How is osteochondrosis related to teeth?
The vertebrae of the cervical spine are small and mobile; important arteries and nerve fibers lie between their processes. With osteochondrosis, the vertebrae sag, and there is a high probability of pinching the nerve roots and arteries that supply the brain. As a result, the patient experiences headaches, dizziness, the functioning of the vestibular apparatus is disrupted, and vision and hearing are reduced.
Pinched nerve fibers transmit a pain signal to the brain in an attempt to indicate that there is a problem. Pain is the only factor that forces a person to see a doctor. Sometimes pain occurs outside the localization of the pathology. The head and jaw may hurt if the trigeminal nerve or teeth are pinched; the pain radiates to the hands and heart. Sometimes the patient himself cannot determine where it hurts.
With osteochondrosis, teeth can really hurt. This is due to inflammation of the nerve roots in the cervical spine. The pain is aching and radiates through the neck into the jaw.
And it happens that due to problems with teeth, a person develops osteochondrosis. For example, with an incorrect bite, the bones of the skull become distorted. The body strives to compensate for the curvature and return the head to a straight position. Then the spine begins to bend.
Pain syndrome in osteochondrosis
The mechanism of pain in osteochondrosis is still not clear.
In the human body, all systems closely interact with each other, therefore, when disorders occur in the intervertebral discs, the nerve processes that are located nearby begin to transmit signals to the spinal cord and brain. This is how a person experiences pain. The nature of pain, its localization and perception depends on various factors. So it can be felt on any part of the nerve and does not give a clear picture of where degenerative and dystrophic changes occur in the spine, in what part of it. If a person is emotionally unstable and prone to depressive disorders, then he will feel pain more intensely.
At the early stage of the disease, there is practically no pain or it goes away quickly. As the disease progresses, the situation worsens, attacks appear more frequently and more intensely. If pain sensations are transmitted to various parts of the body, then we can talk about pinched nerve endings.
cervical osteochondrosis
At the initial stage of the disease, the patient reflexively stretches his neck, and is haunted by a feeling of heaviness and fatigue. Pain appears later when trying to turn or tilt; headaches, fainting – signs of impaired blood flow in the thoracic and cervical region; subsequently the pain is transferred to the arms or between the shoulder blades.
Thoracic osteochondrosis
Although the chest is less mobile than the spine, it is also susceptible to osteochondrosis, although less frequently. It manifests itself in shortness of breath, spasms in the lumbar muscles.
Pain in the lumbar form of the disease
This type of osteochondrosis is characterized by pain in the lower back, radiating to the leg. There are difficulties in flexing and extending the torso, pain in the sacrum, in the gluteal muscles, and in the pelvic organs.
Other types of pain associated with this disease
- head:
Painful sensations in the head cover all areas and are poorly relieved with painkillers, as they are of a detached nature.
- In eyes:
With osteochondrosis, the optic nerve may swell, resulting in decreased visual acuity and a throbbing pain sensation.
- in the throat:
Often there is a dry cough, a sensation of a lump in the throat, and pain when swallowing. The symptoms resemble the clinical picture of tonsillitis. In addition, many patients report a feeling of difficulty breathing, especially in the later stages of the disease.
- in heart:
The difference from true heart pain is the duration of pain in the heart with osteochondrosis (lasts several months). The course of pain is of a wave nature, sometimes intensifying, sometimes subsiding.
- in the chest:
This pain occurs when the patient moves and breathes. Symptoms that occur in the chest during osteochondrosis are disguised as other diseases, so it is important to make a correct diagnosis.
- in the upper limbs:
Painful sensations in the hands with osteochondrosis depend on the location of the disease. They have a shooting, stupid character. It gets worse with movement and even coughing.
- in the leg:
Quite often, leg aches are mistaken for diseases of the vascular system, but there are several characteristic features that indicate the development of osteochondrosis. This is the absence of swelling and protruding veins, in addition, only one leg can hurt.
- in the stomach, stomach:
The development of osteochondrosis can lead to problems with digestion of food, heartburn, and sometimes to a stomach ulcer if the true cause of the disease is not diagnosed in time.
Ways to get rid of painful sensations
Relieving pain and providing the patient with a normal lifestyle is possible with the use of good diagnostics and a correct diagnosis. Pain in osteochondrosis is relieved with medications (NSP, muscle relaxants, warming agents, and others prescribed by a doctor), physiotherapeutic procedures, alternative therapy (paraffin therapy, apitherapy, specialized baths), using spinal massage
, including vacuum, roller.
Author: K.M.N., Academician of the Russian Academy of Medical Sciences M.A. Bobyr
Malocclusion and osteochondrosis
Suppose several teeth are missing on the upper or lower jaw, crowns have been installed, or the patient is undergoing a filling procedure. If the relief of the dentition has changed, the lower jaw is forced to shift - this will lead to overstrain of the maxillofacial muscles and misalignment of the head.
The skull is held in a level position by the first two cervical vertebrae. A distortion of the skull will gradually lead to curvature in the cervical region. As a result, an incorrect bite will lead to scoliosis of the spine, and osteochondrosis will most likely develop against its background.
Our body is structured according to the principle of symmetry. Eyes and ears must be located at the same level in order to properly perform their functions. If a misalignment of the head occurs, the vestibular apparatus detects this violation and tries to compensate for it. To keep the head in a level position, the body decides to compensate for the misalignment by bending the cervical spine.
The vertebrae of the neck receive increased load, gradually collapse, and osteochondrosis forms. Its symptoms include radicular syndrome, chronic pain and crunching in the neck, and difficulty turning the head. The shoulders also become distorted, thoracic scoliosis and osteochondrosis develop, and nerve endings are pinched. The pain radiates to the shoulder blade, arm, jaw. Since the jaw joint is close to the auditory nerve, the patient begins to complain of tinnitus.
To get rid of this problem, complex treatment is prescribed. First, it is necessary to eliminate the dental cause of osteochondrosis. Then periodically undergo a course of therapy, which is aimed at strengthening the muscle corset, restoring mobility, and relaxing the muscles of the back and neck.
The essence of the method
The impact is carried out by a low-frequency acoustic wave, which has a high pulse pressure, the ability to create a rarefaction zone, and fast speed. Thanks to these characteristics, it does not damage soft tissues, working only in the desired area.
There are 3 stages of impact:
- calm - no radiation;
- high pressure, which can reach 500 bar;
- rarefaction - that is, negative pressure after the wave subsides.
First, the sound wave compresses the cells in the area of effect, and then they stretch under the influence of vacuum. The cells receive mechanical stimulation, come to life, and begin to synthesize useful substances. At the same time, angiogenesis and microcirculation improve.
Table 1. Effect of shock wave therapy for osteochondrosis of the cervical spine
| Organs and tissues | Effect of UVT |
| Muscle fibers. | Elimination of spasm, restoration of ion exchange in the cell and intercellular space. |
| Nerve endings. | Blocking the reflex pain arc. |
| Blood vessels. | Improved microcirculation, growth of new blood vessels. |
| Tendons. | Anti-inflammatory effect, increased elasticity. |
| Leather. | Collagen synthesis. |
As a result of the complex effect of shockwave therapy on the body, adhesions, fibrosis, and calcium deposits characteristic of cervical osteochondrosis decrease or disappear. The main action occurs in the area of inflammation, the affected cells are destroyed.
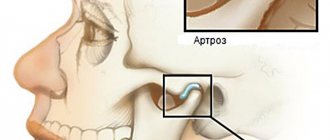
What types of jaw pain can there be?
With osteochondrosis of the spine, teeth may hurt. The pain is one-sided, aching, spreads to the entire dentition, intensifies when the patient chews food. A clear sign of neuralgia is the absence of dental disease. The pain is caused by pinched nerve roots between 1-3 vertebrae. After taking painkillers, the sensations weaken, but return again. The pain radiates to the temple, the back of the head, and the neck muscles may ache.
Pain in the jaw with osteochondrosis has the following features:
- Prolonged pulling, aching sensations;
- Painkillers do not help;
- When chewing, acute painful spasms appear;
- Cheekbones hurt when chewing hard food;
- It's hard to open your mouth completely;
- When chewing, a crunching sensation appears in the jaw.
To confirm the connection between toothache and osteochondrosis, it is necessary to undergo a thorough diagnosis. A bilateral x-ray, tomography of the cervical spine is prescribed, and Doppler of blood vessels is performed to identify possible infringements.
It is also necessary to identify the presence of malocclusion and carry out correction. First, a procedure is performed for forced relaxation of the facial muscles using a small electric current. As soon as the muscle tension disappears, the jaw will return to its correct position.
Then the dentist will be able to correct the dentition, which is aimed at restoring the normal closure of the upper and lower jaw. The missing areas of the dentition are built up, the protruding areas are cut down to eliminate the misalignment.
BAD TEETH AND SPINE
It turns out that the condition of the spine affects how our teeth feel. However, the opposite effect also occurs.
It was dentists who first noticed that after a special hardware medical massage of C0/C1 (the area of the craniovertebral zone) and restoration of the natural structure of the spine, the incorrect position of the lower jaw is automatically corrected and the bite of the teeth is improved (in cases where the displacement of the lower jaw is insignificant).
In extreme cases of malocclusion, simply correcting the atlas will not be enough to completely solve the problem. Additional measures are needed directly on the jaw and, more specifically, on the teeth that are responsible for its incorrect position.
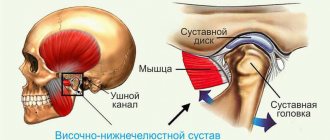
If the patient has trigeminal neuralgia or TMJ syndrome (temporomandibular joint), then their course is only aggravated by an incorrectly located atlas. Correcting these disorders without its correction will not be successful.
Do you have the correct bite and can it be corrected?
Look at your face in the mirror. The mouth is closed, the teeth are closed, but without tension. It is better to take a photo in this position and then examine it carefully. If the jaw is positioned correctly, then the line of the eyes is parallel to the line of the mouth, and a line drawn through the center of the chin and forehead exactly intersects the middle of the face. Are there any deviations from this picture? This means you have a malocclusion.
So often we see people with severe malocclusions who are convinced that everything will get better simply because they wear braces. But this, alas, is not so. The biomechanics of occlusion involves more than just teeth.
Teeth are part of the skeleton. And together with him they participate in all internal interactions and transformations. The skeleton is a system built on constantly occurring compensations (so that its balance is maintained). Therefore, it is absolutely impossible to eliminate flat feet separately or correct posture separately. And separately solve the bite problem.
Correcting an already formed bite can only be done with the help of a comprehensive correction of hard teeth, i.e. bone, tissues of the spine, skull, jaws. Treatment of the masticatory muscles will not give any effect.
There are several ways to change the relationship between height and tooth contact surface. Consultation with a competent dentist who is knowledgeable about the relationship between posture and occlusion is recommended.
Occlusion (dental) - (lat. occlusio) “any contact of the teeth of the upper and lower jaws.” The modern understanding of occlusion includes the relationship between the teeth, masticatory muscles and the temporomandibular joints. In contrast to occlusion, occlusion is the closure of teeth in the ordinary, static position of the lower jaw. Those. Overbite is a common type of occlusion.
When correcting your bite, time is important. To avoid complex consequences, you need to start correcting your bite as early as possible, before reaching adulthood. Another fundamental point: it is better to avoid metal crowns and dentures. The presence of any metal parts in the jaws is harmful to health.
How is bite related to posture?
Just below the lower jaw, complementing its work, is the “hanging” hyoid bone. It is attached by muscles to the back of the skull in the atlas region and is also connected to the lower jaw by muscles. The hyoid bone is the only bone in the body that does not have direct connections with other bones; it is embedded in the muscular structure of the pharynx.
In the body of the hyoid bone there is a mechanism similar to a device such as a building level: it performs static adjustment of the posture. The hyoid bone is a decisive point in the functioning of neuromuscular regulation, on which human posture depends.
If the atlas is displaced, then muscle contractions caused by the misalignment of the atlas and the lower jaw create asymmetric pressure on the hyoid bone. Spatial displacement of the lower jaw, manifested in the form of malocclusion, already causes a stable displacement of the hyoid bone. And this, in turn, changes the tension of the muscle chains that regulate the static position of the body. As a result, the person's posture changes. This process is long but constant. Posture deteriorates, pelvic tilt occurs, and shoulders skew.
This is why the effect does not persist after manual therapy - the main reason that caused these distortions is located higher. As long as the atlas and, if necessary, the jaw are not corrected, the shoulders and pelvis will always return to an asymmetrical position!
Evidence of this is found in the experiences of many patients. After correcting the atlas and bite, their pelvis spontaneously aligned, trying to meet the new conditions. Practice shows that the current orthopedic theory, according to which pelvic displacement is caused by problems with the legs (different leg lengths, etc.) is incorrect in most cases.
How to maintain the correct bite?
German dental surgeon Udo Bahr, after conducting a series of tests on several hundred patients, came to the conclusion that occlusion plays a fundamental role in posture, in other words, that information about a person's posture is somehow stored in the teeth.
After repeated testing and measurements at different stages of the child's development, Dr. Bar concluded that the child's posture was easily modified before the first permanent molar. Until this time, the asymmetries of the children's pelvis can be easily corrected. This effect persists until approximately 15 years of age (if there have been no accidents or injuries) and indirectly affects the correct formation of the jaw and bite. After the age of 15, the jaws are fully formed and, in turn, begin to influence the position of the pelvis and shoulders.
This shows how important the stage of puberty (10-14 years) is for good posture - pelvis, back, neck - and its correction. Later, the posture is forever “laid down” in the structure of the teeth, in the position of the hyoid bone and in the system of muscle tension. Then everything becomes much more difficult to fix. Therefore, if a child’s first vertebra is displaced, it is very important to correct its position in childhood - this will preserve not only his posture, but also good teeth.
In adulthood, due to destruction, improper positioning, removal, and abrasion of teeth, their surface changes greatly. This creates a persistent malocclusion that further compromises the posture and worsens the posture.
In order for an adult to regain good posture, a set of corrective measures should be taken, which must include restoring the balance of the lower jaw . To do this, you will have to change the bite of your teeth using orthodontic methods.
But before taking any action with the teeth after spinal correction, it is important to correctly assess the patient’s occlusion, his posture and their relationship. Only a good orthodontist can do this. Without prior research, there is a high risk of worsening an already serious situation and wasting money.
To consult an atlas specialist, make an appointment online:
View on the map of Ufa Find directions to Atlant, spinal correction center
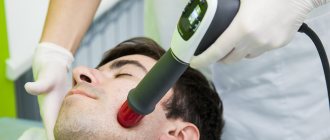
Treatment of neck osteochondrosis with shock wave therapy
UVT is effective at all stages of the disease. The procedure for cervical osteochondrosis lasts no more than 30 minutes. The patient lies face down on a couch or sits on a chair, resting his elbows and head on a high bolster. The doctor lubricates the skin at the site of exposure with sound-conducting gel - this makes the penetration of acoustic waves more effective.
Then he places the nozzle on the patient’s body and turns on the device. All settings are pre-selected individually, taking into account the patient’s characteristics.
You may experience some pain or discomfort during the first two sessions. In this case, the effect is interrupted. After the pain reaction subsides, it continues again. A total of 5–9 sessions are required with intervals between them of 3–10 days.
Table 3 Pros and cons of shockwave therapy for osteochondrosis
| Pros of UVT | Disadvantages of UVT |
| 1. Quick feeling of the effect. Improvement in well-being is noticeable after the first session. 2. Can be used as monotherapy. 3. The session lasts no more than half an hour. 4. No need to visit the clinic every day. It is enough to come once every 5-7 days. | 1. The likelihood of developing pain and discomfort during the first or second session. |