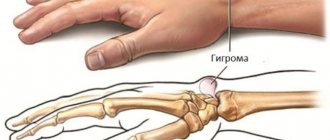
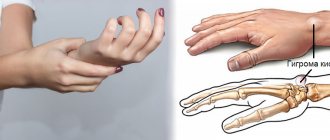
Hygroma of the wrist joint
, cyst, ganglion, synovial hernia are the names of a benign tumor that is localized above the wrist joint. Women get sick more often. In some cases, the formation resolves on its own, without treatment.
Hygroma of the wrist is a round capsule with dense walls, filled with a viscous liquid. Can be located on the outside or on the inside. Transformation into a malignant tumor does not occur. Treatment aims to eliminate the external defect.
Anatomy and causes of hygroma formation
Content:
- Anatomy and causes of hygroma formation
- Symptoms and manifestations
- Indications for removal of hygroma
- Preparatory period and contraindications
- How to remove hygroma
- Removal of hygroma with laser
- Features of hygroma removal depending on location
- Removing hygroma from a child
- Postoperative period
- Complications and relapses
- Hygroma removal without surgery
To date, doctors have not come to a clear opinion about the reason why hygromas appear. Thus, according to the most common theory, the root cause of the occurrence of such cysts is the process of metaplasia (degeneration) in connective tissue cells. As a result, two types of cells are formed: spindle-shaped, from which the capsule is formed, and spherical. The latter are filled with liquid, which is then poured into the intercellular space.
It is noteworthy that in women the disease is diagnosed three times more often than in the stronger sex. In this case, hygromas most often develop in patients between the ages of twenty and thirty years. Scientists have also been able to establish that there is a hereditary predisposition - in other words, blood relatives often suffer from this disease. Some researchers claim that the cause of hygroma can be a constant significant load on the tendon or joint, as well as a single injury.
Fibroids
Skin fibroma is a benign formation that consists of mature elements of connective tissue and can occur on any part of the body. Externally, fibroma looks like a lump or nodule that is skin-colored or slightly different. The neoplasm itself is not dangerous and does not cause pain. However, fibroids often become a pronounced cosmetic defect or cause discomfort as a result of injury, clothing rubbing against it, and other external factors.
The main factors in the development of neoplasms include genetic predisposition, hormonal changes (during puberty, menopause), and disturbances in the functioning of the endocrine system. Depending on the appearance, the following types of fibromas are distinguished: Hard fibroma (dermatofibroma). This neoplasm has a wide base, dense to the touch, and can be convex or slightly pressed into the skin. A characteristic sign of dermatofibroma is the “dimpling symptom,” in which the tumor sinks inward when squeezed with your fingers. Hard fibromas form in both men and women, most often as single cases. Soft fibroma. It is a pouch on a leg, consisting of “nodules” of skin. Soft fibroma is more common in women and men of mature age, as well as in people who are prone to obesity. The neoplasm can be localized on the eyelids, in the armpit, on the neck, in the inguinal folds, and folds under the mammary glands.
Treatment
Fibroids do not pose a threat to human life, however, they are removed in cases of cosmetic defects, which can cause psychological discomfort to the patient and in cases of permanent injury (by clothing, as a result of shaving, etc.).
We use various techniques to remove fibroids. The doctor selects the best option based on the type of tumor, its location and the wishes of the patient.
- Laser removal. The most effective and safe method of getting rid of fibroids. Thanks to the laser, the fibroid is “dried out” layer by layer, leaving no scars. In our clinic, tumors of any shape and size are removed using a laser.
- Electrocoagulation. Excision and cauterization of fibroids is performed using current. With electrocoagulation, the risk of bleeding and complications is minimal.
Symptoms and manifestations
As a rule, in most cases, hygroma is a practically asymptomatic disease. It does not cause any particular inconvenience to patients other than aesthetic ones.
The disease begins with a slight swelling over the joint area. Its distinctive characteristic is its clear demarcation from surrounding tissues. The skin over the tumor can move freely. As a rule, hygromas are single, but sometimes several formations can appear on the same joint.
Hygroma can grow either very slowly, almost imperceptibly, or rapidly. It should be noted that when the tumor begins to increase in size, it inevitably causes compression of the tendons and nerve-blood bundles. In addition, the functioning of the joint is impaired.
Patients are often interested in whether hygroma provokes pain. As a rule, patients feel pain of varying intensity if the tumor is located near the nerves. The pain can be either constant, not too pronounced, or radiating. Sometimes discomfort can appear only after intense exercise. Also, sometimes the hygroma increases slightly after active movement and decreases in size at rest.
As for the skin over the formation, it can either remain unchanged or become rough. In some cases, peeling is observed and the skin becomes reddish.
Preparation
Before the patient undergoes surgery, he must undergo a series of examinations, which include:
- Palpation of the hygroma by a surgeon.
The doctor determines the size and condition of the tumor, evaluates its structure, etc.
- Ultrasound.
This study is mandatory before surgery. During its implementation, it is possible to accurately determine the size, shape and structure of the tumor, as well as its location in relation to other tissues and structures (nerve fibers, joints, tendons, blood vessels).
- MRI
prescribed if the doctor has doubts about the nature of the tumor, or if it is located in hard-to-reach places.
- Hygroma puncture.
The procedure involves collecting the tumor contents, which are sent for histological analysis. Puncture allows us to exclude the presence of malignant cells in the tumor.
General preparation for surgery boils down to taking a blood test for biochemistry and assessing the coagulation system. Blood is also donated for HIV, hepatitis and syphilis.
Indications for removal of hygroma
Today, the most effective way to get rid of hygroma is surgery. If the procedure is performed by an experienced surgeon, the risk of recurrence is significantly reduced.
As a rule, doctors decide that the formation should be removed if it begins to rapidly increase in size. Also, an indication for removal is constant pain, which manifests itself both during movement and at rest. In addition, the tumor is removed if it compresses the nerves, resulting in a disruption of innervation.
Removal must be resorted to if the hygroma disrupts the normal functioning of the joint or the tumor suppurates. The reason for surgical intervention is also the likelihood of spontaneous rupture of the formation and its unaesthetic appearance.
Treatment
Hygroma never degenerates into a malignant tumor, so there is no vital indication for its removal. However, as a rule, a cyst is not only a cosmetic defect, but also significantly worsens a person’s quality of life. As it grows, it begins to put pressure on nerves and blood vessels, causing pain and discomfort when moving.
Conservative methods of treating hygroma have shown to be ineffective: neither medications nor physiotherapeutic procedures can significantly reduce the size of the tumor or get rid of it forever. Even if at the very beginning there may be an illusion of cure, in 90% of cases the tumor appears in this place again. The only method that guarantees complete cure of hygroma with a minimal percentage of relapses is surgical intervention. This is what is used in the treatment of hygroma at the RAMI clinic.
Laser removal of atheroma is recommended if it is not in an advanced stage and is small in size. After all, when working with a laser or radio knife, the doctor only hypothetically assumes the depth of penetration, and in the presence of atheroma, the main goal of the operation is its complete removal - along with all its contents. If at least one millimeter of affected tissue remains, the disease is likely to recur.
Preparatory period and contraindications
Before surgery, it is mandatory to conduct examinations that will help establish an accurate diagnosis. In other words, the surgeon must be one hundred percent sure that he is faced with a hygroma, and not with any other formation. To do this, the doctor conducts a thorough examination of the patient. Its first stage is palpation. By palpating the tumor, the doctor determines its approximate size and makes a conclusion as to whether there are any signs of an inflammatory process.
After this, an ultrasound is performed. With its help, you can estimate the exact size of the tumor and draw a conclusion about its structure. The study also helps determine whether blood vessels have grown into the cyst.
Magnetic resonance therapy is prescribed if the ultrasound is not informative enough and the doctor has any doubts.
To exclude the possibility of a malignant tumor, a puncture is performed. A biopsy is also done if an inflammatory process is present. In this case, a bacteriological culture of the biopsy specimen is carried out on a nutrient medium to determine which antibiotics to use during therapy.
If the diagnosis of hygroma is finally confirmed, the patient is referred for preoperative examinations. As a rule, we are talking about the usual set of tests and examinations. These are general tests, blood biochemistry, blood for viral hepatitis, HIV and syphilis, ECG and fluorography.
As a rule, the patient does not need any special preparation before surgery. The only condition is that you need to choose a period when the patient can reduce the workload without negative consequences - the joint will have to be protected for at least several weeks after the operation.
Like any other surgical intervention, removal of hygroma has its contraindications. The operation is not performed on patients who have recently suffered acute infectious diseases. Also, surgical removal of the tumor is contraindicated in case of problems with blood clotting. In addition, hygromas are not removed for women in an “interesting” position.
Diagnostics
To make an accurate diagnosis, you should consult an orthopedic surgeon. Determining the causes of the disease and treatment methods involves conducting an examination: the doctor must determine the location of the tumor and its size. Of the laboratory tests, only a biopsy will be indicative.
Diagnosis is carried out using:
- MRI or ;
- Ultrasound;
- X-rays;
- If necessary, a puncture of the hygroma is taken.
How to remove hygroma
The question of how exactly a hygroma is removed worries many patients. At the moment, surgery to remove this tumor can be performed in one of three ways. The first is excision, when the surgeon completely cuts out the formation along with the capsule.
The second method is to use a laser beam. In this case, only cells that have mutated are exposed to the laser. The laser does not affect healthy tissue.
Finally, the operation can be performed endoscopically, using special equipment that is inserted through small incisions.
Removing a hygroma is an operation that requires high skill from the surgeon, since the tumor is located in close proximity to the joints, nerves and tendons. Moreover, the removal operation includes several stages, since a hygroma is a hernia, in other words, a protrusion on the synovial bursa, which over time develops into a cyst. Consequently, the surgeon is faced with the task of removing the cyst body itself, as well as the isthmus, after which the synovial bursa must be sutured to its original size.
The most difficult is the removal of hygroma located on the wrist joint. The wrist is a collection of blood vessels, ligaments, joints and nerves, and therefore only specialists in microsurgery of the hand, and not general surgeons, should remove hygroma in this area. The second most difficult procedure is the removal of hygroma of the foot.
Surgery is performed under local anesthesia. Sometimes general anesthesia is used - however, only in cases where the operation will be long and complex. As a rule, the procedure lasts no more than half an hour. Small formations are removed on an outpatient basis.
The operation to remove hygroma consists of the following steps:
- A rubber tourniquet is applied to the limb and anesthetic is infiltrated at the site of the future incision and along the contour of the formation.
- The doctor makes an incision in the skin over the tumor and performs a puncture to extract fluid.
- The surgeon carefully isolates the hygroma from the surrounding tissue. It is not enough to remove only the upper part of the formation, which is easiest to reach. In this case, a significant part of its shell remains deep in the tissue, which will lead to the fact that, a few months after the operation, fluid will begin to collect in the hygroma again. That is why it is so important to highlight the entire shell of the formation, to the places where its base connects to the joint.
- The doctor excises the protrusion and sutures the synovial bursa.
- The surgeon sutures the wound, applies a tight bandage and fixes the joint with an orthosis or splint.
If the patient experiences pain, the doctor may prescribe a pain reliever. Dressings are carried out every day. If there is a threat of developing an inflammatory process, antibiotics are prescribed.
As a rule, the sutures are removed a week after surgery, and the fixing bandage is removed fourteen days later.
The causes are not entirely clear
We cannot say with absolute certainty why a synovial cyst appears in a particular place in a given person. From the point of view of structural changes in tissues, mucoid degeneration of the joint capsule or tendon sheath is described; microtubules are formed in this area through which fluid from the joint or tendon sheath is pumped into the formed cavity (this is how the “bubble” grows). The fact is that the connection between the joint and the hygroma occurs only unilaterally from the joint to the cavity of the neoplasm. The greater the load, the greater the pressure and the faster this hygroma can grow. In case of immobilization or rest, the volume of the tumor gradually decreases. I would compare this process to how a balloon is deflated.
Most often, young women come with such complaints with some tendency towards increased elasticity of the connective tissue (good stretching).
Removal of hygroma with laser
Removing hygroma with a laser resembles conventional surgery. The only difference is the method used to cut the tissues. Instead of a scalpel, a laser beam is used.
There is a misconception that hygroma is removed with a laser without the help of an incision, and no scars remain. Actually this is not true. However, with laser removal, the likelihood of bleeding is reduced, and the wound does not become infected.
During laser removal, the tissue over the hygroma is dissected, after which the hernia is separated as carefully as possible so that the fluid it contains does not get into the surrounding tissue. After the operation, the wound is sutured and bandaged. The bandage is changed every day, and the stitch is removed after about a week and a half.
Another method of laser surgery is also sometimes used. The tumor is punctured using two needles, after which a laser light guide is inserted through one of them, with the help of which the hygroma capsule is burned out from the inside. Using a second needle, the liquid is sucked out. The procedure is completed by applying a pressure bandage.
If we talk about the advantages of laser removal, then this is, first of all, a reduction in the duration of surgery, a decrease in pain, and the absence of bleeding due to the fact that small vessels are immediately coagulated by the laser beam itself. Also, the seam after the operation is very thin and less noticeable.
However, it must be taken into account that with traditional surgical excision of hygroma, the number of relapses is significantly less than when using a laser. This is due to the fact that laser removal does not involve suturing the gate of the formation - in other words, the place where it connects to the joint.
Diagnosis of hygroma
Most often, it is not difficult to diagnose hygroma. Hygromas are clearly visible upon examination, have a spherical shape and are located in typical places. If the hygroma is connected to the tendon sheath of the muscle, then it will move up and down when it contracts.
If there is doubt about the diagnosis, the hygroma can be punctured. For these purposes, the doctor performs a puncture after anesthesia. If a jelly-like transparent viscous liquid is detected, the diagnosis is confirmed.
Hygroma puncture is usually performed under ultrasound control.
Ultrasound (US) plays an important role in the diagnosis of hygroma. It allows you to confirm the diagnosis of hygroma, since a hygroma is a cyst with walls and a cavity filled with fluid. Ultrasound allows you to distinguish hygroma from tumors, for example, lipomas and atheromas, which have a dense structure. Ultrasound also allows you to evaluate which vessels are suitable for the hygroma and their diameter.
In some cases, it is recommended to do an MRI of the affected area. MRI is a very informative research method, as it allows you to determine in detail the size and location of the hygroma.
Features of hygroma removal depending on location
Depending on where exactly the hygroma is located, its removal has a number of features.
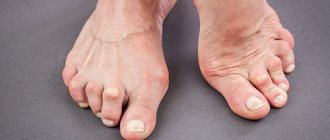
Hygroma of the hand
A cyst on the hand usually forms on the back of the wrist joint. It can also appear on the side of the palm or in the area of the finger joints. Such cysts are considered an occupational disease of people who constantly strain their hands - for example, secretaries and violinists. Also, the number of such hygromas has increased significantly in recent years due to the fact that people spend a lot of time at computers.
Removal of hygroma in the wrist joint is carried out very carefully due to the fact that there are two neurovascular bundles here. That is why such an intervention must be carried out by a very highly qualified surgeon.
Hygroma of the finger
The features of this type of formation depend on where exactly the cyst is located - on the back or on the palmar side of the finger. As a rule, on the dorsal side it usually occurs either at the base of the phalanges or at the interphalangeal joints. The skin over such formations becomes thinner and tighter. In this case there is no pain. If the cysts are on the palmar surface of the fingers, then they can spread to several phalanges. Also, since there are more nerve fibers in the tissues of the palmar surface of the fingers, the patient may experience severe pain.
Very rarely, hygromas form at the base of the fingers. They are significantly smaller in diameter, only up to 0.5 centimeters, but when pressing on the formation, extremely unpleasant sensations occur.
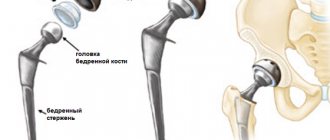
Removal of hygroma of the wrist joint
Often, patients live with hygroma of the wrist joint on the palmar side for several years, and the neoplasm does not bother the patient in any way. However, if the tumor begins to increase in size, if it causes numbness in the fingers and tingling, it is necessary to resort to surgery.
Since the hygroma is located adjacent to the radial artery, the surgeon who will perform the surgery requires high precision and professionalism so as not to disrupt the blood circulation.
Hygroma of the wrist joint is removed either under local or general anesthesia. Some doctors are supporters of general anesthesia, since during the intervention they touch deep tissues in order to completely excise the capsule.
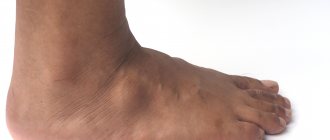
Removal of hygroma of the ankle and foot
Neoplasms on the lower extremity are usually located on the ankle joint or on the foot. As a rule, it is the formations on the foot that are the most painful and most susceptible to trauma due to the fact that shoes can rub the skin. In addition, the weight of the entire body presses on the hygroma. As a result, patients experience severe discomfort when walking. Due to constant trauma, the capsule of the hygroma located on the foot may burst, which is fraught with inflammation and suppuration.
After removal of the hygroma on the leg, the patient will have to walk on crutches for at least a week and a half.
Where can it appear?
In principle, hygroma can appear on any joint or tendon sheath. There are characteristic localizations on the hand:
- Hygroma of the wrist joint can appear on the dorsal (most common) side. In this case, its source is the capsule above the lunate-scaphoid ligament.
- On the palm it comes out near the radial artery (this is where the pulse is felt) from the space between the radioscaphoid and long radiolunate ligaments.
- On the finger, it usually sits at the base on the palmar side in the projection of the skin fold. There it is very small and dense, like a bead. Less commonly, hygroma occurs on the finger in the projection of the proximal interphalangeal joint on the back.
- Mucoid cysts also form on the finger, which are also essentially hygromas, but grow from the distal interphalangeal joint, and not from the tendon sheaths, like the previous two “finger” variants.
I was surprised when I learned that in France hygroma is a disease that we all know in Russia as bursitis of the elbow joint. Well, in fact, they are right, bursitis and hygromas are, in general, the same thing.
Removing hygroma from a child
As noted above, most often cysts are diagnosed in young people aged twenty to thirty years. However, sometimes hygromas are diagnosed in children. It should be noted that often the occurrence of a neoplasm at the ankle joint is provoked by activities in sports sections and dance clubs, during which children are injured or experience serious stress.
If a hygroma is suspected, the child is referred to an orthopedic surgeon, and X-rays and ultrasounds are performed. Based on the test results, the doctor decides whether a conservative or surgical method will be used.
A referral for removal is issued if the formation rapidly increases in size, the child experiences pain not only when moving, but also at rest, and complains of numbness of the limb and limited mobility. Hygroma is also removed if conservative treatment does not bring a positive result.
For children who have not yet reached the age of ten, the operation is performed under general anesthesia. If the child is already ten years old, the doctor focuses on individual indications and performs the intervention under either general or local anesthesia. The sequence of surgery to remove a cyst in a child is the same as in adults. When the tumor is removed, a tight bandage, orthosis or elastic splint is applied to limit the mobility of the injured limb.
The most gentle option for a small patient is to remove the hygroma using an endoscope or laser.
Features of the operation
Excision of the hygroma is an effective way to remove the cyst. You can try to cope with it with the help of a puncture or physiotherapeutic treatment, but no specialist can guarantee a 100% recovery.
Many patients are interested in whether it is possible to remove a hygroma without health consequences. You need to understand that any operation involves a risk of complications, but they will be minimal if the patient undergoes thorough preparation and the procedure itself is performed by a professional. Therefore, it is necessary to select a medical institution where the hygroma can be removed with special care. Doctors must have the necessary qualifications and have permission to perform such operations.
Postoperative period
As a rule, after surgery, the patient leaves the medical facility on the first day. However, he will have to come in for dressings and suture removal.
Despite the fact that the operation to remove hygroma is not considered too complicated, recovery will take a certain amount of time. Immediately after the intervention, a splint is applied to the injured area - a removable plaster bandage. It does not interfere with dressings and treatment of the wound, but at the same time reliably fixes the joint. The splint is removed after about a month, depending on where exactly the hygroma was located and how complex the surgical intervention was. However, even after removing the plaster cast, the load on the joint should be limited as much as possible.
In some cases, after removal of the cyst, doctors prescribe physical therapy and physiotherapy: heating, electrophoresis, magnetic therapy. All this will help restore joint mobility. Complete rehabilitation depends on how carefully the patient follows the recommendations of the attending physician and whether any complications arise after the operation.
Surgical intervention
Laser treatment of wrist hygroma in Germany is the most acceptable method, but in some patients it is still necessary to undergo extensive surgery, which is determined individually. For certain structural features of the hand, treatment of the wrist should be performed using full-fledged surgery.
Surgical treatment of wrist hygroma in German clinics is carried out as follows:
- the specialist makes an incision over the hygroma, the length of which depends on the size of the formation;
- Having carefully separated the surrounding tissue, the doctor excises the cyst from the synovial membrane of the joint and places sutures on the exit hole;
- Having checked that the joint cavity is closed hermetically, the doctor sutures the edges of the wound and applies a sterile bandage;
- the wrist joint is fixed in a stationary state with a special orthopedic design.
During recovery, the patient must comply with the main condition - to limit the mobility of the joint as much as possible in order to create conditions favorable to healing. During the first two weeks, the fixation device should be worn constantly, and for the next 2-3 weeks it can be worn at night. The sutures after the operation are removed on the 7-8th day, but the patient does not have to stay close to the clinic all this time - the sutures can be removed by a surgeon at the clinic at the place of residence.
A team of highly qualified specialists at Deutsche Medizinische Union works to ensure that patients from Russia and the CIS countries can easily access the best medical institutions in Germany, Austria and Switzerland. Full organization of all stages of therapy on our part ensures you a comfortable passage of all diagnostic and treatment procedures.
We control all stages of therapy, discuss unclear points with you, provide an interpreter, accompany you throughout your stay in the clinics, and review invoices. Before returning home, if the need arises, we will help you purchase medications in high-quality foreign pharmacies and contact your doctor. Our team has taken into account all the points that may prevent you from getting the best experience from your trip for treatment abroad.
Complications and relapses
Although removal of a hygroma is considered a relatively minor surgical procedure, complications may occur in some cases. So, an infection can get into the wound, which causes inflammation and suppuration. If the doctor is not sufficiently qualified, he can damage an artery, which can lead to bleeding, or a nerve, which leads to disruption of innervation.
Separately, it is worth mentioning the possibility of relapse after removal of the hygroma. Statistics show that the disease develops again in thirty percent of cases. Doctors have identified the main reasons that can trigger a relapse of the disease. This is, for example, weakness of connective tissue. In addition, the reappearance of the cyst can provoke non-compliance with the regimen after surgery or the patient’s return to the activity that led to the occurrence of hygroma.
Also, the cause of relapse may be insufficiently performed surgical intervention. For example, the surgeon may leave pieces of the hygroma capsule or not close the so-called anastomosis - the place where the hygroma connects to the joint capsule. In most cases, relapse of the disease leads to repeated surgery.
Treatment of hygroma
Excision of the hygroma allows you to remove the hygroma completely, but since the operation does not provide a 100% guarantee that there will be no relapse, according to various sources, even with excision, the risk of relapse sometimes reaches 50%, you can start with conservative treatment methods.
For example, with small sizes of hygroma and with simple hygroma, without the presence of several chambers and jumpers.
Indications for treatment of hygroma are symptoms such as: severe discomfort, severe cosmetic defect, impaired joint mobility. An increase in size leads to compression of nerve endings and blood vessels, so the pain may intensify.
Drug treatments for hygroma are used only for inflammation: medications and physical therapy can remove inflammation, but cannot cure the tumor.
In case of relapse after conservative treatment methods, you need to think about surgical treatment.
Hygroma removal without surgery
Many people are frightened by the prospect of surgical intervention, so they strive to learn how to remove hygroma without surgery. In some cases, removing a cyst without surgery is indeed possible, but you should not make a diagnosis yourself and start fighting the disease.
First of all, it is necessary to carry out diagnostics - x-rays and punctures. These studies will make it possible to exclude the possibility that another type of tumor, which may be malignant, is “masked” under the hygroma. During the puncture, doctors pump out the contents of the cyst and send it to the laboratory for biochemical analysis. Based on the results of the study, the doctor determines the type of treatment that is suitable in each specific case.
If we talk about ways to remove hygroma without the use of surgical manipulations, there are at least five of them. This includes physiotherapy, mechanical methods, puncturing, medicinal and/or homeopathic treatment, as well as the use of traditional medicine.
Physiotherapy
Physiotherapeutic procedures are indicated exclusively for the treatment of small hygroma. They are also used only in cases where there is no inflammation in the affected joint.
So, UHF can be used for deep heating. The procedure stimulates regeneration processes and has an anti-inflammatory effect, and also improves blood flow. Ultrasound treatment has a relaxing effect on muscles, stimulates microcirculation and enriches tissues with oxygen, and also stimulates regeneration processes. Magnetotherapy has an anti-inflammatory effect and stops similar processes in bone and cartilage tissue. Paraffin wraps relieve swelling and help stop the inflammatory process. Finally, salt and soda baths help restore joint mobility.
During a course of physical therapy, you should apply a tight bandage to the affected joint, and also try to limit the load on the affected joint.
Crushing (mechanical method)
Crushing the hygroma is the so-called “old-fashioned” method. Previously, it was used everywhere, but now such a procedure can only be recommended by an elderly surgeon.
The essence of this method is that there is strong pressure on the cyst, as a result of which the shell bursts and the liquid pours into the surrounding tissues. Proponents of this method insist that the contents of the hygroma are sterile, and therefore the liquid resolves on its own. However, the problem is that sometimes this method can provoke the development of inflammation, suppuration and abscess.
Carrying out a puncture
Puncture is a transitional link between conservative and surgical treatment of hygroma. It should be borne in mind that this method is not able to get rid of the cyst once and for all, but it does lead to the temporary disappearance of the tumor.
The essence of the puncture is that the neoplasm is pierced with a needle and the contents are sucked out of it. Drugs are injected into the cavity to prevent the re-accumulation of contents.
However, the fact is that the cyst shell remains in place, therefore, over time, a relapse will still occur.
The procedure is carried out very quickly and is not too painful. The doctor treats the skin over the hygroma with an antiseptic, after which he fixes the cyst with one hand and pierces it with the other at an angle of thirty degrees. After this, the liquid is sucked out until the bulge under the skin completely disappears.
It should be noted that puncture itself is an excellent diagnostic technique. If the fluid that the doctor pumped out of the cyst contains blood or pus, doctors make adjustments to the further course of treatment.
Drug treatment
Treatment of hygroma with medication is indicated in cases where compression of the tissue around the cyst has led to the development of an inflammatory process. In this case, the doctor prescribes treatment based on what type of inflammation was encountered.
Thus, medications are used to treat aseptic (non-purulent) inflammation. Doctors recommend the use of non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, for example, Nimesil or Diclofenac. The use of antihistamines is also indicated.
It should be taken into account that non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs should be taken with caution if the patient has been diagnosed with disorders of the liver and kidneys. Also, when using them, adverse reactions often develop, which should be a reason to stop taking them and immediately visit a doctor.
Homeopathic remedies - herbal preparations - are also often used. This option for non-surgical removal of hygroma is suitable for those who suffer from allergies or individual intolerance to medications.
Best materials of the month
- Coronaviruses: SARS-CoV-2 (COVID-19)
- Antibiotics for the prevention and treatment of COVID-19: how effective are they?
- The most common "office" diseases
- Does vodka kill coronavirus?
- How to stay alive on our roads?
If the doctor diagnoses purulent inflammation, then only surgery can help. In this case, even taking antibiotics will not help, since they simply will not be able to cope with the rapid proliferation of bacteria.
Treatment of relapse
Treatment of hygroma that has recurred is selected by a specialist. The patient should not try to cope with the disease on his own using the previous course of therapy. It may not give any result or make the situation even worse.
Conservative treatment
Children aged two years or less should not use the ointment.
In case of relapse, hygroma can be treated with conservative methods. This treatment option is appropriate if the tumor is small in size. Medicines will help prevent its rapid growth and reduce the severity of painful symptoms.
Recurrence of hygroma is usually eliminated with topical medications. They treat the affected area. It is important to adhere to the treatment regimen that was selected by a specialist.
Doctors recommend using the following medications for this disease:
- Diclofenac ointment to eliminate inflammation and relieve pain in the problem area on the body.
- Hormonal ointment "Diprosalik" for disinfecting tissues and reducing the severity of the inflammatory process.
- Homeopathic gel "Traumel" to suppress the activity of pathogenic microflora and eliminate signs of irritation on the skin.
- Momat ointment to combat itching and inflammation.
A good assistant in eliminating the recurrence of hygroma is Vishnevsky ointment. It is used when applying medicinal applications.
Surgery
Surgery is the best option for treating hygroma and its recurrence.
The effectiveness of radical therapy is that it reduces the likelihood of tumor recurrence by up to 20%. This is a fairly low figure compared to medication and physiotherapeutic courses.
Surgical treatment of recurrent hygroma includes several methods. The first step is to excise the benign tumor. Next, the patient undergoes a rehabilitation period, during which the use of medications is required to treat the affected area.
In most cases, the hygroma is excised surgically. This is the simplest and most accessible method of radical treatment of a tumor. The surgeon makes an incision in the skin and then removes the tumor along with its contents.
Treatment with folk remedies
It is advisable to use freshly collected herbs, not from a pharmacy.
Treatment with alternative medicine methods is practiced by many patients. But they must understand that such therapy does not give a positive result if a person refuses pharmaceutical drugs and surgical intervention, for which there are direct indications. Folk remedies should be used exclusively as an auxiliary treatment, and not as the main one.
The following folk remedies help to cope with the pathological process:
- A solution of sea salt and red clay. To prepare the medicinal composition you will need 2 tsp. the first component and 1 cup of the second. They are mixed with ½ cup of warm water. The finished mixture should be placed on the problem area and covered with a bandage. It is left in this form for the whole day. From time to time the bandage should be moistened with water.
- Sagebrush. Fresh herbs must be thoroughly crushed. Before this, you can grind it to simplify the task of preparing the gruel. The finished mass is applied to the hygroma and covered with a cloth. It is advisable to insulate the compress on top with a scarf. Leave it for 2 hours.
Folk remedies should be combined with ointments that are characterized by anti-inflammatory effects. They can be applied after removing the compress or application.
Physiotherapy
Recovery after removal of an inflamed hygroma will be more successful if the patient continues conservative treatment. Physiotherapeutic procedures can speed up recovery and prevent the recurrence of pathology. We are talking about the following treatment methods:
- Ultrasound therapy.
- Magnetic therapy.
- Soda or salt baths.
Physiotherapy should be carried out in a course that includes at least 10 procedures. Otherwise, it will not give the desired result.