Many patients diagnosed with a hernia of the lumbar spine ask doctors whether it can resolve. If you seek medical help at the initial stage of the disease, undergo treatment and follow all the doctor’s recommendations, you can stop the degenerative process in the vertebral structures and reduce the size of the hernial protrusion. If you neglect the doctor’s prescriptions, the hernia will quickly progress and grow, and the risk of complications will also quickly increase.
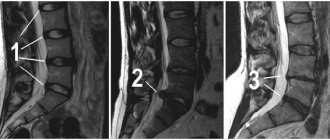
Incarceration in the cervical spine on an MRI image.
general information
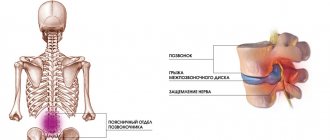
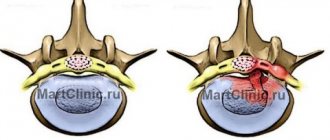
Intervertebral hernia most often forms in the lower part of the lumbar spine, as well as at the point of its transition to the sacral segment. It is this area that experiences the greatest load when the body is in an upright position. Intervertebral discs normally act as shock absorbers, dampening vibration when walking, running and jumping. Increased pressure or its uneven distribution, as well as narrowing of the joint space with osteochondrosis, leads to the formation of first protrusion and then disc herniation.
Make an appointment
Causes
The most common cause of herniation of the lumbar spine is osteochondrosis. Degenerative processes in cartilage and narrowing of the space between the vertebrae inevitably lead to gradual protrusion of the discs. Predisposing factors also include:
- predominantly sedentary work, physical inactivity;
- increased body weight (creates excess load on the spine);
- high growth;
- alternating long periods of inactivity with excessively intense physical activity;
- back injuries;
- systemic dysplasia of cartilage tissue, muscles, etc.;
- impaired blood supply to the lumbar region;
- infections of the spinal column and surrounding tissues (tuberculosis, syphilis, etc.);
- osteoporosis;
- uneven load on the spinal column due to poor posture, hip dysplasia, flat feet;
- work or hobbies that involve frequent heavy lifting;
- metabolic disorders and functioning of the endocrine glands;
- burdened heredity;
- poor nutrition;
- bad habits: smoking, alcohol abuse;
- professional sports with increased load on the lumbar region.
Can a herniated disc go away?
A herniated disc is formed as a result of rupture of its protective fibrous ring and prolapse of the nucleus pulposus. As the protrusion increases in size, it enters the spinal canal, compresses the nerve endings and arteries. It cannot dissolve and disappear on its own, with the exception of isolated cases.
Herniated discs of the lumbar region develop most often - in 150 cases out of 100,000.
What happens in the body of a person who does not receive treatment for a hernia:
- Limitation of mobility. Due to the pain syndrome, a person cannot perform sudden movements, bending, turning, as they increase the load on the lower back and cause discomfort.
- With excessive physical activity and heavy lifting, the load on the damaged disc increases, as a result, degenerative processes progress and the hernia increases.
- In the affected structures, metabolic disorders occur, the intervertebral disc tissue becomes thinner.
If the factors that cause disc destruction are not eliminated, the herniation will become larger. If you consult a doctor, start drug treatment, physiotherapy, attend exercise therapy, the condition improves, the hernia may decrease in size, but it cannot completely disappear. To obtain positive results, long-term treatment is required - several months and even years.
Types and stages
Depending on the direction of the protrusion, hernias are distinguished:
- anterior: located anterior to the vertebral body; are rare and practically do not cause pathological symptoms;
- posterior: bulge towards the spinal canal; one of the most common and dangerous options, since if it is large in size it can compress the spinal cord and its roots, causing pain and neurological disorders;
- lateral: appear on the side of the spinal canal, often damaging the spinal roots passing in this place;
- vertical (Schmorl's hernia): grow in a vertical direction, pressing into the vertebral body.
The stages of the disease are determined by the degree of disc displacement:
- Stage 1 (protrusion): the disc moves relative to its normal position, but does not violate the integrity of the fibrous ring;
- Stage 2 (extrusion): the fibrous ring breaks through, a slight protrusion of the disc is observed;
- Stage 3 (prolapse): the disc hangs into the intervertebral space;
- Stage 4 (sequestration): disc particles come off and fall into the spinal canal; the condition is associated with an extremely high risk of developing paralysis.
When should surgery be done?
From all of the above, it follows that the size of the protrusion is not the only indicator of the need for surgical intervention. This is also significantly influenced by the location of the hernia, its type, the severity of neurological disorders (radicular syndrome), the risk of transition to the sequestration stage and other factors. After all, a 5 mm hernia of a small cervical disc and a large lumbar disc are completely different concepts.
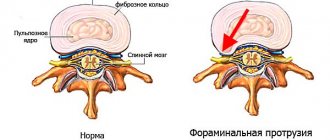
Even a small protrusion, but located in the area of the foraminal openings, can provoke severe pain not only in the back, but also in the buttocks, legs, arms, and is also accompanied by other signs of radicular syndrome, which is also a strong indication for surgery.
In each case, the need for surgical intervention is assessed individually. Only a qualified specialist can give a correct assessment of all factors and, based on this, provide optimal recommendations for further treatment of the hernia.
In this case, the doctor must take into account the possibility of surgical treatment of an intervertebral hernia using percutaneous surgery methods, which can only be used for medium-sized hernias. Due to the fact that they have a huge number of advantages, including high efficiency and safety, they try to give preference to them. But for this it is important not to miss the moment and perform the operation when the size of the hernia is not yet critical.
So, the main indications for surgical removal of a herniated disc are:
- severe, long-lasting pain that cannot be relieved by medications;
- ineffectiveness of properly selected conservative therapy (drug treatment, physiotherapy, massage, exercise therapy) after 1.5 months;
- severe compression of the spinal roots or stenosis of the spinal canal (can occur even with small protrusions due to the congenital narrowness of the spinal canal);
- sequestered hernia;
- pronounced radicular syndrome, leading to a decrease in the motor capabilities of the limbs, disruption of the innervation of the pelvic organs;
- vascular disorders (most important for hernias of the cervical and lumbar spine, since they can compress the radicular arteries passing right there, which are responsible for feeding the spinal cord).
Therefore, it is impossible to say unambiguously at what size of the hernia requires surgery. On average, for herniations of the cervical spine, the critical size is considered to be 5 mm, and for a bulging disc of the lumbosacral region - 9 mm. But if the hernia is foraminal, surgical intervention may be indicated much earlier, and sometimes even when the hernia is 3-4 mm in size.
If the doctor sees a tendency towards a steady increase in the hernia, he can offer the patient to remove it surgically even when its dimensions have reached only 5-6 mm, i.e. they are within the average range. In such situations, it is still possible to remove the pathological protrusion of the disc using the most gentle operations.
The size and type of hernia can be determined using an MRI. Other diagnostic methods are not able to provide equally accurate and unambiguous results.
In certain situations, emergency surgery may be required. It is indicated for sequestered hernia, which is accompanied by severe pain, severe neuralgic complications, disruption of the pelvic organs and forces the person to take a forced position.
Symptoms
The severity of the main symptoms of a hernia of the lumbar spine depends on its size and type. Some patients report only minor discomfort during physical activity, while others suffer from severe pain. The most typical signs of pathology are:
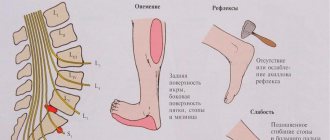
- pain in the lower back, buttock and leg, usually occurring on one side;
- pathological sensations (paresthesia) in the thigh, groin, buttock or leg (tingling, burning, numbness, etc.);
- increased pain and paresthesia with load on the lower back: while walking, sitting, bending, lifting weights;
- limitation of movements in the lower back;
- weakness of the foot muscles, difficulty trying to lift the toes;
- poor posture, stoop, slight tilt of the body to the affected side;
- pallor or redness of the skin in the affected area (lower back, buttock, thigh, lower leg);
- pelvic disorders: complete or partial incontinence of urine, feces, gases;
- sexual disorders: impotence, early ejaculation, anorgasmia;
- leg muscle paralysis.
Symptoms increase as the disease progresses. In the early stages of hernia formation, the patient may be bothered by rare, weak, aching pain in the lower back, which occurs after physical activity and goes away with rest.
Clinical manifestations
The main danger of an intervertebral hernia is paralysis of the patient. Other complications include: dysfunction of the pelvic organs, weakness in the legs, loss of sensitivity in certain areas of the body, etc.
The following clinical manifestations are possible:
- local pain syndrome in the projection of the affected disc
- pain can spread (radiate) to the buttock, along the posterior, posterior surface of the thigh and lower leg on the affected side (ischalgia)
- there may be a feeling of numbness and/or tingling in the area of innervation of the affected roots
- weakness and/or sensory impairment in both or one lower extremity
- dysfunction of the pelvic organs - urination, defecation and potency
- clinical manifestations of degenerative changes in the cervical spine
- if the cervical spine is affected, the pain may radiate to the shoulder or arm, numbness of the hand or fingers
- dizziness, high blood pressure
Diagnostics
Diagnosis of a hernia of the lumbar spine requires consultation with a neurologist. At the first appointment, the doctor finds out the patient’s complaints, the time and circumstances of their occurrence, records information about past diseases and injuries, and chronic pathology. A neurological examination is performed to identify areas of maximum pain, areas of increased or decreased skin sensitivity, changes in muscle strength and reflexes.
Instrumental and laboratory examinations are aimed at confirming the diagnosis and excluding other pathologies with similar symptoms:
- CT or MRI to visualize the protrusion, assess its shape and size, as well as the degree of compression of the nerve roots or spinal cord;
- myelography with contrast: prescribed for suspected spinal cord compression;
- general blood and urine analysis;
- blood chemistry;
- Ultrasound of the abdominal cavity and pelvis (prescribed in the presence of pelvic disorders);
- consultations with a gynecologist, urologist if necessary.
The list of tests and examinations is adjusted depending on the specific situation.
When a hernia won't go away
You should not count on solving the problem without medical intervention for any type and size of lumbar hernia. An unfavorable prognosis for those patients who refuse to go to the doctor, or who, having received doctor’s orders, do not follow them.
If at a young age there is minimal chance of tissue regeneration with a small hernial protrusion, this does not happen in elderly patients. Regenerative and metabolic processes in their tissues are very slow.
A hernia cannot resolve if it was diagnosed more than 5 years ago, the patient did not receive treatment and suddenly decided to undergo therapy. In this case, recovery requires a lot of effort and time, and in case of complications, surgical intervention, for example, video endoscopic microdiscectomy, may be indicated. The endoscope for this manipulation can be seen in the photo.
Treatment of lumbar hernia
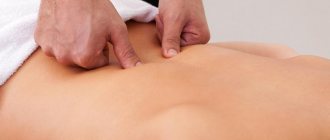
Treatment requires a competent combination of drug therapy, physiotherapy, massage and other auxiliary methods. It is aimed at eliminating pain and neurological disorders, restoring cartilage tissue and nerve fibers.
Drug treatment may include drugs from the following groups:
- non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (indomethacin, diclofenac, ibuprofen): block inflammation and relieve pain;
- glucocorticosteroids (prednisolone, dexamethasone, hydrocortisone): relieve inflammation and swelling, used when NSAIDs are ineffective;
- muscle relaxants (mydocalm, etc.): relieve muscle spasms that arise due to pinched roots;
- chondroprotectors (glucosamine, chondroitin): promote partial restoration of cartilage tissue, stop the process of its depletion;
- B vitamins (milgamma): improve the process of nerve impulse transmission, prescribed for radicular disorders.
In cases of severe pain, drug blockades (injection of the lumbar region with an analgesic solution) or narcotic analgesics can be used. To achieve a lasting analgesic effect, injections of long-acting glucocorticosteroids (diprospan) are prescribed.
Physiotherapy procedures are actively used both during exacerbation and during remission. They help relieve pain and muscle spasms, improve blood circulation and metabolism, speed up recovery processes and enhance the effect of medications. Depending on the symptoms, the following may be prescribed:
- electrophoresis;
- phonophoresis;
- electrical stimulation;
- magnetic therapy;
- laser therapy.
Additional treatment methods include:
- physical therapy: allows you to strengthen the muscular corset of the back;
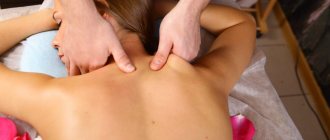
- massage: relaxes muscles, increases blood circulation and metabolism;
- manual therapy;
- acupuncture;
- Spa treatment.
If the size of the hernia is significant and conservative treatment is ineffective, surgical interventions must be resorted to. Modern methods of hernia removal make it possible to use small incisions and shorten the recovery period.
Make an appointment
Types of operations
As already mentioned, they try to carry out surgical treatment of intervertebral hernias using the most gentle methods. These include nucleoplasty and hydroplasty, but they can only be performed if the size of the protrusion does not exceed 6 mm. With a slightly larger value, the issue can be resolved using minimally invasive endoscopic surgery.
If time is lost and the hernia has managed to grow to a large size, the patient will be advised to remove it by microdiscectomy. This is a microsurgical intervention that allows you to completely remove a disc herniation. If there is instability in the spinal motion segment, thanks to the achievements of modern medicine, it can be replaced with an artificial implant or stabilizing system that can fully cope with all the functions of the removed disc.
Surgery can help eliminate an existing hernia, but if you maintain the same lifestyle, there is a high probability of recurrence of the disease or similar deformation of another disc.
Nucleoplasty
Nucleoplasty, as a method of percutaneous surgery, is considered one of the most progressive operations for the removal of intervertebral hernia, since when it is performed, the likelihood of developing complications is reduced to almost 0. The method involves introducing into the center of the affected intervertebral disc under the control of an image intensifier a thin cannula, the diameter of which does not exceed several millimeters. Through it, an electrode is immersed into the nucleus pulposus, which will be used to remove the hernia. More precisely, the nucleus pulposus of the disc will be destroyed, and the hernia, as a result of a decrease in pressure inside it, will be retracted.
Nucleoplasty can be performed using different methods, the differences between which lie in the nature of the destructive agent used. Its role may be:
- cold plasma;
- laser thermal energy;
- radio waves.
Whatever method is chosen, an electrode connected to the appropriate device is immersed into the disc through an already inserted cannula. After turning it on, thermal energy begins to affect the nucleus pulposus, and since the neurosurgeon makes reciprocating movements with the electrode in different directions, this leads to the destruction of the cells of the nucleus pulposus in the places where it touches and the formation of several “passages” that create negative pressure inside the disc. As a result, the volume of the nucleus decreases, and the hernia gradually retracts.
The operation is performed under local anesthesia, and the patient notices an improvement in the condition almost immediately after its completion, but the maximum effect should be expected only after a few weeks. This type of surgery does not require hospitalization, so the patient can leave the clinic on the same day, and it does not involve complex rehabilitation. There is virtually no pain in the affected area after surgery.
But nucleoplasty can be performed with:
- hernia size no more than 6 mm;
- maintaining the integrity of the fibrous ring;
- no signs of spinal canal stenosis;
- absence of serious changes in muscle tone;
- maintaining normal mobility of the limbs.
Since medical practice shows that after laser nucleoplasty, recurrences of hernias in the same discs are observed in 20-25% of cases, it has recently been abandoned in favor of cold plasma nucleoplasty or hydroplasty.
Hydroplastics
Hydroplasty is often called a type of nucleoplasty, but if its implementation involves the use of thermal energy, then when using hydroplasty, part of the nucleus pulposus is destroyed using a powerful pressure of physiological solution. The procedure is carried out by analogy with nucleoplasty, but instead of an electrode, a special hydroresector is immersed in the cannula, which has 2 channels: one for supplying liquid, the other for suctioning it out.
As a result of the action of a strong jet of saline solution, part of the nucleus pulposus is destroyed, fragments of which are immediately evacuated from the body along with the waste fluid. The neurosurgeon precisely controls the volume of intervention to achieve the desired effect.
Unlike nucleoplasty, hydroplasty allows you to influence areas of the nucleus located in direct contact with the fibrous ring, i.e., the hernia itself.
The operation is highly effective and safe, even more so than nucleoplasty. This is explained by the fact that when it is performed, the surrounding tissues do not heat up at all, and therefore do not suffer at all. After both operations, not the slightest trace remains on the skin. The remaining puncture heals on its own; no stitches are placed on it, but covered with a sterile plaster.
Endoscopic surgery
Endoscopic surgery is a minimally invasive intervention that can be used to remove intervertebral hernias in any part of the spine with dimensions starting from 7 mm. Their essence lies in the use of special equipment - a video endoscope. It is inserted through a soft tissue puncture up to 1 cm in diameter into the surgical field through a natural opening between the vertebrae.
Thanks to the presence of a video camera that transmits an image in real time to the monitor, it is possible to examine in great detail all the features of the affected disc and, using a special microsurgical probe, which is inserted into the endoscope cavity, remove the required amount of cartilage tissue. In most cases, the ligamentous apparatus and bone structures are not affected at all. The operation allows not only to resect the hernia, but also to remove the entire disc if necessary.
If surgery is performed on the cervical spine, it is not possible to replace the removed disc with cervical implants or stabilizers using endoscopic equipment.
Endoscopic surgery is performed under general or local spinal anesthesia and is characterized by low tissue trauma, which ensures an easy recovery period. But with its help it is impossible to remove median disc herniations of the cervical spine.
Microdiscectomy
Microdiscectomy is a highly effective operation with the highest capabilities. Its help can be used for any size of hernia, but more often it is carried out when there is a serious threat to the patient’s ability to work. Microdiscectomy allows you to achieve a pronounced decompressive effect, since it makes it possible to completely release a compressed nerve root or remove a separated sequester.
It can be classified as a minimally invasive operation; it does not involve major intervention in the body, since it requires an incision no more than 1.5-2 cm long. Microdiscectomy is performed under general anesthesia and under the control of a special surgical microscope using miniature surgical instruments. After making the incision, the muscles are carefully pulled apart, and then the yellow ligament is cut and, depending on the situation, the neurosurgeon proceeds to remove the hernia.
The effectiveness of the operation is 98-100%, and the probability of relapse if the disc is preserved is no more than 5%.
Microdiscectomy requires hospitalization for 1 day, and then disability for up to 2-3 weeks. The program for restoring the body will include complex drug therapy, physical therapy, physiotherapy, and subsequently massage sessions.
Complications
If a hernia is diagnosed at an early stage, following the doctor’s recommendations allows you to completely get rid of the protrusion. If the patient neglects treatment, the formation increases. Ultimately, this process can cause serious complications. Particles of the disc completely block the spinal canal, compressing the passing nerve roots. Cauda equina syndrome develops, manifested by:
- severe pain;
- loss of control over urination and bowel movements;
- complete or partial paralysis of the lower limbs.
The condition requires immediate surgical attention as nerve function can be restored if the compression is relieved within 24 hours.
Possible complications or what will happen if the operation is not performed on time
Intervertebral hernias are a very dangerous disease, which, in the absence of timely treatment and removal, can lead to serious consequences, namely:
- paralysis of the limbs or the entire body below the level of nerve damage (typical of advanced hernias of the cervical spine, leading to injury and death of the nerves);
- stroke due to a serious cerebrovascular accident;
- loss of control over the processes of defecation and emptying the bladder due to disruption of their innervation;
- serious disorders of the respiratory system, heart, kidneys, caused by infringement of the corresponding spinal roots;
- circulatory disorders of the spinal cord with subsequent infarction;
- persistent erectile dysfunction;
- prolapse of the vaginal walls;
- disability;
- death.
With timely surgery, in 95% of cases it is possible to defeat the disease, completely eliminate the risks of complications and significantly improve a person’s quality of life, returning him to full working capacity. Modern operations are characterized by a high degree of safety, so you should not be afraid of them, since delay is fraught with the development of serious consequences, which are much more dangerous than a neurosurgeon’s scalpel and occur much more often than complications of operations. And if you pay close attention to your health and undergo a full course of treatment when the slightest deviation from the norm is detected, then you will not only be able to cope with the hernia using percutaneous surgery methods, but also not bring the situation to the point where you have to undergo surgery.
Prevention
Prevention of lumbar hernia means caring for your body in general and the spine in particular. Doctors recommend:
- observe the work and rest schedule, get enough sleep;
- adhere to the principles of proper nutrition, ensure the supply of sufficient vitamins and microelements;
- avoid excess body weight;
- regularly engage in sports without striving for records (at the amateur level);
- walk more in the fresh air;
- do gymnastics to strengthen your back;
- avoid lifting heavy objects;
- undergo a timely examination by a doctor and follow all his recommendations.
Hernia of the cervical spine
A herniated cervical spine is a very dangerous condition, leading to various and sometimes very serious complications.
The volume of the neck is small, but the most important vessels and nerves are concentrated in it, and the spinal canal is quite narrow. In addition, the cervical spine is the most mobile in humans and the cervical spine bears the load almost all the time.
Treatment of a cervical hernia should begin as early as possible, when the first symptoms appear.
Causes
A hernia in the cervical spine can occur at any age. The risk of developing a cervical hernia is higher in patients who are overweight and in those whose spine is subject to increased physical stress.
Reasons also include:
- degenerative-dystrophic changes and processes in tissues
- injuries to the vertebrae or ligaments of the neck
- hereditary predisposition
- incorrect posture
- pathology of bone and cartilage tissue is different - osteochondrosis, osteoporosis, scoliosis
- increased load on the cervical spine in athletes, especially when lifting weights
- hard physical labor
- long-term static load when working at a computer
- a sedentary lifestyle leading to weakened neck muscles
How does a hernia manifest?
Most often the hernia is localized at the level of the 5th, 6th or 7th cervical vertebra.
The following symptoms are identified:
- acute or chronic pain in the neck area
- pain may spread to the shoulder joint, shoulder, hand
- numbness of the hand, sensation of “pins and needles”, decreased sensitivity of the hand
- headaches, dizziness
- rises in blood pressure, tinnitus
- irritable and tearful
In addition, in the initial stages of the disease, the pain syndrome is low intensity and unstable, and is aching in nature.
As the disease progresses, the patient's well-being worsens. The pain is constant, often unbearable. Partial numbness of the upper extremities occurs, gait is disturbed, various autonomic disorders and muscle atrophy appear.
Complications
If you notice the symptoms described above, it is very important to consult a doctor promptly. There is a very high risk that as the disease progresses, a hernia in the cervical spine will compress one of the arteries that supplies it. In this regard, the nutrition of the brain will be disrupted, which over time can lead to a stroke. In addition, as the disease progresses, the disc begins to compress the nerve roots. In this case, the innervated organs will function worse.
Some patients relieve pain with medications, but it is impossible to stop the progression of the disease in this way. The development of an inflammatory process in the neck muscles can lead to cervical radiculitis.
Diagnostics
When you contact the Bone Clinic, you will undergo an x-ray, which helps identify pathology in the bone structure of the cervical spine.
The doctor may also prescribe an ultrasound of the neck vessels.
In addition, if necessary, the doctor will prescribe you a magnetic resonance imaging scan, which will not only reliably localize the hernia, but also determine its size.
Treatment
- Physiotherapeutic procedures relieve painful symptoms and muscle spasms
- massage helps restore tone to the neck muscles and improve trophism of soft tissues
- Exercise therapy can restore the functioning of muscles and ligaments, swimming is especially useful
- hirudotherapy relieves swelling and improves blood circulation
To restore tissue and prevent the progression of the disease, doctors at the Bone Clinic can prescribe drug therapy.
Prevention
To prevent the development and progression of the disease, it is very important to adhere to the following recommendations:
- an active lifestyle and gymnastics help strengthen the neck muscles
- normalization of body weight
- avoid increased physical stress on the cervical spine and hypothermia
- choosing the right pillow
- if the disease is present, courses of maintenance conservative therapy 1-2 times a year, because it is much easier to slow down the progression of the disease than to fight complications
Treatment at the Energy of Health clinic
Lower back pain may well be a symptom of a herniated lumbar spine. If you begin to notice discomfort, seek help from the neurologists of the Health Energy clinic. We will conduct a thorough diagnosis to accurately identify the cause of pain and prescribe a comprehensive treatment tailored to the individual characteristics of your body:
- effective drugs to relieve pain and neurological disorders;
- drug blockades;
- injections of prolonged hormonal agents;
- physical therapy with the preparation of an individual set of exercises for home training;
- all types of massage;
- physiotherapy and manual therapy, acupuncture;
- preparation of documents for sanatorium-resort treatment.
Disc herniation in the thoracic spine
Pain and subsequent restriction of movement are common. Of all locations, it is most rarely found in the thoracic region compared to the lumbar and cervical spine.
As the process progresses, the hernia puts pressure on the spinal cord root, causing various disorders.
Causes
Among the main causes of hernia in the middle part of the back, doctors identify osteochondrosis. You can read about the treatment of osteochondrosis using traditional methods in another blog article
Predisposing factors are:
- metabolic disease
- consequences of injuries of the lumbosacral spine
- excessive physical activity, sudden bending, heavy lifting
- curvature of the spine (scoliosis), dysplasia (underdevelopment) of the hip joints
- obesity
- muscle weakness
- sedentary lifestyle
- age-related changes
- heredity
- sedentary work
Symptoms
In the initial stage of the disease, the patient feels a burning sensation, discomfort and stiffness in the chest and back. In this situation, the main thing is to contact a neurologist and orthopedist in time in order to promptly receive qualified help. One of the main symptoms is girdle pain. In addition, there may be a loss of sensation in the legs and arms, and general muscle weakness. Often in people with this disease, reflex muscle activity increases.
Consequences
A hernia in the middle part of the spine is a very insidious disease, since its symptoms are often mistaken for other diseases. As a result, the hernia grows more and more, squeezing the roots of the spinal cord. What is dangerous is the development of paralysis.
Treatment
Depending on the stage of the process, treatment tactics can be either conservative or surgical.
That is why, when the first symptoms of the disease appear, you need to consult a specialist and not self-medicate. Only with timely contact with a specialist can the progression be stopped and possible complications prevented.
Methods used in the Bone Clinic:
- Physiotherapeutic procedures relieve painful symptoms and muscle spasms
- massage helps restore tone to the neck muscles and improve trophism of soft tissues
- Exercise therapy can restore the functioning of muscles and ligaments, swimming is especially useful
- hirudotherapy relieves swelling and improves blood circulation
To restore tissue and prevent the progression of the disease, doctors at the Bone Clinic can prescribe drug therapy.
Prevention
The main activities are:
- exclusion of excessive loads, both sports and professional
- normalization of body weight
- sleeping on a moderately firm mattress
- active lifestyle
- strengthening the muscle corset, swimming
- giving up bad habits
Advantages of the clinic
“Health Energy” is a modern multidisciplinary clinic that diagnoses and treats various diseases in adults and children. We offer:
- consultations with doctors of various profiles;
- comprehensive diagnostic programs to assess the condition of the body;
- targeted examinations to make a specific diagnosis or exclude it;
- organizing remote consultations with foreign doctors to obtain an alternative opinion;
- modern and time-tested treatment regimens, selected individually;
- physiotherapy, massage, physical therapy and other auxiliary treatment methods;
- all types of certificates and conclusions, registration of certificates of incapacity for work;
- organization of rehabilitation after illnesses and injuries;
- organization of sanatorium-resort treatment.
A hernia of the lumbar spine seems harmless only at first glance. It is this pathology that can most likely lead to complete or partial paralysis of the legs and a disorder of the pelvic functions. Do not bring the disease to its extreme stage; in the early stages it can be eliminated without surgery. Sign up for a consultation with the neurologists at Energy of Health.
Probability of disappearance of hernia formation
Cases have been established in which patients' hernial protrusion in the lumbar region decreased by 70%. This is a rare phenomenon, and it is possible only with a sequestered hernia, when the contents of its core enter the spinal canal and are perceived by the body as a foreign body. All the body’s forces are directed toward the breakdown of tissues, and phagocytosis begins. This is a process in which the body’s protective cells, macrophages, recognize the prolapsed fragments of the hernial protrusion as foreign, capture them and dissolve them.
The launch of such a process is possible in the body of young people - up to 23 years old. At an older age, and even more so in the elderly, such a reaction of the body is impossible.
The rate of resorption or resorption of hernial elements also depends on individual characteristics. The chances of rapid dissolution increase with good tissue nutrition. In one patient, 5 blood vessels may approach the affected structures, and in another, 10. In the second case, the process of the body’s fight against pathology will go faster.
A patient with a sequestered lumbar hernia with compression of the S1 nerve root was observed. After examination, surgery was recommended for her. But after 8 months, the clinical manifestations and muscular-tonic syndrome completely regressed, which was confirmed by MRI results (see figure). After independent regression of the vertebral hernia, the patient continued to have moderate pain, which was caused by musculoskeletal pathology (source - scientific article “Regression of the herniated disc of the lumbar spine”, authors - G. Yu. Evzikov, A. I. Isaikin, A. V. Kavelina and etc.). But such cases are rare; one cannot refuse treatment and rely on the possibility of self-resorption of the hernial protrusion.
When receiving adequate conservative therapy, in 50% of patients with diagnosed intervertebral herniation, all clinical symptoms decrease or disappear within a month. For large lumbar hernias, recovery may take up to six months or a year.
Calcification of hernia
Another option when a vertebral hernia disappears is the process of decalcification or its “impregnation” with calcium. If the factors that caused the hernia are eliminated, the calcium concentration in the disc cartilage gradually increases. There is less moisture in the hernial protrusion, it becomes denser and, as it were, “blocks” the hole in the ruptured fibrous disc. The nucleus pulposus can no longer move outward from the middle of the disc; its exit is closed.
There is a gradual stabilization of the patient’s condition, as the protruding part of the hernia slowly dries out, accordingly, the compression of the nerve endings decreases, and the pain subsides. Over time, the size of the hernial protrusion decreases due to the removal of inflammatory edema, which develops when soft tissues and spinal nerve roots are compressed.
The process of soaking a hernial bulge with calcium takes several months for sizes no more than 4 mm. If the intervertebral hernia is large, defoliation can take up to 2–3 years.
Chemonucleolysis
Chemonnucleolysis is a treatment method in which a special drug, chemopapain, is injected into the hernial sac through a catheter under local anesthesia. The enzymatic drug liquefies the tissue of the hernial protrusion, which the doctor then removes from the body.
This minimally invasive method of treating a hernia can be performed once a week. As a result, small disc bulges resolve in about a month. To prevent the hernia from appearing again in the same place, a special modeling compound is injected into the fissure of the fibrous ring. Subsequently, it prevents the nucleus pulposus from protruding outward.
Resolving a hernia in this way does not lead to complete recovery. The drug destroys the hernial sac, but disruption of biochemical processes in one vertebra provokes structural destruction of neighboring vertebrae, increasing the risk of the formation of new vertebral hernias. To stabilize the condition, it is necessary to constantly carry out treatment and engage in physical therapy.