs from closing and act like the "abductor panties" that orthopedists have used in the past to help shape the hip joints properly.
It is especially important to adhere to this rule in the first weeks after childbirth, until the mother’s hormones leave the child’s body and the ligaments supporting the joint become stronger. Massage and gymnastics in courses of 10-15 massages with an interval of 1 month + general massage daily
Massage and gymnastics strengthen the muscles that limit movement in the joint and ensure its stability.
Selecting a device and rules for its use
Orlette splint
Which device is suitable in each specific case is determined only by the doctor. He will offer several options, taking into account the cost of each device. Parents should pay attention to the following points when purchasing:
- size range;
- quality of the outer layer;
- presence and strength of fixing parts.
When selecting a design, it is recommended to run your hand over the entire surface of the device to check for hard seams, joints or other defects.
The doctor must show you exactly how to put the child in the spacer. In each specific case, the splint is attached at different heights of the baby’s limbs.
In general, the donning scheme is similar for all tires:
- Place the baby on his back on a hard surface, spreading his legs as the orthopedist showed.
- Place the thigh muff on one leg at the level indicated by your doctor.
- Securely secure the fastening devices so that the cuffs do not fall off.
- Repeat for the second leg.
It is necessary to ensure that the device fits well on the child’s limbs and does not slip during movements, otherwise there will be no point in wearing it. To do this, you can build a vest like a bodysuit from durable and non-slip fabric.
It is important to clearly regulate the degree of hip extension. This can be done using a special wheel (on a Vilensky tire) or in another way specified in the instructions for use.
Parents of children with dysplasia note: the sooner treatment is started, the sooner the splint can be removed and the baby can be given the opportunity to develop normally, crawl and walk.
Among the recommendations, it is worth highlighting the need for individual selection of spacers: in addition to standard sizes, you can order an individual tire. It is important to choose comfortable clothes so that the structure does not slip and securely fixes the child’s legs.
Even if it seems to the parents that the child is healthy and enough time has passed, only a doctor can stop wearing an orthopedic device. It is recommended to use the design for at least 4 months.
Treatment
Early diagnosis of the disease is very important, because the earlier treatment for dysplasia is started, the more effective the result will be. For example, detection of joint pathology in a child at 6 months can lead to treatment that lasts several years and does not always bring complete recovery. That is why it is necessary to determine the presence of disorders in the first two months of the baby’s life.
The consequences of untreated dysplasia are extremely severe: severe gait disturbances, frequent pain, early disability. Treatment of pathology after a year will no longer be effective. Early detection of the problem and active treatment are the principles of combating dysplasia. Only in this case can the consequences of pathology be alleviated or completely reduced to zero.
Treatment should be comprehensive, using special devices that provide extension and flexion of the baby’s legs, massage and therapeutic exercises. The following orthopedic devices are widely used.
- Pavlik stirrups are a device invented by the Czech orthopedist Pavlik at the beginning of the last century. It is made of soft fabric and consists of leg bending straps and a chest bandage. Ensures the correct position of the head of the joint in the socket, and over time the position of the hip joint is corrected. The good thing about the device is that it does not completely limit the child’s movements - he just cannot straighten and close his legs. Depending on the age, Pavlik stirrups are put on differently, so the first time putting them on should be done by a doctor;
- Freika's pillow is a splint that fits between the child's legs and is secured using waist and shoulder belts. The legs are wide apart and bent at the knees. The degree of separation of the legs and the duration of wearing the Freik pillow are determined only by an orthopedist;
- The Vilensky splint (better known as a spacer) has the form of a metal pipe with a spreader width adjuster and leather cuffs with lacing. The width of the spread is regulated by the doctor. You need to wear the splint around the clock for 4–9 months, removing it only when swimming;
- The Volkov splint is a complex plastic structure of several parts, reminiscent of a corset. Provides complete immobility of joints.
At first glance, most of these devices seem barbaric, and looking at the child’s discomfort in the spacers, parents are overcome with pity. But treating hip dysplasia in children is not an easy process. You should be patient: these inconveniences are for the good, because in advanced forms, surgical methods are used, after which the child is forced to spend up to six months in a cast. So tires, stirrups and cushions are not the biggest problem, but for the sake of your health you can endure it. The consequences of hip dysplasia in children bring much more suffering.
Additional measures
Complete treatment of dysplasia is impossible without massage. The complex of massage movements includes rubbing, spiral stroking, kneading, careful bending and spreading of the child’s legs. For a high-quality and effective massage, you need to contact a specialist and undergo a full course of procedures.
Therapeutic exercises are also a necessary measure. The exercises are performed together with massage and include bending and spreading the child’s legs, bending and pressing the legs to the stomach, rotating movements of the joints, kneading and stroking the surface of the joints. Gymnastics stimulates blood circulation, improves joint mobility and normalizes muscle tone. The therapeutic effect will be noticeable only with regular exercise.
Another well-known measure for the treatment and prevention of dysplasia is wide swaddling. There is a version that severe forms of pathology in the last century were provoked by tight swaddling, when the child’s legs were tightly pressed together. In fact, the risk of dysplasia and its mild forms can be corrected in the first weeks of life with the help of wide swaddling. It is simple to do: before swaddling the baby, you need to place two folded diapers between his legs. This will ensure a slight separation of the legs and normalize the position of the joint.
Types of splints used for dysplasia
Vilensky splint
In serious cases of DTS, if there is a chance to avoid surgery, complex structures are used - Vilensky, Volkov, Orlett fixing devices, Tübinger orthosis. The advantage of splints in comparison with simple orthopedic devices is that spacers for hip dysplasia can be used for both newborns and children up to three years of age. Long-term exposure allows you to correct the condition of the hip joint without surgery in cases where the disease is diagnosed at the age of 1 year and older. Sometimes splints are prescribed individually for children over three years of age for recovery after reduction of a dislocation.
The most common option is the Vilensky splint . Its structure is quite simple: two straps with lacing and a metal spacer between them. Tires are available in three sizes:
- small – up to three months;
- average – 3 – 12 months;
- large - older than a year.
The orthopedic device is worn constantly, put on under the supervision of a pediatric orthopedist. The spacer can be removed only during water procedures. The average course of therapy is nine months. They purchase the device in medical equipment stores, including online. The price of a Vilensky tire starts from 2000 rubles. At points of sale of orthopedic goods, the price will be higher, but you can try on the splint and select the exact size.
Vilensky tires from different manufacturers are on sale: Moscow CITO, Zatsepin Metropolitan Hospital, Pushkin Orthopedic Institute named after Turner and German manufacturers. Differences in cost and additions to the fixture.
Tübinger orthosis
Tübinger orthosis – a saddle-shaped insert is attached to the shoulder structures with straps. The length and spread of the legs can be adjusted, which is an advantage for a rapidly growing and active child. Velcro is used instead of lacing. The device costs from 6800 rubles.
The Orlette splint for dysplasia is a modern modification of the above-mentioned orthoses. It is a rigid belt with couplings that are attached to the hips and prevent the child from cramping his legs. On the outside, the metal inserts are covered with a delicate and soft fabric that does not rub sensitive skin. The convenient device reduces the time required to reduce the joint. Costs from 6000 rubles. The Orlette orthosis is available in different sizes: for infants up to six months and for children up to one year.
The Volkov splint for hip dysplasia for a child is somewhat different from previous devices. Consists of two polyethylene parts: on the back and on the stomach. These parts are fastened together with special side elements for the lower leg and thigh. The device holds the legs most rigidly, making it quite difficult for the child to move them. Adjustment of fixation is not provided, so parents prefer more modern and comfortable options. It is difficult to find such a device on sale; its cost starts from 1000 rubles.
The most serious cases require a cast. This is a traditional way to treat dysplasia. It is used for late diagnosis, when other therapy is ineffective, after surgery.
Causes
Congenital dislocation of the hip in an infant occurs for the following reasons:
- hereditary predisposition;
- the baby's weight is too large or small at birth;
- breech presentation of the fetus;
- first or late pregnancy;
- improper nutrition of a pregnant woman, bad habits;
- gynecological diseases that prevent the baby from moving through the birth canal;
- vitamin deficiency;
- infections during pregnancy.
The hormone relaxin, which is responsible for relaxing the muscles and softening the bones of the pregnant woman, plays an important role in the appearance of dysplasia in the baby. But it affects not only the woman’s body, but also the fetus. When its concentration is high, the hip bones become very soft and subluxation or dislocation may occur during childbirth.
Possible complications when using tires
There are no significant contraindications to wearing a splint; it cannot be used for irreparable congenital hip dislocations. Also, the design is prescribed only if there are indications and after examination in a medical institution. Self-treatment is not allowed.
Wearing a splint may cause some discomfort. Since the device is used for a long time, the child gets used to this condition.
Complications are only possible if the device is put on incorrectly - the position of the joint will be incorrect, and the effectiveness of the device will decrease. Another point is rubbing the skin against hard parts. It is important to choose a device that is sized, with soft and elastic parts.