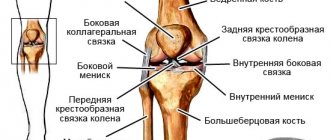
What is a sprain
Ligaments are bands of connective tissue that surround and strengthen a joint.
Their ends are attached to the mating bones. Thanks to ligaments, the joint can only bend in a certain direction. Any external force aimed at bending a joint in an unnatural direction can lead to spraining, the first signs and first aid for which will be discussed below. The connective tissue that secures the articulation of bones is highly durable and lacks elasticity. She is unable to stretch. When a tensile load is applied, fibers rupture, which, depending on the severity of the injury, can range from a small part to a complete rupture of the ligament. Therefore, in traumatology there is no concept of “sprain”; instead, the term “rupture” is used.
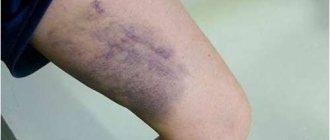
When an injury occurs, along with the rupture of connective tissue fibers, blood vessels usually rupture, which leads to internal hemorrhages with the formation of hematomas and the appearance of swelling.
Let's consider all aspects regarding the definition, causes, types, symptoms of sprains and first aid for this condition.
Possible complications and injury prevention
If a muscle strain is not treated and the prescribed set of rehabilitation measures is not completed, then the development of complications is possible. They can be expressed in:
- the formation of scars, which significantly reduce the elasticity of muscle fibers;
- myositis (muscle inflammation).
- joint instability;
To prevent sprains, you should consider some recommendations:
- Before training, you need to warm up your muscles. Only after this can you start doing any exercises. You cannot make sudden movements without first warming up;
- Eating right, exercising and taking vitamins will help strengthen your muscles, which will also reduce the likelihood of injury.
- you should not wear uncomfortable shoes;
- By rationally organizing the space in your home, you can prevent injuries in your home;
How to distinguish a sprain from other joint injuries
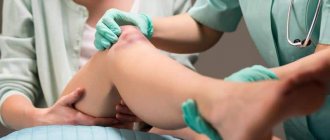
Although the principles of emergency care for various types of sprains are the same as for other types of injuries, it is advisable to assess the severity of the injuries before visiting a traumatologist. This will allow you to take additional measures and choose the right tactics that will help avoid complications.
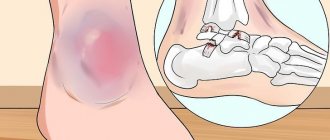
The easiest type of injury is a bruise. It is accompanied by rupture of blood vessels and the formation of hematomas, but the structures of the joint, bones and ligaments remain intact. Its symptoms are pain after injury, which soon decreases and is felt only when pressing on the injured area. The bruise is usually accompanied by swelling, but the range of motion of the injured limb does not decrease.
Dislocation occurs due to displacement of the articular surfaces relative to each other. It can be recognized by the unnatural position of the bone, changes in the shape of the joint, as well as sharp pain when trying to move. The victim should be given first aid for dislocations and sprains, trying not to disturb the deformed joint. Its reduction should only be done by a traumatologist, who must be contacted within the first 24 hours after the injury.
A fracture is usually characterized by sharp pain with movement, numbness at rest, and swelling in the injured area. When pressing on the injured area, acute pain is felt. The victim urgently needs to apply splints, as well as take other emergency measures used for sprains and dislocations, and then be taken to a medical facility.
Sprain and rupture of ligaments can be suspected by the direction of action of the traumatic load. For example, if during a fall your foot twisted sharply or your knee turned inward or outward, then with a high degree of probability a sprain can be assumed. Symptoms are aching pain at rest and sharp pain when moving, which only intensifies over time, and swelling may occur.
A sprain can be distinguished from a fracture by the absence of pain when pressing on the joint. Ligament rupture can be no less dangerous than a fracture. If there is severe pain and immobility, the injured person needs to call an ambulance, and if the condition is not very serious, then within one to two days after the injury you need to see a traumatologist. First aid for a sprained ligament should be provided immediately.
Causes
Muscle strain is one of the most common injuries among professional athletes. They get it when jumping, running, lifting heavy objects, falling, spraining and other actions. However, it cannot be said that an ordinary person who has nothing to do with sports cannot receive a similar injury.
Anyone can stumble, fall, place their foot awkwardly, or, for example, overwork in the countryside, dragging heavy logs. All this can also cause a violation of muscle integrity.
What you will need for first aid
To properly provide first aid in the event of a sprain, you must have in your first aid kit regular and compression bandages, painkillers, as well as a cooling pack, which can be replaced with the following available means:
- cold accumulator for thermal bag;
- pieces of ice from the freezer, tied in a bag;
- finely chopped frozen vegetables;
- bag of snow;
- a heating pad filled with cold water.
It is desirable that the cooling agent can easily take any shape for better fit to the injured area. An elastic and simple bandage, as well as a cooling pack, should always be in your home, office, or car first aid kit in order to be able to provide first aid for a sprain as soon as the need arises. In case of open wounds, you need to have sterile dressing material. Also, to immobilize the injured limb, splints may be needed, which can be replaced with any oblong-shaped objects at hand.
Classification of muscle injuries
Muscle injuries are classified as grade I, II or III injuries. This depends on the number of damaged fibers, as well as clinical data and instrumental diagnostic data.
- Grade I (mild) sprains affect a limited number of fibers in the muscle. In this case, there is no decrease in muscle strength and the full active and passive range of motion is maintained. Pain or tenderness is usually not felt until the next day.
- With grade II (moderate) sprains, approximately half of the muscle fibers are damaged. The pain is usually accompanied by swelling and decreased muscle strength.
- Grade III (severe) strains are a complete tear of the muscle. This means that either the tendon has torn away from the muscle belly, or the muscle belly itself has been torn in two. Severe swelling and pain, as well as complete loss of function, characterize this type of sprain.
Stages of assistance
Before considering what the sequence of providing pre-medical first aid for a sprain is, we note what absolutely cannot be done. After a blow, the first reflex movement is to rub the bruised area. It is better to refrain from this, since rubbing activates blood circulation, and if the vessels are damaged, then hemorrhage into the surrounding tissue will increase, which will lead to the growth of a hematoma.
The same applies to heating the damaged area. In the first two days, it is forbidden to apply warm heating pads to the injury site, take a hot bath or shower, or make warming compresses. This can be done only after 48 hours, when the threat of hemorrhage from damaged vessels has passed.
First aid steps for a sprain include resting the injured joint, cooling, and compression. Painkillers are also used if necessary. We briefly covered the stages of first aid for a sprained ligament victim, and now we will look at each of them in detail.
Peace
The first step in helping with muscle and tendon sprains is to keep the injured joint immobile. This allows you to achieve two goals - to stop the development of pathological processes caused by injury and to reduce pain.
The victim must be laid down, placing the joint in a position in which pain is minimal. In this case, it is desirable that the injured area is above the level of the heart. This reduces blood supply to the injured area. If there is a suspicion of a fracture or ligament rupture, it is recommended to immobilize the limb using splints. But this must be done after the stages of bandaging with an elastic bandage and cooling. Splints are applied on both sides of the injured area, extending beyond it, and attached to the limb using bandages. It is necessary to place a soft cloth under the splints to avoid damaging the skin.
Compression
The next stage of first aid for an injured person with sprained muscles and ligaments is the application of a tight bandage, which, on the one hand, provides fixation of the joint, and on the other hand, slightly compresses the damaged vessels and reduces internal hemorrhage. It is best to use a compression bandage for this purpose, but if this is not available, you can make a tight bandage with a regular bandage or strips of clean fabric. If there are wounds on the skin, they must be covered with several layers of sterile dressing material before applying a tight bandage. The bandage should be tight, but in moderation, it should not interfere with blood circulation in the limb, because when a ligament is sprained, providing first aid, everything should be done to improve, and not worsen, the condition of the injured person. If, some time after applying a tight bandage, the skin of the limb turns blue or, conversely, becomes too pale, the bandage must be loosened.
Cooling
First aid for a sprain also includes applying cold to the injured area. This helps stop internal bleeding. Immediately after the injury, cold exposure should be 25–30 minutes, and then for two days, cold should be applied for ten minutes every two hours, excluding sleep time. When using cooling agents, wrap them in a cloth and make sure the dressing does not get wet, especially if there are wounds on the skin.
Strengthening muscles after stretching
Physical therapy and physiotherapy will help speed up the healing process and recovery after a sprain. These procedures are usually prescribed to anyone who has suffered a second or third degree injury.
Physiotherapy
In order for the damaged muscle to become elastic and strong again, certain exercises should be performed. This is where physical therapy is expressed. This will also help prevent future strains in part by restoring the normal condition of the muscle.
The complex is selected by a specialist in physical therapy – a physical therapy doctor. The load and set of exercises are prescribed individually and depend on the degree of damage and location.
In most cases, physical therapy begins with the simplest exercises - isometric, consisting of slight muscle tension, but without motor load. The load gradually increases as the injured ligaments strengthen.
Physiotherapy
In order to stimulate the healing of torn fibers, as well as to relieve pain, various physiotherapy procedures are prescribed. Such treatment begins 3-4 days after injury.
The most common procedures are:
- electropheresis (6, 8 or 10 sessions). It is usually done using a painkiller;
- UHF (6-8 sessions).
- magnetic therapy for sprained ligaments (10-15 sessions);
- amplipulse (8-10 sessions). During this procedure, low-frequency current is applied to the human body for therapeutic purposes;
Speaking about what else can be done when a muscle is strained, it is worth noting: massage is also useful during treatment. It helps improve blood supply to the damaged area of the body and also stimulates muscle nutrition. This significantly shortens the rehabilitation period.
Compress with Dimexide
The use of Dimexide helps relieve pain, normalize blood flow and speed up recovery. Therapeutic compresses prevent blood stagnation and the formation of blood clots.
Dimexide
To prepare the product, you need to dilute 50% Dimexide with water in equal proportions. A gauze pad is soaked in the resulting mixture and then applied to the aching ligament. Cover the top of the compress with a napkin. Leave for half an hour. The application period must not exceed 14 days.
It is recommended to prepare the compress with gloves so as not to accidentally transfer the medicine to the mucous membrane of the eye with your hands.
This drug, like others, has contraindications, so its use is permitted after consultation with a doctor.
Predisposing factors
Three types of muscles are at possible risk of injury:
- Biarticular muscles. Movement in one joint increases the passive tension of the muscle and causes it to become overstretched.
- Muscles that contract eccentrically. Eccentric contractions, characteristic of the deceleration phase of activity, can significantly increase muscle tension and lead to overload and damage to myofibers.
- Muscles with a higher percentage of type II fibers. These are the muscles that perform high-speed contractions, as a result of which they are most often subject to injury. Much of the muscle activity during running and sprinting is eccentric, which explains why such loads are most often found in sprinters or “speed athletes.” The most commonly injured muscles are the hamstrings, calf muscles, quadriceps, hip flexors, hip adductors, erector spinae, deltoid, and rotator cuff muscles.
Urine compress for sprains
You can do rubbing and compresses using your own urine. It is better to use fresh urine or store it in a cool place and in a tightly closed container. For compresses, you should take morning urine, since it contains an increased concentration of biologically active substances. When applying compresses at night, it should be immobilized with an elastic bandage. Urine can be preheated in a water bath.
Which compress to use for a sprained ligament, warm or cold, will depend on the course of the injury. When there is no acute inflammation and the general condition is satisfactory, warm urine can be used. In other cases, only cold compresses are used to avoid complications. It is recommended to use urine compresses no more than twice a week.
Urine bags should not be used under the following conditions:
- individual intolerance;
- venereal diseases;
- Inflammatory processes of the genitourinary system and kidneys;
- Undergoing radiation therapy and chemotherapy;
- Pregnancy (after consultation with a doctor).
Home treatment with compresses can be carried out only after examination by a doctor. Folk remedies will only complement the main treatment.
From olive oil
Olive oil contains vitamins A, K, C, E, fatty acids, tocopherol, sterols and antioxidants. It can be used for rubbing and compresses. To prepare it, boil 250 g of oil and add a tablespoon of chamomile flowers. After 15 minutes of infusion, you can soak gauze in it.
Boil olive oil with beeswax in a water bath. The cooled mixture is applied to the sore spot. An infusion of St. John's wort oil can be used to speed up tissue healing. Half a glass of flowers is poured with oil, the mixture is infused for 21 days in a dark room.