Subacromial bursitis of the shoulder joint.
Subacromial bursitis is an acute, subacute or chronic inflammatory process that affects the subacromial bursa of the shoulder joint, located between the head of the humerus and the acromion of the scapula. Exudate forms and accumulates in it, which leads to pain that increases with flexion and extension of the joint, abduction of the upper limb or lifting it upward. The shoulder joint swells, movements in it are severely limited, and body temperature often rises. The causes of the development of pathology are functional overloads, for example, frequent and monotonous hand movements.
To diagnose subacromial bursitis, radiography, MRI, and CT are used. A bacteriological examination of the inflammatory exudate extracted by puncture is required. Treatment of acute and subacute pathology is conservative, with pharmacological drugs, applying ice compresses, and wearing an orthosis. For chronic subacromial bursitis, the patient is indicated for surgical intervention.
Description of the disease
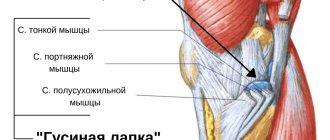
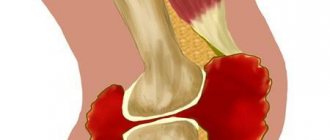
Subacromial bursitis gets its name from the organ that is affected by this disease. The human shoulder joint is made up of several structures, which include muscles, nerve endings and a bone frame. The latter is surrounded by a number of cavities, which are commonly called synovial pouches. They are filled with a special liquid that protects bone structures from damage.
Due to the influence of negative factors on this part of the human body, deformation of the subacromial pocket occurs. Its walls are affected by the inflammatory process. Under negative influence they begin to thicken and harden. Subsequently, the fluid that fills the bag is affected. It changes its viscosity and increases in volume. Often this fluid contains impurities of purulent masses and blood.
It is these processes that characterize the development of subacromial bursitis of the shoulder joint.
Location of the subacromial bursa, which is affected by this disease
Pathanatomy
Normally, the bursa is a narrow, slit-like cavity with a small amount of fluid produced by the inner lining. It is localized in places where bony protrusions come close to the skin. Protects the skin and underlying tissues from possible injury. There are about 160 such bags in the human body, most are located in the area of large and medium-sized joints.
When inflamed, the inner lining of the bursa begins to produce more fluid. The bag increases in size and takes on the appearance of a filled bag. The composition of the fluid depends on the type of inflammation. With aseptic inflammation, serous exudate accumulates in the bursa, and when infected, pus is formed. An acute purulent or long-term aseptic process can cause the formation of adhesions, areas of scar tissue, foci of fibrosis and calcification.
Causes
Subacromial bursitis, which occurs in the shoulder joint, is caused by various reasons. These include the following factors:
- Constant sports activity;
- Sprains and ligament injuries in the shoulder joint;
- Arthritis of various types;
- Arthrosis, which is caused by chronic somatic diseases;
- Allergic pathologies;
- Autoimmune disorders;
- Infectious lesion of the problem area.
Men between 25 and 45 years old are most at risk of developing this type of bursitis. Women are less likely to experience this deviation. The inflammatory process in the joint capsule may well be triggered by hypothermia, a cold or a seasonal virus.
The disease affects athletes who play golf, tennis and basketball professionally. It is these sports that require constant elevation of the upper limbs.
Portrait of a typical victim of the disease - a young man who subjects his arms and shoulders to serious stress
Causes and provoking factors
The cause of the development of acute infectious subacromial bursitis is a minor injury (cut, burn, scratch) or purulent inflammation (bedsore, boil, carbuncle). Pathogenic bacteria, usually staphylococci, penetrate into damaged tissue and begin to multiply. Then the microbes are transferred by lymph to the subacromial bursa, infecting the synovium and provoking the development of the inflammatory process.
With some injuries (deep cuts or punctures), epidermal or Staphylococcus aureus enter the bag directly from the surface of the skin. Pathology can occur even when falling from a bicycle, if it is accompanied by the formation of a hematoma on the shoulder or damage to soft tissues. The likelihood of infection of the bag increases significantly with a decrease in the body's defenses. The following diseases and conditions predispose to the development of pathology:
- alcoholism;
- diabetes;
- long-term use of hormonal drugs;
- severe renal pathologies;
- scleroderma;
- rheumatoid and gouty arthritis;
- salt deposition in the subacromial bursa.
The cause of chronic subacromial bursitis is constant, prolonged mechanical irritation of the shoulder as a result of professional activity or intense, frequent sports training.
Excessive loads are one of the causes of inflammation of the subacromial bursa.
Symptoms of subacromial bursitis
The clinical picture of different types of bursitis has common features. Therefore, only a competent specialist can distinguish one type of pathology from another. With the development of subacromial disease of the shoulder joint, the patient will complain of the following symptoms of malaise:
- Soft tissue swelling and swelling in the shoulder;
- Problematic movement of the diseased joint;
- Painful sensations when raising and lowering the arm;
- Increased body temperature;
- Feeling of weakness and apathy.
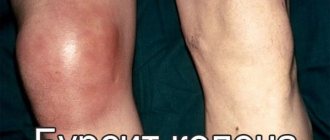
Swelling and swelling of the shoulder are the main symptoms of the development of subacromial bursitis. The skin in this area begins to redden and stretch. Due to the growth of the tumor, a person loses the ability to freely move the upper limb. With further development of the pathological process, severe pain will occur. It will intensify in the evening. Many patients notice that the pain can move to the area of the scapula and elbow.
Advanced forms of subacromial bursitis are accompanied by an increase in body temperature. This symptom indicates the development of an inflammatory process in the body. The patient complains of fever and dyspepsia. To get rid of such symptoms, he has to be treated in a hospital.
The prolonged course of a painful condition negatively affects a person’s general well-being. He becomes exhausted and tired. There are also signs of lethargy and irritability.
The course of subdeltoid bursitis, as well as a disease in which the subacromial region is affected, has similar symptoms.
Pain when trying to raise your arm is also typical for other diseases of the shoulder joint.
Exercises for hip bursitis
To reduce the likelihood of developing bursitis, you should perform exercises aimed at strengthening the hip abductors:
- Starting position: resting your hands on the table surface, position your body at an angle, as for push-ups. In this case, the back should be absolutely straight. Take one of your hands to the side and put it back. Do the same with the other hand. Repeat 5-10 times.
- Starting position: standing. Bend the knee of one leg, while turning the pelvic area in the opposite direction. Then smoothly tilt your body towards your leg. Do the same with the other leg. Repeat 5 times.
Diagnostics
Only a competent specialist can correctly identify the disease that worries a person. Before making a diagnosis, the doctor will ask the patient to undergo a series of diagnostic procedures and tests. They will allow him to identify disorders present in the body.
The following diagnostic procedures help to examine the patient’s body in detail:
- Radiography. The resulting images enable the doctor to determine the size of the inflamed bursa, as well as see the amount of biological fluid in this cavity;
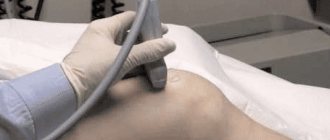
- Ultrasound. Allows you to visualize the inflamed area. Thanks to this, the doctor can accurately identify the disease;
- MRI. It is considered one of the most informative diagnostic methods for this disease. This study is usually required in severe cases of the pathological process.
Additionally, the doctor may prescribe a blood test for the patient to identify the course of the inflammatory process in the body. After a detailed diagnosis of the right or left joint, he will select the optimal treatment for the patient.
Diagnosis of pathology
An experienced doctor is able to quickly diagnose this pathology. Diagnostics includes the following steps:
Inspect the affected area for redness and swelling;
Questioning the patient. This manipulation allows you to accurately determine the cause of the disease and the duration of its course;
Radiography. This will allow us to identify the location of the inflamed lesion and its size;
Puncture of fluid from the joint capsule. Such a study makes it possible to study its composition and the presence of purulent contents;
Ultrasound diagnostics. It is carried out to determine the exact location of the inflamed area;
Magnetic resonance imaging of the shoulder.
Treatment methods
Treatment for subacromial bursitis takes time. With this disorder, patients are offered various types of therapy that help restore the inflamed area. When fighting this disease, an integrated approach is required. In this case, it will be possible to get rid of the pathological process in the shoulder joint in a short period.
Drug therapy
With subacromial bursitis of the shoulder joint, it is imperative to take medications that can help suppress the development of this disease. Most prescribed medications for this diagnosis help cope with painful symptoms that haunt the patient.
Treatment of subacromial bursitis is usually carried out with non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs. Painkillers are also required. Doctors usually prescribe:
- "Ibufen";
- "Diclofenac";
- "Ibuprofen."
Anti-inflammatory drugs are prescribed both for oral administration and for application to the shoulder
Additionally, products for external use are used. With the help of ointments you can cope with pain and inflammation. However, such medications do not affect the functioning of internal organs. For subacromial bursitis, local remedies are prescribed:
- "Lioton 1000";
- "Voltaren";
- "Fastum Gel".
In case of chronic and complicated course of the disease, antibacterial drugs will be required. Ideally, an antibiotic should be administered to the inflamed joint after a puncture is performed and the infected fluid is removed from it.
Physiotherapy
It is recommended to treat subacromial bursitis, which affects the shoulder joint area, with special gymnastics. It includes a number of simple exercises that allow you to strengthen the muscle corset and improve the mobility of the shoulder joint. For physical therapy to bring positive results, it should be done regularly.
Physiotherapeutic procedures
Physiotherapy helps restore the previous mobility of the shoulder joint. For subacromial bursitis, the following types of treatment are recommended:
- Electrophoresis;
- Laser irradiation;
- Phonophoresis;
- Magnetotherapy.
These procedures are performed only on patients who have no contraindications to them.
Physiotherapy is an effective complement to drug treatment
Surgical treatment
If the disease is too advanced and medications do not give a positive result, then the patient is sent for surgery. The essence of surgical intervention for bursitis is partial or complete removal of the affected tissue of the synovial pocket. After this, the cavity is thoroughly washed with a special composition with an antibacterial effect.
During rehabilitation, it is important to take antibiotics to prevent the development of a secondary infection. The duration of the patient's recovery after surgery depends on its success and compliance with medical recommendations for caring for the sore arm.
ethnoscience
With the permission of a doctor, you can combine drug therapy with non-traditional remedies proposed by traditional healers. Help to cope with the manifestations of subacromial bursitis of the shoulder joint:
- Lotions with propolis and medical alcohol;
- Lotions with raw potatoes;
- Rubbing the affected area with a mixture of petroleum jelly, eucalyptus and lavender oil.
If the disease is at an early stage of development, then folk remedies will help stop the spread of the inflammatory process. They will also eliminate the need for surgery.
Surgical intervention
In the case of a serious infectious lesion of the subacromial bursa, ineffectiveness of antibiotic therapy, or rapid spread of the pathological process, the bursa is promptly excised.
Then the patient is shown long-term treatment with antibacterial agents to prevent the formation of purulent exudate. The therapy is long-term, as healing takes several weeks and sometimes months.
When chronic, indolent, aseptic bursitis is diagnosed, the patient is immediately offered surgical intervention. This form of pathology does not respond well to conservative therapy, so the most reliable way to get rid of it is to remove the subacromial bursa. The operation is planned, usually minimally invasive. The wound surface heals after 7-10 days. The likelihood of relapses after surgery is minimal - 2.5% of cases.
At the rehabilitation stage, physiotherapeutic measures are carried out. To restore all functions of the shoulder joint, daily exercise therapy or gymnastics is necessary.
Prevention
The best prevention of the development of subacromial bursitis of the shoulder joint is compliance with rest and occupational hygiene. Severe overload of the upper limbs should be avoided. Otherwise, it will not be possible to prevent their injury.
When the first signs of bursitis appear, you should immediately seek medical help. Self-medication for such a disorder will lead to a worsening of the condition.
Related Articles
Heel bursitis: symptoms, treatment with medications and folk methods
Arthritis of the shoulder joint: symptoms and treatment
Hip bursitis: types, symptoms and treatment methods
Ankle bursitis: photos of symptoms, medication and alternative treatment
Bursitis of the knee joint: symptoms and principles of treatment
Principles of treatment of subdeltoid bursitis of the shoulder joint