Arthroscopic resection of the meniscus (meniscectomy) is a rational method of treatment when it is not possible to achieve the desired results with alternative methods and drug therapy. The specialists at our medical group clinics have modern equipment and successfully use the latest surgical techniques to eliminate any problems associated with damage to the ligaments, muscles and joints of the knee. We offer high-quality medical care on favorable terms and guarantee positive treatment results for our patients.
Arthroscopic meniscal resection: what is it?
The concept of arthroscopic resection of the meniscus means partial or complete removal of the affected part. Given the low degree of invasiveness of the procedure, today arthroscopy is the most common and effective method of surgical treatment. The operation is characterized by safety and minimal risk of negative consequences after surgery. External exposure to the diseased area is limited to minimal incisions. Next, the necessary manipulations are performed from the inside, through the introduction of an arthroscope.
Just a few hours after meniscus surgery, the patient can step on his foot. Hospital stay is limited to 1-2 days after surgery. After 1-2 weeks, you can gradually increase the load on the knee. Resection of the medial meniscus using the arthroscopic method guarantees restoration of the joint, including return to sports.
Diagnostic examination
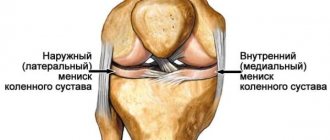
The medial (internal) element is most susceptible to damage, since at the anatomical level it is less mobile than the opposite (external) meniscus, which makes it too vulnerable in case of unsuccessful movements, powerful pushes and blows, uncharacteristic turns of the leg in the knee area. Undoubtedly, the lateral component can also suffer an unpleasant fate, however, as observations show, it is damaged 3 times less often. Surgery on the medial type of meniscus of the knee joint is therefore more in demand.
You can understand that the integrity of the fibrocartilaginous tissues is compromised by the sudden appearance of severe pain and the sensation of a peculiar crunch. Also, due to the rupture, the following arise:
- lumbago (locally) when making movements;
- decreased limb mobility;
- suppression of motor functions of the knee
; - difficulty moving, especially when walking up stairs;
- painful clicking followed by knee jamming (blocking movements);
- local swelling, inflammation, local increase in temperature.
Important! Absolutely any cartilage injuries must be treated strictly! You won’t be able to make an accurate diagnosis on your own; you can only assume that something bad has happened to one of the menisci. Only a special diagnostic examination by an orthopedist-traumatologist can confirm or refute your assumptions.
First, the specialist listens to the patient’s complaints, performs a visual and palpation examination, checks the range of motion not only of the knee joint, but also the hip joint, assesses the pain factor by controlled provocation of pain, and tests muscle tissue for the ability to conduct stimulation. All initial findings indicating a clear meniscus problem must be supported by effective imaging to determine:
- in which areas the damage is concentrated;
- what area does it cover;
- what direction and form is this traumatic formation;
- whether nearby structures are damaged (ligaments, capsule, etc.).
For this purpose, they resort to highly informative diagnostic methods that can clearly visualize the anatomical object under study, these include:
- magnetic resonance computed tomography (MRI);
- ultrasound examination of the knee (ultrasound);
- diagnostic arthroscopy
.
As for x-rays, a similar technique can be useful, but only with contrasting of the joint. With conventional radiography, the meniscus
not visible in the photographs. After establishing an accurate diagnosis, the doctor decides which treatment tactics are best applied in a particular case. The patient may be sent for surgery on the meniscus of the knee joint or prescribed conservative therapy.
And in this case, arthrosis of the last stage was diagnosed.
It is impossible not to warn that the risk group includes not only people involved in sports, but also patients who have chronic joint ailments (arthritis, gonarthrosis, etc.). knee surgery at any time.
: The meniscus is easily injured in such conditions.
Fibering of tissues in the joint cavity also indicates trauma.
When and why is resection of the medial meniscus prescribed?
Indications for resection of the medial meniscus are the following types of damage:
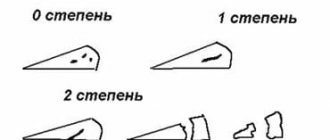
- Meniscus tear in the central part in the vertical direction.
- Detachment of any of the fragments.
- The occurrence of a meniscus tear in the peripheral area with displacement.
- The occurrence of a meniscus tear in the peripheral area without displacement.
As a result of complete removal of the meniscus, it is possible to relieve the patient from pain and blockage of the knee. In this case, complete removal of the meniscus can cause dystrophic changes at the level of the knee joint over time. Thus, previously used meniscectomy methods provoked the development of arthrosis in 85 out of 100 patients 15 years after the operation.
Today, resection of the medial meniscus is performed mainly with preservation of the intact part of the cartilage or provides the possibility of restoring the integrity of the cartilage tissue. Specialists at the multidisciplinary clinic “Your Doctor” strive to limit themselves to partial, that is, partial resection of the meniscus, as a result of which the function of the knee joint remains unchanged and the osteoarticular apparatus is not destroyed.
Partial removal of the meniscus is aimed at high-quality processing of the inner edge parts of the meniscus to achieve an even edge. If signs of destructive changes are detected at the level of cartilage tissue, the doctor will prescribe additional treatment for the meniscus to strengthen the articular ligament. This means that the risk of arthritis and other pathological changes is practically eliminated.
Causes of knee meniscus injuries
Damage to cartilaginous plates includes traumatic, degenerative damage, partial and complete ruptures. Damage can be isolated, that is, affecting only the menisci, or combined, when there is injury to ligaments, tendons, joint surfaces of bones, etc. There are two main causes of damage:
- Traumatic. As a rule, the culprit is the rotation of a bent or half-bent shin when the leg is under load, for example, while playing football, skating, skiing, etc. Damage can also occur when falling onto a surface with protruding edges (curb, stairs), jumping from a height on straight legs, that is, any impact that falls on the knee area will cause injury.
- Degenerative. They are observed in people over 45 years of age and are more often associated with rheumatism and gout. The first disease provokes damage to large joints - elbow, knee, ankle. With rheumatic arthritis, several joints are involved in the process at once, causing pathological processes in the joint capsule. Swelling of the periarticular tissues and malnutrition of the menisci are observed. This leads to degenerative processes, loss of strength of cartilage plates, and their inability to withstand heavy loads. With gout, uric acid crystals appear in the joints, which causes inflammation and pain. The disease causes thinning and loss of strength of the menisci.
Traumatic injuries are predominantly found in athletes; they often experience repeated injuries, which lead to chronic injuries and the development of meniscopathy. In the future, this may cause an unexpected tear of the meniscus during squats or rotation of the knee.
How is the meniscus resection procedure performed?
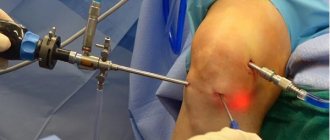
The procedure for arthroscopic resection of the meniscus or its separate part is performed using the endoscopic method. During surgery, the doctor uses an arthroscope. In the area of the sore knee and the location of the meniscus, 3 minimal incisions are made to:
- introduction of a device that visualizes the articular cavity on the screen,
- introduction of an auxiliary surgical instrument,
- administration of saline during surgery.
Necessary manipulations in the meniscus area are carried out under the control of equipment to visualize the area of work. Particles of damaged areas of the meniscus are removed from the cavity of the knee joint along with saline solution. Next, the meniscus flaps are removed, followed by alignment and suturing of its edges. The torn parts of the meniscus are fixed with sutures using special medical clamps. Complete removal of the meniscus is carried out only if it is completely destroyed.
Features of the blood supply to the menisci
The outer edge of the cartilaginous plates is firmly connected to the joint capsule, the inner part is directed towards the articular cavity. Blood vessels in the form of small capillaries are present only in the outer part. In connection with this feature, 3 zones are distinguished in the menisci:
- red - has its own network of blood vessels, as it is fused with the joint capsule. Due to good blood supply, damage in this area can heal on its own without surgical intervention;
- intermediate (the border of the red and white zones) - has practically no blood vessels, the meniscus receives nutrition from the red zone. Spontaneous healing is extremely rare, but recovery is possible after surgery;
- white (inner part) - there is no blood supply, since blood vessels do not fit into this area. The cartilage plates in the white zone are nourished by synovial fluid. Tears cannot heal on their own; surgery is required to remove the affected tissue.
It is the nutritional characteristics of the zones that explain the frequent need for surgical treatment and the ineffectiveness of conservative methods.
Benefits of arthroscopic meniscectomy
The meniscus is subjected to the necessary manipulations without making complex incisions on the outside. Thus, it is recommended to remove the meniscus or its fragments using the cavity method only if there are concomitant pathological changes in the knee joint that do not allow endoscopic surgery. The meniscus is sutured using general anesthesia or epidural anesthesia, so the patient does not experience pain.
The list of advantages of endoscopic resection of the medial meniscus with an arthroscope includes the following:
- Maximum accuracy in diagnosing damage and destruction of the meniscus.
- Almost complete absence of external damage to the skin and soft tissues.
- Low level of blood loss during removal of the meniscus and its fragments.
If you are concerned about the meniscus in your knee, then the doctors at Vash Doctor Group will take care of solving the problem with the least risk and discomfort, returning your usual quality of life.
Consequences of untreated meniscus injuries
If a person does not seek help from a doctor after receiving an injury, this can lead to a number of negative consequences:
- complete separation of part of the cartilage;
- hemorrhage into the joint cavity;
- violation of the ligamentous apparatus;
- muscle atrophy of the affected limb;
- arthrosis, arthritis, synovitis;
- joint blocking;
- disruption of the structure of cartilage tissue.
This is not a complete list of problems that can arise if left untreated. The consequences of damage to the meniscus can be especially severe for people who have arthrosis and rheumatoid arthritis.
Often, after receiving an injury, acute pain subsides after some time and the victim regards this as recovery. But after a certain time, the affected meniscus makes itself felt again, but with a number of degenerative-dystrophic changes that can cover the entire bone joint. And if, with a timely visit to a doctor, it was possible to solve the problem using gentle methods, then in advanced cases, total removal of the meniscus and endoprosthetics may be required.
Recovery after meniscus resection
After the patient has had the meniscus or part of it removed, the knee area requires the use of a cold compress. Additionally, painkillers may be prescribed. If, after removal, nothing bothers the patient, and no signs of infection are detected, you can begin to develop the knee joint. The patient is recommended to walk with crutches, perform flexion-extension movements with the legs and other exercise therapy exercises. Physiotherapeutic procedures and massage help shorten the rehabilitation period.
You can learn more about complete or partial meniscectomy (removal of the meniscus) in consultation with the doctors of our clinic. Make an appointment online and receive qualified medical care for meniscus damage in a comfortable environment for you!
Make an appointment
Symptoms of meniscus damage
When menisci are injured, acute and chronic periods are distinguished. As soon as a person is injured, he experiences pain of varying degrees. It can have a clear localization, that is, it can be felt exactly at the site of damage or spread throughout the entire joint space. If a fragment of the meniscus is separated, this significantly complicates movement, since the particle will fall into the area between the articular surfaces of the tibia and femur.
If the injury is minor, the person may experience slight discomfort or painful clicking in the knee. If a large part of the meniscus is torn, this can cause blockade of the knee joint - the inability to straighten or bend the knee either independently or with anyone’s help. If a rupture occurs in the area where blood vessels are located, they rupture and blood flows into the joint cavity, which is called hematrosis. It looks like swelling above the patella area.
Symptoms depend on which meniscus was damaged. When the medial side is affected, the following are observed:
- severe pain inside the joint;
- lumbago throughout the entire limb when trying to strain the leg;
- inability to bend the knee.
When the lateral ligament is damaged, pain occurs along the lateral ligament when trying to rise to the affected limb, and joint blockade occurs.
If the victim does not consult a doctor, after the pain and other symptoms subside, a chronic period begins - after about 2-3 weeks. From time to time it makes itself felt with various symptoms: pain, discomfort in the knee, difficulties with movement, etc.
Diagnosis of meniscus tear
An experienced doctor may already suspect problems with the meniscus during the patient’s initial visit and external examination. To make a final diagnosis and select adequate therapy, you may need:
- X-ray examination (for better visualization of the joint, x-rays are taken in two projections);
- Ultrasound of the knee joint;
- MRI (magnetic resonance imaging);
- joint puncture (to collect fluid from the joint cavity and examine it in the laboratory);
- arthroscopy (examination of the joint from the inside through small punctures using special endoscopic equipment).
Treatment of menisci in Germany may include additional research, as well as consultations with other specialists.
Indications for meniscectomy
A torn meniscus in the knee is treated primarily with a meniscectomy. Your attending physician will perform the necessary surgery, the nature of which will depend on your medical conditions (general condition of the knee, age, any complications associated with the injury). If a torn meniscus causes pain and swelling, it means that the damaged edges of the meniscus will be removed. Your orthopedic surgeon will try to keep as much meniscal tissue intact as possible to prevent long-term complications.
A must read! Help with treatment and hospitalization!
knee arthroscopy
knee arthroscopy
- long recovery;
- long-term stay of a person in a hospital;
- higher risk of complications, the development of which requires additional treatment;
- more blood loss (transfusion costs).
Mainly, open surgery is more expensive due to the higher cost of postoperative treatment. Whereas arthroscopic intervention itself may be more expensive than arthrotomy. But in general, calculations at the state level show that arthroscopy is on average 15-20% cheaper than open surgery. Postoperative treatment costs usually do not exceed 30% of the cost of arthroscopy itself, while with arthrotomy they are significantly higher. Therefore, minimally invasive treatment is being used more and more often. While surgical interventions with open access are gradually becoming a thing of history.
Preparing for surgery
At the preparation stage, a specialist is consulted. All important points are identified and the presence of allergic reactions is clarified. In case of bleeding disorders, appropriate medications are prescribed. Preoperative examination includes a consultation with a therapist, as well as a standard set of laboratory tests (clinical and biochemical blood tests, HIV test, tests for hepatitis B and C, syphilis (RW), blood group and Rh factor, general urine test, as well as a coagulogram ). No special diet is required as the operation is performed under local anesthesia. It is recommended to limit your intake of heavy meals the day before. Alcohol is excluded from the diet a week before arthroscopy.